What should I do with impaired fasting glucose?
The diagnostic criteria for diabetes is very clear, usually the fasting blood glucose level exceeds 7.0mmol/L or more, regardless of whether there are typical symptoms of diabetes, can be clearly diagnosed as a diabetic problem, and the normal range of fasting blood glucose is 3.9~6.1mmol/L, if the fasting blood glucose level is more than 6.1 but not yet exceeded the diagnostic criteria of diabetes 7.0, is a situation between diabetes and normal blood glucose range, we call it impaired fasting blood glucose. a condition between diabetes and normal blood sugar range, which we call impaired fasting glucose.
If you belong to the situation of impaired fasting blood glucose, it is recommended that you go for another glucose tolerance test, especially for those who have the typical three more and one less symptoms of diabetics although their fasting blood glucose has not exceeded 7.0. There are times when impaired fasting blood glucose is found to be a problem if the glucose test reveals that their blood glucose is more than 11.1 at 2 hours after glucose intake, and those who have the typical symptoms of diabetes. Again, it is possible to make a clear diagnosis of a diabetic problem. For such a situation, you should pay attention to dietary regulation in life, strengthen the basis of exercise, through the reasonable use of medication to control blood glucose levels, pay more attention to postprandial blood glucose monitoring, try to control blood glucose levels down.
And if it is simply a problem of impaired fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose is normal friends, generally can be counted as a pre-diabetic condition, for this situation, generally is not recommended to take hypoglycemic drugs to solve the problem. Impaired fasting blood glucose, that our body for the metabolism of blood sugar has begun to have problems, but the problem is not serious, if the positive intervention control, fasting blood glucose back to normal levels, is also completely possible, if you do not care about it, the development of new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus chances are also very high.
There are a lot of friends found fasting blood sugar damage is very worried, want to know fasting blood sugar damage will develop into diabetes? In fact, not, clinical research data show that about 25% of the patients with impaired fasting blood glucose problems, through reasonable management and improvement, blood sugar can be restored to normal levels, and the reason for the recovery, and these friends on the life of strict self-discipline and the related metabolic problems of the active management, has a very important relationship.
What causes impaired fasting blood glucose? Generally speaking, there are 2 main issues to consider, one is insufficient insulin secretion, impaired fasting blood glucose corresponds to the insufficient secretion of insulin in the early phase, and if the insufficient secretion of insulin in the late phase after meals, the chances of abnormal glucose tolerance (2-hour postprandial glucose more than 7.8, but not more than 11.1) are higher; in addition to insufficient secretion of insulin, insulin resistance is also one of the important causes of impaired fasting blood glucose, usually said to be related to hepatic insulin resistance, and what causes impaired fasting blood glucose? In addition to insufficient insulin secretion, insulin resistance is one of the most important causes of impaired fasting blood glucose, which is usually associated with hepatic insulin resistance, whereas in the case of glucose tolerance abnormalities, there is often a combination of hepatic and muscular insulin resistance.
Therefore, to improve impaired fasting blood glucose and normalize blood glucose levels, the most important thing we should do is to control insulin secretion, as well as to improve insulin resistance in the liver, which requires us to actively correct our unhealthy lifestyles and lifestyle factors, and to improve the ability to metabolize blood glucose.
Improvement of impaired fasting blood glucose, the first thing to mention, or we often talk about diet regulation and exercise to control blood glucose, this is an important aspect of diabetic patients to control blood glucose, the same is also impaired fasting blood glucose, to restore the level of fasting blood glucose is an important aspect. Diet and exercise are 2 aspects of life conditioning, but at the same time is also inseparable from the 2 aspects, through the diet to control energy intake, through exercise to regulate the consumption of energy, the utilization of blood glucose, for the control of body weight, to improve the insulin resistance, etc., have a very important role, the specific how to dietary conditioning, how to exercise we talk a lot of it, not to say too much, in short, adhere to the healthy Good eating habits, according to the amount of activity, comprehensive control of the amount of food, neither eat too little to cause hypoglycemia risk, but also do not eat too much, resulting in loss of control of blood glucose, adhere to a reasonable and effective aerobic exercise, to achieve a balance of food and movement is the basic principle of diet and exercise to regulate blood glucose, all the changes are not different from the same.
If you have the problem of obesity, the phenomenon of impaired fasting blood glucose, we must pay more attention to the strict control of weight, obese impaired fasting blood glucose if not actively control their weight, the development of new-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus has a greater chance, the weight control down, the visceral fat will follow the reduction of liver fat, is to improve the secretion of insulin and insulin resistance is an important aspect of the problem, therefore, many of the time, if you can successfully lose weight, the problem of impaired fasting blood glucose is also solved. times, the problem of impaired fasting glucose is solved if weight loss can be successfully achieved.
For friends with impaired fasting blood glucose, we also need to remind you that, in addition to focusing on changes in blood glucose levels, but also do not forget to other metabolic indicators of the regulation and improvement of blood pressure, blood lipids, blood uric acid, are closely related to the decline in the level of the body's metabolism, and if there are other metabolic diseases, do not actively regulate the intervention, the chances of blood glucose to further increase, so that you have high blood pressure, please actively regulate the blood pressure level. Therefore, in the management of fasting blood glucose at the same time, if you have high blood pressure, please actively regulate the level of blood pressure, if you have high blood lipids, please control the level of blood lipids, if the blood uric acid is elevated, you should also pay attention to the management and control, if necessary, should also be reasonable to take medication to control the blood pressure, blood lipids, blood uric acid, control the metabolism in these areas, will also help to improve the impaired fasting glucose, and reduce the risk of new onset of diabetes. Reduce the risk of new-onset diabetes.
First, let's talk about what "impaired fasting glucose" means. As the name suggests, the fasting blood sugar is impaired, has exceeded the normal level, but has not reached the level of diabetes. The normal fasting blood glucose for a healthy person should not exceed a maximum of 6.1mmol/L and less than 7.8mmol/l 2 hours after a meal.
Impaired fasting blood glucose means that the fasting blood glucose is more than 6.1mmol/L but has not reached 7.0mmol/L. If the fasting blood glucose reaches 7mmol/L, it belongs to the range of diabetes. Fasting blood glucose impaired this state, although not reached diabetes, but has been abnormal, known as "pre-diabetes", is the occurrence of diabetes in high-risk groups, so to speak, has been "a foot has stepped into the door of diabetes". If not prevented in time, it is very easy to develop diabetes. If you have impaired fasting blood glucose, you should go to the hospital in time to do oral glucose tolerance test, to see the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose and pancreatic islet function.
Why does fasting blood glucose rise? Fasting blood glucose depends on the state of insulin secretion by the pancreas during fasting, if the insulin produced during fasting is insufficient, fasting blood glucose will rise; on the other hand, it depends on the liver. For blood sugar, the liver is like a bank, the liver can store the blood sugar that can't be used by human beings to keep the blood sugar not high; when fasting or starving, the liver can release the sugar into the blood vessels to keep the blood sugar not low and to maintain the life activities of human beings. And when fasting blood sugar is impaired, most of it is thought to be caused by poor functioning of the liver bank. These common factors include obesity, fatty liver, alcoholic liver, etc. Due to too much fat in the liver, which affects the liver's ability to process glucose, the excess sugar cannot all be deposited into the liver, and too much sugar is released outward, leading to elevated fasting blood sugar.
How to recover from "impaired fasting glucose"? One third of impaired fasting blood glucose develops into diabetes, for a longer or shorter period of time. Therefore, it is important to take decisive measures to prevent diabetes from occurring and it can be reversed to normal. Since the problem is in the liver, it is important to actively improve the state of the liver. This is especially true for obesity and fatty liver, which is the source of all diseases. Losing weight and removing fatty liver is key. It is important to exercise in moderation to lose weight and eliminate the general belly. Adhere to physical exercise, at least 5 times a week, 30-60 minutes each time. Such as fast walking, jogging, swimming, playing ball and so on, according to the strength. Through three months of exercise exercise effect is not good, can be through a small amount of drug prevention and recovery, such as metformin, pioglitazone, etc., are used to prevent diabetes and treat fatty liver.
A friend asked: the physical examination found that the fasting blood sugar is 6.5mmol/L, checked the 2-hour postprandial blood sugar is normal, belongs to the impaired fasting blood sugar, how is it? Can it be normalized?
To answer this question, some brief knowledge of what impaired fasting glucose is and the graded management of blood glucose is required.
Impaired fasting glucose, one of the blood glucose abnormalities that occurs in blood glucose management, is a condition that is not yet diagnostic of diabetes, yet exceeds normal blood glucose norms and has a measured 2-hour postprandial glucose that is within the normal range. It sounds quite complicated, look at the criteria for graded blood glucose management and it becomes quite clear:
Normal blood glucose Fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 4.4-7.8 mmol/L
Impaired fasting blood glucose Fasting blood glucose 6.1-7.0 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 4.4-7.8 mmol/L
Elevated postprandial blood glucose Fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 7.8-11.1 mmol/L
Abnormal glucose tolerance Fasting blood glucose 6.1-7.0 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 7.8-11.1 mmol/L
Diabetes mellitus Fasting blood glucose greater than 7.0 mmol/L or 2-hour postprandial blood glucose greater than 11.1 mmol/L
This shows that impaired fasting glucose is simply a condition in which fasting glucose is between normal and diabetic, while glucose at other points in time is within the normal range.

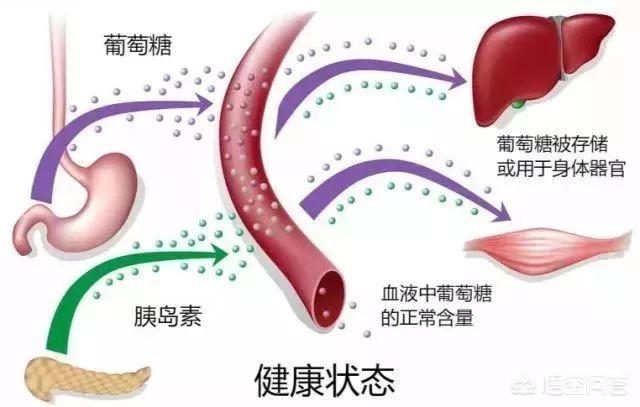
We know that the level of blood glucose is regulated by insulin secreted by pancreatic islet cells in the body. Enough insulin in the body is necessary to promote the utilization of blood glucose and maintain the blood glucose at a normal level; when insulin secretion is insufficient, the blood glucose cannot be effectively utilized, and then blood glucose will be elevated, and the amount of insulin is determined by the secretion function of the pancreatic islet cells.
In the absence of meals, blood glucose is at a lower level, and pancreatic islet cells only need to secrete a small amount of insulin to meet the need to regulate blood glucose, and the insulin secreted at this time is called basal insulin. Just like our daily work, just follow the steps to complete.
When the meal with the rise in blood sugar, the pancreatic islet cells will be stimulated to increase the secretion of insulin to cope with the need for elevated blood sugar, the secretion of insulin at this time is called meal time insulin, as if the work needs to work overtime, you must double the work in order to complete the task as well.
When fasting blood sugar is impaired, the following happens:
When work is usually unhurried and there is no stimulus such as bonuses, employees may just cope with their daily work, and the pancreatic cells may not secrete enough basal insulin, and the result is an increase in fasting blood sugar.
If they are instructed to work overtime and are incentivized by bonuses, employees will be motivated to work harder, and pancreatic islet cells will secrete enough mealtime insulin to satisfy the need for elevated blood glucose after meals.
To summarize, when fasting blood glucose is impaired, the pancreatic islet cells do not secrete enough basal insulin, but they are still able to complete the secretion of insulin at mealtime, indicating that the pancreatic islet cells themselves do not have a major problem, and there is no problem with their ability to respond to the increase in blood glucose after a meal. In this case, it is sufficient to adjust the ability of the islet cells to secrete basal insulin.

The main reason for the decline in the ability of pancreatic islet cells to secrete basal insulin is usually not a lesion of the islet cells, which is mostly seen in overweight and obesity, sedentary, lack of exercise, smoking and alcohol abuse, irregular work and rest, and stay up late for a long time, which means that as long as these bad habits are changed in a timely manner, the ability of pancreatic islet cells to secrete basal insulin will be restored to normal, and the fasting glucose will be reduced to the normal level.
In the same way, when abnormal glucose tolerance occurs, it can be restored to normal by improving lifestyle. The reason why they can be restored to normal is that pancreatic islet cells themselves do not undergo serious lesions or decrease in number, if the islet cell lesions are serious or dead due to lack of attention, the ability to secrete basal insulin or mealtime insulin will be decreased and irreversible, and diabetes will occur. Diabetes mellitus occurs, and the help of hypoglycemic drugs is needed to compensate for the dysfunction of pancreatic islet cells and achieve the goal of blood glucose control.
With this knowledge, do you have a good idea of how to manage your blood sugar, especially what to do when abnormalities such as elevated blood sugar occur?
I hope this answer can help you, welcome to click on the attention and leave a message, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge.
Type 2 diabetes generally goes through a period of pre-diabetes, a stage that includes several conditions such as impaired fasting blood glucose and abnormal postprandial blood glucose and glucose tolerance.
What is impaired fasting glucose?
Let's start with a diagnosis of normal blood sugar and diabetes.
Normal blood glucose is fasting blood glucose at 4.4-6.1mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose is less than 7.8mmol/L; the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is that if the patient has the typical symptoms of diabetes mellitus, such as thirst, excessive drinking, and lethargy, the patient is diagnosed with diabetes mellitus if there is a blood glucose that exceeds the standard on one occasion. That is, fasting blood glucose exceeds 7.0 mmol/L and postprandial blood glucose exceeds 11.1 mmol/L. If there are no typical symptoms of diabetes, two blood glucose results exceeding the criteria of 7.0 or 11.1 mmol/L are needed to diagnose diabetes.
From the above criteria of normal and diabetes, there is another range between normal and diabetes, that is, the state of fasting blood glucose between 61-7.0 mmol/L and postprandial blood glucose between 7.8-11.1 mmol/L is called prediabetes.

Impaired fasting blood sugar glucose is a common state of pre-diabetes. Pre-diabetes can be reversed to a normal population, so it is very important to seize this period and manage it in a timely manner.
And unhealthy lifestyle, obesity, drinking and smoking, stress and other factors are risk factors for the onset of diabetes, but also can be changed, when they find themselves in a state of impaired fasting blood sugar, to be removed against the risk factors for the onset of diabetes, then there is a possibility of reversal of pre-diabetic state, and long-term to maintain blood sugar in the normal.
Diet control, consistent exercise, weight loss, abstaining from smoking and alcohol, and maintaining emotional stability are important to ensure improvement of impaired blood sugar.
Eat more vegetables and fruits and other foods containing more fiber, whole grain diet, coarse and fine combinations, insist on exercising for at least 30 minutes a day, reduce weight to normal standards, maintain BMI between 18-24, increase muscle mass, reduce body fat, drink 1,500-2,000ml of water a day, and undergo regular physical examination. It is recommended to perform glucose tolerance measurement once every six months to clarify your glucose metabolism status for timely intervention and treatment.
I am Dr. Sun, who loves life and food, pay attention to Dr. Sun's talk about sugar, continue to learn quality health knowledge, attention to the message will be replied!

According to the standards promulgated by the WHO and the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) in 1999, the state of having a fasting blood glucose less than 7.0 mmol/L and a 2-hour plasma glucose between 7.8-11.1 mmol/L after 75 grams of oral glucose is called impaired glucose tolerance. It is a high-risk factor predictive of type 2 diabetes and has a higher risk of developing type 2 diabetes than the general population.

If blood glucose values are within these two ranges, appropriate interventions can reduce the chances of developing type 2 diabetes or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes.
So by what kind of intervention exactly?
1, the first is dietary treatment, through a reasonable diet to limit the intake of carbohydrates;
2、If the patient is overweight, it is recommended to lose weight and keep the weight within the standard range;
3. Change the bad lifestyle and develop a good and healthy lifestyle;
4. Exercise sensibly to control blood sugar levels through simple exercises;
5, if the above effect is not good, reasonable through the drug intervention metformin, α-glucosidase inhibitors, thiazolidinediones (TZDs), metformin and TZDs combined intervention and weight loss drug orlistat can reduce the risk of diabetes mellitus in the pre-diabetic population.

Impaired fasting blood glucose is actually a more specialized concept in medicine, which means that the fasting blood glucose is higher than normal, but lower than the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, for example, a fasting blood glucose value between 5.6 and 6.1 is called impaired fasting blood glucose.
In fact, impaired fasting blood glucose is generally recognized clinically as some of the early manifestations of diabetes, that is to say, if it is not actively control is very likely to develop into type 2 diabetes, but simply check out the impaired fasting blood glucose is generally possible to develop in three directions.
Maintained. That is, the blood sugar in the body is maintained at this stage for a long time will not be severe, nor will it alleviate the persistent presence of impaired fasting blood sugar.
Transition to type 2 diabetes. Because impaired fasting glucose is some of the symptoms of pre-glycemia, if it is not adjusted or intervened by scientific diet, the end result is very easy to occur as diabetes.
Return to normal blood sugar. With scientific diet as well as exercise interventions, some people can return to normal blood sugar levels.
Because the impaired fasting blood glucose has not reached the judgment boundary of diabetes, so generally can not be controlled by the use of insulin, so for the impaired fasting blood glucose for the people, usually through the adjustment of their diet and appropriate increase in physical exercise is better.
Dietary adjustments. For example, the usual daily life for high-calorie food must be appropriate control, while avoiding excessive intake of sugar.
Physical activity. Ensuring a good diet and work routine, and increasing physical activity can speed up the body's blood circulation and metabolic rate, thus effectively preventing impaired fasting blood sugar from developing into type 2 diabetes.
You make a glaring error by mentioning the title of this question; it's not impaired fasting glucose, it's impaired fasting glucose regulation.
So what can be done about impaired fasting glucose regulation?
Impaired glucose regulation is pre-diabetic and consists mainly of impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance.
Impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance are reversible and are compensatory stages of disorders of glucose metabolism in the human body, but it is more prone to diabetes than normal, and also has an increased risk of cardiovascular and microvascular disease, so patients in this category should be on high alert. If properly regulated, they can enjoy good health, and vice versa, they may develop diabetes. Therefore, these individuals should have their glucose tolerance status checked regularly and be proactive in preventing progression to diabetes.

How should impaired glucose regulation prevent diabetes? First of all, we should eat a reasonable diet. In our daily life, we should pay attention to controlling the intake of carbohydrates, lowering the intake of fat, especially animal fat, and increasing the intake of vitamins and fiber in food. High-fiber foods can slow down the decomposition and absorption of carbohydrates, but also conducive to gastrointestinal movement and blood glucose control, but generally do not recommend porridge, because porridge is easy to absorb, a short period of time can result in high blood sugar.
It is also necessary to exercise moderately to reduce weight and enhance physical fitness. Patients with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance should insist on exercise, exercise at least five times a week, 30 minutes each time, generally moderate physical activity sports, such as brisk walking, jogging, tai chi, taiji sword, cycling, stair climbing, climbing hillside, etc. Exercise can make calorie consumption increase, insulin sensitivity increase, overweight people should reduce their weight, and as far as possible to achieve the ideal weight.

Pharmacologic interventions are also part of the treatment of impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance. Commonly used drugs include metformin, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, metformin improves insulin resistance, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors slow down the conversion of disaccharides and starchy polysaccharides to glucose, ultimately lowering fasting and postprandial hyperglycemia. Pharmacologic treatment of impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance not only significantly reduces the occurrence of diabetes, but also significantly reduces the risk associated with the development of cardiovascular disease complications of diabetes. In addition, patients with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance should have strict blood pressure control and correction of dyslipidemia while lowering their blood glucose.
Patients with impaired fasting glucose and impaired glucose tolerance should undergo regular glucose monitoring, with comprehensive examinations every three to six months, which include measurement of fasting and postprandial glucose, oral glucose tolerance tests, and pancreatic islet function tests.
What are your thoughts or opinions please leave a comment below, move your finger please give me a like or follow thanks!
Thanks for the invite!
Normal fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1mmol/L, 6.2-7.0 is impaired fasting glucose regulation, two consecutive fasting blood glucose greater than 7.0 can diagnose diabetes. Two hours after meal blood glucose and random blood glucose less than 7.8mmol/L is normal, 7.8-11.1 is impaired glucose tolerance, greater than 11.1 diagnosis of diabetes.
Whether it is impaired fasting glucose or impaired glucose tolerance, you can control your blood glucose through diet plus exercise without medication for the time being during this period. Diet is mainly low-salt and low-fat diet, and exercise is mainly aerobic exercise, including walking, etc. In addition, patients with hypertension should keep their blood pressure around 130/80. In addition, patients with high blood pressure should control their blood pressure at around 130/80. The most important point is to regularly monitor blood glucose, timely consultation.
[Learn more about medical knowledge, welcome to follow me to discuss Oh]

First, let's look at what is meant by impaired fasting blood glucose, impaired fasting blood glucose means that the fasting blood glucose is higher than normal, but has not reached the level of diabetes, for example, the fasting blood glucose is >6.1 moles per liter but <7.1 moles per liter, but the two-hour postprandial blood glucose is normal, <7.8 moles per liter, at this stage belongs to impaired fasting blood glucose.
In fact, impaired fasting blood glucose is a transitional stage, from normal fasting blood glucose to becoming diabetic, so it is important to be aware of the following during this stage.
First, patients with impaired fasting glucose should also pay attention to vitamin intake while eating dietary fiber
High-fiber food can slow down the decomposition and absorption of carbohydrates, but also conducive to intestinal peristalsis, so that the body's metabolism is normal and conducive to the balance of blood sugar. Fasting blood sugar impaired patients due to reduced food intake, will cause the supply of vitamins and trace elements is insufficient, so pay attention to the intake of vitamin foods, so it is advisable to eat more fresh vegetables.
Secondly, patients with impaired fasting glucose should control their total calorie intake
The proportion of calories consumed should be adjusted according to the patient's actual condition. The total number of calories is usually determined by weight, age, sex and physical activity, with the principle of keeping the weight slightly below or within the standard weight range. The standard is: [(height - 100) x 0.9] to estimate the total daily calorie requirement.
Third, patients with impaired fasting glucose, to prevent complications
Disturbed fat metabolism, high blood lipids and rapid development of atherosclerosis are obvious symptoms of diabetes. Impaired fasting blood glucose is a cause of diabetes and should not be ignored. Therefore, the cholesterol content in food must be controlled, generally no more than 300 mg/day, equivalent to one egg per day. Eat less or no animal fats and high cholesterol animal organs food.
Clinically diabetes is categorized as diabetes mellitus and pre-diabetes. Impaired fasting glucose is a type of prediabetes. Fasting blood glucose is recognized as impaired when the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is in the normal range, i.e., postprandial blood glucose is less than 7.8 mmol/L, and fasting blood glucose is between 6.1 mmol/L and 7.0 mmol/L.
Impaired fasting blood glucose is a stage of transition from normal to diabetes, in which patients who pay attention to food therapy and exercise methods, blood glucose may gradually become normal, that is to say, it is reversible. People must not miss this opportunity, must change the lifestyle. Otherwise you may become a real diabetic.
I am a type 2 diabetic, that is to say, I do not know how to change my lifestyle at this stage of impaired fasting blood glucose, so I hope you will take warning. I used to love fried food, chocolate, ice cream, now these foods for me is absolutely prohibited, now every day to take medication, and at night to play insulin, a variety of not allowed, in fact, diabetes is also very painful. Hey ......
Today, my present, I hope that you must must intervene with a positive mindset when your fasting blood sugar is impaired, and here's how to manage it.
1. Control your diet and reduce the total calories in food. Eat more low-fat foods and more vegetables. Eat more sugar-lowering foods: buckwheat, onions, fungus, and so on.
2. Reasonable exercise, reduce weight. Eliminate general belly is very important, adhere to physical exercise, fast walking, jogging, riding.
3. Have a good mind and mood. Worry, sadness and nervousness can cause blood sugar to rise. Keep your spirit happy and smile often, and your blood sugar will slowly adjust to normal.
I'm not sure if the advice I'm giving you today is practical or not, so if you like my article, you're welcome to retweet and like it 👍, thank you!




This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.