How long does it take to detect HIV infection?
AIDS is a very dangerous disease, why is it dangerous? Why is it dangerous? Because it does not cause a little bit of damage to the human body, not to a certain part of the body, but to the whole body. We've seen a lot of public service announcements about AIDS, and it's becoming more and more well known as more and more cases are found in colleges and universities.
The United Nations has reported that there are nearly 40 million people infected with the AIDS virus (HIV) worldwide, 49% of whom do not know they are infected with HIV, and about 57% of whom are not taking treatment drugs. This statistic reaffirms the invisibility of HIV in the population! Many people who are not actively screened after a risky exposure can easily become an invisible source of infection.
1. How exactly does AIDS harm our bodies?
There are two main types of immune cells in our body, which we can understand as defense cells, and it is these two types of cells that we rely on to survive in a germy environment, they help us to defend ourselves against the stimuli and damage brought by the outside world, like a spear and a shield against the enemy (germs), and at the same time they are both indispensable to not only defend against the enemy, but also to kill the enemy at times.
They are T-cells and B-cells, of which AIDS is in the infringement of T-cells (CD4 + T-cells, a type of T-cells), when the T-cells are killed, the human body's immune system will be significantly reduced, and may be other people a sneeze can make you catch a cold! Some people may think that it is just to kill the virus, right? Yes, it is to kill the virus in order to cure AIDS, but in fact, the current medical level can not do it.
First of all, we have to understand that HIV is a kind of virus, and the antiviral drugs that we often hear about are only to assist in clearing the virus and promoting its excretion, but it is basically impossible to kill the virus, which is why even without treatment, viral colds can be cleared up by one's own strong resistance! Only our body's immunity can fight the virus, and the so-called antiviral drugs cannot kill the virus.
2. What is the rate at which HIV infects the human body?
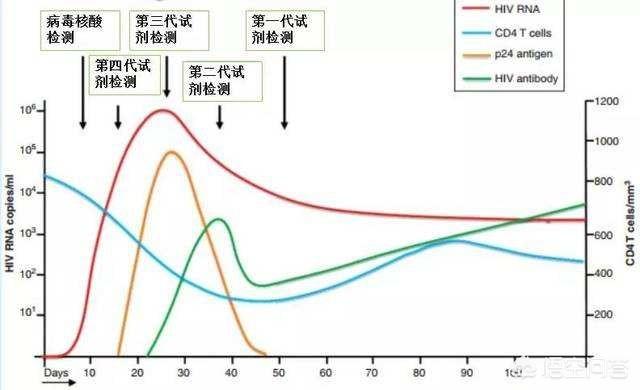
AIDS alias Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS) is caused by HIV infection, once infected, it reaches the lymph node tissues of our body very quickly (within 2 days), the virus can be detected in the peripheral blood in about 5 days (soon, it doesn't take years), and in the short term, the CD4+ T-cells will decline (acute infection period), then return to normal again. Thereafter the human body is present with HIV, in the chronic infection period, including asymptomatic infection and symptomatic infection, this period can last from a few months to decades; in the asymptomatic infection period T cells decline slowly and do not show significant discomfort, the symptomatic period T cells decline rapidly, the body's immune collapses, infections, tumors and other diseases appear.
3. How is the invasion of HIV into the human body understood?
After the above, you may still not understand that there is no way to get rid of HIV. Even if it can't be killed, it can be excreted from the body, right?
Let me give you an example, HIV is like a spy sent by the enemy, it can duplicate itself (one to two), and it can also disguise itself! The T-cells in our body are our soldiers; when HIV enters the body and is found by our army, we will attack it because it will hide, so after attacking some of them, a few are left hidden out of our sight, and our team has the upper hand!
As time goes by, millions of our soldiers are secretly killed by HIV, a few at a time, can't be seen at all, and HIV replicates itself, one turns into two, two turns into four (it's really slow to notice, so there's nothing the body isn't, asymptomatic infection period, this period can be a long time); suddenly one day the general realizes that there are fewer soldiers, so he starts to attack HIV on a large scale, but HIV can Transfiguration, today it looks like this, tomorrow it looks like that, it can't be captured; our body's soldiers are also partially destroyed by HIV, there are not enough soldiers to capture HIV (HIV has the upper hand, symptomatic infection period, also called AIDS period)! HIV begins to destroy our T-cells, immunity begins to decline, we grow in an environment with all kinds of viruses and bacteria, the same bacteria that used to be there, and our bodies don't have enough resistance to get sick!
This is probably what happens when HIV attacks the body, eventually the immune cells are depleted and the body becomes a culture medium for bacteria and viruses and eventually dies. So HIV itself does not cause disease, but harms the body by destroying its immune barrier.
HIV infection can be detected in as little as a few days, and it can be months to years before we reach the stage of AIDS where it is uncertain, and a negative test occurs when the viral load is below our minimum test, but it does not mean that HIV is not present!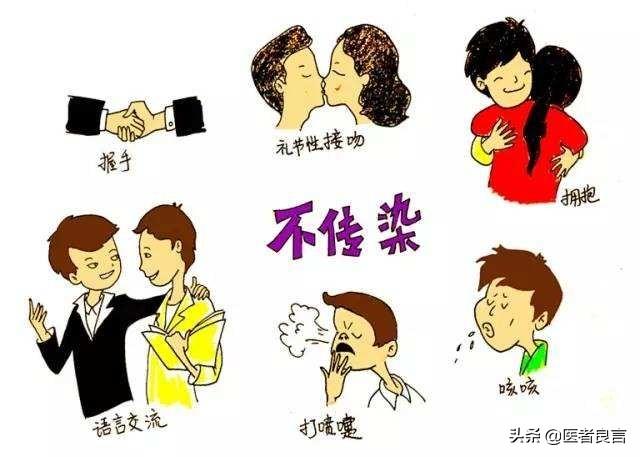
Final Summary: HIV transmission is mainly through blood, sex, mother and child, etc., shaking hands, hugging are not contagious, if accidentally exposed (with the possibility of AIDS), you can take blocking drugs in time, as soon as possible to test! Don't drag your feet on time, everyone's immunity is different, so the asymptomatic period exists for different lengths of time, and early treatment is the only way to hopefully get it under control! Also, please don't discriminate against people with AIDS, most of them are innocent victims, everyone wants to be healthy.
Purely hand-typed, it is not easy, if you feel that the writing can also be rewarded a praise, point a concern, if you have any questions can be left below ......
From the subject's question to ask should be if infected with AIDS, how long should be able to detect HIV antibodies. Clinically, there is a window period after HIV infection, during which HIV has not yet produced the corresponding antibodies, so the antibodies cannot be detected, but in the window period, it is already highly infectious. If blood transfusions are given to HIV patients in the window period, they are also very susceptible to HIV infection.
I. What is the AIDS window period?
Many people may not understand what the AIDS window period is. In fact, it refers to the period of time from the day the HIV virus enters the body, such as the day of sexual misconduct, blood transfusion and other behaviors that may be infected with HIV, to the time when it is possible to accurately detect whether or not the infection has been detected, which is called the window period.
Second, how long is the AIDS window period?
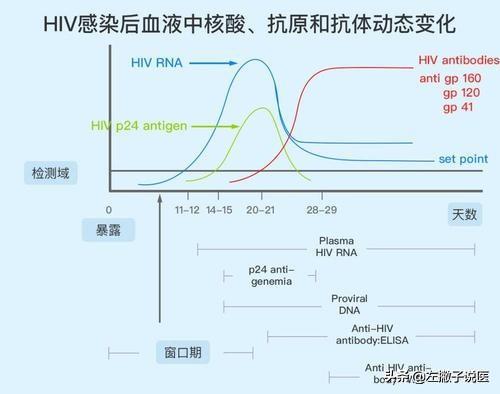
When HIV enters the human body, it produces viral nucleic acid in 10 days to 4 weeks, produces viral P24 antigen in 2 to 4 weeks, and finally produces antibodies after 3 to 12 weeks. And the length of the window period also varies from individual to individual, such as the amount of exposure to the virus, the individual's own immune system response and other factors, generally 2 weeks to 3 months, and China's current CDCs are generally recognized as the window period of AIDS is 3 months.
However, with the sensitivity of testing reagents, the window period for AIDS has been gradually shortened. In recent years, the World Health Organization has made it clear that the window period for AIDS is 14 to 21 days. Although no HIV antibody can be detected during the window period, HIV is already present in the body, so the window period is also contagious.
If you pass an HIV antibody test after 3 months and the result is negative, you can completely rule out the possibility of HIV infection.
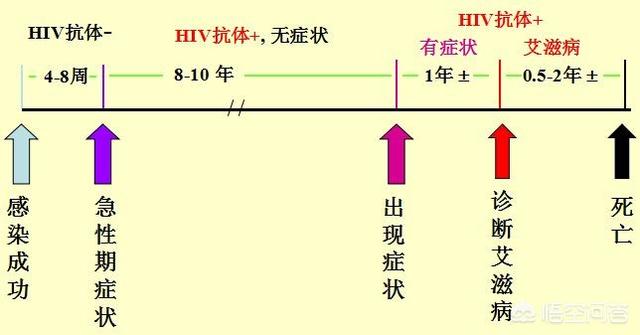
In fact, in addition to the window period of AIDS, there will be a latent period, even if it is infected with AIDS, the production of HIV antibodies, effective patients will not immediately appear symptoms of AIDS, the incubation period can be as short as 6 months to 1 year, usually 8 to 10 years, the longest can be up to 20 years. Therefore, some patients who do not have HIV antibody test do not know that they are AIDS patients, and it is even easier for them to transmit the virus to other people, and other people to other people, which results in more and more AIDS patients, and some of them are only found in their old age.

III. Is there no cure for HIV infection?
The greatest concern of many people should be whether there is no cure if they are accidentally infected by HIV and they have to wait for death? In fact, HIV can be blocked in the early stage of infection. If after the occurrence of high-risk behavior or know the HIV-contaminated needle prick, within 72 hours, preferably within 48 hours, within 2 hours of the best results, timely take HIV blocking drugs. And the success rate of HIV blocking medication is also more than 99% when taken consistently for 28 days. So take the blocking drug as early as possible.
If you have an occupational exposure in a hospital and are accidentally stabbed with an HIV-contaminated needle, you will know that you need to take the blocking medication in time. However, if you are infected by HIV in the community, there are many people who do not know that they can take HIV blocking medication, and they will only feel that the world has collapsed, that their life is over, and that all that is waiting for them is death.
IV. Post-title remarks
In the case of AIDS, it has been said a thousand times or ten thousand times that the most important thing is to be clean and protect yourself well in order to stay away from AIDS.
Author's note: I'm very happy to popularize health-related knowledge for everyone, I'm left-handed to say medical, every day in simple language for you to popularize professional medical knowledge, the code word is not easy, if you like my article, help me to point a praise! If you still have questions, you can leave a message in the comments section, welcome to pay attention to, forward, thank you for your support!
Thanks for the invitation!
I don't know what the owner means by normal, is it from being infected with HIV to being able to detect HIV antibodies in the body? Or from the time of infection to the appearance of clinical symptoms?
Let's start with the time from HIV infection to the time when HIV antibodies can be detected in the body. In fact, none of us can know whether we are infected with HIV or not, so we all take the occurrence of high-risk behavior that may transmit HIV as a starting point, and then start to calculate the time when HIV antibodies can be detected. If the infection occurs in this high-risk behavior, the current use of nucleic acid testing method can be detected in about 10 days, the four-generation enzyme reagent can be detected in 2-4 weeks, and the three-generation enzyme reagent can also be detected in 2-8 weeks,. To be on the safe side, it is generally recommended to test after 3 months. If the HIV antibody test is negative at this time, the possibility of HIV infection can be ruled out. We call this time period the window period. A 6-month period is extremely rare.
Secondly, from the time of HIV infection to the appearance of clinical symptoms, this period of time is generally called the incubation period. there is an acute phase of HIV infection, at this time there will be some cold-like symptoms, many people will think that it is a cold, and the treatment method is to use the treatment of colds, this process will last about 2-4 weeks. This process will last for about 2-4 weeks. After that, there will be no symptoms like normal people until some common symptoms of HIV infection appear, such as prolonged low-grade fever, prolonged unexplained diarrhea, and various skin rashes, etc. The doctor will ask if you have gone through the acute phase. At this point the doctor will ask if the person has gone through HIV-related high-risk behavior and test for HIV antibodies. This time period tends to vary from person to person and is basically 0-30 years with an average of 8-12 years.
To summarize, as to how long it takes to detect AIDS, it all depends on our awareness of AIDS prevention, if we are clean and have a strong sense of prevention, then we won't have to worry about this; if the awareness of AIDS prevention is weak, we must go to the test in a timely manner after the occurrence of high-risk behaviors, and we will be happy that there is no infection, and once infected, we will start the antiviral treatment as soon as possible.
HIV infection is quickly detected, but HIV infection is not the same as AIDS, and it takes an average of nine years or more to progress to the appearance of AIDS symptoms.
1. AIDS window period for 14 ~ 21 days, window period HIV infection can not be detected, after the window period to detect H Ⅰ V antibody negative, then you can rest assured.
window periodIt refers to the period between the entry of HIV into the human body and the production of a sufficient amount of HIV antibodies in the blood that can be detected by the test method. Although no HIV antibodies can be detected during the window period, HIV is already present in the body and is contagious.
AIDS was first discovered in 1981, and limited to the backwardness of the testing methods at that time, the window period was generally considered to be 3 months in the 80s and 90s, and was written in the medical textbooks of various countries. When the enzyme-linked assay and double original sandwich method appeared, the window period was shortened to 6 weeks, and the third and fourth generation of double original sandwich method or chemiluminescent method, which is widely used now, can be shortened to 14~21 days. The World Health Organization (WHO) clearly indicates that the window period of AIDS is 14~21 days. It means that there isPeople who have high-risk sexual behavior, or who have been contaminated with HIV-infected blood (e.g., police officers, medical personnel), go for an HIV test 14 to 21 days after the event, and can rest assured if it is negative.

HIV testing is voluntary, free and confidential.Worried about HIV infection, you can go to the local CDC for HIV testing. Now that the country has invested so much in the prevention and treatment of AIDS, HIV testing is free and confidential to encourage suspects to voluntarily and actively participate in the test. As a reminder, the test is only free at the CDC, but if you go to the hospital, you will need to pay for it.
You can take HIV blocking medication.If there is a high degree of suspicion or clear certainty that there is an exchange of body fluids with an HIV-infected person, or a person who may be infected for occupational reasons, such as medical personnel in the course of their medical work or police officers inadvertently coming into contact with HIV-containing blood in the performance of their official duties, which we refer to as occupational exposure, they can take AIDS-blocking medication. AIDS blocking drugs are commonly used in our country:Raltegravir + emtricitabine + tenofovir. The combination of these three drugs, taken within 72 hours, can block HIV infection with up to 95% effectiveness.
4 The average incubation period between HIV invasion and the development of AIDS is 9 years, and can be as short as a few months or as long as 10 years. HIV invasion can be divided into three stages.
Acute phase.It usually occurs 2 to 4 weeks after the initial infection.behave like a cold.Fever, rash, muscle and joint pain, and swollen lymph nodes for several days.It disappears after a few days to 2 weeks and HIV tests can be negative and contagious.
asymptomatic phase. clinicallyAsymptomatic, but contagious.This period usually lasts 6 to 8 years.
AIDS period1) develop AIDS-related symptoms:Persistent fever, night sweats, diarrhea for more than 1 month, weight loss of more than 10%, neuropsychiatric symptoms such as memory loss, personality changes, headaches, seizures, dementia, and persistent generalized lymph node enlargement.
2)Various opportunistic infections and tumors appear.Various systemic tissues can be involved, such as the respiratory system presenting with pulmonaryPneumocystis pneumonia, which is the most common and leading cause of death;Toxoplasmic encephalitis and various viral meningitis in the central system; various enteritis in the digestive system; thrush, etc. in the mouth; malignant lymphoma, Kaposi's sarcoma and other malignant tumors.
Summary: HIV can be detected 14 to 21 days after infection, and it takes an average of 9 years to progress to the appearance of AIDS symptoms.

Nowadays, society is becoming more and more open, but many people do not consider the consequences when seeking passion, and after the incident, they are worried about all kinds of things, and AIDS is the problem that many people are worried about. Sexual contact has also become the main means of transmission of AIDS, which is also the main problem faced in the prevention and control of AIDS, the other two means of transmission of AIDS (blood transmission and mother-to-child transmission) can be effectively controlled, but the sexual contact is more difficult to control, although the use of condoms is now advocated, but there are still a lot of people who have a weak sense of self-protection, and do not use a condom. Some people have asked me how long it takes to detect HIV. Next, Dr. Wu will talk to you about this topic.
What is HIV? Why is AIDS so scary?
As we all know, AIDS is caused by a virus called Human Immunodeficiency Virus (also known as the AIDS virus, abbreviated as HIV), which mainly destroys the immune system of human beings, and eventually makes the human body's immune system defective, and the patients eventually die of a series of infections and various malignant tumors. No cure for AIDS has been found yet, and AIDS can be spread, so everyone is afraid of this disease. However, AIDS is not that scary. Controlled by effective antiretroviral drugs, AIDS can also be lived well.
How long does it take for HIV to be detected?
We test for AIDS mainly to detect HIV antibodies, the human body needs a certain period of time to produce antibodies after infection with HIV, this period is called the "window period", mostly 14~21 days, during this period of time because the human body has not yet produced antibodies, so we can not detect AIDS, generally after this period of time can be detected. This shows that it does not take many years to detect AIDS, and it can be detected in less than a month!
The human body is not suddenly infected with HIV, the virus will take several years before the human body's immune system will be overrun, as fast as two or three years, or even more than ten years, which is a period of time we call the incubation period. During the incubation period, people infected with HIV do not look any different from normal people, nor do they have any special symptoms, which is an important source of infection and also a difficult point in the prevention and control of HIV.
Finally, Dr. Wu urged everyone to be clean and learn to use condoms correctly, do this, in fact, AIDS is far from ordinary people.
I am a general practitioner who uses easy-to-understand words to spread health knowledge to everyone, follow me, you have a family doctor. If you find it useful, you can forward it to your friends who need it!
It usually takes 2 weeks and 3 months to detect HIV infection. This is because when HIV enters the body, it can only be detected by clinical methods if sufficient antibodies are produced. The period between the entry of HIV into the body and the production of sufficient antibodies in the blood to be detected by clinical methods is called the window period. That is to say, in the window period can not detect AIDS, only after the window period can be detected HIV, this window period is generally 2 weeks and 1 3 months, so it takes 2 weeks and 1 3 months after the infection of AIDS can be detected, the length of the window period with the amount of infected viruses and infected people's physical fitness is related. Although no HIV antibody can be detected during the window period, HIV is already present in the body, so the infected person in the window period is also contagious.


Before answering your question, let's first clarify two concepts:AIDS and HIV.
1. What is AIDS?
AIDS is a systemic infectious disease caused by the infection of the organism with the human immunodeficiency virus (also commonly known as HIV). It is caused by HIV attacking the body and destroying CD4+ T lymphocytes, resulting in defective cellular immunity and reduced defense against infection and cancer. Its source of infection is HIV-infected people
and AIDS patients, mainly through sexual contact, blood transmission and vertical transmission from mother to child.
2. What are the symptoms of AIDS?
When it comes to the symptoms of AIDS, many people will be on the right track, especially those who are afraid of AIDS, and those who have had high-risk behaviors. Even if they have taken an HIV test at the CDC or in the hospital, and the result is negative, in the course of their daily work, they will repeatedly ask for advice on the phone to find out if they are missing out on the diagnosis, or if the test reagents are not sensitive, in short, they will use all kinds of reasons to be on the right track, and repeatedly ask to be tested again. In short, they will use all kinds of reasons to be in the right place, and repeatedly ask to be tested again, which is what we often call the fear of "AIDS" mentality.
Getting back to the point, let's talk about the symptoms of AIDS.
The onset of AIDS is divided into three phases:Acute phase, usually occurring 2 - 4 weeks after the initial infection, most symptoms are mild and fever is common.
An asymptomatic period, usually 2 - 10 years or more, may present with symptoms such as swollen lymph nodes.
In AIDS, diarrhea (stools more than 3 times/day), weight loss (more than 10% weight loss in 6 months), night sweats, memory loss, headache, apathy and other neuropsychiatric symptoms, fever, and swollen lymph nodes are common.
3. What are the diagnostic methods for AIDS?
Mainly HIV antibody test, CD4+ T-lymphocyte test, and HIV nucleic acid test.
4. What are the treatments for AIDS?
At present, the most widely used method is cocktail therapy, which emphasizes comprehensive treatment, using a variety of antiretroviral drugs in combination, and when AIDS is combined with other infections, other drugs and treatment plans can also be selected according to the condition. However, regardless of which program, at present, AIDS cannot be cured, but only improve the symptoms and prolong the patient's life.
In fact, AIDS is not as terrible as we think, it is now included in the ranks of chronic infectious diseases, is preventable and not curable. As long as we are clean, use condoms correctly for safe sex, refuse drugs, don't share needles, don't share razors, don't get your ears pierced, avoid unnecessary injections and blood transfusions in medical operations, and give antiretroviral drugs to mothers before giving birth after they have been found to be infected with HIV in a pregnancy test, then we can do a good job of preventing AIDS.
5. What is the AIDS virus (HIV)?
HIV, the full name of Human Immunodeficiency Virus, is an acquired immunodeficiency virus that specifically attacks T-lymphocytes in the human body. It is widely found in the blood, semen, vaginal secretions, breast milk and cerebrospinal fluid of infected people.
HIV and AIDS are two different concepts that are often easily confused. In fact, HIV infection is not necessarily AIDS, because AIDS has a certain incubation period. After the infection of HIV, only when it develops, we can call it AIDS.
6. HIV testing!
Currently there are many ways to detect HIV, buy HIV test strips online is one of the easiest way, but no matter whether the test is positive or negative, don't panic or relax, because there is a certain amount of false positives in this test, there is a window period for HIV, after the test, it should be in 3 months (now the fastest test method can be confirmed within a month) to the local CDC! After the test, you should go to your local CDC after 3 months (the fastest test now can be confirmed within a month) to have your blood drawn again for a confirmatory test to confirm the diagnosis!
Hi everyone, I'm a doctor who works with HIV at the CDC, and I'm here to answer your questions.
Let's first distinguish between the concepts of AIDS (AIDS) and HIV infection:
AIDS is defined as a human infection with HIV after a certain incubation period, CD4 <200, and the appearance of AIDS-related signs or symptoms such as opportunistic infections;
HIV-infected persons are those who are infected with HIV and have a positive diagnostic test for HIV antibodies, but whose CD4 cells are still in the "normal range" and who do not have any clinical symptoms or signs of HIV infection.
In my work, I have also come across many cases in which people who are afraid of HIV or have engaged in high-risk behaviors are afraid of being infected with HIV and are afraid or unwilling to undergo a test, and they are counting on the signs or symptoms to determine whether they are infected with HIV or not.
If infected with HIV, the incubation period of AIDS is generally 2-10 years, with the earliest being half a year and the longest being up to 20 years before signs or symptoms related to AIDS appear. However, HIV antibodies can be detected within one month.
According to the 2018 edition of our HIV Treatment Guidelines, HIV antibodies can be eliminated more than 80% in half a month and completely eliminated in a month with the latest reagents.
If you have had high-risk behaviors and are afraid of being infected with HIV, I suggest that you go to the CDC or a hospital as soon as possible to do the appropriate tests, and if you are not infected, you can completely let go of it and live and work well. In my work, I have come across many, many cases of HIV fear, some of which have seriously affected their normal lives.
If you are tested for HIV infection, early treatment is helpful for later treatment. The 2019 edition of the U.S. Guidelines for the Treatment of HIV clearly states that treatment is prevention, i.e., U=U, and that the probability of transmission of HIV through the sexual route is 0 when the viral load in the body is below the lower limit of detection.
Lastly, I hope each of us cleans up our act. If you have had high-risk behavior please get counseling and testing as soon as possible.
If you have had unprotected sex, you can take HIV blocking medication, clinically called PEP, and you can consult your local CDC for the exact place to buy it.
Dear friends, if you have any questions about AIDS related issues, please follow me for private consultation, I have some experience in counseling for HIV intervention, and I also welcome you to share your own stories about HIV or about AIDS, thank you.
First, let's look at how healthcare workers are treated when they are exposed to AIDS (HIV) and have an occupational exposure.
Occupational exposure of healthcare workers, that is, healthcare workers have loss of skin or mucous membrane contact with body fluids, blood, or medical equipment or objects containing body fluids or blood of HIV patients when they come into contact with AIDS (HIV) patients. The process of treatment and the passage is shown below:
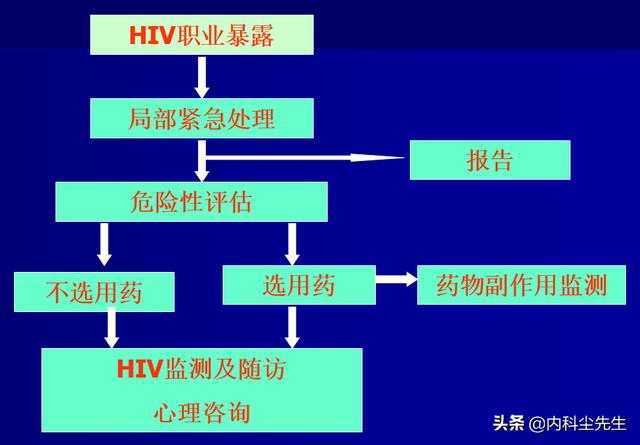
Specifically for:
1. Assessment: Level of exposure and assessment of viral load levels at the source of exposure.
2. Implementation of preventive medication.
The grading of exposure and the assessment of the viral load of the exposure, as well as the timing of medication administration, should be referred to in order to assess whether or not one is infected with HIV.
I. Grading of exposure
1. Level 1 exposure:
Contamination of damaged skin or mucous membranes, small exposure and short exposure time.
2. Secondary exposure:
Contamination of damaged skin or mucous membranes, where exposure is extensive and prolonged; or punctures or cuts to the skin, where the damage is minor, such as epidermal abrasions or needle-stick injuries.
3. Tertiary exposure:
Punctures or cuts to the skin, but the damage is more severe in the form of deep wounds or cuts with clearly visible blood.
As for the assessment of viral load levels at the source of exposure, a laboratory assessment is required.

II. Timing of medication
Prophylactic medication should be initiated as soon as possible after an occupational exposure to HIV, preferably within four hours and no later than 24 hours; prophylactic medication should also be administered if more than 24 hours have elapsed. Exposed persons should be tested for HIV antibodies immediately, 6 weeks, 12 weeks, 6 months, and 12 months after exposure, and the toxicity of the medication taken should be monitored and managed.
Infection with HIV is only a process; it is the progression to AIDS, or AIDS, that is the key to the disease.3 Stages of the AIDS Course
AIDS, also known as Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome, is caused by infection with the Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The consequences of acquiring the disease are severe immunosuppression, leading to infections, induction of tumors and neurological symptoms.
However, HIV infection does not necessarily progress to AIDS immediately, as HIV has a long incubation period and is generally thought to take several months to 10 years or more to develop into AIDS.
There are 3 stages in the progression of AIDS, which tells you how the disease progresses through AIDS
Phase 1: Early ---- resistance
Also called the acute phase, just like a cold, HIV is a virus, so it shows similar symptoms, such as sore throat, fever, and muscle aches.
Because the pathogenicity of the virus is related to the number of viral replications, if the infected person's immune ability is not very poor at this time, he/she will produce an immune response and inhibit the replication of HIV virus by himself/herself, so the symptoms such as sore throat, fever, and muscle aches and pains will be gradually relieved after 2-3 weeks.

Phase 2: Medium-term ---- Holding
Some cases of AIDS can last for years or never reach the end stage, which is the stage where the body's immune function is at war with the virus.
In this period, due to the suppression of immune function, the virus replication is at a low level, and the body may have no obvious symptoms, or there may be swelling of lymph nodes in the body, and occasionally fever, malaise, and skin rashes.
Stage 2: Late ---- immune collapse
The destruction of the phase of phase-in leads to a collapse of immune function and a tendency to opportunistic infections (where germs that are normally weak in pathogenicity take advantage of the situation) and malignant tumors.
Symptoms that occur are persistent fever, malaise, lethargy, diarrhea, and neurological symptoms such as impaired consciousness, cognitive impairment, and sensory deficits.
How long does it take to detect HIV infection?
There is a window period for HIV infection, during which HIV antibodies cannot be detected, but HIV can be detected through HIV nucleic acid testing. The World Health Organization (WHO) has clearly indicated that the window period for HIV infection is 14 to 21 days.
What is the window period?
The period of time between when the HIV virus enters the body and when antibodies to the HIV virus can be detected in the blood using a test is called the window period.

Which method is used to monitor HIV at the hospital during the week?
Generally, when you go to the hospital to check for AIDS, you are tested for HIV antibodies by drawing blood, in fact, the test for AIDS is divided intoInitial screening and confirmation of diagnosis.
HIV antibody tests like this one are for initial screening, and after a positive test, a specimen needs to be sent to the CDC for HIV nucleic acid testing to confirm the diagnosis.
Finally, as an infectious disease, although testing is important, it is also necessary to clarify whether the source of infection and the means of transmission are compatible. People living with AIDS and those infected with HIV during the window period are the source of infection, of which sexual contact transmission, blood transmission, and mother-to-child transmission are the means of transmission. If there is no contact with the infectious agent through its transmission route, the chance of infection is not high.
The window period for AIDS has been shortened to 14 to 21 days with the current technology, during which it is difficult to detect HIV and its antibodies from the infected person, but as soon as the window period is over, the body produces enough antibodies to reach the level that can be detected by the test method. The diagnosis of AIDS is thus confirmed;
There is a concept mentioned here - the window period of AIDS. In simple terms, it is the period of time from the moment of infection to the detection of HIV antibodies in the patient's body, the length of which may vary according to individual differences, but it rarely exceeds 21 days, so if you suspect that you are at risk of infection, you can take a test 14 to 21 days after the event. Therefore, if you suspect that you are at risk of infection, you can take a test 14 to 21 days after the event, and if no antibody is detected, it is a negative result, which means you are not infected with HIV. Of course, if you are not assured, you can repeat the test 3 months after the event, and if it is still normal, then the chance of infection is close to zero;
In addition, the length of the AIDS window period may also be related to the administration of AIDS blocking drugs. Generally speaking, people with a clear history of exposure can be blocked from AIDS by the triple drug (raltegravir + emtricitabine + tenofovir), and the blocking rate within 72 hours can even reach 95%, but this also means that there are still 5% of the exposed people who are not able to escape the risk of infection;
However, among these 5% of infected persons, there are people who can maintain a negative antibody test result for a fairly long period of time, which may be as long as several months or even more than a year, in other words, their window period of AIDS has been prolonged, so we cannot help but speculate that, or it is possible that the blocking drug also has an effect on the length of the window period of AIDS, of course, this requires a lot of experimental evidence.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.