What are the causes of high fasting blood sugar?
There are four main types of diabetes: i.e. Type 1, Type 2, Stress and Gestational diabetes. Today's focus is on type 2 and stress diabetes.
The main causes of type 2 diabetes are relative insulin deficiency and decreased insulin sensitivity of target cells. Because hyperlipidemia interferes with insulin efficiency, the typical high blood glucose profile that occurs when combined with a severe hyperlipidemic condition is both high fasting and postprandial blood glucose. For example, a fasting blood glucose of 10 and a postprandial blood glucose of 15.
The focus of the regimen is: lipids and diet!
Stress diabetes is temporary diabetes caused by increased secretion of insulin antagonist hormones such as adrenocorticotropic hormone, catecholamines, glucagon, and growth hormone during severe stress.
It is important to note that even typical type 2 diabetics can experience a significant stress response that must be taken seriously! Stress is also a major cause of disturbed or even abnormally elevated blood glucose.
The typical blood glucose profile seen in stress diabetes is high fasting, high and normal after meals, and occasionally hypoglycemia. For example, yesterday's fasting glucose was 9 and postprandial glucose was 8, today's fasting glucose is 8 and postprandial glucose is 15.
Conditioning focuses on: eliminating stress!
The most likely scenario for unstable blood sugar is that a stress response has been triggered!
Our body has a very sophisticated blood glucose regulation mechanism. There are many different hormones in the body that affect blood glucose levels, in addition to insulin, there is also glucagon, adrenaline, growth hormone secreted by the anterior pituitary gland, thyroxine, catecholamines, and so on. Stress, tension, late nights, insomnia, alcoholism, high workloads, poor diet, and frequent hypoglycemia are all common stress stimuli that can easily lead to elevated blood sugar!
The latest diabetes research confirms that constant tension and stress are the main triggers for diabetes! When we are in a state of stress, the brain needs to consume a lot of blood sugar in order to ensure proper functioning and the body experiences a hypoglycemic condition. Sugar being the main source of energy, once a hypoglycemic situation occurs, the body initiates a hypoglycemic stress response, glucagon is elevated, insulin action is inhibited, hepatic glycogen breaks down blood glucose, and proteins as well as fats in the muscles are converted to blood glucose through gluconeogenesis, increasing the body's blood glucose reserves.
If emergencies recur, the body is in a state of combat readiness (stress), the demand for blood glucose rises dramatically, sympathetic nerves are excited, adrenocorticotropic hormone is secreted (the most potent glucagon), glucagon (the predominant glucagon hormone) is continually elevated to promote the production of glucose from protein fats through gluconeogenesis, and large amounts of free fatty acids are replenished into the bloodstream to provide raw materials for the elevation of blood glucose.
In a state where the body is actively raising sugar and adrenocorticotropic hormone and glucagon are secreted in large quantities, both glucose-lowering medications and insulin become ineffective! When the stress is over and the drugs work, they again cause a sudden drop in blood sugar!
Therefore, in the case of stress diabetes or high blood glucose caused by severe stress, the use of medications and insulin to lower blood glucose can trigger a worsening of the stress response!
Because this type of diabetes generally does not require glucose-lowering therapy, doctors generally don't talk to you about stress diabetes, even though most diabetes is triggered by stress. But we can still see three typical phenomena:Sumuje phenomenon, dawn phenomenon, dusk phenomenon.
The phenomenon of Sumuje, which is also a stress reaction, theIt is the phenomenon of hypoglycemia followed by hyperglycemia. Sometimes severe hypoglycemia leads to reactive hyperglycemia that can last for several days. This is because the body's secretion of glucagon, growth hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, and epinephrine are all significantly increased in order to avoid the damage of hypoglycemia, so that each low blood sugar is followed by a high blood sugar.
Dawn and dusk phenomenaAssociated with elevated growth hormone and glucagon, it is typically seen in people with type 1 diabetes or on insulin therapy, with elevated blood glucose in the morning and at dusk.
Diabetes is one of the most misdiagnosed of several diseases
British Prime Minister Theresa May, after two years of incorrect treatment for diabetes, found out that she had been misdiagnosed with the wrong type of diabetes, which is laughable and deplorable to say the least, but, that's the current state of the art in medical diagnosis and treatment of diabetes!
Routine hospital tests to confirm the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus mainly include: biochemical tests (liver function; blood lipids; fasting blood glucose; kidney function; uric acid; lactate dehydrogenase; creatine myrosinase, etc.), glycosylated hemoglobin, and glucose tolerance test.
Typically, whenever blood glucose exceeds the standard values (fasting blood glucose greater than 7 mmol/l and postprandial blood glucose greater than 11.1/l), you are labeled as diabetic. Glucose is then generally treated as type 2 diabetes, i.e. insulin deficiency, regardless of impaired pancreatic function and reduced insulin secretion.
Knockout! Hospitals almost never check for adrenocorticotropic hormone (GC), glucagon, catecholamines, epinephrine, and other hormones that cause a rise in blood glucose, and don't screen for stress and other factors that trigger high blood glucose. As a result, stress diabetes or blood sugar abnormalities caused by stressful stimuli are not recognized and are highly susceptible to misdiagnosis and delay.
How can you self-identify the type of stress diabetes?
If there is no decrease in insulin secretion, blood glucose tends to rise abnormally, often accompanied by symptoms of hypoglycemia: such as sweating, hunger, panic, trembling, pallor, etc., and in severe cases, mental incoherence, agitation, irritability or even coma. Or there are obvious triggers of stress factors of the wrong habits, you can suspect that you are stress triggered high blood sugar or stress diabetes, furthermore, you can communicate with your doctor, supplemental testing of adrenocorticotropic hormone (GC) and pancreatic hyperglycemic hormone, so as to avoid misdiagnosis of the wrong condition.
Five principles of Vista diabetes conditioning:
First, regulating blood lipids
We help a large number of obese people with type 2 diabetes, through weight loss to reduce blood lipids, blood sugar can return to normal. The reason is that the state of high blood fat, the body's utilization of blood sugar efficiency greatly reduced, in other words, hyperlipidemia patients need higher blood sugar to meet the body's needs, need to do is to reduce high blood fat rather than simply lowering sugar. Be careful not to eat a lot of delicate rice and noodle food, this kind of food rises sugar too fast and lowers sugar fast, and then the excess sugar will be converted into cholesterol, which is the most easily overlooked reason for high blood lipid and thus affecting sugar metabolism!
Fat is a concern for many people, especially diabetes is also prone to lipid metabolism disorders, but the intake of high-quality fats and oils is essential, flax oil, olive oil, deep-sea fish are good choices. Sugar, fat, protein in the provision of calories, there must be vitamin B participation, in order to be fully converted and utilized. Foods rich in B vitamins include lean meats, malt and brewer's yeast.
Lipid regulation avoids the use of statin lipid-lowering drugs. Although statin is a first-line lipid-lowering drug, by inhibiting the conversion of blood glucose to cholesterol, it leads to an increase in the amount of blood glucose retained in the bloodstream, which can lead to an increase in blood glucose.
Second, regular meals
A balanced intake of brown rice, mixed beans, fish, meat and vegetables is required. Don't diet, eat low glycemic index foods don't think too much about dieting to lower your sugar, make sure you keep yourself away from hypoglycemic conditions. Hypoglycemia is a dangerous condition that triggers the body's active glycemic actions: glucagon elevates, hepatic glycogen releases blood glucose, which is used to balance blood glucose levels. If hypoglycemia persists, adrenocorticotropic hormone, glucagon secretion increases, and fatty proteins are converted to blood glucose through gluconeogenesis, while inhibiting insulin action and insulin secretion, and a large amount of free fatty acids enter the bloodstream to prepare raw materials for further pushing of high blood glucose Preparation. Carbohydrates mainly refer to the rice and noodle food that we often eat, because rice and noodle food is now more and more finely processed, lack of necessary dietary fiber and vitamins, glycemic too fast, will stimulate excessive secretion of insulin.
Diabetes should avoid delicate rice and noodle staples and add brown rice, roughage, mixed grains and beans and vegetables, which can be good for smoothing out post-meal blood sugar. Mixed beans and brown rice, because they are rich in fiber or directly supplemented with fiber, allow for slow absorption of sugar and lipids without roller coaster changes in blood sugar and lipids.
For diabetes, the most important nutrient for smoothing blood sugar and lipids is: dietary fiber!Dietary fiber slows the absorption of sugar and fat from the intestines, preventing a rapid rise in blood glucose and lipids after meals, which in turn slows the pressure on the pancreas and liver. And, because dietary fiber allows the body to absorb blood sugar slowly, it smoothes blood sugar while maximizing the use of food nutrients to avoid hypoglycemic conditions.
Third, screen for stress
This is critical! Otherwise the body will release large amounts of glucagon to raise blood sugar while suppressing insulin action when blood sugar is desperately needed. Possible situations that can lead to stress are: late nights, high workloads, stress, fear, pressure, negative emotions, irregular diets, and frequent hypoglycemia are all common stressors that can trigger a rise in blood sugar. Stressors such as stress and emotions have a much greater impact on blood glucose than traditionally recognized!
Fear and nervousness lead to increased secretion of adrenaline, resulting in elevated blood glucose Stress and anxiety trigger an increase in catecholamine secretion, which inhibits insulin action and leads to elevated blood glucose Puberty, pregnancy, menopause and mental stimulation, trauma and other causes lead to increased secretion of thyroxine. Thyroxine can promote the absorption of glucose by the small intestinal mucosa, and at the same time promote glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis, thus elevating blood glucose. Eat a regular diet, avoid triggering stress injuries, and take care of rest and relaxation!
Many people do not know how to relax, even sleep can not get a good rest, need to learn the spring mountain step therapy and self-relaxation training. Spring Mountain Step Therapy: Walk slowly one hour after meals, walk with the heel on the ground first, the palms of the feet to the ground, then five toes to pick up the ground, so that the toes are fully in contact with the road surface. By stimulating the reflex zones of the soles of the feet, the body and emotions wait until the relaxation, when walking, the breathing mode is two inhalation and one exhalation.
Fourth, pay attention to testing blood sugar
Again, don't overemphasize hypoglycemia. It is important to understand that diabetics need higher blood sugar than the average person, and that blood sugar will naturally come back down only after stress and other causes of insulin resistance have been eliminated. Diabetes should never be overly lowered through the drug insulin, trying to regulate blood sugar in one step, the result is often too fast. For example, some doctors recommend dieting, exercise to lower sugar, and tight control of blood sugar, but do not know how to prevent the risk of hypoglycemia, which is a very dangerous practice. Even if you put two candies in your pocket, you can't resist the damage that hypoglycemia can do to your body, and when you feel hypoglycemic, the damage has already happened.
People with diabetes must be alert to the possibility of hypoglycemia, each low blood sugar triggers a stress response, both make the next low blood sugar more likely and make the blood sugar reserve higher. This is why the average person doesn't get hypoglycemic until they have a blood sugar of 2.8 or less, whereas a diabetic can get hypoglycemic with a blood sugar of 3.9, and in some cases, with a severe stress response, even with a blood sugar as low as 5!
Fifth, insist on abdominal breathing
There is a 19-fold difference in energy gained from sugar metabolism between hypoxia and aerobic! Many people breathe so shallowly that before the first half of their breath goes in, the second half is already out, no gas exchange is realized, and the body is actually in a state of chronic hypoxia. The lack of energy also causes the body to actively raise sugar! This is why most diabetics have symptoms of fatigue and weakness. Drumming the stomach while practicing inhalation allows for an adequate supply of oxygen. Adequate oxygen helps the body achieve normal metabolic reactions, allowing for sufficient energy while reducing metabolic wastes that are harmful to the body.
Now more diabetic patients do not have the typical symptoms of three more and one less, but generally have fatigue and weakness and other energy deficiency, indicating that more is the problem of blood glucose metabolism and energy utilization problems, hypoxia is also a stress stimulus, in the tension, stressful conditions are more prone to muscle hypoxia. Hypoxia can also cause the body to elevate blood glucose, and lowering glucose at this time may aggravate the energy deficit and worsen the condition.
If abdominal breathing is difficult to adhere to initially, getting up and moving around every half hour and taking a few deep breaths can also be a good way to improve hypoxia. As for exercise, because it increases energy expenditure and may trigger hypoglycemia, the time, method, and amount of exercise required for different types of diabetic exercise are different, and this article does not provide a detailed introduction, so if you are interested, you can check out my Q&A about diabetic exercise.
Diabetes is not scary, what is scary is that you may have been creating your body's need for high blood sugar all along, and the medications you are using may be accelerating this trend even further, if you are willing to stop, reflect on your misbehavior and change it, you will find that dysglycemia is easy to change.
For more on diabetes, hyperuricemia, hyperlipidemia, ketogenic diet, stress, etc., check out my Gnosis Q&A. Previously sanatorium guided slow disease recovery, full set of non-drug regimens are in there. 418 answers in Wukong.
vista specializes in non-drug conditioning and gives you all the dry stuff!
Thanks for liking and following and retweeting!
In daily life, some people get up in the morning fasting after measurement, will find that its fasting blood sugar is at a relatively high level, what is the cause of this?
1. Eating too much. As we all know, the individual's diet has a more direct relationship with its blood glucose level, if you eat too much, or too much intake of some high fat and high protein and other high-calorie foods, then the patient in the premise of glucose-lowering drugs or insulin remains unchanged, the calories can not be fully consumed, will be converted to sugar into the blood, and ultimately lead to the occurrence of fasting blood glucose is too high.
2. Eating too little. This point is actually easy to be ignored by many people, but in the clinic is relatively common. Some people in the morning 2-3 o'clock will appear low blood sugar, and in the morning there is the phenomenon of high blood sugar, this phenomenon is mostly seen in patients with type 1 diabetes. As the patient's insulin overdose will induce hypoglycemia, at this time the body out of self-protection, the body's glucagon, growth hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone secretion will be significantly increased, so that every time after the occurrence of hypoglycemia and then appear to have high blood sugar.
3. Suddenly too much or suddenly reduce the patient's exercise. If the exercise is suddenly increased, it will lead to hypoglycemia in the early morning, which will increase the secretion of glucagon in the body, and the fasting blood glucose will be increased in the morning. Another reason is due to a sudden decrease in exercise, resulting in excess calories are not consumed, ultimately leading to the occurrence of hyperglycemia.
Instructor: Ren Zhengxin, Attending Physician, Department of Family Medicine, Zhangye People's Hospital Affiliated to Hexi College.
Specialties: 21 years of clinical work in general medicine, the scope of treatment includes diabetes, coronary heart disease, common diseases of women and children, as well as comprehensive analysis and management of daily physical examination.
If you find this article useful, please feel free to like or recommend it to your friends and follow [Medlink Media].
For diabetes we are no strangers, we are more or less around a few diabetic relatives, friends or strangers, or maybe we are diabetic ourselves. Diabetes is common in middle-aged and elderly people, the incidence of obese people is relatively high, so the usual weight loss work must be done. In the case of ensuring that the body's basic nutritional needs, to do low-fat, low-protein, low-salt and low-sugar diet, and at the same time to exercise more, which can reduce the chances of developing diabetes, but also can control the development of diabetes.
In order to prevent the occurrence of diabetes as well as the need to control blood sugar work, usually we have to do a good job of blood sugar testing work, which fasting blood sugar check is particularly important. However, we should also know, not because of high fasting blood sugar, recognized as diabetes, for the absence of symptoms, to diagnose diabetes, not only the fasting test to exceed the normal value, then the postprandial blood glucose is also needed to exceed the normal value, so that the diagnosis can be confirmed.

Don't worry too much even if your blood sugar tests high when you are fasting, this is not necessarily diabetes and can be caused by several reasons:
First, excessive obesity, this group of people is prone to high fasting blood sugar, which is also a potential population of diabetes, mainly because of the relatively slow metabolism of this group of people muscle.
Second, insulin secretion is low, easy to make fasting blood sugar increase.
Third, excessive emotional or mental stress, which is known to cause blood sugar fluctuations.
Fourth, the amount of exercise is significantly reduced, insulin can not effectively play a role, resulting in high blood glucose.
E. Consuming too many sweets or sugary drinks, which can easily cause high blood sugar in a short period of time.
VI. Low blood sugar followed by rebound hyperglycemia is known as the SOMOGYI phenomenon.
Seven, taking certain drugs, such as prednisone, dexamethasone and other drugs that can cause high blood sugar, such as taking certain cough syrup.
VIII. Alcohol consumption can lead to hypoglycemia as well as hyperglycemia.
Nine, diabetic patients, in the event of illness or other emergency situations, the original dose of insulin or oral hypoglycemic drugs used is insufficient, and so on.
At the same time, it is important to note that fasting blood glucose is best measured in the early morning at 6:00~8:00 a.m. Blood is taken without hypoglycemic drugs, breakfast or exercise before blood collection. If the time of fasting blood collection is too late, the measured blood glucose value is difficult to truly reflect the patient's therapeutic effect, and the result may be on the high or low side.

Click on the bottom of the page [Learn More] to see more answers or ask the doctor a question for free!
Follow "Family Doctor Online" headline, more health Q&A easy to see~~~~
To answer your question, high fasting blood glucose is the meal last night, calories, not released, so cause high fasting blood glucose, try to eat a low-calorie diet, the calories of the meal, through the exercise to consume the body's calories, the body feels sweaty on the good, keep your mouth shut, and open your legs!
The causes of high fasting blood sugar need to be analyzed on a problem-specific basis.
First, the onset of diabetes mellitus "fasting blood glucose as the main manifestation", the postprandial blood glucose increase is not obvious. This is often due to the presence of more obvious "insulin resistance" in this part of the liver. The liver is a storehouse of glucose, and during fasting, glucose from the liver is transported to the blood vessels to provide the body with energy. When there is insulin resistance, glucose from the liver is continuously transported to the blood vessels, and the amount of glucose transported increases, resulting in a high concentration of glucose in the blood vessels during fasting, which raises fasting blood glucose. If this is the case, it can be treated with metformin.
Second, diabetes has been diagnosed, and the treatment process is always high fasting blood glucose. There are three possibilities to consider in this case:
1) As stated above, the liver insulin resistance is not being addressed with measures as above.
(2) "Sumuje phenomenon". When hypoglycemia occurs at night, especially in the second half of the night, the body initiates a self-protection program to raise blood glucose by stimulating the sympathetic nerves and secreting hormones, and then finds that the fasting blood glucose is high in the morning. This situation is often related to factors such as excessive use of therapeutic drugs or insulin, and failure to eat a reasonable meal before bedtime, which requires adjustment of the treatment program.
3) "Dawn phenomenon". In the second half of the night, during the dawn phase, the body secretes hormones that raise blood glucose (e.g., growth hormone, glucagon, glucocorticoids, etc.), while the amount of insulin that lowers blood glucose may be insufficient, resulting in an imbalance in blood glucose regulation and high fasting blood glucose. This situation also requires adjustment of the treatment program, such as increasing the amount of medication or insulin dosage.
4) How to identify "Sumuje phenomenon" and "dawn phenomenon"? Take a blood glucose measurement at 2:00 a.m. If you have low blood glucose at 2:00 a.m. and high fasting blood glucose in the morning, it may be "Sumuje phenomenon". If there is no hypoglycemia at 2:00 a.m. and high fasting glucose, it may be the "dawn phenomenon". Take different measures according to this.
5) High fasting blood sugar can also be caused if you eat too much at night or if you stay up late, have a poor night's sleep, or are anxious.
Causes of high fasting blood sugar
1,
fasting blood sugar
One of the reasons for the high level of low exercise
Insufficiently effective insulin, excessive intake of sweets or sugar-sweetened beverages, excessive
obese
The rebound hyperglycemia after hypoglycemia is known as the SOMOGYI phenomenon. Alcohol consumption can cause both hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. It can cause
abnormally high blood sugar level
or if you have taken certain medications.
cough suppressant syrup
The reason for high fasting blood glucose is to control the total calories. What we have to do after figuring out the cause of high fasting blood glucose is to control the total calories, which should be determined according to the patient's nutritional status, weight, age, gender and physical activity, etc., so as to control the blood glucose.
2. Fasting
hyperglycemia
Reason No. 2
antihyperglycemic drug
Insufficient doses of substances used
insulin
Insufficient dose of glucose (e.g., insulinotropic agents) to effectively control postprandial blood glucose at normal levels.3, high fasting blood sugar causes of the third by the rebound early morning fasting high blood sugar
3.1. Rebound early morning fasting hyperglycemia is characterized by the patient's excessively low blood glucose during the night, in
hypoglycemia
The stimulation of glucagon in the body,
adrenaline
In addition, the secretion of hormones such as corticosteroid and growth hormone, which have antagonistic effects on insulin, increases, and the patient's body cannot correspondingly increase the amount of insulin secretion to counteract the effects of these glucagon, which gradually raises the blood glucose and leads to fasting hyperglycemia in the early morning. Most of these cases occur after the patient goes to sleep, and the symptoms are mild and senseless.
3.2 However, there are more serious cases, such as patients may wake up because of hunger, panic, sweating and other symptoms, at this time, if you immediately measure the blood glucose, the value is often lower than 2.8mmoI/L. The reason for this situation is mainly due to the excessive dosage of hypoglycemic drugs. In the treatment method, we should consider reducing the dosage of hypoglycemic drugs before dinner or bedtime to avoid hypoglycemia; we can also try to avoid hypoglycemia by eating a cooked egg or drinking a cup of milk before bedtime to correct the fasting hyperglycemia in the early morning. It should be pointed out in particular that when the patient has severe hypoglycemia, intravenous injection should be given immediately.
wines
Sugar or immediate food to quickly correct hypoglycemia.
This is a very specialized question to ask, and if you just use a textbook answer, the answer is simple: high fasting blood glucose can indicate that your pancreatic beta cells are functioning abnormally, and that there is insufficient secretion of basal insulin.
But why does this happen? It is more complicated when analyzed in terms of the mechanism of occurrence.
First, the fasting blood glucose value is the blood glucose value measured after an overnight fast of 8-10 hours (except for drinking water) and after a blood collection before breakfast on day 2.
In other words, fasting blood glucose is the value of blood glucose that is at a relatively constant level in our body, excluding the fluctuating disturbances in blood glucose caused by our eating and activities during the day.
For a normal person, this constant fasting blood glucose value will be maintained between the range of 3.9-6.1mmol/l, and the factors affecting the high and low fasting blood glucose can be insulin, the nervous system, and endocrine hormones, which are 3 factors, among which, insulin is the main factor regulating fasting blood glucose in our body, and it is also the only factor that can reduce fasting blood glucose in our body.
So how do insulin, the nervous system, and endocrine hormones contribute to high fasting blood sugar? They are described below for reference only.

Mechanisms of insulin causes of high fasting blood glucose
Insulin is a hormone secreted by the beta cells of the pancreas, the glands in our pancreas, and it is also the only hormone in our body that lowers blood sugar.
Insulin promotes the uptake and utilization of glucose in the blood by the tissue cells throughout our body, and at the same time, inhibits the breakdown of glycogen into glucose in our body, preventing blood sugar from rising; it even prevents non-glycemic substances in the body from being converted into glucose, resulting in a rise in blood sugar.
As you can see, insulin lowers blood sugar in 3 ways:One is to promote the uptake and utilization of glucose by tissue cells; the other is to prevent the conversion of glycogen to glucose; and the third is to prevent the conversion of non-sugar substances to glucose.
Therefore, fasting blood sugar is elevated when the following 5 conditions occur.
Scenario 1:Absolute insulin secretion is insufficient;
Scenario 2:Impaired insulin utilization;
Scenario 3:Absolute insulin deficiency + impaired insulin utilization;
Scenario 4:Relative insulin underproduction;
Scenario 5:Relative insulin deficiency + impaired insulin utilization.
These are the 5 insulin causes of high fasting blood sugar.

Mechanisms of neurologic causes of high fasting blood glucose
We know that the nervous system includes the central and peripheral nerves, which in turn include the sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves, among others:
1. Sympathetic nerves can inhibit insulin secretion, resulting in insufficient insulin secretion, and, therefore, are able to raise fasting blood glucose.
2. Parasympathetic nerves can stimulate insulin secretion, therefore, can make fasting blood sugar lower.
It follows that the regulation of fasting blood glucose by the nervous system, theIt's ultimately through insulin;At the same time, the nervous system's regulation of fasting blood glucose, which works in both directions, isIt can either make fasting blood sugar high or low.

Mechanisms of endocrine hormonal causes of high fasting blood glucose
There are many endocrine hormones present in our bodies that can affect fasting blood glucose, including insulin (which is also a hormone), but, with the exception of insulin, which can lower fasting blood glucose, all other hormones can only raise fasting blood glucose.
These hormones are: growth hormone, adrenaline, glucocorticoids, thyroxine, etc., and even glucagon, a hormone secreted by the alpha cells in the pancreatic islets.
It can be seen, it is because insulin is the only hormone in our body to reduce fasting blood sugar, other hormones are elevated fasting blood sugar, so, insulin appears to be alone, once our body's insulin abnormalities, insufficient secretion, we not only do not have a second hormone to help us lower blood sugar; on the contrary, these other hormones will become emboldened, more frantically elevate fasting blood sugar.
In summary: There are many reasons for high fasting blood glucose, but the three most important are insulin insufficiency and/or impaired utilization, sympathetic/parasympathetic regulation, and endocrine hormone action.
Do you agree with me?
Daily update on health hotspots, medical pain points; if what I say, is exactly what you think, then please like, retweet, follow Zhu Xiaojun said health!
Special note: All recommended medications in the comments section should be tried with caution and never purchased with a call!
Introduction:Fasting blood glucose (GLU) is defined as the blood glucose value measured after overnight fasting (at least 8 to 10 hours without any food, except for drinking water), blood taken before breakfast, the most commonly used test indicators for diabetes, what causes high fasting blood glucose?
Common causes of elevated fasting blood sugar are:1. Too many meals or too much high-calorie food intake on the previous day, especially eating a large amount of high-calorie food at dinner; 2. Eating too late and lasting too long the previous night, such as attending a dinner party, etc.; 3. Insufficient exercise on the previous day, especially bed resting immediately after dinner; 4. Missing or underdosing of hypoglycemic drugs; 5. Insufficient insulin injection dose, or forgetting to inject insulin, or insulin failure; 6. Own pancreatic hypoglycemia, basal insulin secretion is insufficient; 7. Dawn phenomenon: due to the dawn time in the morning (3 to 9 o'clock), the patient's plasma insulin level decreases, and the secretion of glucose-raising hormone increases; 8. Sumuje reaction: after hypoglycemia in the early hours of the morning, the body, out of self-protection, will secrete some glucose-raising hormones on its own, which will lead to the increase of fasting blood glucose; 9. Other factors: whether there is a Other factors: whether there is a cold, fever and other conditions.
Fasting blood glucose is the blood glucose measured after a person has fasted for 8 to 12 hours, i.e., the blood glucose in the early morning fasting state. Ideally, fasting blood glucose should be controlled between 3.9 and 6.0 mmol /mL.
There are three main causes of high fasting blood sugar:
First, the patient has hypoglycemia at night, under the stimulation of hypoglycemia, the body's pancreatic glucagon, adrenaline, corticosteroid and growth hormone and other hormones that have an antagonistic effect on insulin are secreted in excess, and the patient's body can not correspondingly increase the amount of insulin secretion to counteract the effect of glucagon, which leads to the rise in fasting blood glucose.
Second, blood glucose begins to rise in the second half of the night, resulting in high fasting blood glucose in the early morning. Studies have shown that sugar users usually secrete more growth hormone and corticosteroid in the second half of the night, resulting in a decrease in insulin action in the body.
Third, improper control of total food calories and inadequate vitamin supplementation, high-fiber foods can ease the decomposition and absorption of carbohydrates, which is conducive to balancing blood sugar, and adequate vitamins can help the body's metabolism.
Fasting blood glucose mainly reflects our basal blood glucose level. After dinner, our blood sugar gradually decreases to below 7.8mmol/L about 2 hours after meal, and below 6.1mmol/L about 3 hours after meal. After sleeping at night, the body's metabolism gradually slows down, and the consumption of blood glucose gradually decreases, and the nighttime blood glucose almost stays at 3.9-6.1mmol/L, and lasts until the morning, which is the normal fasting blood glucose. Then, what are the causes of elevated fasting blood glucose? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze it for you.
在Insulin sensitivity of peripheral tissues、Adequate amount of insulin、Insulin and glucagon regulatory balanceIn this case, our fasting blood glucose can remain in the normal range: 3.9-6.1 mmol/L. Elevated fasting blood glucose, on the other hand, is mostlyInsulin resistance, insufficient insulin secretion, relatively increased glucagon secretioncaused by insufficient to keep fasting blood glucose in the normal range.
The most common cause of insulin resistance is obesity. Long-term obesity leads to metabolic disorders, so that tissues are less sensitive to insulin, and the utilization and intake of glucose is reduced, resulting in elevated fasting blood glucose. For this group of patients, weight control and diet control are the main conditioning methods, through exercise, reducing the intake of high-calorie food, and lowering the weight by about 7-10% within 1 year, insulin resistance can be effectively improved.

- Insufficient insulin secretion is not sufficient to lower blood glucose at night, resulting in elevated fasting blood glucose. In type 2 diabetes mellitus, early stage is mainly insulin resistance, accompanied by mild insulin secretion insufficiency; in the later stage, it is mainly insulin secretion insufficiency, resulting in elevated blood glucose. In the early stage of type 2 diabetes mellitus, exercise, diet and oral hypoglycemic drugs are used to regulate blood glucose, while in the later stage, insulin is mainly used to regulate blood glucose.
- The relative increase in the secretion of glucagon will also cause an increase in fasting blood glucose, also known as the "dawn phenomenon". At 4-8 am, glucagon is gradually secreted, which is a normal physiological phenomenon. The increased secretion of glucagon will raise blood glucose. If insulin secretion is sufficient at this time and there is no insulin resistance, blood glucose can be controlled in the normal range, but if insulin secretion is insufficient or there is insulin resistance, blood glucose will be raised. For this part of patients, it is usually recommended to control blood glucose through exercise and dietary regimen first, and if it is ineffective, the only way to control blood glucose is to use long-acting hypoglycemic drugs before bedtime, such as diethylstilbestrol, glycemic insulin, and other long-acting drugs.
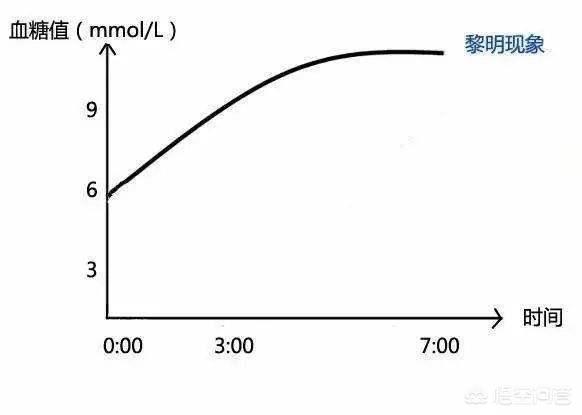
- There is also a condition that can cause an increase in fasting blood glucose, which we call the Sumuje reaction. The reason for this phenomenon is because an overdose of glucose-lowering medication before bedtime causes a nocturnal hypoglycemia, which leads to an increase in the secretion of glucagon, which in turn causes hyperglycemia after the hypoglycemia. By adjusting the dose of bedtime hypoglycemic drugs can keep blood sugar in the normal range.
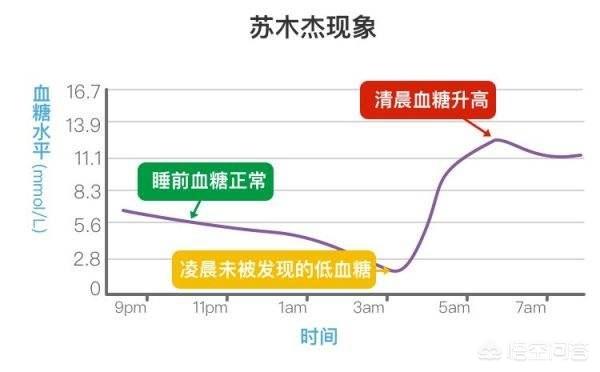
In summary, elevated fasting blood glucose is mostly caused by insulin resistance, insufficient insulin secretion, relative increase in glucagon secretion, and sulforaphane response. Fasting blood glucose level can be improved by reducing weight, controlling diet, increasing exercise, and adjusting glucose-lowering treatment program.
Thank you all for reading!
Welcome to learn more about medical senlution and health knowledge!
Note: The images in this article come from the Internet, if infringement of copyright, please contact to remove. The content of the article is only as a health science popularization, not as a medical advice or opinion, does not have medical guidance conditions.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.