How can I tell if my child has a viral or bacterial cold?
As the weather turns cooler, many children are prone to catching colds, and because of the new crown epidemic, many parents don't want to take their children to the hospital. So if you have a cold, how do you distinguish between a viral or bacterial cold at home? How to choose the medicine? I'll talk to you about this below.
In general, most of the children's colds are caused by viral infections, can account for almost 80% to 90%, while the bacterial infection is less than 10%, there are some co-infections, only learn to distinguish the difference between them, so that the targeted medication, in order to have a better effect.
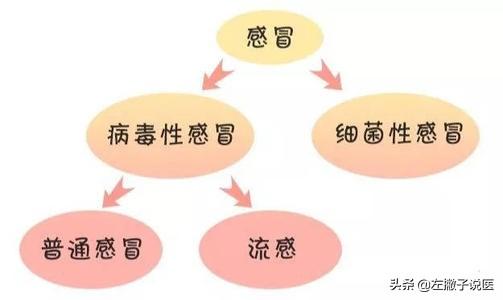
Therefore, we can differentiate by these following aspects:
●1.Look at the child's mental state: Generally speaking, if it is a viral infection, the child's toxic symptoms are relatively mild, although the cold, but they are still in good spirits; if it is a bacterial infection, the child's systemic toxic symptoms are relatively heavy, the mental aspect is often poor, the whole person is listless, and will feel very tired, powerless to move, and so on.
2.Look for symptoms in the throat pharynxIn general, if it is a viral infection, then the pharynx usually does not appear pus secretion, and we can observe that the patient's pharyngeal tonsils are only congested, the color is relatively bright red, and there are some vesicles and follicles can be seen; if it is a bacterial infection, then in addition to pharyngeal tonsillar congestion, the most obvious feature is that there is a pharyngeal pus discharge, pus, and pain is more pronounced. The most obvious feature is that there is pus discharge and pus spots in the pharynx and the pain is more obvious.
3.watch sb's nose: Generally speaking, viral infections do not cause inflammation, so the runny nose is usually clear and the sputum coughed up is relatively small and thin; in the case of bacterial infections, since inflammation occurs, the runny nose is usually pus and there is more coughing up of sputum, which is usually yellow and pus.
4.For fever reductionIf a cold is accompanied by a fever and fever reduces with antipyretic drugs, if it is a viral infection, then taking antipyretic drugs will have a more obvious effect of fever reduction, and the general body symptoms will be improved, but this is only temporary, the effect of the drug is over also the temperature will rise again; if it is a bacterial infection, taking the same antipyretic drugs, generally ineffective, and the general body symptoms are not significantly improved.
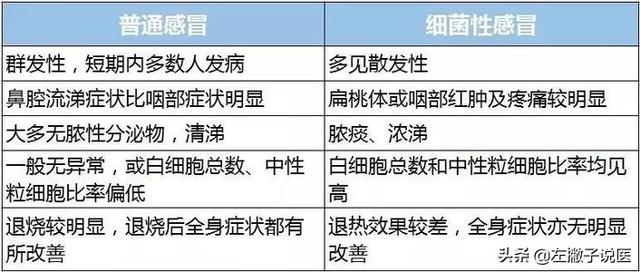
The above mentioned some clinical symptoms to distinguish between viral colds and bacterial colds, but in addition to relying on the above clinical symptoms, but also need some tests to better distinguish, because sometimes these two different colds can be combined colds, this time you have to rely on blood tests.
When we take our children to the hospital, the doctor will often ask us to draw blood for a routine blood test as well as a CPR test, and in some cases even add a test such as calcitoninogen or serum amyloid A. The doctor will also ask us to take a blood test to check for the presence of the amyloid A protein.We'll show you how to simply determine a viral cold from a bacterial cold with these lab tests again.
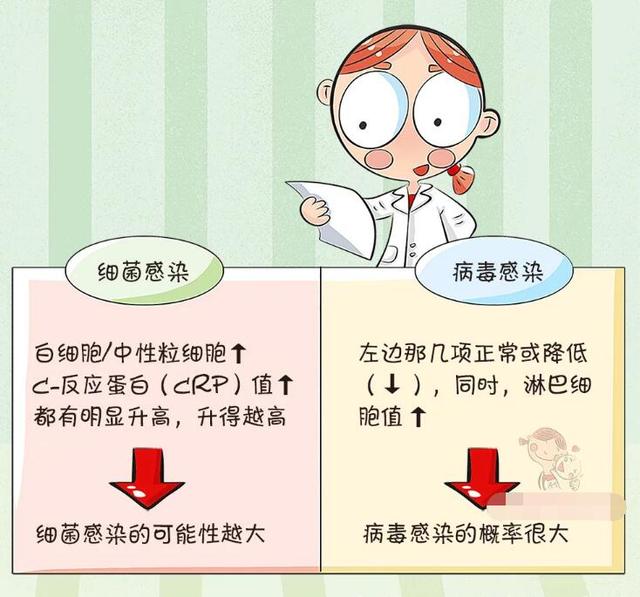
●① Viral colds: Generally speaking, in infections caused by viruses, the total number of white blood cells is low or normal, the proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes is usually not elevated, while lymphocytes tend to be elevated; and then look at the CPR test and the calcitoninogen test, the results are usually normal.
● ② Bacterial infections: Generally speaking, in infections caused by bacteria, the total number of white blood cells tends to increase, and the proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes also increases, and lymphocytes generally decrease, but sometimes the total number of white blood cells is not high, but the proportion of neutrophilic leukocytes increases; and CPR test, calcitoninogen test, the results are also elevated.
Therefore, some of the above lab results can be used to determine viral colds from bacterial colds in a clinical setting.As long as the total number of white blood cells is low or normal, the percentage of lymphocytes is increased, and CRP and calcitoninogen are normal, then a viral infection is indicated; as long as the white blood cells are elevated, CRP is elevated, and calcitoninogen is elevated, then a bacterial infection is indicated.
After this determination, you will know how you should be medicated; if it is a viral cold, then treat it with antiviral medication, and if it is a bacterial infection, then treat it with antibiotics.
Of course, in clinical practice, there are often children with co-infections, that is, in the early stages of the cold is a viral infection, the development of the later stages of the combined bacterial infection, so this time according to the clinical symptoms and the results of the comprehensive analysis and judgment, and then consider the use of medication.

Author's note: I'm very happy to popularize health-related knowledge for everyone, I'm left-handed to say medical, every day in simple language for you to popularize professional medical knowledge, the code word is not easy, if you like my article, help me to point a praise! If you still have questions, you can leave a message in the comments section, welcome to pay attention to, forward, thank you for your support!
Now that fall and winter have arrived, the temperature difference between morning and evening has increased, and many children will have a cold. One reason is that some children are weak, poor immunity, some because of the temperature difference in dressing and undressing caused by the wind cold, and some because and cold children play together, together with the class and lead to infected with a cold. After a child has a cold, some cough and runny nose, some high fever, but also some sore throat and tonsils are enlarged, many parents can not distinguish between the child in the end is not a cold, to the hospital will usually be a blood draw, the blood drawn after the doctor looked at the laboratory tests will tell you that the child is either a viral cold, or bacterial cold, and then it is a targeted treatment.

But this year, because of the existence of the new coronavirus epidemic, many parents are reluctant to take their children to the hospital, especially pediatrics, fall and winter pediatric respiratory departments of major hospitals are overcrowded, even to see a child with a cold is to register and queue up and wait for a long time, many parents do not get tired of, physically and mentally exhausted.
So, as a parent of a child, how can you tell if your child has a viral or bacterial cold?
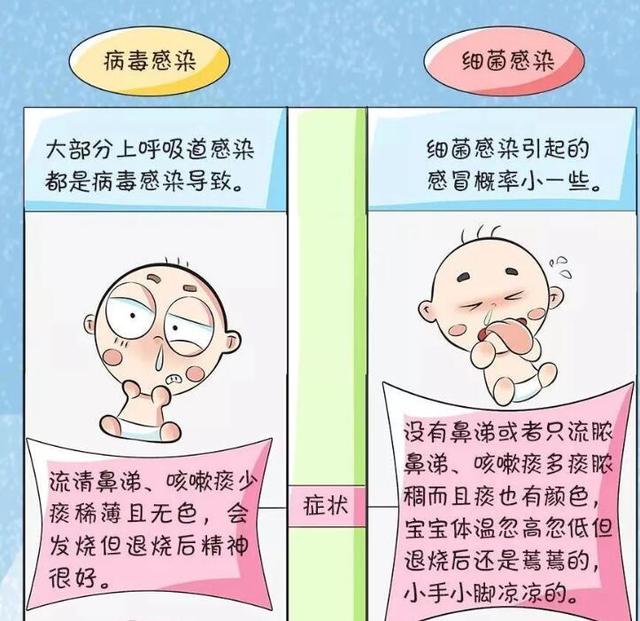
The first method: laboratory tests.This is also a relatively accurate way to do it after the test is done at the hospital. A lot of parents got the child blood routine labs, do not know what each represents, also can not read. Blood routine is mainly to see whether the child is infected with viruses or bacteria, (today mainly about colds, other laboratory items will not be mentioned) in general, white blood cells (WBC) significantly higher, neutrophils increased, lymphocytes decreased, which is often bacterial infections; and white blood cells have no significant change or slightly lower, neutrophils normal or slightly higher, and lymphocytes increased, is often viral infections. (This method requires professional interpretation. (This method needs to be interpreted by professionals, and parents should only use it as a reference, because there are occasional or specific situations in clinical laboratory tests, for example, there are bacterial infections in which the white blood cells are not high).
The second method: look at the state of the child:Viral cold children's mental state is almost unaffected, at most because the nose is not smooth, runny nose, coughing and other causes discomfort, the child may be inactive, but definitely does not affect the mental state, that is to say, still able to play can play; bacterial colds are often due to bacterial infections, the systemic symptoms of the heavier, there will be depressed, do not want to eat, and even lethargy, listlessness phenomenon.
The third method: look at the child's stool. Viral colds tend to have loose watery, eggdrop soup-like stools, consistent with typical rotavirus infections, or adenovirus infections; whereas bacterial colds children have mucus-pus-blood stools and loose pasty stools due to bacterial infections, and bacterial release of toxins into the bloodstream caused by inflammatory septic infections of the intestinal tract.
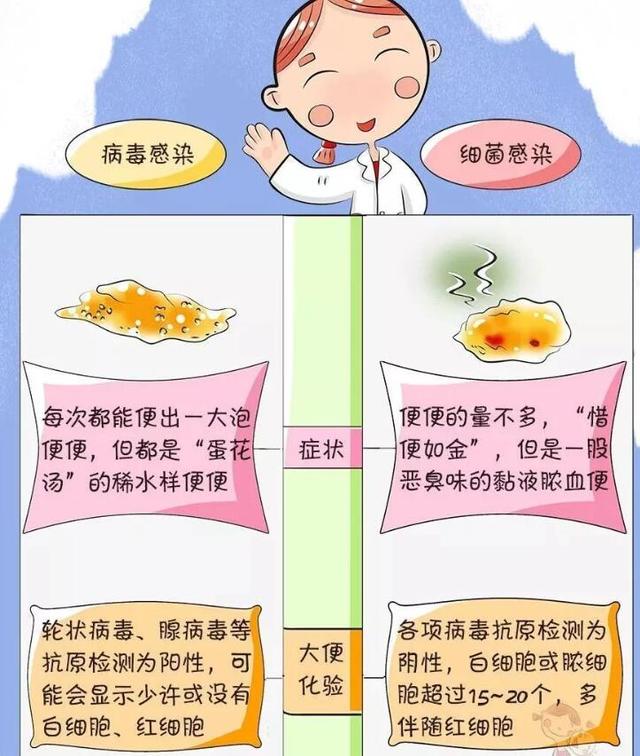
Fourth method: look at your child's nose: Children with colds tend to have runny noses. A runny, watery nose is a viral cold, and a milky yellow, pus-filled nose is often a bacterial cold.
Fifth method: look at the child's sputum:Viral infections children have little sputum and clear water sputum, colorless, accompanied by a cough; bacterial colds cough up pus sputum, cough is more violent, easy to cause pneumonia, body temperature fluctuates, and the child's spirit is poor after the fever goes down.
Method 6: Look at your child's tonsils:The tonsils of a child with a viral cold are absolutely free of pus and appear smooth and bright red, and may have herpes or follicles; the tonsils of a child with a bacterial cold may have a purulent discharge on top, be dark in color, and not smooth.
From these methods, in general, can determine whether the child is a viral cold or bacterial cold, for the next treatment provides the basis for treatment. So, parents found that the child has a cold, how to deal with it?
1、Prevent cold and keep warm. Especially in the fall and winter, the temperature difference between morning and evening is large, the temperature is low, the child's immunity is greatly reduced, coupled with the dry air, pathogenic microorganisms are more likely to spread, the child is easy to catch a cold.
2, the child runny nose cough, you can give the child with saline nasal cleaning, keep the airway open, sore throat cough, you can give the child more hot water, supplemental water, keep the upper respiratory tract moist.
3, if the child fever, you can try to use a hot towel to the child to scrub, try to physical cooling, or as the case may be to add clothing, if the continuous fever continues to not fall, then you should go to the hospital in a timely manner symptomatic treatment.
Summarize: Children's colds are a big headache for parents, but as long as they learn the basics and master some related skills, I believe that children's colds can be easily dealt with. Whether the child is a viral cold or bacterial cold, the general principle of differentiation in the above also listed six methods, in general enough to identify. In addition, the child cold should not blindly use drugs, because the child's various systems are not well developed, blind use of drugs may cause serious consequences, should follow the doctor's advice.
This article is for popular science study only, can not be used as a basis for clinical diagnosis and treatment, pictures from the network, if any infringement, contact to delete, thank you.
I am General Practice Dr. Zhou, your neighborhood general practitioner. It's not easy to write, so I'm sharing this for free, and I hope you'll give me a like! Thank you, Dr. Chow.
In fact, this is a concern for many parents and whether or not doctors use antibiotics. Most children's colds are viral infections, but some are caused by bacterial infections. So how do parents or doctors determine whether a child has a viral or bacterial cold? You may want to consider the following factors to identify.

1, the child cough with yellow sputum is often suggestive of bacterial infection.
2. The child starts with clear snot, which gradually turns into yellow snot and lasts for more than a week. Or there are symptoms of earache.
3, fever for more than a week without a downward trend, or the temperature drops and rises again, suggesting bacterial infection.
4, before the disease have eaten fire food or stimulate spicy food, no obvious symptoms of sneezing and sneezing.
5, the child's fever is often accompanied by chills and skin florid.
The above clinical signs are often suggestive of a bacterial cold.

6. Blood tests for high white blood cells, with neutrophils predominating.
7. High ultrasensitive CRP, excluding immunologic factors as the cause.
8. Calcitoninogen is elevated, with higher levels suggesting a more severe infection.
9, serum amyloid A viral cold is elevated, bacterial infections are also elevated, that how to judge, if the white blood cells are normal, CRP is not high, serum amyloid A is elevated, suggesting viral infections, if the white blood cells are high, CRP is high, serum amyloid A is high suggestive of bacterial infections.
10, sometimes the cold for the initial viral infection, later there may be a combination of bacterial infection, so there is no absolute absolute what infection, sometimes according to the child's condition changes, if necessary, and then laboratory tests, according to the laboratory tests and then adjust the necessity of antibiotics.
In short, pediatric colds also require vigilance for changes in the child's condition. Many pneumonias also begin as cold symptoms, and colds can also cause viral myocarditis, especially in younger infants with fever, so be sure to rule out other serious infections and don't assume that your baby's fever is just a common cold.
(Images from the Internet, such as infringement will be deleted, please contact me)
Dr. Ke is a pediatrician with extensive clinical experience, specializing in children's digestive and respiratory disorders, chronic cough, Helicobacter pylori infection, chronic gastritis, functional constipation, liver function abnormalities, chronic diarrhea, milk protein allergy, and other difficult problems and nutritional development of infants and young children, as well as feeding counseling. For more information about pediatrics, please visit Dr. Ke Youjian online.
With health as a companion, with the doctor as a friend, welcome to forward the praise, comment attention, praise and share is a virtue. Questions can be left, Dr. Ke in the break time will be on the typical questions targeted answer.

When parents rush their children to the hospital, the pediatrician will usually ask the child to check the blood count or C-reactive protein after consultation and listening to the patient, why is this? This is not because the doctor wants to charge more, but to clarify whether it is a viral infection, a bacterial infection or a mixed infection.
Viral colds are more prevalent, accounting for about 80-90% of upper respiratory tract infections, and most of them are rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, adenoviruses and so on. Symptoms are mostly sneezing, running water, cough, a small amount of white sputum, itchy throat, spirit is still good, etc. Severe cases may have high fever, chills, headache, etc., and are usually cured in about 7 days.
The incidence of bacterial cold is less, about 20-30%, which can occur alone or secondary to immunity decline caused by viral cold. Symptoms include obvious sore throat, coughing up yellow purulent sputum, poor spirit, etc. Fever is mostly low to medium, high fever is rare, irritability, etc. Tonsillar congestion can be seen on examination.

Although there is a distinction between viral and bacterial colds in terms of symptoms and signs, relevant tests are essential.
1. Blood counts: viral colds have normal or low white blood cell counts, with a marked increase in the proportion of lymphocytes; bacterial colds have markedly increased white blood cell counts and neutrophils, sometimes with signs of toxicity such as leftward shifting of the nucleus.
2. C-reactive protein: generally not elevated in viral colds, markedly elevated in bacterial colds
3. Calcitonin (PCT): not increased in viral infections, generally increased in bacterial infections, better sensitivity than C-reactive protein.
Clinically, antimicrobials can be used for mixed colds and bacterial colds where the immune system is lowered after a viral infection and a bacterial infection follows. As for simple viral infections, there is no need for prophylactic use of antibacterial drugs.

Respondent: Wu Su, M.S., M.A.
Welcome to Life Calling for more useful health knowledge.
Cold is an illness that we all get and is the one we are most familiar with, it is also a common illness in pediatrics. It is logical that we should know the most about this disease, but the truth is that most of us common people don't really understand what colds are all about.
Sort out viral or bacterial!!!!
About 90% of colds are caused by viruses. Colds caused by viruses can be self-cured, with the virus being cleared by the body in 5 to 7 days, so antibiotics are not needed for such cases, and symptomatic treatment is all that is needed. Colds usually do not require the use of antiviral drugs, such as amantadine, ribavirin, etc. (except for influenza). The so-called "anti-inflammatory drugs" (i.e., antibiotics) such as penicillin and cephalosporins are commonly used to treat bacterial infections, but have no effect on viral infections, and are prone to cause side effects, as well as accelerating bacterial drug resistance.From this point of view, the viral cold is in fact with the drug "can not cure", because the virus has not been a special drug treatment (analogous to HIV, hepatitis B virus, etc., but the cold virus pathogenicity is weak), the cold is ultimately self-healing by the body's own immunity to overcome.

The table below describes in more detail the differences between viral and bacterial colds:


Tell us about two very common phenomena of medication errors:
Often doctors prescribe ribavirin granules and amantadine preparations for children with colds, which is wrong.
In the CFDA-approved instructions for ribavirin, it states that it is indicated for viral pneumonia caused by respiratory syncytial virus, and cutaneous herpesvirus infections. In the United States, the oral form of ribavirin is only used in combination with interferon for the treatment of chronic hepatitis C in adults.The latest edition of the WHO's list of essential medicines emphasizes that when ribavirin is used in children, it is only for the treatment of epidemic hemorrhagic fever. So, ribavirin simply doesn't work for the common cold, so please don't abuse it.
The other is amantadine. Evidence-based medical research abroad shows that amantadine is basically ineffective against cold and flu viruses, and foreign countries no longer add this ingredient to compound cold and flu medicines. China's drug regulatory authorities have asked cold and flu medicines containing amantadine to revise their specifications from "children under 5 years of age should be used under the guidance of a physician" to "children under 5 years of age are not recommended to use amantadine". "In the "Contraindications" section, the following phrase was added: "Due to the lack of data on the safety and efficacy of the product in newborns and infants under 1 year of age, the product is contraindicated in newborns and infants under 1 year of age".
The child has a cold.More than 90% are viral infections. Colds we usually categorize into common colds and specific types of colds. The majority of common colds are rhinovirus infections, while a small number are caused by respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus, human metapneumovirus, coronavirus, hemolytic streptococcus, streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and mycoplasma infections. In contrast to the prevalence of viral infections, children with colds and fever due to bacterial infections tend to be in the later stages of the cold course and have a higher probability of co-infections. The same is true for specific types of colds. Herpes isthmus is caused by coxsackievirus infection, and pharyngeal conjunctival fever is triggered by adenovirus types 3 and 7. The influenza virus is behind the flu. When the viral infection is prolonged, it is more likely to be combined with bacterial infections.
This can be seen in the common cold: usually the child's nose is clear at the beginning of the cold, but later it turns into a thick runny nose. A change from clear to pus-filled snot is a good indicator of a possible bacterial infection. A simple blood test at a healthcare facility can determine whether your child has a viral or bacterial infection. When a child has a viral infection, the white blood cell count is normal or low, the neutrophils are decreased, and the lymphocyte ratio is relatively high. Virus isolation and serologic testing can identify the causative agent. Immunofluorescence and enzyme-linked techniques, as well as molecular biotechnology, can provide an early diagnosis of pathogen confirmation. When a bacterial infection is present, the blood count may show elevated leukocytes and neutrophils, and pharyngeal paper cultures may be used to identify the causative organisms prior to the administration of antibiotics.Elevated CRP (C-reactive protein) and PCT (procalcitonin) may be considered as a possibility of a bacterial infection.
Antibiotics are only indicated for bacterial infections. We hope that parents will not make their children take "cephalosporin" or "amoxicillin" as soon as they catch a cold, as this is not the right thing to do, and can even lead to gastrointestinal disorders, which can do more harm than good.
I'm pediatrician Dr. Nan Fish and I'm happy to answer your questions.
Indeed, when a baby catches a cold, the cause has to be clarified first, which involves subsequent symptomatic treatment.
In general.This is how you can differentiate between a viral or bacterial cold:
1, viral colds have the characteristics of a group attack, such as the family one to two, two to three, or a large number of children in the kindergarten have been hit. Bacterial colds are usually a "one-man war" and do not infect others.
2. Viral colds come on strong. Bacterial colds may drag on for two or three days before getting worse.
3. Viral colds usually do not have pus and sputum; bacterial colds do.
4. Viral colds usually have a runny nose, and bacterial colds have their main symptoms in the throat.
5, go to the hospital to do blood routine, viral cold, the general total white blood cell count is low, early neutrophil percentage is high, bacterial cold both high.
Therapeutic differences:
1, most of the baby's cold, are mostly viral colds, do not need fluids, follow the doctor's instructions to take medicine, drink more water and rest.
2. Bacterial colds require consultation with a doctor and, in severe cases, treatment with fluids.
Fish Xiaonan: 80s pediatrician mom, attending physician at Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine.
Today's Headline Outstanding Self-media Brand of the Year, Headline Health Gold Prescription Author, Health Headline of the Year.
Colds are routinely categorized into common colds and influenza, the former mainly caused by rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, adenoviruses, and the latter by influenza viruses; the questioner's intention should be how to distinguish between viral and bacterial upper respiratory tract infections; the former only requires symptomatic treatment, while the latter may require the use of antimicrobial drugs; common colds are the most common illnesses in children as well as adults, and the upper respiratory infections that they mainly cause include Rhinitis, pharyngitis, in general the cold can destroy the normal function of the nasopharyngeal mucus cilia system, reduce the barrier defense ability, and then secondary bacterial infections, the upper respiratory tract infections of the common pathogens include Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, Haemophilus influenzae, Catamorium, etc.; how to distinguish between viral and bacterial infections through the relevant examination and clinical manifestations? How about the empirical medication for viral or bacterial infections?

1. Clinical tests:
If the white blood cell (WBC) count or neutrophil percentage in routine blood tests is not significantly higher than normal, viral infection is considered, and vice versa; C-reactive protein (CRP) and calcitoninogen PCT (PCT) can also be used to determine the presence of bacterial infections, and it should be noted that CRP has a high sensitivity but not a high specificity, and PCT has a slightly lower sensitivity but a high specificity, in short A higher than normal CRP does not confirm the presence of a bacterial infection, but a high PCT basically confirms a bacterial infection.
2. Clinical symptoms:
If the patient presents with symptoms such as high fever, sore throat, abdominal pain, swollen and painful cervical lymph nodes, red and swollen tonsils (with purulent discharge), bacterial infection should be suspected; if symptoms such as cough, rhinitis, runny nose, hoarseness, stomatitis, conjunctivitis, diarrhea and other symptoms are present, the possibility of viral infection is considered high, and the diagnosis of bacterial infection or not can not be made on the basis of the clinical manifestations alone, but it can assist in determining the severity of the disease and whether or not to Antimicrobial drugs are given empirically at the first opportunity.

3. Duration
Viral upper respiratory tract infections usually resolve spontaneously in 7 to 10 days (some shorter), while bacterial infections may get progressively worse without the use of appropriate antimicrobial drugs, and of course there are some bacterial upper respiratory tract infections that resolve spontaneously without the use of antimicrobial drugs, which is related to each individual's autoimmunity as well as the virulence of the bacteria.
4. Medication options:
Viral infections, for the common cold patients given antipyretic, rehydration, relief of nasal thia and other symptoms of the drug can be, the main drugs are acetaminophen, ibuprofen (antipyretic), drugs containing pseudoephedrine (relief of nasal thia symptoms), etc., if the influenza, the systemic symptoms of its heavier than the common cold, the onset of the disease within the initial 48h given to the anti-influenza virus drug oseltamivir (Tamiflu), can shorten the duration of the disease, but over 48h However, it is not recommended to use it beyond 48h.
For bacterial infections, drugs are selected based on the common causative organisms of upper respiratory tract infections, and commonly used are amoxicillin, amoxicillin clavulanate potassium, cefaclor (Hicklaw), cefixime, ceftriaxone, and azithromycin.
Precautions: 1) viral upper respiratory tract infections should not be given antibacterial drugs, not only has no therapeutic effect, but also increases the incidence of adverse reactions and the rate of bacterial drug resistance; 2) preventive vaccination for children with influenza vaccine, Streptococcus pneumoniae vaccine, Haemophilus influenzae vaccine can significantly reduce the incidence of bacterial upper respiratory tract infections; 3) the initial onset of upper respiratory tract infections are mostly caused by viruses, but bacterial infections can not be excluded, so this is an empirical statement of greater probability and is not absolute.
The authoritative interpretation of Pharmaceutical Affairs, unauthorized reproduction, plagiarism will be punished.
Colds and fevers are one of the most common illnesses in daily life, especially in winter and during the change of seasons! Most colds are viral infections thatMajor pathogenic viruses include influenza viruses, rhinoviruses, coronaviruses, parainfluenza virusesHowever, a small percentage of people with colds have bacterial infections, especially if they have been sick for a long time! For adults with normal immunity, viral colds are usually completely self-healing, but for children or the elderly with weakened immunity, viral colds are more difficult to recover from.If we can clarify whether it is a viral or bacterial infection in the early stages of a cold, and use medication for antiviral or antibacterial treatment in advance, recovery from a cold may be slightly faster! (Especially for bacterial colds)

So how do you determine if it's a viral or bacterial infection?
The first method is to take respiratory secretions and do bacterial culture and drug sensitivity tests, according to the type of bacteria detected, the appropriate antibacterial drugs will be selected. If no pathogenic bacteria are present, it is proved to be a viral infection, and antiviral drugs, such as oseltamivir, can be tried. However, bacterial culture takes time, usually about 3 days before the result is available, and the best treatment period may be missed.
second typeThe method needs to test the doctor's diagnostic experience!It is divided into two main areas, symptom presentation and test indicators!
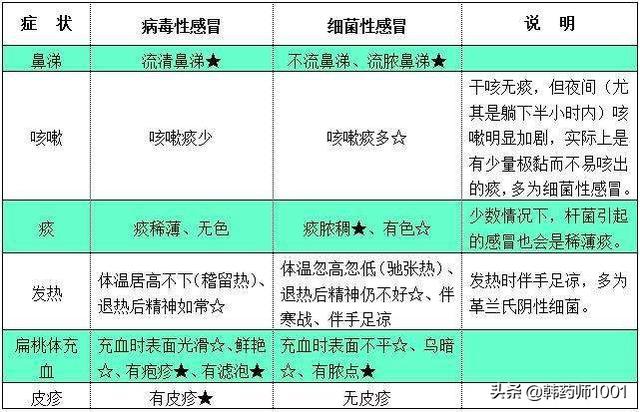
symptomatic behavior
Viral cold patients, usually runny nose, sputum thin and colorless, fever with high temperature, after fever as usual, tonsils with herpes follicles, skin rash。
Bacterial cold patients, usually runny nose, cough sputum, sputum pus thick, body temperature fluctuates, after the fever is gone, the spirit is still not good, accompanied by chills, hands and feet cold, tonsils congestion when the surface is not flat, dark, with pus spots.
Inspection Indicators
In patients with viral colds, blood white blood cell counts are normal or low, neutrophil ratios are usually not elevated, lymphocyte counts are elevated or lowered, and c-reactive protein and procalcitonin are usually normal as well!

In patients with bacterial colds, blood white blood cell counts and neutrophil ratios are generally high, lymphocytes are low, and c-reactive protein and calcitoninogen are generally high!
When a child catches a cold, the parents are distressed and suffer, and have pity on the parents! Parents are advised not to spoil their children too much, but to let them have a balanced diet, eat more fresh fruits and vegetables, and do more exercise to strengthen their immunity!We hope that people will learn more about this knowledge themselves and doctors will gain more clinical experience, so that together we can fight the disease and welcome a healthy life!

I am Pharmacist Han, dedicated to explaining the complex and difficult knowledge of diseases in plain words to help you manage your body. Your likes and concerns are my greatest motivation! In addition, if your family and friends have similar troubles, please forward this article to them!
Parents can differentiate between them by the nature of the snot, the color of the phlegm, and the duration.
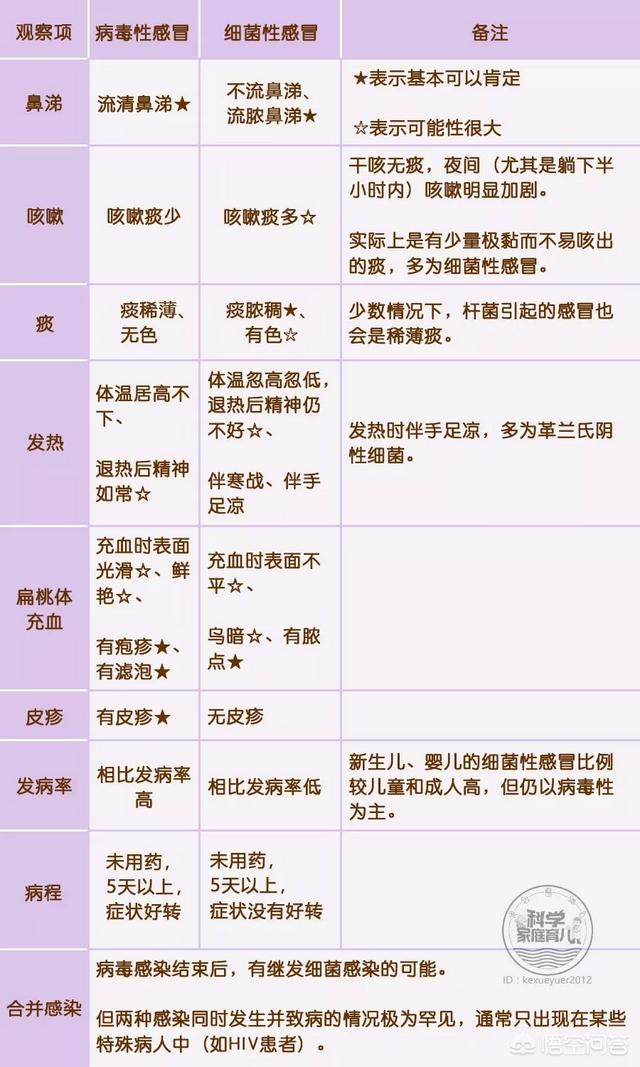
Whether it's a viral or bacterial cold, they are self-healing illnesses and parents just need to take good care of the symptoms.
When it comes to viral colds, stop using antibiotics, they don't work!
If your baby's temperature exceeds 38.5℃ and he or she is not in good spirits, coughs frequently for too long, or has a runny nose for more than two weeks, it is important to take medication and seek medical attention.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.