To what extent is a blockage in a coronary artery considered coronary artery disease?
Coronary heart disease is the abbreviation of coronary heart disease, which is a heart disease caused by atherosclerosis or spasm of the coronary arteries leading to narrowing or occlusion of the coronary arteries, followed by myocardial ischemia, hypoxia and necrosis. In general, coronary heart disease is diagnosed when the stenosis of a coronary artery exceeds 50%, in terms of the degree of stenosis alone.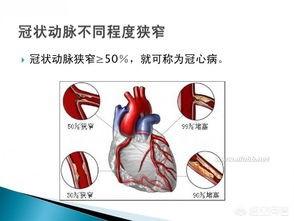
For patients with coronary heart disease, when the degree of stenosis does not exceed 75% is often asymptomatic myocardial ischemia, general physical activity is not limited, only in strenuous labor chest tightness, chest pain and other discomfort. With the further aggravation of stenosis, angina pectoris may occur, which may then lead to ischemic cardiomyopathy and arrhythmia. When the coronary artery is completely narrowed, it will lead to the emergence of acute myocardial infarction.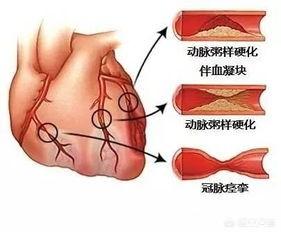
For patients with a clear diagnosis of coronary heart disease, they should actively seek medical treatment and standardized treatment under the guidance of doctors. To maintain good living habits, to achieve a reasonable diet, appropriate regular exercise, quit smoking and alcohol, weight control, regular work and rest and maintain a good state of mind. And individualized medication, it is recommended to take aspirin and statin drugs for a long time, while using other drugs according to the condition, for those who have hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia and other underlying diseases, also need to actively treat the underlying disease.
We hope that you correctly understand that coronary heart disease is not scary, focusing on prevention and regular treatment. For patients with coronary artery stenosis of more than 75% or frequent angina attacks or acute myocardial infarction, we suggest that stenting is feasible to open the blood vessels quickly and restore the blood supply. And if the lesion is complex with many underlying diseases, coronary artery bypass grafting can be considered. While we standardize the treatment, we should also pay attention to monitoring and regular review.
If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a comment at the end of the article to discuss. Follow the author for continuous daily updates on health knowledge.
Coronary heart disease, i.e. coronary heart disease, is caused by myocardial ischemia, hypoxia and necrosis due to stenosis or occlusion of coronary arteries for various reasons. Generally, coronary heart disease can be diagnosed when the degree of coronary artery stenosis ≧ 50%. The diagnosis of patients with coronary heart disease mainly relies on clinical symptoms such as chest tightness, chest pain, etc., and is clarified with tests such as coronary angiography.
Coronary heart disease is divided into five main categories: asymptomatic myocardial ischemia, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, ischemic cardiomyopathy and sudden death type. Its treatment methods mainly include lifestyle intervention, drug therapy, stent intervention and coronary artery bypass grafting, etc. The specific treatment plan should be decided after the doctor's comprehensive assessment of the condition.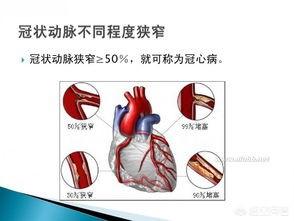
Coronary heart disease patients should maintain a good lifestyle, low-salt, low-fat, low-sugar diet; appropriate and regular exercise, aerobic exercise-based, step-by-step; smoking cessation and limitation of alcohol, do not drink the best, when the condition is stable can be appropriate to drink red wine; weight control, obese attention to weight loss; regular work and rest and to maintain a good state of mind. At the same time, it is recommended that patients with coronary heart disease take aspirin and statin drugs for a long time.
For those with underlying diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, etc., it is also necessary to actively treat the underlying diseases and control blood pressure, blood sugar and blood lipids up to standard. For patients with angina attacks, it is also necessary to always have nitroglycerin. For patients with frequent angina attacks, coronary artery stenosis of more than 75% or acute myocardial infarction, stent intervention is feasible. For people with complex coronary artery lesions or many underlying diseases, coronary artery bypass grafting is also feasible when necessary. While we standardize the treatment, we should also pay attention to monitoring the changes in the condition and regular review.
Thanks for reading, this article was originally written by @General Practice Sweeper, welcome to like, comment, reprint, follow the author, get more health knowledge. Please correct any deficiencies. Images are from the internet and are for reference only.
Coronary artery disease can be diagnosed by a 50% or greater stenosis in any of the major coronary vessels, but this criterion is too rigid, and the presence or absence of objective evidence of myocardial ischemia to diagnose coronary artery disease may be more significant.
First of all, the so-called coronary heart disease refers to the imbalance of the balance between the blood supply of the coronary arteries and the oxygen consumption of the heart, resulting in temporary or continuous ischemia and hypoxia of the heart muscle and thus the occurrence of angina pectoris, infarction, arrhythmia, heart failure, etc. as the clinical manifestations of heart disease. The common pathophysiological basis of coronary heart disease is coronary artery atherosclerosis, the diagnosis of coronary heart disease mainly relies on the results of coronary CTA or coronary angiography, if the degree of coronary artery atherosclerosis reaches the degree of luminal narrowing of more than 50%, it can be diagnosed with coronary heart disease; there is coronary atherosclerosis but narrowing of less than 50%, the diagnosis of coronary artery atherosclerosis.
The reason why stenosis of more than 50% is defined as coronary heart disease is because the human body has a strong compensatory function, in general 50% stenosis below the lumen will not cause significant ischemia of the myocardium, can meet the general activities of the human body's myocardial oxygen consumption, and only lumen stenosis of more than 50% may lead to an imbalance of vascular blood supply and myocardial oxygen consumption.
But this criterion is a little too mechanical, for example, a patient with only 40% coronary stenosis, but he smokes, there may be coronary spasm caused by angina and even the onset of infarction; or his plaque is vulnerable plaque, sudden rupture of acute myocardial infarction will occur, clinically, many infarction patients are occurring in the coronary stenosis of only 50% or so of the patients is the reason. So whether there is objective evidence of myocardial ischemia diagnosis of coronary heart disease is more significant.
Of course, as long as there is coronary atherosclerosis, the principle of drug treatment is pretty much the same, must be lifelong use of statin lipid-lowering drugs, aspirin, metoprolol, etc., especially patients with vulnerable plaque should pay close attention.
Coronary atherosclerotic heart disease (CHD) is a heart disease caused by atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries (coronary arteries), causing narrowing or occlusion of the lumen of the arteries, leading to myocardial ischemia and hypoxia or necrosis, referred to as coronary heart disease, or also known as ischemic heart disease.In fact, coronary blood flow has a large reserve functionWhen the body's strenuous activity, the body's oxygen demand increased significantly, at this time the coronary artery can be dilated, the blood flow up to the usual 6-7 times as much.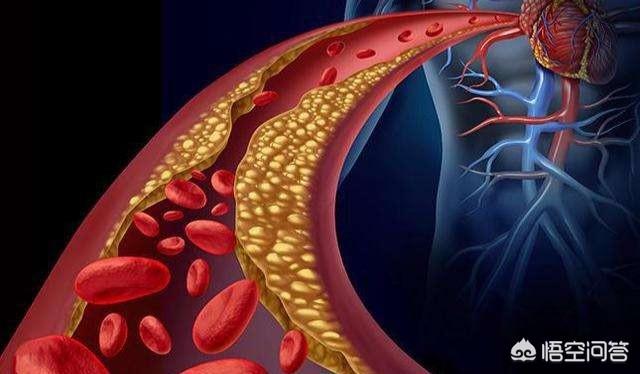
However, when there is a fixed stenosis in the coronary artery(stenosis >50% to 75%)The symptoms of angina pectoris are not obvious in a quiet fashion, but exercise, tachycardia, and emotional excitement that cause an increase in myocardial oxygen demand can lead to a transient imbalance between myocardial oxygen supply and demand, triggering angina pectoris! This is the typical coronary heart disease - angina. The clinical reality is that we can diagnose coronary artery disease on the basis of the patient's symptoms and the cause of coronary artery disease that he or she possesses (e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, etc.). Of course, with the results of coronary angiography or coronary CTA, it will be more intuitive.
The clinical reality is that we can diagnose coronary artery disease on the basis of the patient's symptoms and the cause of coronary artery disease that he or she possesses (e.g., hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, etc.). Of course, with the results of coronary angiography or coronary CTA, it will be more intuitive.
more importantly, coronary heart disease is a chronic, progressive disease, when there is atherosclerosis, even if there is no stenosis >50%-75%, no typical manifestations of coronary heart disease, we do not need to intervene? Of course we need to intervene! Maximizing the rate of progression of coronary stenosis and avoiding ischemic cardiomyopathy is the wisest choice. The way to delay coronary atherosclerosis is to control high risk factors. Actively treat hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, quit smoking and drinking, low-salt and low-fat diet, reduce the intake of saturated fatty acids and trans fatty acids, regular work and rest, do not stay up all night, maintain ideal weight and so on. It is important to treat in normal times, when angina or heart attack occurs and stenting is needed, it will be troublesome!
The way to delay coronary atherosclerosis is to control high risk factors. Actively treat hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, quit smoking and drinking, low-salt and low-fat diet, reduce the intake of saturated fatty acids and trans fatty acids, regular work and rest, do not stay up all night, maintain ideal weight and so on. It is important to treat in normal times, when angina or heart attack occurs and stenting is needed, it will be troublesome!
Doing science popularization with heart - for the public with true feelings - Dr. Zhang Online - Welcome to your attention!
The degree of blockage in the coronary vessels is the most intuitive data available to patients with coronary artery disease to assess their risk.The current most authoritative criterion for confirming the diagnosis of coronary artery disease is 50% stenosis, but the data must be derived from coronary angiography, not coronary CT, which is not particularly accurate and has some margin of error.
However, coronary artery disease is not entirely dependent on the degree of stenosis and blockage!
First of all, the reason for the test, coronary angiography is different from the tests we usually do, it is an invasive test, there is some harm and risk to the human body, if everyone is fine to go for coronary angiography, then it is very dangerous and not cost-effective.
Then there is the cause of the condition. Since it is not possible to do coronary angiography directly, we need to do an assessment and analysis of the condition, which requires information such as the patient's age, medical history, symptoms, signs, and duration of the attack to make a preliminary judgment, and then do some non-invasive tests, electrocardiography and cardiac color CT or something like that before deciding whether or not an angiogram is needed to further confirm the diagnosis.
Finally, the location of the different, the human body has a lot of blood vessels, they are blood flow "merit", at most the difference between the main trunk or branch just, this time we need to determine exactly which blood vessels, which location of the stenosis blockage, which is closely related to the patient's condition, and even more so, affecting the patient's subsequent treatment program.
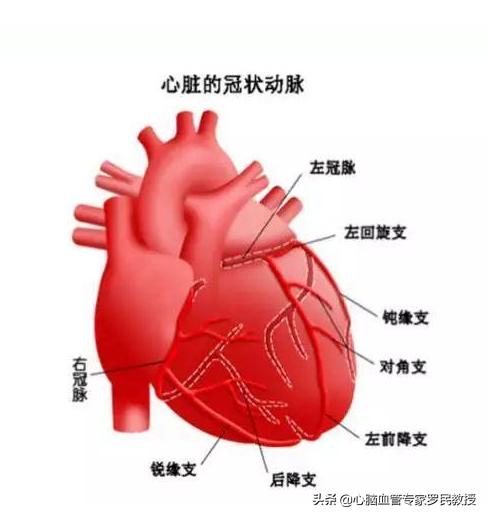
There is a direct link between the degree of stenotic blockage and the condition!
Although we can't determine the condition entirely by the degree of stenosis blockage, side-by-side considerations can still provide some insight into the patient's condition.
Degree <50%: known as coronary atherosclerosis, which is not considered as a disease although it requires attention for intervention.
50% ≤ Degree: this is when it is known as coronary heart disease and requires immediate relevant treatment, regardless of any abnormalities.
75% < degree < 90%: this represents an intermediate stage of the disease and requires consideration of targeted treatment based on information such as clinical symptoms and location of the blockage.
90% I hope my answer helps you! If there's anything you don't understand, comment and private message me!
I'm Dr. Small Eyes, and I hope I my answer, helps you.
At what level of severity of coronary artery stenosis do we consider coronary artery disease?
In general, we believe that regardless of the location of the coronary artery stenosis, we believe that we can diagnose you with coronary heart disease when the stenosis is more than 50% or more.
However, if you have a stenosis between 30% and 50%, we believe you can be diagnosed with coronary atherosclerosis.
What should I do if I have coronary heart disease?
Dr. Small Eyes believes that you need to take regular medication.
This includes aspirin enteric-coated tablets or clopidogrel bisulfate tablets, and you will need to take statins, including atorvastatin calcium tablets, reserpidine calcium tablets, and other such medications.
It can help stabilize the section to some extent and reduce blood lipids.
At what level do we need to place a bracket.
We consider stenting to be necessary when the stenosis is more than 80%.
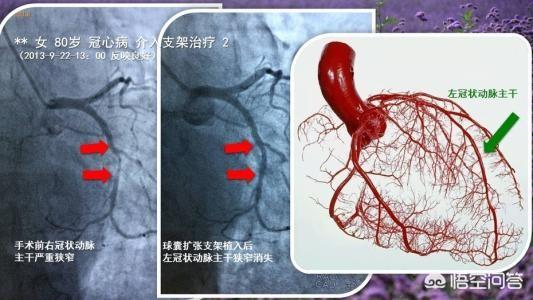
Finally, Dr. Small EyesThe thing I hope to tell you is that your diagnosis of coronary heart disease is not a death sentence.
please pressTake regular medication and have regular reviews.
If there's anything you don't understand, you can comment and let me know
Seems like 80/100 would have to be braced
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.