Where does the plaque in the blood vessels go after the body has a stent? What do I need to be aware of?
Where does the plaque in the blood vessels go after a stent? This is a good question, and those who are able to ask this question are generally said to be thoughtful people. This is because they have thought about stenting in detail and may have conducted appropriate research to ask such a question. Today, Dr. Zhang will try to answer this question.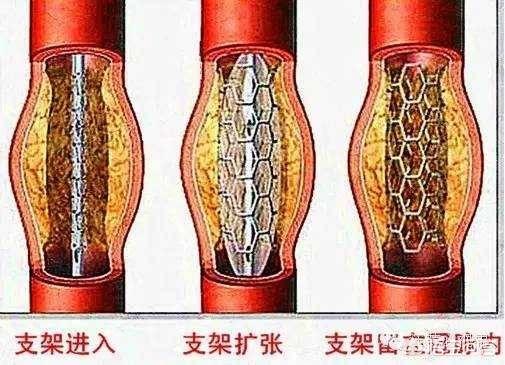
As a rule, severe atheromatous plaques are formed in the blood vessels to the extent that they block the blood vessels and restrict blood flow by more than 50%, and in severe cases by more than 75%. Stent implantation is possible only when the blockage reaches 75% or more and the body develops symptoms of myocardial ischemia. But where does the original atheromatous plaque go during stent implantation? It should be said that most of the atherosclerotic plaque is squeezed under the stent, while a small amount of atherosclerotic plaque detachment may flow with the blood flow to the distal end of the vessel, and eventually undergoes mechanization and is absorbed at the distal end of the vessel. As shown in the figure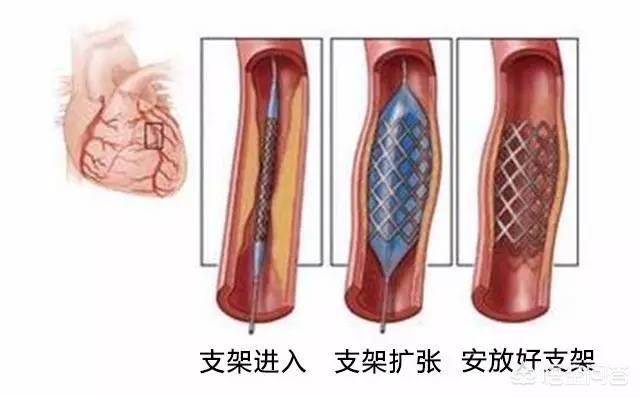 It does not mean that the plaque disappears after the stent is implanted in the body, it only means that the plaque is temporarily squeezed by external force, and if you cannot take medication on time and change your lifestyle, the plaque will still grow again.
It does not mean that the plaque disappears after the stent is implanted in the body, it only means that the plaque is temporarily squeezed by external force, and if you cannot take medication on time and change your lifestyle, the plaque will still grow again.

Thanks for the invite! Extraordinarily good question, answered a little late.
There are two questions, answered separately.
The first question is, after stenting, where does the plaque in the vessel go?
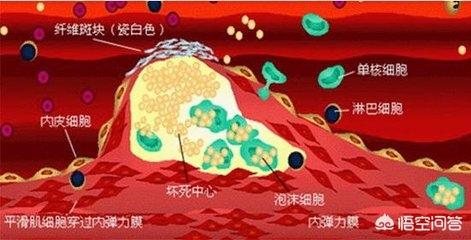
The body has a stent ......? The question that should be asked is where did all the plaque that was blocking the vessels go when stents were put in the arterial vessels, mainly the coronary arteries?
Where did the plaque go? The plaque got squished apart and stuck to the vessel wall.
The stent is propped open inside the blood vessel. The process of propping open (dilating the blood vessel) involves pressure, which squeezes the cholesterol and necrotic cells that have built up in the plaque, spreading them out under the intima and sticking them to the wall of the blood vessel, sandwiched between the stent, the lining of the blood vessel (which the stent is tightly attached to), and the wall of the blood vessel.
At this time, the lining of the blood vessel will be torn. This is very easy to understand, just like a pile of flour to be flattened to be rolled thin, if there is a filling inside, during the process of rolling thin, the filling is large thin skin will break the skin, the stenting process, blood vessel wall changes are also similar.
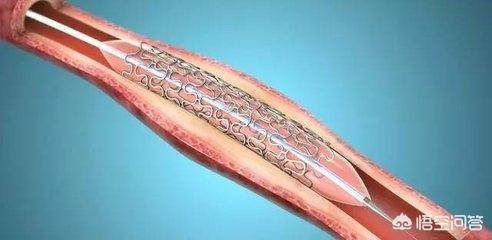
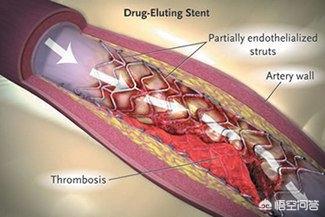
Therefore, the post-stenting period (intimal tear, rough wall) is particularly prone to thrombosis and requires intensive antiplatelet therapy. This is why a combination of two antiplatelet agents is required after coronary stenting. It is not until this intimal tear is repaired, the endothelial cells cover (grow all over) the surface of the stent, and the surface of the vessel is smooth that the high risk passes, and only then can it be switched to single-agent antiplatelet therapy. And due to the different varieties of stents, the growth period of epithelial cells is also different, sometimes in order to inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscle of the blood vessel wall (which can cause blood vessel restenosis), it is also necessary to coat the surface of the stent with medication (that is, drug-coated stents), which will delay the healing of the intima even more, and the treatment of the double antiplatelet therapy will be required to be a little longer.
What's more, although the plaque at the stent site squeezes away, it will be redeposited if the blood lipid is high; moreover, there is more than one plaque on the blood vessel wall, and plaque in other areas will also redevelop if no attention is paid to controlling blood lipid. Therefore, the cholesterol-lowering treatment required after stenting should be continuous and strict.
Thus comes the answer to the second question.
After stenting, you also need to pay attention to antiplatelet to prevent thrombosis, cholesterol to prevent atherosclerosis, and to prevent thrombosis and restenosis in the vessel after stenting.
Of course, there are also treatments to improve blood supply, and patients suffering from myocardial infarction have to have treatments to protect the myocardium, prevent myocardial remodeling, and protect cardiac function; in the case of cerebrovascular disease, there is also the issue of rehabilitation. But the main and basic thing is to adhere to the anti-platelet and cholesterol-lowering treatments, and in addition to drugs, a healthy lifestyle must not be neglected!

(Image from the Internet)
You are referring to coronary stent implantation, right? If so, let's share this question medically from the perspective of coronary atherosclerotic heart disease.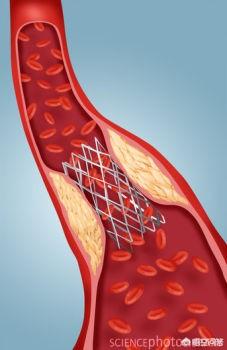
First, it has been clarified that the coronary arteries of the patient's heart have severe stenosis (e.g., ≥50% stenosis of the left main coronary artery) with atherosclerotic plaque formation, and when we put the vascular stent in, we use the elasticity of the balloon and the stent to hold up the narrowed lumen. Meanwhile, the previous atheromatous plaque is squeezed between the vessel and the outer wall of the stent, theIt didn't go away.
Thereafter, that narrowed coronary artery is temporarily opened, but the plaque is still there, the factors that promote plaque formation are still there, and that, the risk of re-formation of plaque blocking the lumen of the blood vessel is still there, and very likely! That is why, after stent implantation, patients are asked to make dietary and lifestyle changes, and to take long-term medications to prevent plaque from blocking the blood vessel again.
First of all, quit smoking, it is well recognized that smoking damages the endothelium of the blood vessels, it promotes the formation of restenosis, or the formation of atheromatous plaques in the blood vessels elsewhere in the heart, it's up to you whether you quit or not!
Second, limit alcohol consumption, currently recommended small amounts of alcohol, foreign research has confirmed that can reduce the risk of cardiovascular mortality to a certain extent. According to U.S. standards, according to their different amounts of alcohol, 14g-28g of pure ethanol per day is the standard amount of alcohol, you can be based on the alcohol content of beer, red wine, white wine, etc. roughly projected, women are often 14g, men 28g, but this is just a reference, each person's tolerance level of alcohol is not the same, so only for reference.
Third, reduce weight, low-fat diet, appropriate exercise, mood relaxation, regular work and rest, if you have diabetes ah, high blood pressure, control blood sugar and blood pressure standards. Doesn't it sound like the ideal, TV, novels in the world of idyllic life ah! Haha, yes, coronary heart disease patients is to this ideal life. I didn't do it before, but can I do it now?
Fourth, adhere to the long-term secondary prevention regimen your doctor has given you for coronary artery disease, this is written last, but it is really the most important! Stick to aspirin, statins, beta blockers, ACEI/ATB, etc., as long as it's your regimen, and don't get the silly, lucky idea that "I'm feeling good now, I must be better, I'll try going off my meds," because they're the ones who have most of the reoccurring problems after stenting!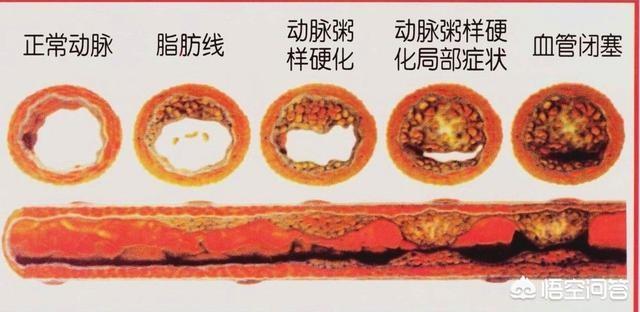
The article concludes by wishing readers good health!

What other questions do you have? Please leave a message.
Always know, always consult, be prepared, please add attention to oh!
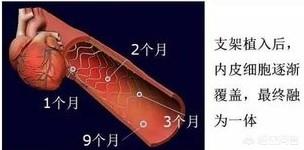
Cardiac stents are commonly used in the treatment of coronary artery stenosis ≥75 or occlusion, the stent through the peripheral radial artery or femoral artery to reach the stenosis site, and then through the high-pressure expansion of the balloon will make the stent tightly attached to the endothelium, and at the same time will also be the plaque extrusion under the stent, and then with the endothelium of the vascular endothelium will be completely covered with the stent (re-endothelialization), that is the stent and the vascular fusion of the body as a whole, and can not be taken out. Therefore, the plaque does not disappear after stenting, most of it is squeezed under the stent, and a small portion of it is dislodged and absorbed mechanically with the blood flow.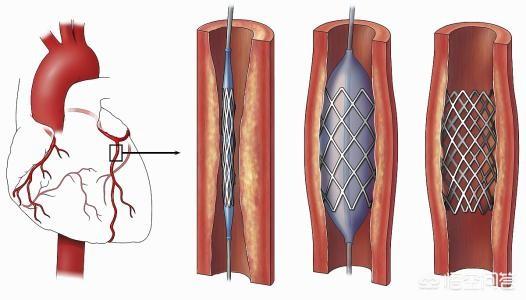 Cardiac stent implantation can quickly open narrowed or occluded blood vessels, restore blood supply, and subsequently reduce myocardial ischemia, hypoxia and necrosis. It should be noted that stent implantation, although permanent, is not a permanent solution. It is also necessary to actively improve lifestyle and cooperate with medication after stenting in order to control the condition stably in the long term and avoid thrombus formation within the stent, which may lead to restenosis.
Cardiac stent implantation can quickly open narrowed or occluded blood vessels, restore blood supply, and subsequently reduce myocardial ischemia, hypoxia and necrosis. It should be noted that stent implantation, although permanent, is not a permanent solution. It is also necessary to actively improve lifestyle and cooperate with medication after stenting in order to control the condition stably in the long term and avoid thrombus formation within the stent, which may lead to restenosis. Daily life after stenting should pay attention to: ① light, low-salt, low-fat diet, avoid spicy stimulation, high cholesterol, high-fat and spicy food; ② appropriate exercise, avoid large-scale physical activity in January, January gradually increased, step by step, in order to their own chest pain and other discomforts appropriate; ③ strict cessation of smoking, restriction of alcohol, do not drink alcohol is best, the condition of the stabilization of the appropriate consumption of red wine; ④ weight control, obese people should actively lose weight; ⑤ maintain a good state of mind, avoid anxiety, depression, anger and other emotions; ⑥ regular work and rest, avoid staying up all night. Obese people should actively lose weight; ⑤ Maintain a good state of mind, avoid anxiety, depression, anger and other bad emotions; ⑥ Regular work and rest, avoid staying up late.
Daily life after stenting should pay attention to: ① light, low-salt, low-fat diet, avoid spicy stimulation, high cholesterol, high-fat and spicy food; ② appropriate exercise, avoid large-scale physical activity in January, January gradually increased, step by step, in order to their own chest pain and other discomforts appropriate; ③ strict cessation of smoking, restriction of alcohol, do not drink alcohol is best, the condition of the stabilization of the appropriate consumption of red wine; ④ weight control, obese people should actively lose weight; ⑤ maintain a good state of mind, avoid anxiety, depression, anger and other emotions; ⑥ regular work and rest, avoid staying up all night. Obese people should actively lose weight; ⑤ Maintain a good state of mind, avoid anxiety, depression, anger and other bad emotions; ⑥ Regular work and rest, avoid staying up late. After stenting also need to be under the guidance of the doctor for drug treatment, mainly including: ① if there is no contraindication, long-term use of aspirin, statins; ② with the use of clopidogrel or tegretol for at least one year; ③ according to the condition of the use of drugs such as ACEI / ARB class, β-blockers and nitrate; ④ monitoring of adverse drug reactions, such as bleeding, muscle pain, etc.; ⑤ regular rechecking of routine blood, coagulation, liver and kidney function, blood lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, etc., and improve the cardiac ultrasound and coronary angiography if necessary; ⑥ Actively treat hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia and other underlying diseases, and control blood pressure, blood sugar and blood lipids up to the standard.
After stenting also need to be under the guidance of the doctor for drug treatment, mainly including: ① if there is no contraindication, long-term use of aspirin, statins; ② with the use of clopidogrel or tegretol for at least one year; ③ according to the condition of the use of drugs such as ACEI / ARB class, β-blockers and nitrate; ④ monitoring of adverse drug reactions, such as bleeding, muscle pain, etc.; ⑤ regular rechecking of routine blood, coagulation, liver and kidney function, blood lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, etc., and improve the cardiac ultrasound and coronary angiography if necessary; ⑥ Actively treat hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia and other underlying diseases, and control blood pressure, blood sugar and blood lipids up to the standard.
Thanks for reading and good health to all. This article was originally written by General Practice Sweeper on Today's Headlines & Wukong Q&A.
With the continuous progress of medicine, patients with coronary artery stenosis can be treated by putting in a heart stent through interventional surgery. Many patients are very puzzled: after the stent is put into the body, where do the blood clots and atherosclerotic plaques of the blood vessels go? What are the problems that need to be paid attention to after the stent is put in?
At present, the most used stent in domestic clinic should be drug-coated stent, that is to say, put into the cardiovascular stent coated with drugs, to drug inhibit the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells, to prevent the formation of thrombus. Drug-coated stent tracer is good, impervious to x-ray, biocompatible, has better anti-thrombotic function, and itself uses titanium alloy material with reliable expansion performance, good support and coverage, which is very in line with the requirements of hydrodynamics. Therefore, patients with cardiovascular stenosis, after putting in the stent in line with the surgical indications, it can expand the narrowed blood vessels, and at the same time, it can dissolve the thrombus, dissolve the atheromatous plaques in the blood vessels gradually, open up the blood vessels, and through the blood flow flushing, let the plaques slowly become smaller, and with the metabolism of discharged out of the body.
After the interventional surgery into the drug stent, in order to avoid the re-formation of blood clots, but also need to use the double antiplatelet drugs, such as aspirin and clopidogrel matching, the use of time at least 1 year, during the period of time can not be discontinued, in order to avoid the occurrence of stent thrombosis. Although after cardiac stent treatment, but patients with coronary heart disease, there is a re-occurrence of vascular stenosis may occur in the future, so the patients long-term use of coronary heart disease-related drugs, treatment of primary disease is very important, such as the use of ACEI drugs to lower blood pressure, delayed cardiac remodeling, diabetic patients should be actively using medication to control their blood glucose. If high blood fat patients, also need to take atorvastatin calcium tablets to lower blood fat; in addition can not drink, can not smoke, control emotions, can not be overly excited. Exercise after surgery also needs to be gradual, it is recommended to do with physical strength in line with some of the exercise.
Click on the bottom of the page [Learn More] to see more answers or ask the doctor a question for free!
Follow "Family Doctor Online" headline, more health Q&A easy to see~~~~
A heart stent does nothing more than hold open a narrowed or completely blocked blood vessel and restore blood supply to the heart. The plaque inside the blood vessel is still there, and the risk factors that form it are not eliminated by stenting. If the patient thinks that after the stent surgery, the body is completely recovered and relaxes, then the next heart attack will not be far away.
Statistics show that 1 year after stent surgery is the high incidence of heart attack recurrence, and during this period of time, patients need to pay extra attention to the recurrence of heart attack. Coronary atherosclerosis is the main cause of narrowing and blockage of heart vessels, and the formation of atherosclerotic plaques is related to chronic diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes mellitus and hyperuricemia. In order to prevent the re-stenosis and blockage of blood vessels, it is necessary to start from controlling blood pressure, blood fat, blood sugar, uric acid and other indicators.
For patients who have had heart stent surgery, there are two other points that are very important to emphasize:
One is that one must be steadfast in accepting lipid-lowering treatment. Many experts advocate that patients should take statin lipid-lowering drugs for a long period of time, regardless of their lipid targets, in order to avoid the re-formation and growth of atherosclerotic plaques;
Secondly, antiplatelet therapy must be adhered to. Within the first year after cardiac stent surgery, most patients need to take two kinds of antiplatelet drugs, which is the so-called antiplatelet dual therapy; after one year, many patients have to insist on taking one of the antiplatelet drugs until the doctor thinks that they can stop taking them.
Many people think that since cardiac stenting is a "target not a cure", they should simply not put in a stent. This idea is unrealistic in most cases. "Time is myocardium". If the blocked blood vessels are not opened and the blood supply to the myocardium is restored within a short period of time, the patient may not be able to be resuscitated. So far, emergency cardiac stent implantation is an extremely effective measure to save the patient's life.
After coronary stenting, most of the plaque that caused the stenosis will be compressed, and a small portion will rupture into the blood vessel. The most important thing after stenting is to take medication for life to avoid restenosis of the stent.
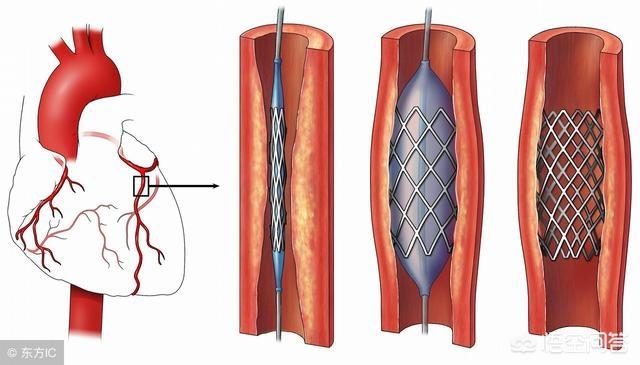
Coronary stenting is a procedure in which the surgeon first delivers a very thin catheter through a radial/femoral artery puncture to the narrowed area of the coronary artery, then dilates the stenosis with a balloon, and finally delivers a stent to this stenosis to release it to hold open the narrowed vessel. During this process, most of the arterial plaque in the stenosis is compressed between the stent and the coronary vessel, and a small amount of broken plaque drifts away with the blood flow and is gradually absorbed. Coronary stenting does not actually eliminate plaque from the coronary arteries, but only compresses it through balloon dilatation and stent release, exchanging space for time, temporarily relieving the coronary stenosis, and in the long term, continuing to use medication to inhibit or delay the formation of plaque.
In addition, even if we strictly follow the current international recommendations of the drug optimization treatment program based on the treatment, coronary stenting patients will still have about 3%-6% per year will occur again stenosis blockage, especially in the non-smoking cessation, blood pressure, blood glucose, lipids have not been controlled in patients with a higher incidence rate. Therefore, the most important thing for post-coronary stenting patients is to continue to take aspirin + Polivir double anti-platelet aggregation drugs for one year, lifelong use of statin lipid-lowering drugs to stabilize plaque, control blood pressure and blood glucose, quit smoking and limiting alcohol, improve the bad lifestyle, and regular review and follow-up.
We all know that arterial plaque can block blood vessels, and when the stenosis reaches 75% or more, stents can be considered to ensure blood flow.So did the plaque in our bodies disappear after the stent was put in?
This question may not have occurred to many people, let's start with the principle of stenting. The so-called cardiac stent is a stent that is delivered to the stenosis site through the peripheral artery, and then the stent is expanded by a balloon to make it close to the endothelium, and at the same time squeeze the plaque under the stent, and then as the endothelium of the blood vessel is repaired it will cover the stent completely (reendothelialization), and the stent will become a fusion with the blood vessel, and it can't be taken out. Therefore, theThe plaque did not disappear after stenting, and most of it was squeezed under the stent, while a small portion was dislodged and flowed with the bloodstream, and was eventually mechanically absorbed.
This also means thatCardiac stenting isn't a one-off. The plaque isn't eliminated, it's just propped up, thePlaque can still form in the stent and lead to restenosis if lifestyle improvements and medication are not actively pursued after the procedure.
What do I need to be aware of after stenting?
①Light Diet
A low-salt, low-fat diet is the mainstay, avoiding spicy and stimulating foods, high cholesterol, high fat and spicy stimulants.
②Appropriate Exercise
Avoid significant physical activity in January, and gradually increase it after January, in a gradual manner, so that you do not have chest pain and other discomforts.
③Strictly abstain from smoking and limit alcohol consumptionIf you don't drink alcohol, it's best not to, and if you do drink alcohol, it's best to choose red wine and to drink it sparingly.
④Weight control, obese people should actively lose weight.
⑤ Maintain a good state of mind.Avoid bad emotions such as anxiety, depression, and anger.
(vi) Regular work and rest, avoiding late nights.

Medication is also required after stenting, under the supervision of a physician.Primarily, aspirin and statins should be used for a long time, along with clopidogrel or tegretol for at least one year. If high blood pressure is present, take antihypertensive medication as appropriate.
Regularly review the blood routine, coagulation, liver and kidney function, blood lipids, blood glucose, blood pressure, electrocardiogram, etc., and improve the cardiac ultrasound and coronary angiography if necessary.
Chief Cardiovascular Physician M.S. Thanks for the invitation! Exceptionally good question, answered a little late. There are two questions, answered separately. The first question is, after stenting, where does the plaque in the blood vessel go? Did the body get a stent ......? The question that should be asked is where did the plaque that was blocking the blood vessels, mainly the coronary arteries, go after a stent was placed in the arterial vessels, mainly the coronary arteries? Where did the plaque go? The plaque was squeezed apart and stuck to the wall of the blood vessel. The stent is held open inside the blood vessel. In the process of propping up (dilating the blood vessel), there is pressure, so that the cholesterol and necrotic cells built up in the plaque are squeezed out, spread out under the intima, and stick to the vessel wall, sandwiched between the stent, the intima (the stent is tightly fitted to the intima), and the vessel wall. At this point, the intima gets torn. This is very easy to understand, just like a pile of pasta to be flattened to be rolled out thinly, if there is a filling inside, during the process of rolling out thinly, the filling is big and the thin skin will break the skin, during the process of stenting, the vessel wall will change in a similar way. Therefore, post-stenting (intimal tear, rough wall) is particularly prone to thrombosis and requires intensive antiplatelet therapy. This is why the combination of two antiplatelet agents is required after coronary stenting. It is not until this intimal tear is repaired, the endothelial cells cover (grow all over) the surface of the stent, and the surface of the vessel is smooth that the high risk passes, and only then can it be changed to single-agent antiplatelet therapy. And due to the different varieties of stents, the growth period of epithelial cells is also different, sometimes in order to inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscle of the blood vessel wall (which can cause restenosis), it is also necessary to coat the surface of the stent with medication (also known as drug-coated stents), which will delay the healing of the vessel lining, and the treatment of double antiplatelet therapy will be required for a longer period of time. Also, although the plaque at the stent site is squeezed and dispersed, it will be redeposited if the blood lipid is high; moreover, there is more than one plaque on the vessel wall, and the plaque in other parts of the vessel will be redeveloped if no attention is paid to controlling the blood lipid. Therefore, cholesterol-lowering therapy is required to be continuous and strict after stenting. Thus comes the answer to the second question. After stenting, you also need to pay attention to anti-platelet to prevent thrombosis, cholesterol-lowering to prevent atherosclerosis, and to prevent thrombosis and restenosis in the vessel after stenting. Of course, there are also treatments to improve blood supply, and patients suffering from myocardial infarction have to have treatments to protect the myocardium, prevent myocardial remodeling, and protect cardiac function; and in the case of patients with cerebrovascular disease, there are also rehabilitation treatments. But the main and basic thing is to adhere to the anti-platelet and cholesterol-lowering treatments, and in addition to drugs, a healthy lifestyle must not be neglected!
And due to the different varieties of stents, the growth period of epithelial cells is also different, sometimes in order to inhibit the proliferation of smooth muscle of the blood vessel wall (which can cause restenosis), it is also necessary to coat the surface of the stent with medication (also known as drug-coated stents), which will delay the healing of the vessel lining, and the treatment of double antiplatelet therapy will be required for a longer period of time. Also, although the plaque at the stent site is squeezed and dispersed, it will be redeposited if the blood lipid is high; moreover, there is more than one plaque on the vessel wall, and the plaque in other parts of the vessel will be redeveloped if no attention is paid to controlling the blood lipid. Therefore, cholesterol-lowering therapy is required to be continuous and strict after stenting. Thus comes the answer to the second question. After stenting, you also need to pay attention to anti-platelet to prevent thrombosis, cholesterol-lowering to prevent atherosclerosis, and to prevent thrombosis and restenosis in the vessel after stenting. Of course, there are also treatments to improve blood supply, and patients suffering from myocardial infarction have to have treatments to protect the myocardium, prevent myocardial remodeling, and protect cardiac function; and in the case of patients with cerebrovascular disease, there are also rehabilitation treatments. But the main and basic thing is to adhere to the anti-platelet and cholesterol-lowering treatments, and in addition to drugs, a healthy lifestyle must not be neglected!
Thanks to my headline friends for the invitation to answer the question.
This is an interesting question, and it's safe to say you've asked the main point. Stenting is often done when a blood vessel is severely blocked, and without stenting it is likely that the body is in imminent danger. However, stenting does not improve the volume and number of plaque in the blood vessels, especially those vessels without stenting, the plaque still exists, stenting only expands the volume of the blood vessels, so that they will not be in danger immediately, and it does not guarantee that the plaque will not block the blood vessels after stenting (I am sure that you have heard of cases where you have stenting, and then you have a Darbyshire operation), so you should not take it lightly and still have to be careful in your diet. Therefore, you should not take it lightly after the stent is put in place, and you still have to be careful with your diet. There are many people who feel good after having a stent put in and then just let it go, only to have problems later on.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.