What is the appropriate blood glucose control for a 70-year-old diabetic? What do I need to pay attention to in my daily life?
Diabetes mellitus is more commonly seen in patients after the age of 50, seventy years old almost about twenty years of the disease. The patients themselves have formed the medication habits under the guidance of the doctor. Generally speaking, if the fasting blood glucose is controlled below 7mg/mol, there will be fewer complications, and it is not necessary to pursue below 6.
There is also no need to test blood glucose frequently, so as not to increase the stress of the mind, diabetes is an endocrine disease, emotional fluctuations will affect the blood glucose value. If you have the conditions, you can do glycated hemoglobin to detect the change interval in the last month. If you feel that the recent changes in eating habits or insomnia, etc. can be temporary testing of blood glucose, according to the results of the test to adjust the medication and lifestyle habits. The control of fruits can be adjusted according to the changes of blood glucose, stable blood glucose can be consumed two hours after the meal about a quarter of a fruit, do not eat two kinds of fruits at the same time, but also to control the intake of high sugar, such as grapes, watermelon, the amount should be controlled to less than 50 grams.
Diabetic patients do a good job of self-management, cooperate with doctors, change bad habits, moderate exercise. Take steps to control your mouth.
There are more and more diabetics around, and it's no longer a disease of the elderly, the incidence of young and middle-aged people and even children is on the rise.
So, what is the standard of blood sugar for a normal person? And what is the blood sugar control standard for diabetics? Here's a detailed look.
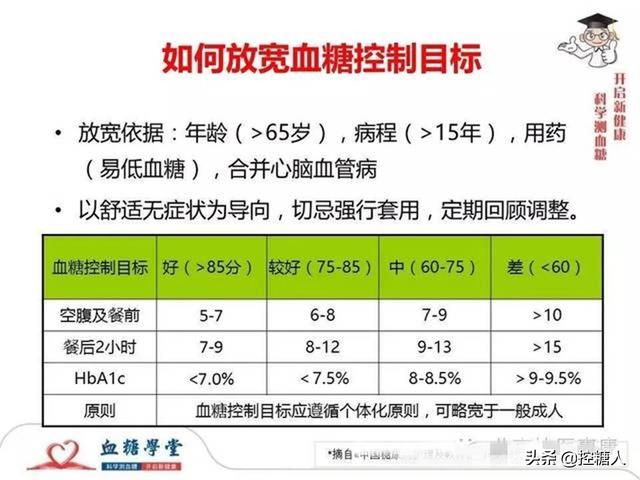
For 70-year-olds without diabetes and for all healthy people, it is important to keep fasting blood glucose below 6.1 and two-hour postprandial blood glucose below 7.8.
However, for diabetic patients in their 70s, it should be said that as long as the older diabetic population is over the age of 60, this glycemic control standard should be appropriately relaxed.
We recommend that older diabetic patients over the age of 60 keep their fasting blood glucose at 8 mmol/L and their two-hour postprandial blood glucose at less than 10 mmol/L. This is mainly for patients with stable blood glucose and no significant complications or comorbidities.
If the 70-year-old diabetic patient has a long course of disease and may have significant acute or chronic complications, such as cardiovascular lesions, cerebrovascular lesions, etc., he or she may also be able to relax the glycemic criteria appropriately under the above criteria.
This on the one hand can ensure the supply of blood sugar in the brain of the elderly to maintain the normal operation of the brain, on the other hand, if the blood sugar control is too strict, but may be prone to hypoglycemia, hypoglycemia is even higher than the danger of hyperglycemia, severe hypoglycemia is very easy to aggravate the condition, and even make the elderly life-threatening.
Therefore, for diabetic patients over 60 years of age, including 70 years of age, the standard of glycemic control is relatively loose compared to that of young diabetic patients, do not be overly strict, the main purpose is to ensure that the sugar is stable, no hypoglycemia, and to ensure the safety of the elderly's life, which is the main therapeutic purpose, and the starting point of the establishment of the standard of glycemic control.

What should elderly diabetics be aware of on weekdays?
Diabetes is a chronic disease, which means it is progressive, and most older diabetics have a long history of the disease, by which time pancreatic islet function has been more severely impaired. The damage to the body from high blood sugar has also set in, and there are likely to be multiple complications.
Therefore, for elderly people with diabetes, the first thing you should do is to have a physical examination once a year to check your physical condition, and at the same time, blood glucose measurement should not be left behind, and it needs to be adhered to.

The main things that you should be aware of in your daily life when you have diabetes in the elderly include:
1, diabetic patients should quit smoking and limit alcohol, balanced diet, regular work and rest, refuse to stay up late, work and rest, adhere to aerobic exercise, and develop good living habits. Maintain normal weight, refuse obesity, strict control of diabetes, learn to relax and maintain a good state of mind.
2, the use of drugs need to be careful, according to the doctor's requirements, according to personal constitution and condition, regularly choose to take Chinese and Western medicines, do not abuse the hypoglycemic drugs, do not arbitrarily change the drugs or dosage, change the drug or stop the drug is best to be carried out under the guidance of a doctor.
3, regular monitoring of blood glucose and keep records, observe the changes in blood glucose, pay attention to various indicators of the body, such as blood lipids, blood pressure, glycated hemoglobin, etc., pay attention to the corresponding complications, such as liver function, renal function, electrocardiogram and ophthalmology, and if there is any abnormality to be treated at the earliest possible time.
4, hypoglycemia is very harmful, need to pay special attention to preventing hypoglycemia, usually do not overly control the diet or strenuous exercise, and do not too much pursuit of normal blood sugar standards.
Thanks for reading, feel free to like and follow, and I wish you happiness and well being!
Hello! I'm an endocrinologist and I'll answer this question!
Diabetes control standards are generally glycated hemoglobin 7.0 or less, fasting blood glucose 7mmol / L or less, 2 hours after meal 10mmol / L or less, but this also needs to be adjusted according to the patient's specific situation. Older diabetic patients with glycated hemoglobin can be appropriately relaxed to 7.5 or 8.0, blood glucose fasting below 8 or even below 10, after meals below 11 or even 12 or 13 are sometimes acceptable. It is up to the doctor to decide on the specific target based on the duration of the disease, medication, complications or co-morbidities, and whether or not hypoglycemia occurs frequently.
Older diabetics should pay special attention to the following
1. Prevent hypoglycemia, because hypoglycemia induces the risk of serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, so life and treatment should be particularly regular, and regular hospital review. Measure blood sugar promptly if there is any discomfort.
2. Elderly diabetic patients are often combined with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, etc., and should be treated by the relevant departments if they have related problems.

Please follow me! You can get a steady stream of professional and standardized knowledge and information on diet, exercise, fat and weight loss, as well as the prevention and treatment of metabolic diseases such as diabetes! Welcome to leave a message to discuss. Thank you!
Thanks for the invite.
Regardless of age, the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is the same, and the criteria are fasting blood glucose ≧ 7.0 mmol/L or two-hour postprandial blood glucose ≧ 11.1 mmol/L or random blood glucose ≧ 11.1 mmol/L. Once the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is established, standardized treatment should be carried out under the guidance of the doctor, and the lifestyle should be actively improved and medication should be individually administered in order to steadily control the blood glucose and reduce the occurrence of complications. complications and improve the quality of life.
For diabetic patients aged 70 years, who are already in the advanced age group, we recommend that fasting blood glucose should be kept as low as possible at 7.0 mmol/L, two-hour postprandial blood glucose should be kept as low as possible at 10.0 mmol/L, and glycosylated hemoglobin should be kept within 7.0%.
Of course, the specific control goal of blood glucose should also still be determined according to their own situation, and individualized goals need to be set under the guidance of doctors. For younger diabetic patients with a short disease duration, no complications, long life expectancy, and no hypoglycemic episodes, the glycemic control goal should be more stringent. It can also be relaxed for diabetic patients who are older, have a long disease duration, many complications, short life expectancy or frequent hypoglycemic episodes.
For diabetic patients, they need to pay attention to a reasonable diet in daily life, control the total daily calorie intake, and increase the intake of fresh vegetables and coarse grains; they need to exercise regularly, mainly aerobic exercise, step by step, and it is appropriate for them to have no chest pain and other discomforts; and they need to pay attention to quitting smoking and limiting alcohol, and controlling their body weight. At the same time, you need to take medication regularly under the guidance of a doctor, and use insulin replacement therapy if necessary, as well as pay attention to monitoring changes in blood glucose, and pay attention to regular review.
Thanks for reading and good health to all. This article was originally written by General Practice Sweeper on Today's Headlines & Wukong Q&A, Copyright © All Rights Reserved.
Thanks for the invite!
Health Prophet: Let's learn about diabetes, find out if blood glucose normals are age-related, control the progression of diabetes through lifestyle interventions, and prevent diabetic complications.
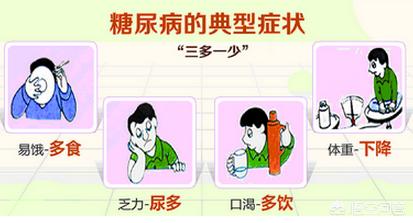
What is diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disease, the pathology of which is caused by a decrease in the body's secretion of insulin or a decrease in the body's sensitivity to insulin.
Blood glucose normals in relation to age?
Age does not have much to do with blood glucose, for adults, the normal range of blood glucose is the same, regardless of age. Generally fasting whole blood glucose is 3.9-6.1 mmol/L, 2 hours after meal: blood glucose ≤ 7.8 mmol/L.
Note to diabetics:
Take your medication on time and monitor your blood sugar
Diet should control the total daily energy intake, avoid the intake of high sugar, high fat, high glycemic index foods, increase the intake of satiety, vitamin, dietary fiber-rich foods
Take a walk 30 minutes after a meal to stabilize blood sugar
Take care to prevent hypoglycemia, especially nighttime hypoglycemia
I hope my answer can let you gain, pay attention to my today's headlines / Wukong Q&A account can get more health-related knowledge, I am your side of the health manager, if you help, please click to support, if you have any questions can be commented with me to discuss!

As the saying goes, "life is 70 years old", diabetic patients over 70 years old are in fact senior patients.
Elderly patients should not be too strict in controlling blood sugar, because blood sugar control is too low, but all over the body uncomfortable. I'm sure some old sugar lovers have experienced this situation.
So, what is the right blood sugar control for a 70-year-old diabetic?
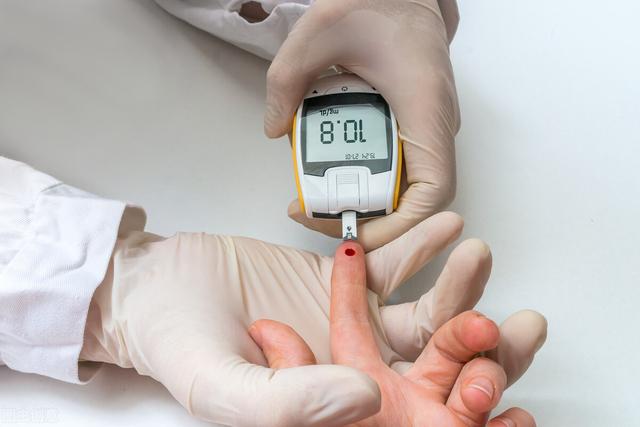
Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) is the gold standard for clinical assessment of long-term glycemic control, with a normal reference value of 4% to 6% by standard testing methods.
For most patients with type 2 diabetes, HbA1c should be controlled at ≤7.0% and more strictly at ≤6.5%.
For diabetics over 70 years of age, this also needs to be considered in the context of the duration of the disease, whether there has been severe hypoglycemia, the presence of small- or large-vessel complications, and life expectancy.
If the duration of diabetes is short, no severe hypoglycemia has occurred, no vascular complications have occurred, and the life expectancy is long, you may consider controlling HbA1c at 6.5%-7.0%, mean fasting glucose at 7.7 mol/L, mean 2-h postprandial glucose at 9.1 mol/L, and overall mean glucose at 8.6 mmol/L....
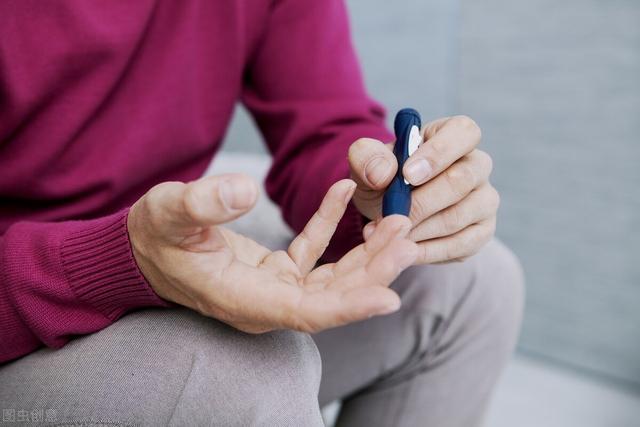

If the patient has a history of severe hypoglycemia, or has many comorbidities and a short life expectancy, a more generous HbA1c control goal of < 8% may be used, which is acceptable. Fasting glucose around 8 mol/L and postprandial glucose < 11.1 mol/L after 2 hours.
In addition, diabetes mellitus is usually associated with hypertension and hyperlipidemia, so comprehensive control should be emphasized.
In addition to the criteria for glycemic control, optimal blood pressure control in elderly diabetic patients is <150/90 mmhg, total cholesterol >4.5 mmol/l, triglycerides >1.7 mmol/l, and LDL >2.6 mmol/l.
What do I need to be aware of in my daily life?
1. Pay attention to prevent hypoglycemia, usually carry candies and cookies with you, once panic, hand shaking, cold sweat, etc., eat a piece in time to replenish blood sugar. If food is ineffective, you need to take glucose or candy directly by mouth.
2. Pay attention to a well-controlled diet, and eat a low-sugar, low-fat diet.
3. Pay attention to appropriate exercise, avoid sitting still and inactivity for a long time, so as not to induce lower extremity venous embolism. #Doctors Super Team #Disease prevention and control knowledge #Health popularization contest
How much should I control my blood glucose in a 70-year-old diabetic? Such a question is often asked, it seems that age and the control of the indicators of the relevant chronic diseases, has a close relationship, but in fact, for diabetes control goals, although it is true that different situations have different requirements, but the age is not the main key factors.
The main factors that are still considered as to what is the appropriate level of blood sugar control for diabetes are as follows:
The duration of diabetes.
Self-regulatory glycemic control in diabetics;
Life expectancy profile of diabetics;
High and low risk of hypoglycemia.

This may be a bit abstract, let's take an example to illustrate it, for example, Lao Wang and Lao Li, also 70 years old elderly friends, also have diabetes, Lao Wang's diabetes found less than 10 years, and has been very good control of blood glucose, there is no serious diabetic complications, health status is better, the risk of hypoglycemia is also very low, in this case, we recommend that the old king's Glycemic control target should be set relatively strict, generally glycated hemoglobin should be at least less than 7.0%, if the body tolerates, can also be glycated hemoglobin level control to 6.5% is also possible, glycated hemoglobin is a response to the long-term glycemic control of the indicators, for our daily blood glucose monitoring, generally fasting blood glucose is not more than 7.0mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose does not exceed 10.0mmol/L for 10.0mmol/L as a limit, good blood glucose control, can better slow down the development of diabetes, reduce the risk of various cardiovascular and renal, retinal, peripheral nerves and other aspects of complications brought about by high blood sugar.
Old Li's situation is not so ideal, his diabetes is early, although he was diagnosed with diabetes when he was in his 30s, but due to the good state of his body at that time, he didn't feel anything and didn't control it much. Over the years, various complications have gradually appeared, his renal function has declined, and his cardiovascular risk is also high, and his blood glucose can't be controlled effectively by oral medication, and he needs to take insulin in most cases. In order to control blood glucose, many times there have been symptoms of hypoglycemia, diet and exercise control, has not been able to do a good job, for such a situation, we will establish the old Li's glycemic control goals can be appropriately relaxed to control glycated hemoglobin at 7.0-8.0% for the control of glucose goals, corresponding to the fasting blood glucose level of no more than 7.5, 2 hours after meals, the blood glucose level does not exceed the 11.0 limit, to minimize hypoglycemia. Such a situation can reduce the risk of hypoglycemia and increase the safety and tolerability of glycemic control in diabetic patients, on the other hand, it should also try to control the blood glucose smoothly and reach the standard, in order to reduce the further progress of complications brought by hyperglycemia and related acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular risks.
Through the above 2 examples, we should be able to understand that although the same 70-year-old, the same diabetic patients, due to the different conditions of the patients, their glycemic control goals are not the same, the reason why to emphasize the personalized development of glycemic control goals, the ultimate goal, or in order to better safeguard the patient's health, to improve the patient's life treatment and life expectancy. If the actual situation is ignored, and the blood sugar is strictly controlled within the qualified range by intensifying blood sugar lowering, for some diabetic patients with poorer physical condition and greater difficulty in blood sugar control, the risk of severe hypoglycemia may occur, and severe hypoglycemia, if it lasts for a long time uncorrected, will damage the brain's health, and also cause sympathetic nerve excitation and increase the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular emergencies, such as cardiac infarction and cerebral infarction. The risk of cardiovascular emergencies such as heart attack and cerebral infarction will be increased. Such a way of controlling glucose is an unsuitable and unhealthy way of controlling glucose, and the ultimate goal of setting up our glucose control goal is:Maximize your health benefits by controlling your blood sugar levels as much as you can while keeping your health tolerant.
For the 70-year-old elderly diabetic control goals, there is a more relaxed control situation, for example, such a diabetic patient, blood glucose is difficult to control, there is a serious risk of hypoglycemia, at the same time, repeated co-infections, or has occurred in acute cardiovascular and cerebral vascular lesions, has basically no self-management ability, and at the same time, no other person can be able to carry out good nursing care of the case of The glycemic control target of diabetic patients can be appropriately relaxed, and it is generally recommended that diabetic patients in this situation should control their glycosylated hemoglobin between 8.0 and 8.5%, corresponding to a fasting blood glucose level of no more than 8.5, and a postprandial blood glucose level of no more than 13.9 as the target, which also ensures that the patient's body tolerates and the safety of glucose lowering, and controls the blood glucose level as much as possible, and reduces hyperglycemia. This is also to ensure the patient's tolerance and glucose-lowering safety, so as to control the blood glucose level as much as possible, and reduce the health hazards and risks caused by high blood glucose.
The 70-year-old elderly control of blood sugar, in addition to combining their own physical condition reasonable development of sugar reduction goals, follow the doctor's prescription medication to control blood sugar, in daily life, the same need to pay attention to the reasonable arrangement of diet and exercise, these aspects of the safety and sugar reduction goals, the same is different from person to person. 70 years old diabetic patients, through dietary control of sugar, and not just control their mouths, eat less so simple, how to eat Reasonable, but also to ensure that the body's adequate energy supply, choose a reasonable dietary structure, to develop good eating habits, are very important aspects, but also in the diet should also take into account other aspects of metabolic levels, such as high triglyceride problem of diabetic patients, diet should pay attention to control the intake of high-fat diets, and high uric acid problem of friends, pay attention to reduce the intake of purine, in short, 70 years old! In short, 70-year-old diabetic patients, the principle of good dietary arrangements, on the one hand, to ensure that the body's energy and nutrient supply, on the other hand, to help blood glucose dietary control, while also taking into account other aspects of metabolic problems in the body's conditioning.
In terms of exercise, reasonable exercise, on the one hand, help elderly diabetics blood sugar control, on the other hand, also helps the body's muscle strength and flexibility to maintain. However, how to "reasonably" set up exercise is something that needs to be considered individually. For example, for a 70-year-old diabetic patient with normal physical ability, the choice of exercise should be different from the physically weaker one, and the physically normal one can combine his or her own situation with moderate-intensity exercise, such as brisk walking and jogging. You can choose, while the weak can according to the situation, in the three meals in the indoor reasonable activities exercise. Diabetic exercise should pay special attention to the protection of the foot, with diabetic foot problems of friends are generally not recommended to carry out too much with the foot side of the exercise, in addition in the process of exercise, but also to avoid violent force, as well as pay attention to the risk of hypoglycemia.
Hello, thank you for the invitation.70-year-old patients with diabetes who have fewer or no complications, the elderly are in relatively good health. In this case, it is generally recommended that fasting blood glucose be controlled between 4.4 and 7.0 mmoI/L. Two-hour postprandial blood glucose control is below 10 mmoI/L. If the elderly person has comorbidities or even other comorbidities. Life expectancy is less than 5 years, in this case, the control standard can be moderately relaxed. Fasting blood glucose can be controlled at 7~9mmoI/L. Postprandial blood glucose can be relaxed to between 11~13mmoI/L.
There are a few things to keep in mind in your life:
First, control the diet, control the diet is the basis of controlling blood sugar. Elderly diabetics also need to control their diet. Especially control the amount of staple food. Diet control can reduce blood sugar fluctuations and delay the occurrence of complications.
Second, reasonable exercise, exercise is very favorable to blood sugar, not only can lower blood sugar. It is good for blood lipids, heart function, lung function. Elderly people should pay attention to the ability to do. Combined with their own actual situation for exercise.
Third, to prevent hypoglycemia, carry glucose products or food with you to prevent hypoglycemia. Because hypoglycemia is easy to cause hypercoagulable state of the body, inducing cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, leading to increased mortality of elderly diabetic patients.
Fourth, timely monitoring of blood glucose, monitoring blood glucose can prevent the rise of blood glucose, prevent the occurrence of acute complications, take timely measures to lower sugar and stabilize blood glucose.
Fifth, regularly to the hospital to review liver function, kidney function, blood lipids, ion, glycated hemoglobin, urine microalbumin, 24-hour urine protein quantitative. As well as for a variety of complications of the examination, to understand the progress of complications, and take timely measures to deal with. To prevent the emergence of serious complications. For example, diabetic foot, diabetic nephropathy.

A diabetes specialist answers this question.
To answer this question, let's first look at what are the three levels of diabetes control goals and what criteria are used to set each.
There are three levels of diabetes control goals:

Universal control objectives
The universal control goal is the same standard that most diabetics need to follow, which is a fasting blood glucose of less than 7.0, a postprandial blood glucose of less than 10.0, and a glycosylated hemoglobin of 7.0% or less, which is very easy to remember. For most adults with diabetes, this is the standard of control that needs to be followed.
Strict control objectives
For pregnant women, young patients with first-onset diabetes and diabetes without complications, the recommended goal is strict control. In this case, it is strict for pregnant women, because it is necessary to ensure the normal growth and development of the fetus and the life of the pregnant woman. As we all know, gestational diabetes or diabetes combined with pregnancy diabetes control requirements of 3.3-5.1, to be lower than the control standards of non-diabetic patients, and the corresponding glycated hemoglobin should be less than 6.5%.

I think young first-onset diabetes, if there are no complications, should try to keep their blood glucose level below 6.5% in order to minimize complications.
Loose control targets
This goal is applicable to diabetics who have had diabetes for a long time, have various chronic complications, combined cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, recurrent hypoglycemia and diabetics with psychiatric disorders, and for whom a loose glycemic control goal is applicable. That is, glycated hemoglobin below 7.5%, fasting below 8, postprandial below 12 is also permitted.
Going back to our original question, what is the blood glucose control for a 70 year old? It depends on the duration of this elderly person's illness, the comorbidities and complications that have developed, the usual glycemic control, and so on.

It is possible to stay below 6.5 fasting if the elderly person has a first onset of diabetes with medications that don't cause hypoglycemia. Staying below 7.0 fasting and 10.0 after meals will be more common.
However, if the elderly have complications or cardiovascular disease, then lax control measures are needed.
Currently, diabetes management has entered the era of individualized diagnosis and treatment, and blood glucose targets are not also one-size-fits-all, with different management strategies for different populations such as the elderly, pregnant women, and pediatric patients.
Elderly people have a longer course of diabetes, hypoglycemia symptoms are often more serious, which has a great impact on the subsequent control, so the elderly suffering from diabetes in reducing the risk of blood glucose at the same time, but also to ensure the effectiveness of glucose lowering, the clinic is now often adopted "7, 8, 9" strategy, that is, the age of 70 years old fasting blood glucose control at 7mmol / L below, 80 years old control in 8mmol / L below, 90 years old control in 9mmol / L below, to ensure that in the effective lowering of sugar, does not increase the risk of complications at the same time, does not increase the risk of hypoglycemia.
Of course, diet and life management as the basic treatment of diabetes, elderly diabetics should pay attention to the following points in their lives to help better control blood sugar.
What should older people with diabetes be aware of in their lives?
1. Changes in eating habits
Regularly quantitative meals, small meals, change the habit of eating refined white rice and noodles, the staple food more to add some coarse grains, wheat embryo, etc., usually eat more beans, vegetables, but these are based on the total calorie balance of the dietary adjustments made on the basis of.

2, pay attention to the order of meals
It has been clinically found that the eating order of soup, vegetables and then the main meal is more conducive to blood glucose control.
3. Maintain a healthy weight and waistline
Most diabetic patients are actually either obese or overweight, and need to go through a reasonable and healthy diet to reduce weight, which also helps to lower blood glucose, improve blood lipids and blood pressure, but do not use dieting, fasting and other extreme ways to reduce weight.

4. Ensure adequate sleep
Elderly people sleep less, so it is easy to ignore the impact of sleep on blood sugar, too much or too little sleep will increase the appetite, thus accidentally eating too much, which is not conducive to blood sugar control, and even increase the risk of complications, so the day's sleep time to maintain the best 7-8 hours.

5. Exercise
If the elderly are in good physical condition, you can properly carry out physical exercise, but remember, must be measured, and do not exercise on an empty stomach.
6. Low-sodium diet
Diabetes is not really that scary, what is scary is its complications. A low-sodium diet helps lower blood pressure, protect the kidneys and reduce the risk of complications.
7、Real-time monitoring of blood glucose
Measuring blood glucose regularly every day to keep it at a normal level helps the patient understand how certain foods or exercises affect it.

8. Prevention of heart disease
Heart disease is also one of the complications of diabetes and it is recommended that patients can have regular checkups to prevent it in real time.
9、Try to avoid bumps, bruises, falls
Diabetes triggers the risk of infection and the patient's wounds heal more slowly, if you are injured, you should clean the wound properly and in a timely manner, consume antibiotic medication and sterile bandages to dress the wound, and if the situation does not get better, seek medical attention in a timely manner.
10. Cessation of smoking
Quitting smoking reduces the risk of both blood pressure, stroke, heart disease, and kidney disease, as well as the risk of death caused by diabetes.
11. Keep in a good mood and get tested regularly
Long-term stress, mental tension will make the blood sugar rise, learn to give yourself decompression and relaxation, maintain an optimistic and positive state of mind, and regularly go to the hospital for relevant examinations, actively cooperate with the treatment, do not give up on yourself.

Finally, I would like to emphasize that diabetes is not scary, even if you have the disease, actively cooperate with the treatment at the same time, control your daily diet, live a healthy life, maintain an optimistic mindset, and live with diabetes peacefully for the rest of your life.
Being friends with a nutritionist can solve all kinds of problems in your diet. Feel free to tease: the Clarke Nutrition Institute.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.