Do I need to take medication for a blood sugar of 7.7 fasting and 12.3 after a meal? What is the reason?
As you may know, the normal fasting blood glucose value is 3.9-6.1mmol/L, and the postprandial blood glucose value is: <7.8mmol/L. The values of fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose mentioned by you are higher than normal, and it is recommended that you check the glycated hemoglobin again, and if it is higher than the normal value as well, then you have to use hypoglycemic drugs, and if you don't need to use drugs to lower the blood glucose, the complications of diabetes will occur, and the condition will be more complicated and harmful to the body. If you don't use medication to lower your blood sugar, complications will occur, which will make your condition more complicated and more harmful to your body.
This situation should go to the endocrine metabolism department of the hospital to do diabetes diagnostic examination, combined with the physical condition, the general test of fasting blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, but also do a glucose tolerance test. If all three of them reach the diagnostic index or one of the two reaches close to one, then the diagnosis of diabetes can be confirmed. If the test results are between normal and diagnosed, it may be pre-diabetes. Whatever the case may be, the doctor will make the appropriate treatment. In the early stages of diabetes, it is important to adhere to medication and dietary control, as well as exercise interventions. However, it is important to note that it may not be a good thing for individual doctors to ignore pre-diabetic patients and not give proper medical advice! Pre-diabetes should generally be given dietary control and exercise interventions, and if necessary, should also be controlled by appropriate medication. This condition seems unlikely to be avoided in older people, but it can effectively control the progression of the disease and the degree of non-progression or slow progression of the disease.
Diabetes mellitus is a common metabolic disease in China. After the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, a reasonable glucose-lowering program should be formulated according to the degree of elevation of blood glucose to reduce various acute and chronic complications brought about by hyperglycemic state and lower the risk of cardiovascular events. If fasting blood glucose is 7.7mmol/L and postprandial blood glucose is 12.3mmol/L, do I need medication to lower my blood glucose? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze for you.
The normal range of fasting blood glucose is 3.9-6.1mmol/L, and the normal range of 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is 4.4-7.8mmol/L. Diabetes can be diagnosed if there are symptoms of "drinking more, urinating more, eating more, and losing weight" accompanied by a fasting blood glucose of ≥7.0mmol/L, or a blood glucose of ≥11.1mmol/L at any time, or if there are no symptoms of "three more and one less", then review the blood glucose on another day to reconfirm the diagnosis. If there are no symptoms of "three more and one less", the blood glucose will be rechecked on another day to reconfirm the diagnosis. Therefore, if the fasting blood glucose is 7.7mmol/L and the postprandial blood glucose is 12.3mmol/L, and if the symptoms of "three more and one less" are combined at the same time, the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus should be considered. After the diagnosis of diabetes, not all patients are given medication to lower blood glucose, but should be based on the level of glycosylated hemoglobin to formulate a glucose-lowering program. Glycated hemoglobin is an indicator that reflects the overall control of blood glucose in the last three months, and its normal range is 3-6%. When glycated hemoglobin reaches 7%, medication should be considered to lower blood glucose.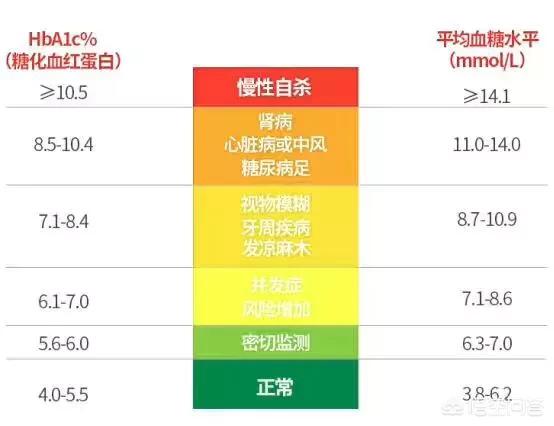
The choice of glucose-lowering drugs varies with the degree of elevated glycosylated hemoglobin. Newly diagnosed diabetic patients, if glycated hemoglobin is located in 7-9%, can first choose oral drugs to control blood sugar, such as metformin, acarbose, sulfonylurea hypoglycemic drugs, gliclazide hypoglycemic drugs, etc., single-drug treatment of blood glucose does not meet the standard, can be sequentially two, three lowering of blood sugar, until glycated hemoglobin is controlled at less than 7%; if glycated hemoglobin reaches 9%, or by the triple oral hypoglycemic drug treatment glycated hemoglobin is still greater than 7%, insulin should be given to control blood glucose.
It's important to note thatIn addition, while giving medication to control blood glucose, lifestyle intervention should be carried out throughout the treatment, with dietary attention to controlling the quality and quantity of food, strict diabetic diet, less easy-to-elevate blood glucose food, and controlling the total amount of food intake per day and per meal; appropriate exercise, weight reduction, and cessation of smoking and limitation of alcohol are more conducive to the control of blood glucose.
In summary, fasting blood glucose 7.7mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose 12.3mmol/L, the diagnosis should consider diabetes mellitus. For treatment, attention should be paid to lifestyle changes and a reasonable glucose-lowering program should be formulated according to the level of glycosylated hemoglobin.
Thank you all for reading!
We are looking forward to your attention and presenting more health knowledge to you!
Note: The images in this article come from the Internet, if infringement of copyright, please contact to remove. The content of the article is only as a health science popularization, not as a medical advice or opinion, and does not have the condition of medical guidance.
Hyperglycemia is diagnosed when the plasma glucose concentration exceeds certain criteria. Normally fasting blood glucose is usually between 3.9 and 6.0 mmol per liter, and postprandial blood glucose should be between 3.9 and 7.8 mmol per liter.
If the fasting blood glucose is greater than or equal to 6.1 mmol per liter, or the postprandial blood glucose or the two-hour postprandial blood glucose is greater than or equal to 7.8 mmol per liter, it can be defined as high blood glucose. However, hyperglycemia is not necessarily diabetes, and the criteria for diagnosing diabetes have certain reference values for blood glucose.
Thanks for the invite!
For patients with increased blood glucose, first of all, we have to clarify whether they have diabetes or not. As for the cause of diabetes, it is still not very clear, but the main consideration is that it is caused by the interaction of genetic and environmental factors. The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is mainly based on fasting blood glucose and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, of course, it is better to be able to combine with glycated hemoglobin. Diabetes is diagnosed when fasting blood glucose is equal to or greater than 7.0 mmol/L, or when 2-hour postprandial blood glucose or 2-hour glycemic load blood glucose is equal to or greater than 11.1 mmol/L, accompanied by the symptoms of "three more and one less", and if there are no symptoms, repeat the test on another day. If there are no "three more and one less" symptoms, diabetes can also be diagnosed if the blood glucose still meets the above criteria when the test is repeated on another day.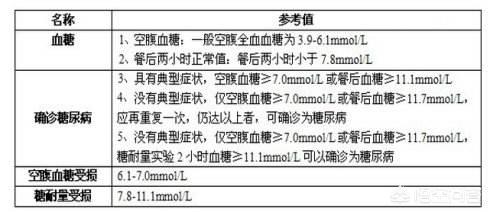 For newly detected diabetes, if there are no complications or other related diseases, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, etc., lifestyle intervention treatments such as diet and exercise can be carried out for 1-3 months first. Mainly low-salt and low-fat diet, limit total energy intake, reasonable and balanced diet, eat more vegetables, moderate amount of fruits, drink sufficient amount of water, quit smoking and limit alcohol, keep a good mood, insist on daily aerobic exercise for 30 minutes, at least insist on aerobic exercise for 5 times a week, and actively lose weight to control the weight in the standard body weight range. Through life intervention, can reduce blood glucose level, if can reach the normal range, that is, fasting blood glucose is less than 6.1mmol / L, 2 hours after meal blood glucose is less than 7.8mmol / L, you can not have to take medication; if not able to be to the normal range, it is recommended to add the use of hypoglycemic drugs, the specific drugs can be based on their own actual situation reasonable choice.
For newly detected diabetes, if there are no complications or other related diseases, such as hypertension, coronary heart disease, stroke, etc., lifestyle intervention treatments such as diet and exercise can be carried out for 1-3 months first. Mainly low-salt and low-fat diet, limit total energy intake, reasonable and balanced diet, eat more vegetables, moderate amount of fruits, drink sufficient amount of water, quit smoking and limit alcohol, keep a good mood, insist on daily aerobic exercise for 30 minutes, at least insist on aerobic exercise for 5 times a week, and actively lose weight to control the weight in the standard body weight range. Through life intervention, can reduce blood glucose level, if can reach the normal range, that is, fasting blood glucose is less than 6.1mmol / L, 2 hours after meal blood glucose is less than 7.8mmol / L, you can not have to take medication; if not able to be to the normal range, it is recommended to add the use of hypoglycemic drugs, the specific drugs can be based on their own actual situation reasonable choice.
If the above blood glucose is the blood glucose after the lifestyle intervention, or the blood glucose that has been present for more than 3 months, it is recommended to add glucose-lowering drugs. Commonly used hypoglycemic drugs include biguanides, sulfonylureas, non-sulfonylurea agonists, α-glucosidase inhibitors, insulin sensitizers, insulin preparations, GLP-1 receptor agonists, DPP-4 enzyme inhibitors, and proprietary hypoglycemic drugs. Generally for type 2 diabetes if there are no contraindications, it is recommended that metformin be the first choice for treatment.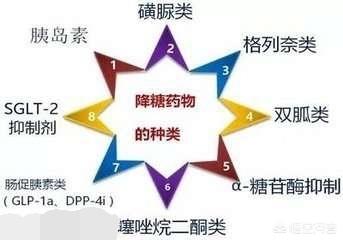
Diabetes treatment is precious, only long-term unremitting adherence to the treatment of blood sugar control can achieve satisfactory results. The above mentioned blood sugar should be able to obtain excellent results if treated actively!
Note: The pictures are all down from the network, if any infringement please notify the deletion!
As people's health awareness grows, more and more people are checking up on their health, and more and more of them may find such blood sugar conditions, which can be diagnosed as diabetes from the blood sugar results. However, some diabetics will also complain, the doctor said I have diabetes, but do not give me medication, in the end, this situation need to take medication?
Some people say, "Well, it has to be medicated! Without medication, there will be complications! In some cases, insulin therapy is needed!
Some people may also say that this blood sugar is okay, elderly, no need to take medication! Is this correct?
All of these statements may be true.
It depends on the patient who possesses this glycemic state.
No need for hypoglycemic drugs
For people with first-onset diabetes who have such blood glucose results, although the diagnosis of diabetes can be confirmed according to the diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus, but according to the principles of diabetes mellitus treatment, it is necessary to use hypoglycemic drugs for hypoglycemic treatment only if the blood glucose can not be reduced to the target range on the basis of lifestyle modification and dietary and exercise treatments.
Both blood glucose results are relatively close to the target ranges of 7.0 fasting and 10.0 postprandial. On the basis of the generally less healthy diet of the country, a little attention to diet and exercise patterns can return blood glucose to normal, so no medication is needed.
Must use hypoglycemic drugs
For diabetic co-pregnancy, or if the blood glucose of the pregnant population is high to this extent, medication is necessary to control the blood glucose, because it is concerned about the health of the mother and the fetus, and if the blood glucose can not be controlled in the target range, there may be a dangerous situation of miscarriage, preterm labor, intrauterine distress of the fetus and other dangerous situations, which will jeopardize the life of the mother and the child.
This condition must be treated, and it must be treated with insulin, as there are no oral hypoglycemic agents approved for use in pregnant women.

No need for hypoglycemic drugs
For the elderly, combined with a variety of chronic diseases, cardiac and cerebral disorders, mental disorders, life expectancy is not long in this part of the population, if the blood glucose in this state, do not need to use hypoglycemic drugs.
The goal of glycemic control in this segment of the elderly is to take loose control measures, with a target range right at the fasting 7-9 and postprandial 6-12 states, and there is a possibility of hypoglycemia in this population if glucose-lowering medications are used, which can induce a more serious and dangerous state.
To summarize:
For people in a glycemic state of 7.7 fasting and 12.3 postprandial, the choice of treatment regimen is based on the characteristics of the population. The goal of glycemic control varies from population to population. Some are fine with diet and exercise therapy alone, while others must be treated medically. Some need to keep their blood glucose in a lower range, while others have more lenient control measures. It is important to communicate actively with your specialist, not to take things for granted, to learn more about diabetes, and to take basic measures such as diet and exercise.
I'm Dr. Sun, telling you interesting stories about the process of practicing medicine; follow Dr. Sun's talk about sugar for continued quality health knowledge!
Do I need to take medication for a blood sugar of 7.7 fasting and 12.3 after a meal? What is the reason?
First of all, it is recommended that you go to the hospital for a checkup to clarify whether you have diabetes or not. Fasting blood glucose of 7.7 mmol/L and postprandial blood glucose of 12.3 mmol/L are both over the standard value.
We all know that fasting blood glucose is one of the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, general fasting blood glucose monitoring two consecutive times are greater than 7.0mmol / L, then you can diagnose the patient is diabetes, fasting blood glucose 7.7mmol / L, has exceeded the normal fasting blood glucose value, need to be alert to diabetes.
Diagnosis of diabetes mellitus in addition to fasting blood glucose test, there is also a 2-hour postprandial blood glucose test, postprandial blood glucose, as the name implies, is the blood glucose value after eating a meal, in general, postprandial blood glucose is indeed slightly higher than the fasting blood glucose, which has a great relationship with the diet of our Chinese population, the diet is characterized by high-carbohydrates, rice and noodles are mainly, coupled with the fact that we are accustomed to resting after a meal, so it is easy to postprandial blood glucose is high. Under normal circumstances, with the absorption of carbohydrates, blood glucose begins to rise after 10min after eating. In normal people, blood glucose peaks at 0.5~1h after a meal, and the normal value is <7.8mmol/L.
Postprandial hyperglycemia refers to the process of food digestion and absorption of blood glucose peaks above the normal range, that is, 1h ~ 2h after ingestion of blood glucose level > 7.8mmol / L. Postprandial 12.3mmol / L, obviously has been far above the normal value, and even belongs to the high.
If the examination confirms the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, then it is recommended to take medication in time, especially if the postprandial blood glucose is high, diabetic patients can be in postprandial hyperglycemia for 2/3~3/4 time in a day, and therefore, postprandial hyperglycemia is more hazardous than the fasting blood glucose elevation. Postprandial hyperglycemia can cause postprandial metabolic disorders and abnormal tissue cell function, and one postprandial hyperglycemia may be a hazardous load to an individual. Studies have shown that postprandial hyperglycemia leads to an increased risk of vascular disease complications and is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular events.
The terrible thing about diabetes is not in itself, but in the complications it causes, even if the blood sugar is high, the body does not hurt, in fact, the harm of high blood sugar has begun, it is recommended to pay great attention to, even if the medical checkups, once diagnosed, should be actively treated.
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! Also, if you have family members with blood sugar-related troubles, please pass this article on to them!
Of course you need to take medication, diabetes diagnostic criteria is 2 times blood glucose fasting>7.O or 2 hours after meal blood glucose>11.1, your blood glucose has reached the standard of diabetes, of course, you need to take medication. High blood glucose level will corrode human organs and produce various diseases, such as cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, eye diseases, diabetic foot and so on, it is recommended to timely treatment.
In this case, you should go to a regular hospital to find a doctor to do a checkup, to see if you need to take medication, or usually in the living and diet, should pay attention to what, in order to benefit their physical and mental health.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.