What is normal blood pressure for a 70 year old male?
谢邀.
On June 9, 2018, the 28th European Conference on Hypertension and Cardiovascular Protection, released the ESC/ESH 2018 Hypertension Guidelines developed by the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).
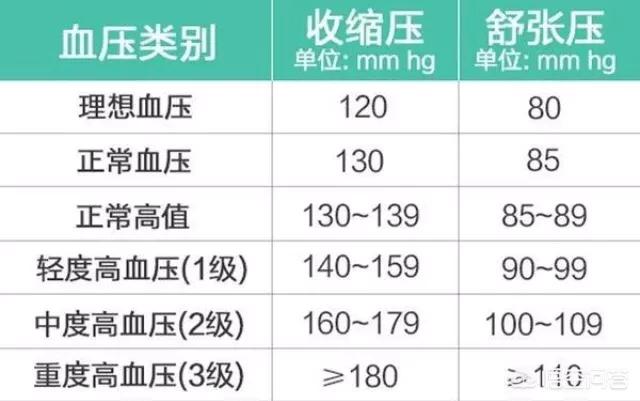
Below is a table of blood pressure standards.
Elderly people around 70 years old commonly have hardening of the blood vessels, the elasticity becomes poor, the blood vessels can not be normal contraction and diastole, the systolic blood pressure (high pressure) will be a little higher than normal, diastolic blood pressure (low pressure) on the contrary, relatively normal.
healthy and vigorousThe recommended systolic (high) blood pressure for older adults should be maintained at 130 to 140 mmHg, and diastolic blood pressure should be maintained at 80 to 90 mmHg.
Combined diabetesAt that time, the high pressure should be maintained at 130 to 140 mmHg and the low pressure should be maintained at about 80 mmHg.
combined heart failureAt that time, blood pressure should be controlled at about 140/90 mmHg.
combined coronary heart diseaseAt that time, high pressure should be maintained at 120-130 mmHg and low pressure at 70-80 mmHg.
When controlling blood pressure in older adults, care should be taken not to keep it too low.It is permissible to go slightly above the required standard, but never too low。
Usually should pay more attention to low-salt, low-fat and low-sugar diet, quit smoking and alcohol, healthy and reasonable comprehensive nutritional diet, exercise, regular work and rest, adjust the mentality, keep a happy mood!

The age of 70 belongs to the old age stage of life, and its blood pressure level will be relatively high compared to the young population, but under normal circumstances, regardless of our age, our normal blood pressure range does not change. According to our latest guidelines, the normal blood pressure level of our population is systolic blood pressure ≥90mmHg and <140mmHg, diastolic blood pressure ≥60mmHg and <90mmHg. Therefore, the normal blood pressure level of our 70 year old men is also within this range.
The human body's blood pressure is in the process of dynamic change, with the increase of age, blood vessels will gradually harden, the elasticity becomes poor, the systolic and diastolic function are all down, the corresponding blood pressure level will also increase, but should be within the above range, China's 70-year-old men's blood pressure in the average of 130/80mmHg or so. Once it exceeds the above range, regardless of age, it is considered to be an increase in blood pressure; while below the above range, it is considered to be a decrease in blood pressure.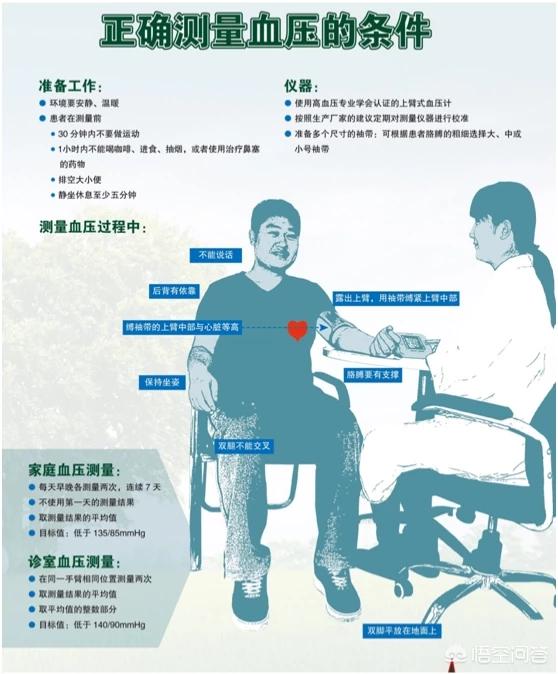
Accurate and standardized measurement of blood pressure measurement is one of the main prerequisites for us to understand the health status of the organism, because the mercury column sphygmomanometer measurement is relatively complex, requiring professionals to operate, coupled with the current electronic sphygmomanometers are also relatively reliable, so it is recommended that we use the appropriate cuff electronic sphygmomanometer to measure blood pressure. We should rest quietly for at least five minutes before blood pressure measurement, avoiding strenuous exercise, staying up late, drinking alcohol, tea and coffee. The first time we measure blood pressure, we should measure the blood pressure of both upper arms, and then each time we choose the arm with the higher blood pressure to measure.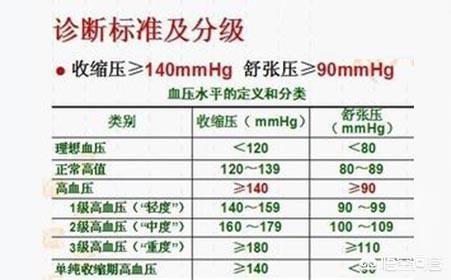
Although the latest U.S. guidelines set 130/80mmHg as the diagnostic standard for hypertension, due to differences in ethnicity and specific national conditions, the current standard for hypertension in China is still 140/90mmHg. The diagnosis of hypertension is based on a systolic blood pressure ≥140mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure ≥90mmHg measured three times in non-same day without taking antihypertensive medications. Once diagnosed, hypertension should be treated with regular medical care, low-salt diet, smoking cessation and alcohol restriction, weight control, regular work and rest, and good attitude, and antihypertensive drugs should be used according to the condition of the patient, and changes in the condition should be monitored during the use of the drugs and regular checkups should be conducted.
Thanks for reading and good health to all. Copyright © All Rights Reserved. Follow the author for more health knowledge.
The normal range of blood pressure for a 70-year-old male is the same as for an average adult: when the blood pressure is below 140/90 mmHg and above 90/60 mmHg, it is normal; when the blood pressure is higher than 140/90 mmHg on three non-same-day occasions, the diagnosis is hypertension. It should be noted that although the normal range of blood pressure in the elderly (65-79 years old) is not different from that of the general population, the timing of our intervention, the choice of antihypertensive drugs, and the target value for lowering blood pressure are different from those of the general population and need to be emphasized when the blood pressure rises.
When to Start Pharmacologic Antihypertensive Therapy in the Elderly
In the general population, if the blood pressure is not up to 160/100mmHg, and there is no comorbidity of several risk factors, target organ damage, clinical complications, or diabetes, the blood pressure can be controlled by lifestyle changes first; if lifestyle control is ineffective or if the blood pressure is up to 160/100mmHg or if the blood pressure is at high risk, very high risk, and if the blood pressure is higher than the target blood pressure by 20//10mmHg, then only antihypertensive medication will be initiated. However, in the elderly, the timing of blood pressure intervention is different. If there is no specific coexisting disease, medication should be given to control blood pressure when the blood pressure reaches 150/90 mmHg; in order to reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, medication can also be given to lower blood pressure when the blood pressure reaches 140/90 mmHg.
How to choose antihypertensive drugs for the elderly
Due to the hardening of the arterial wall and decreased vascular elasticity, most of the elderly people's blood pressure rises mainly in systolic blood pressure, diastolic blood pressure rises insignificantly or normally, and blood pressure fluctuates, the risk of cardio-cerebral and cerebral vascular events is significantly increased. In view of these characteristics of hypertension in the elderly, when we choose antihypertensive drugs, we do not recommend preferred β-blockers, because β-blockers can reduce peripheral vascular resistance and further reduce diastolic blood pressure, and we can choose Pulidoids, sartans, diphenhydramine, hydrochlorothiazide, which are more conducive to the treatment of hypertension in the elderly; secondly, give priority to the selection of long-acting antihypertensive drugs, which can provide 24-hour continuous control of blood pressure Secondly, long acting antihypertensive drugs are preferred because they can control blood pressure continuously for 24 hours, significantly reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, and only need to be taken once a day, so the elderly have good adherence to the drug, which is helpful for the treatment; when the initial treatment is given, the drug should be given in small dosage because the elderly have reduced hepatic and renal functions, and the metabolism of drugs in the body slows down and the effect of the drug extends for a longer period of time, which is easy to induce hypotension. It should be noted that in the antihypertensive treatment, should also pay attention to a healthy lifestyle: early to bed, early to rise, a balanced state of mind, appropriate exercise, weight reduction, smoking cessation and restriction of alcohol, low-salt diet, high-potassium diet and so on.
What range of blood pressure should be controlled in the elderly
Our primary goal for hypertension in the elderly is to keep blood pressure below 150/90mmHg, or below 140/90mmHg if tolerated. However, recent studies have found that it is more beneficial to prevent acute cardiovascular events if systolic blood pressure can be kept below 130mmHg in the elderly. It should be noted that if there is a combination of multiple cardiovascular risk factors, or if there is already a complication of cardiac, cerebral, or renal damage, the target value of blood pressure reduction should be controlled below 130//80mmHg.
In summary, 70-year-old men.Normal when blood pressure is below 140/90 mmHg and above 90/60 mmHg。If there is no special coexisting disease, when the blood pressure reaches 150/90mmHg, medication should be given to control the blood pressure; in order to reduce the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, when the blood pressure reaches 140/90mmHg, medication to reduce blood pressure can also be used to reduce blood pressure, medication to reduce blood pressure at the same time, attention should be paid to change the lifestyle; antihypertensive drugs preferably Prilosec, sartans, diphenhydramine, hydrochlorothiazide, with a long-lasting antihypertensive drugs are appropriate, and the small dose of the initial administration of the drug The primary goal of blood pressure lowering is to control blood pressure below 150/90mmHg, or below 140/90mmHg if tolerated, and below 130mmHg for systolic blood pressure, which is more beneficial, and if cardiac, cerebral, and renal complications have already appeared, the target value of blood pressure lowering should be controlled below 130//80mmHg.。
Thanks for reading!
Note: Images are sourced from the internet, please contact for removal if copyright is infringed!
Low pressure around 80, high pressure around 130--140
Seventy years old is the old age stage, but adults over 18 years old in China, blood pressure standards are the same. High pressure exceeds 140mmHg, low pressure exceeds 90mmHg, as long as it meets one of them, it is considered high blood pressure, of course, the diagnosis needs to be strict conditions, such as different dates, quiet state measurement of blood pressure exceeds the above standard more than twice.
Ideal blood pressure 120/80 mmHg
Normal blood pressure 130/85 mmHg
High normal values 130-139/85-89mmHg
High blood pressure over 140/90 mmHg
Have regular medical checkups. If you are diagnosed with high blood pressure, make sure you have regular follow-ups and take your medication as prescribed by your doctor. Blood pressure should preferably be kept below 130/85mmHg.
For 70-year-old patients, blood pressure is relatively normal if it can be around 140/90mmHg, but in theory, 70-year-old patients, the standard systolic blood pressure range is 100-120mmHg, and the standard diastolic blood pressure range is 60-80mmHg. However, in practice, it is not recommended that the elderly patients, the blood pressure will be lowered too much. If the patient has diabetes or kidney damage, it is recommended to control the blood pressure below 130/80mmHg, which is relatively ideal, as the blood pressure itself is subject to many factors. What is relatively normal for a 70 year old is also dependent on a number of factors, such as the patient's actual body weight, and whether the patient has any other accompanying medical conditions.

What is normal blood pressure for a 70 year old male?
Let's look at the division of blood pressure first.
Normal blood pressure <120 and <80 Normal high values 120 to 139 and/or 80 to 89
Hypertension ≥140 and/or ≥90
Grade 1 hypertension 140-159 and/or 90-99
Grade 2 hypertension 160 to 179 and/or 100 to 109
Grade 3 hypertension ≥180 and/or ≥110 simple systolic hypertension ≥140 and <90
At 70, you're already elderly, so you need to know the full picture of hypertension in the elderly.
Older people with high blood pressure
Hypertension is the most common chronic disease. More than half of the elderly suffer from hypertension, and the prevalence of hypertension is close to 90% in people aged ≥80 years, making it the primary risk factor for stroke, myocardial infarction, and even cardiovascular death.
With a hypertension control rate of 18% in the elderly, the prevention and control of hypertension in the elderly still has a long way to go. Older adults are a unique group with hypertension prevention, diagnosis, assessment, and treatment strategies that are significantly different from those of the general population.
Definition and Classification of Hypertension in the Elderly Hypertension is diagnosed in older adults ≥65 years of age who have a systolic blood pressure (SBP) ≥140 mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) ≥90 mmHg when their blood pressure is measured 3 times on non-same days without the use of antihypertensive medications. Elderly people who have had a clear diagnosis of hypertension and are being treated with antihypertensive medication should also be diagnosed with geriatric hypertension even though their blood pressure is <140/90 mmHg. Elderly hypertension is graded in the same way as for adults in general.
Assessment of Frailty in Elderly Hypertension Frailty is one of the manifestations of aging and its incidence increases significantly with age. Frailty is one of the most important factors affecting the benefit of antihypertensive therapy in older adults.
Antihypertensive treatment for hypertension in the elderly should emphasize the systolic blood pressure to reach the standard, and gradually make the blood pressure reach the standard under the premise of being able to tolerate. After initiating antihypertensive treatment, it is necessary to pay attention to monitoring the changes in blood pressure to avoid adverse reactions brought about by too rapid lowering of blood pressure.
Comprehensive intervention risk factors in the pursuit of blood pressure reduction to achieve the standard at the same time, for all reversible cardiovascular risk factors (such as smoking, dyslipidemia or obesity, abnormal glucose metabolism or uric acid elevation, etc.) intervention treatment, and at the same time focus on and treatment of related target organ damage and clinical disease. Most patients require long-term or even lifelong adherence to treatment.
medication
Basic principles of antihypertensive drug application in the elderly
(1) Small doses: a small effective therapeutic dose is usually used for initial treatment, and the dose is gradually increased as needed
(2) Long-acting: as far as possible, use 1 time / d, 24h continuous antihypertensive effect of long-acting drugs, effective control of night and early morning blood pressure
(3) Combination: If monotherapy is unsatisfactory, combination therapy with two or more low-dose antihypertensive drugs can be used to increase the antihypertensive effect, and single-tablet compounding can help improve patient compliance
(4) Moderation: most elderly patients need to be
I am pharmacist Li, every day and you talk about health, welcome to pay attention! If you still have questions about health, welcome to leave a message to consult, after seeing will be the first time to respond.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.