What is the best medical checkup program to do if you are afraid you have cancer?
Thanks for the invitation to give my opinion as a gastroenterologist!
Nowadays, with the developed life counseling, many people will spread the news once they get cancer, especially when the celebrities get cancer, which leads many people to have the fear of cancer. In addition, if you occasionally feel bad and check the Internet, you will find that many symptoms are similar to the clinical manifestations of cancer, which makes you even more afraid and worried.
When doing gastroenteroscopy in clinic, we came across this kind of situation, one person in the family found stomach cancer, and the whole family ran to the physical examination of gastroenteroscopy. A friend of mine, with a group of drinking friends, often smoke and drink together and eat late-night snacks, very happy and happy, but one of them had blood in the stool to do colonoscopy to find out colon cancer, and then a group of friends were scared to death, because often smoke, drink, eat late-night snacks, stay up late, and as a result, all of the friends who played together lined up for gastro-enteroscopy for a month, which is of course nothing wrong, at least to check it, we are all relieved, and do not have to be afraid all day. I don't need to be scared all day. Fortunately, the results are no big problem.
Back to the question asked by the subject:
If you are really afraid of cancer, you should go to a relatively large hospital, at least a second-class hospital or above, for a comprehensive physical examination. Comprehensive physical examination includes not only blood sampling, but also medical equipment examination of clinical auxiliary departments, such as ultrasound of the whole stomach: including ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, both kidneys, prostate gland, thyroid gland, and so on. Gastroscopy and colonoscopy. Don't take a chest X-ray if you have smoked, it is better to have a chest CT, and for women, it also includes the breast and uterus and ovaries.
Why do I need a physical gastroenteroscopy?
At present, gastrointestinal tract tumors account for more than half of all tumors, early esophageal cancer and gastrointestinal cancer can only be detected through gastroenteroscopy, other examinations such as ultrasound, CT, magnetic resonance imaging and other examinations can not detect early gastrointestinal and esophageal cancers, so the routine comprehensive physical examination should include the examination of gastroenteroscopy.
Therefore, if you want to have a physical examination, it is best to have a full set of blood tests + gastroenteroscopy + full abdominal ultrasound + lung CT, and if a woman has to add the uterus, ovaries, breasts and other tests, so that the full set of tests down to the estimated 3,000 or so, and if the examination is okay, almost can rule out more than 90% of cancers.
Of course, if there is difficulty, it is best to let the clinician to assess the first also can focus on some organs, for example, you repeated epigastric pain, check the gastroenteroscope is no problem, then may need to check the upper abdomen CT or MRI to rule out the liver, gallbladder, pancreas problems. This is probably because the pancreas is not seen very clearly on ultrasound.
Feel free to follow and leave a comment to discuss any questions!

As far as general surgery is concerned, it's mainly cancer of the abdomen. If all three of the following tests are done, and if they're all good, you can basically rule out cancer of the abdomen, and don't bother spending any more money on anything else.
1. Plain scanning + enhanced CT of the whole abdomen
Many people don't realize that abdominal CT is also divided into plain and enhanced. What's the difference? A CT scan of the whole abdomen is cheap, a few hundred dollars for a general look. For further detail, you need to go for contrast and enhancement CT, which is a medicine injected into the blood vessels during the examination so that the arterial and venous vessels are visualized in the enhanced CT image. Because all the abdominal organs have blood vessels to supply blood, each organ can be seen more clearly than in a plain CT, which is also much more expensive.
For example, I am seeing a patient in an outpatient clinic. The patient first has an ultrasound that reveals a mass on the liver that cannot be characterized. At this point, if only a plain CT is done, it may not be possible to go and determine the nature of the mass. With a scan + enhancement CT, I can observe what the mass looks like on the scan CT without contrast. With contrast, what the mass looks like when the blood vessels in the liver are filled with contrast. Based on the imaging characteristics of hepatocellular carcinoma, I can then go on to determine if the mass is hepatocellular carcinoma.

By combining plain and enhanced CT, it is possible to look at tumors in the abdomen dynamically. The organs of the abdomen are divided into solid organs and cavernous organs; CT is better for the solid organs of the stomach (e.g., liver, pancreas, spleen, etc.) and less effective for the cavernous organs (gastrointestinal tract, ureters, etc.). This is why two other tests need to be added: gastroscopy and colonoscopy.
2.胃镜
The stomach can't be seen clearly on ultrasound because the gas in the stomach interferes with the doctor's judgment. If you look at it with a CT, you mainly look at the outer lining of the stomach. At this time, gastroscopy was created to allow doctors to look at the inner lining of the stomach under direct vision.
A growth on the stomach can be seen clearly under a gastroscope. Then, a little bit of the mass tissue is taken to the pathology department for biopsy, which can determine whether it is stomach cancer or not. If it is stomach cancer, according to the results of gastroscopy and CT, a clinical stage can be derived to see whether it is early stomach cancer or middle or late stomach cancer, so as to guide the subsequent treatment.
3. Enteroscopy
A colonoscopy works in much the same way as a gastroscope, in that it also looks at diseases of the colon (also known as the large intestine) under direct vision. If it's a growth on the outer wall of the colon, a CT can look at it. If it is a growth on the inner wall of the colon, a colonoscopy is necessary. The colonoscopy is done from the rectum and sigmoid colon, to the descending colon and transverse colon, and finally to the ascending colon and cecum. It also looks at the opening of the appendix and the end of the small intestine. Again, a biopsy is taken for pathology and the benign or malignant nature of the tumor is determined based on the pathology results.
These are the "three axes" of the general surgeon. After the three axes, if no tumor is found, abdominal cancer can basically be ruled out.
Why do you say largely ruled out?
First, there is still not much clinically available for tumors of the small intestine. Although there are small bowel scopes and capsule endoscopes, the results are not very satisfactory.
Second, particularly small tumors in the stomach, say less than 5mm, are sometimes not visible.
Third, for gynecological and urological tumors, it is sometimes necessary to go to a specialist to find the tumor.
To summarize, whole abdominal scanning + enhanced CT, gastroscopy and enteroscopy are the more reliable means to investigate abdominal tumors at present.
I'm Dr. Zheng from General Surgery, so if my answer was helpful, you can like it. Learn more about medicine and click to follow me.
Why do some people have medical checkups every year, but still lose the chance of surgery when cancer is detected? When we have a physical examination, if it is organized by the unit, including blood, urine and feces, liver and kidney functions, abdominal ultrasound, electrocardiogram, these are the most basic ones, so can these examinations detect cancer and can they detect cancer at an early stage? Actually, it is not.
But it is not possible for you to go to the hospital to do all the tests, on the one hand, the cost is too much, on the one hand, suffer too much, eat more radiation. If you have to do all the blood tests in the hospital, it is estimated that you have to have hemorrhagic shock, the following I respectively for different cancers to say the most suitable tests and those who need to do, it is recommended to collect. Your like is my biggest support.
1. Lung cancer's greatest fearLow Dose Chest CT。
Most people's physical examination reports are chest radiographs, but screening for lung cancer both experts and guidelines preferred low-dose CT, which can detect early lung cancer, low-dose CT radiation is smaller than ordinary CT radiation, although there is a certain amount of radiation, but overall the benefits outweigh the disadvantages. The following types of people are recommended to have chest CT once a year.
1. if the patient is older than 40 years and has smoked for more than 20 years;
2. Family history of malignant tumors;
3. Passive smokers with long-term exposure to second-hand smoke;
4. Those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pulmonary fibrosis;
5. Those who have been exposed to cooking fumes for a long time;
6. High-risk occupations, exposure to asbestos, uranium, etc;
2, stomach cancer, esophageal cancer is most fearedgastroscopy。
If you have an upset stomach and suspect a problem on your stomach, an ultrasound, imaging, or radiograph is not as good as a gastroscopy. Because our digestive tract is a cavity. Like you want to know what's inside a box, the best way is to open the box, but open the box is like doing surgery on our body, the cost is too high, this time through the cracks in the box, stuffed with a light with a camera, you can see clearly what's inside the box, the box is clean inside the wall, ultrasound, X-ray is like standing on the outside and guessing what's happening on the inside, if the box is rotten on the outside, the cancer has lost its chance of surgery. If the outside of the case is rotten, then the cancer has lost its chance of being operated on. Screening gastroscopy is recommended for the following groups of people, age greater than 40 years combined with any 1 of the following:
1. People in areas with high incidence of stomach cancer; including (Linqu County of Shandong Province, Zhuanghe County of Liaoning Province, Changle County of Fujian Province are the most representative, followed by Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, Jilin, Jiangsu, Shanghai and other parts of the region also belong to areas with high incidence of stomach cancer, and residents of the above areas should raise their awareness of preventing stomach cancer, and undergo gastroscopy and other relevant examinations every year.)
2. Helicobacter pylori (Hp) infected individuals;
3. Previously suffered from chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric polyps and other diseases;
4. First-degree relatives of stomach cancer patients; first-degree relatives include parents, siblings, and children.
5. Presence of other risk factors for gastric cancer (e.g. intake of high salt, pickled diet, smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, etc.).
And although capsule endoscopy is less aggravating, capsule endoscopy is not a substitute for a gastroscopy.
3, Colon Cancer FearFingerprinting and colonoscopy.
A colonoscopy is recommended for the following people:
1. Unexplained blood in the stool.
2. Abnormal bowel movements, chronic diarrhea or long-term constipation.
3. Pain in the lower abdomen or a lump can be felt.
4. Recently, bowel habits are different from before.
5. Unexplained anemia or wasting.
6. A family history of colorectal cancer.
7. Patients treated with colon endoscopy after colon surgery.
It is recommended that the above people have regular colonoscopies under the supervision of a doctor.
People over the age of 50 are advised to get a routine fecal and colonoscopy once a year. And the anal finger test, also known as the popper, is a test that is embarrassing but cheap and affordable and can detect rectal cancer.
4, Liver cancer is afraid to draw blood for AFP and liver ultrasound.
If you have hepatitis B, hepatitis C, cirrhosis, a family history of liver cancer, or other autoimmune liver disease, it is recommended that you have a blood test for AFP (alpha-fetoprotein) and an abdominal ultrasound every six months.
5, Breast Cancer Fear of Ultrasound and Mammograms.
Ultrasound is recommended for women under 40 and molybdenum for those over 40.
The average woman under the age of 40 can do a self-examination, which is to observe the breasts themselves for lumps, overflow, changes in appearance, etc., and seek medical attention when problems are detected.
Mammograms are recommended every 1 year for women over the age of 40, or 2 years if there are no problems for several years in a row.
In the case of dense breasts, which are more glandular, ask for a mammogram.

6, Cervical Cancer's Biggest Fear TCT (Cervical Cytology) and HPV Testing
Cervical cancer a kinder cancer because it now has a vaccine to prevent it and is the only cancer that can be prevented with a shot.
Cervical cytology is performed every 3 years in women aged 21-29 years.
Women aged 30-65 years with cervical cytology screening every 3 years or HPV testing every 5 years or cervical cytology and HPV testing every 5 years.
Women older than 65 years with previous regular screening and negative results do not need to be screened.
Does your physical include any of these tests?? We hope that each person will choose the most suitable medical checkup program according to his or her own situation, which is an effective medical checkup!
Secondly, if your physical examination includes findings of: chronic superficial gastritis, liver cysts (less than 5cm), premature heart beats, bone spurs, calcified foci in the liver, pelvic fluid less than 3cm, uterine fibroids (less than 5cm), breast hyperplasia, cervical erosion, and thyroid nodules, and it so happens that you don't have any symptoms, you don't need to deal with any of the above conditions, and you just need to have a regular review according to your doctor's instructions.
Anything else you'd like to know about medical exams, or what you can't read in a medical report, feel free to leave it in the comments section!
Follow me for more health tips!
Hello, I'm Dr. Knowles Blue.
When it comes to cancer, many people will feel panic and shiver, because more or less have been in contact with some relatives, friends and colleagues who have cancer, such as a few months ago, they had a good dinner together, how to recently heard that the person is no longer there. Although there are many treatments for various malignant tumors, many people find malignant tumors when they are already in advanced stages, and the treatment effect is very poor. So early detection of malignant tumors is very crucial to seize the best time for treatment. And how to find it early? Many people find advanced malignant tumors without any symptoms. That's right, health checkup is very important. Our daily physical examination also includes other aspects of the examination, today we will speak separately about the detection of malignant tumors, what should be done? Starting from our current high incidence of these tumors, not everyone has to do these tests, for those who have high risk factors, you can selectively do some of the appropriate tests.

1. Lung cancer
(1) Lung cancer is the cancer with the highest incidence rate in ChinaThe causes of lung cancer are not particularly well understood. The causes of lung cancer are not particularly clear at present, including at least smoking, air pollution, occupational exposure, ionizing radiation, heredity, chronic lung diseases, diet and so on. When it comes to lung cancer, it is still important to emphasize over and over again to quit smoking, quit smoking, quit smoking, for yourself and for your family, and second-hand smoke is also very harmful.
(2) The most common symptom of lung cancer is an irritating dry cough or blood in sputum.Sometimes the symptoms of coughing are not so typical, and there are many, many diseases that cause coughing, and even some people don't have any symptoms, so many people find out when they are in the middle or late stage of lung cancer. The most common medical checkup for everyone in daily life is chest X-ray, including the medical checkup for employees in our hospitals, which is also a chest X-ray. In fact, for the detection of early lung cancer, chest radiograph is less meaningful.So for people who are more at risk and more likely to develop lung cancer, it's best to have a low-dose chest CT to be able to detect early-stage lung cancer under 1cm.We all know that CT examination has radiation, and radiation is one of the factors of lung cancer, so why is it still recommended to do CT? This side is talking about low-dose chest CT, its radiation dose is relatively small, and can meet the requirements of initial screening, for high-risk groups, the benefits outweigh the disadvantages, do a CT just to receive a relatively small dose of radiation, compared with the omission of the discovery of early stage lung cancer, which is a big loss? Just think about it.
(3) Who needs it? The following groups of people are at high risk. Age greater than 40 years, smoking for more than 20 years; family history of malignant tumors; long-term exposure to second-hand smoke; patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease or pulmonary fibrosis; long-term exposure to cooking fumes; occupational exposure, exposure to asbestos, uranium and other substances.
2、Stomach Cancer
(1) The occurrence of gastric cancer is multifactorial, and research suggests that it is related to diet, Helicobacter pylori infection, precancerous lesions, heredity and other factors. Pickles, pickled and smoked foods, and moldy foods can increase the risk of stomach cancer.People whose parents have stomach cancer, TA is 2~3 times more likely to develop stomach cancer than ordinary people. Some precancerous lesions, such as chronic atrophic gastritis, atrophic gastritis with intestinal epithelial hyperplasia, may become cancerous under the action of some factors.
(2) There is no obvious difference between the early symptoms of stomach cancer and those of common gastritis and gastric ulcer, which are only stomach pain, upper abdominal discomfort or even no symptoms at all. The most direct and accurate way to detect stomach cancer is to do gastroscopy.A gastroscope is inserted through the mouth through a tube with a high-definition camera on the front and delivered to the stomach, allowing you to see inside the stomach.
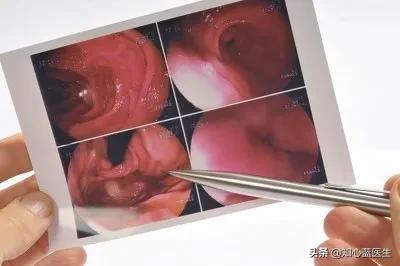
3、Colorectal cancer
(1) The incidence of colon cancer is related to genetic factors, dietary habits, etc. Low-fiber and high-protein diet, fried and baked foods are risk factors, and smoking is also a risk factor for colon cancer. Many bowel cancers are transformed from adenomas.
(2) Symptoms of colon cancer include abdominal pain, diarrhea, black stool, constipation, change in bowel habit, change in stool trait and pattern, and emaciation.

(3) For colon cancer and rectal cancer screening, colonoscopy is the most important test.Gastroscopy to gastroscopy looks like through a long tube with a high-definition camera at the front end from the anus into the rectum, followed by the rectum, sigmoid colon, descending colon, transverse colon, ascending colon, there is no intestinal cancer, a glimpse of it, the premise is to do a good job of intestinal preparation, otherwise all the feces is to see clearly.
4、Esophageal cancer
(1) Typical symptom of esophageal cancer is the feeling of blockage in swallowing, which is manifested as the feeling of blockage in eating hard and lumpy food in the early stage, and gradually develops into the feeling of blockage in eating semi-liquid. In the middle and late stages, it can be manifested as retrosternal pain, dysphagia, emaciation and so on.
(2) The most effective and convenient test is endoscopy, which is actually the same as gastroscopy, because gastroscopy passes through the esophagus, so it is also able to see the esophagus clearly and whether there are any lesions.
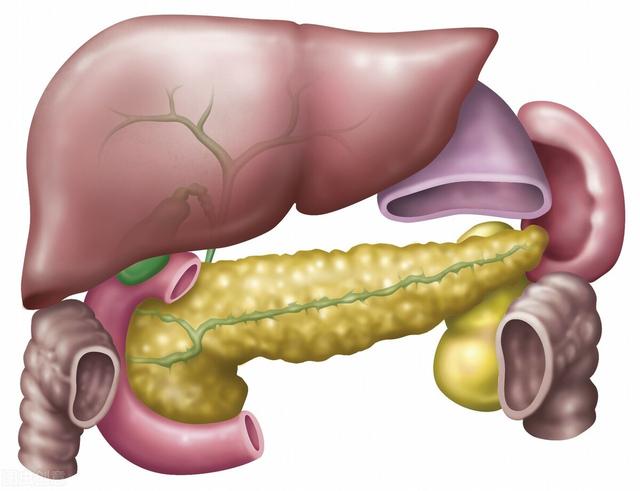
5. Liver, gallbladder, pancreas, kidneys, ureters, bladder, prostate, uterus, ovaries, thyroid gland
These organs are written together because they are all very sensitive to ultrasound, which means that they can basically be clarified by ultrasound. Ultrasound is non-invasive, radiation-free and very good, but it requires a high level of diagnosis from the sonographer, which can vary greatly from doctor to doctor.
6. Breast cancer
The mammary gland is a superficial organ and women are very much able to touch it themselves to see if there are any specific nodules to be found. For most people a breast ultrasound is sufficient for a physical examination, while for those with high risk factors, a mammogram should be done. Mammograms are more accurate than ultrasounds, but because they are radioactive, they are not recommended for everyone, and if the ultrasound reveals a problem, you may want to consider having another mammogram.
7. Cervical cancer
The development of cervical cancer is closely related to human papillomavirus infection, and the HPV vaccine, which has become very popular in recent years, is used to prevent cervical cancer. Then how to detect it at an early stage? It requires a gynecologist to conduct a gynecological examination, direct observation, or retaining a specimen of cervical cells.

8. Brain tumors
Brain tumors are best detected with a CT of the head; ultrasound and plain radiographs are unreliable. However, because brain tumors are relatively rare, most people's physical exams are not specifically going to screen for brain tumors.
9. Malignant tumors of the blood system
This tumor is often overlooked, but it should be mentioned because I have seen far too many patients in the hematology-oncology specialty wards. For example, leukemia, myelodysplastic syndromes, aplastic anemia, etc., unlike these imaging tests mentioned earlier, as long as the blood is drawn for a routine blood test can have a lot of hints, and the routine blood test is relatively inexpensive, about 35 to 40 yuan.
In conclusion, malignant tumors are serious diseases, with different symptoms and different examination methods for different parts of the tumor, some of which are good to treat and have a better prognosis, and some of which are difficult to treat and have a worse prognosis. Overall, for malignant tumors, early detection and early treatment is definitely better. Physical examination program can only check how big some of the tumors are, it is impossible to check all of them, some malignant tumors you may not have heard of, such as skin cancer, gum cancer, laryngeal cancer, tongue cancer, bone cancer, nasopharyngeal cancer, thymus cancer ......, there are malignant tumors of the heart, it is unbelievable, isn't it?
Follow Dr. Know Your Heart Blue to learn more about the heart.
Cancer is the second leading cause of death among residents in our country, and having cancer often means losing one's money, which has to be feared. Timely detection of early-stage cancer is the key to improving outcomes. For example, the 5-year survival rate for advanced lung cancer is only about 20%, yet early-stage lung cancer, which can be surgically removed, has a 5-year survival rate of over 90%. So what tests can you do if you are afraid you have cancer?
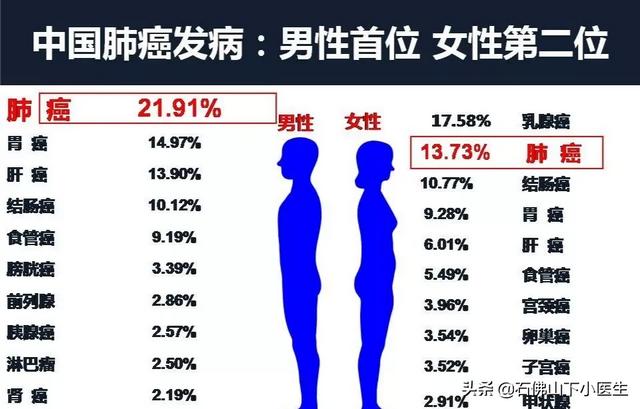
I. Low-dose spiral CT of the chest
- This low-dose spiral CT is mainly used to screen for lung cancer. Lung cancer is the cancer with the highest incidence and mortality rate in our country, and the physical examination definitely cannot miss the lung.
- Low-dose spiral CT is preferred for screening lung cancer because of the lower radiation dose compared to conventional CT.
- Nowadays, the number of people who find small nodules in their lungs is increasing, which may be caused by the increase in the number of people who have medical checkups. Compared to people who do not have medical checkups, it is good that medical checkups can detect lung nodules in time, and then review them regularly, and if the doctor suspects that the lung nodules may be malignant, timely surgery can be done.
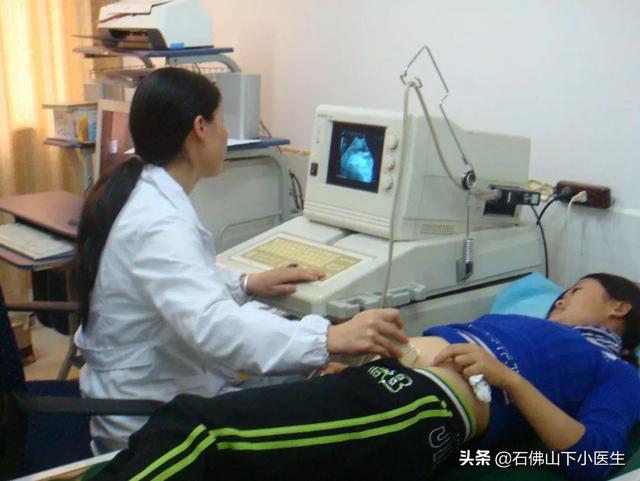
Second, color ultrasound examination
Color ultrasound is also good, has no effect on the body and is not expensive.
For men, the following items need to be checked:
- Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, both kidneys, bladder, prostate, and thyroid.
- The above tests can detect liver cancer, gallbladder cancer, pancreatic cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, prostate cancer, and thyroid cancer.
- The above tests can also detect some factors that may lead to cancer and draw attention to them in advance. For example, ultrasound found gallbladder polyps, found thyroid nodules, these should be reviewed regularly.
For women, the following items need to be checked:
- Ultrasound of the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, both kidneys, uterus and adnexa, thyroid and breast.
- Breast cancer is the most prevalent cancer in women, while cervical cancer, endometrial cancer, and thyroid cancer are all highly prevalent in women.
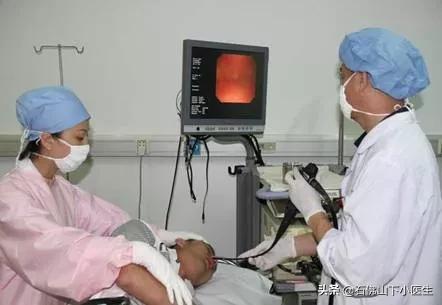
3, digestive endoscope
- Gastrointestinal endoscopy includes gastroscopy and colonoscopy, which can detect stomach cancer, colorectal and intestinal cancer, and esophageal cancer.
- Stomach cancer is the second most prevalent cancer in men and the fifth most prevalent cancer in women, of; colorectal cancer is the fourth most prevalent cancer in men and the third most prevalent cancer in women.
- Esophageal cancer has the fifth highest incidence in men and the ninth highest incidence in women.
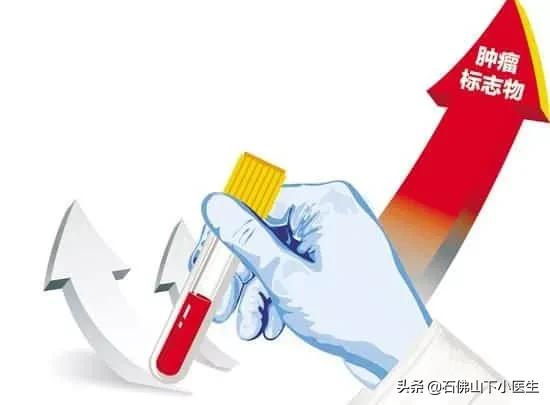
IV. Tumor marker tests
- Tumor markers are blood tests that, if abnormally elevated, may be indicative of certain tumors.
- Elevated carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA), for example, may indicate colorectal, pancreatic, stomach, or breast cancer. It's not a one-to-one indication, but at least it provides direction for further testing.
V. Female cervical smears
- Female patients may also undergo cervical smears for cytology to screen for cervical cancer.
VI. Other
- Moles in areas that rub easily, such as the soles of the feet, can be seen by a doctor to see if they might turn into melanoma.
- Brain tumors can also grow in the brain, and a brain CT or MRI can also be done.
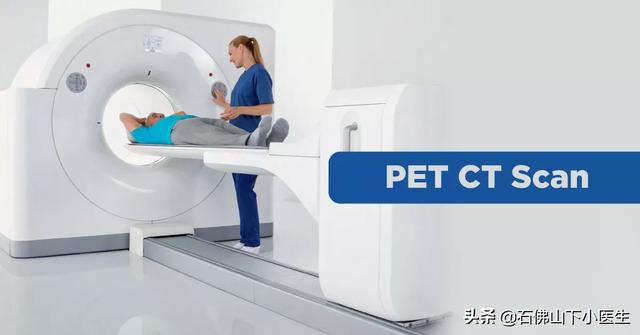
- Some people, who are more anxious, may just suspect that there is something wrong with their body, even though they have had a medical checkup that is all good. But the physical examination cannot check the whole body. For such people, you can just take one step and check PET-CT or PET-MR.
Summary:
- The prognosis of early cancer and late cancer is very different. For the sake of one's health, one should emphasize on health checkups after the age of 40. If there is a family history of cancer, the age of medical checkup should be further advanced.
Fear of cancer, go to the hospital for a medical examination those programs are better?
There are so many cancers at present that we can only go for medical check-ups to synthesize a preliminary screening for cancers with a relatively high incidence rate at present.
The tests that are done are also still routine which ones:
1, the three major routines. Blood routine, urine routine, stool routine. We must not underestimate this ordinary three routine, in fact, its test results can screen out many cancers. Blood routine can see whether there is leukemia, and many malignant tumors caused by anemia. Urine routine can screen out urinary tract tumors. Stool routine can screen out whether there are digestive tract tumors.
2, Film taking. It can screen for lung cancer, osteosarcoma, tumors in the spinal canal, as well as detecting bone metastases in some cancers.
3, Ultrasound. It can develop cancers of many parenchymal organs in the abdominal cavity, such as pancreatic cancer, liver cancer, gallbladder cancer, bile duct cancer, uterine cancer in gynecology, ovarian cancer, and thyroid cancer in the neck.
4, as well as routine liver and kidney function tests, needle biopsy for cervical cancer, and screening for tumor markers such as AFP in the liver.
However, as a young medical examiner, without any physical discomfort, it is recommended to do these routine tests initially, and then do further tests when problems are found, and there is absolutely no need to go to the hospital as soon as the CT, MRI, imaging and other non-conventional tests.

This is an interesting question because the undeniable fact is that the incidence of cancer (actually, it is more specialized to call it malignant tumor) is increasing and more and more people are dying of cancer. Therefore, everyone is afraid of getting cancer. So, as the title suggests, what targeted tests should we do during medical check-ups to detect cancer at an early stage?
First of all, I think this answer should vary from person to person. For example, those who are older than 40 years old, or who smoke, should first opt for a lung CT to screen for lung cancer. And if you have a family history of stomach cancer, you should consider a gastroscopy to screen for the possibility of stomach cancer. And those who live in areas with a high incidence of esophageal cancer, such as Shibi County in Hebei Province, need to have their esophagus checked.
Secondly, I think we should also consider the incidence of diseases. For example, in our country, lung cancer, thyroid cancer, prostate cancer, liver cancer, stomach cancer and colorectal cancer are all very common malignant tumors, so lung CT, thyroid ultrasound and prostate ultrasound are some of the things you need to consider.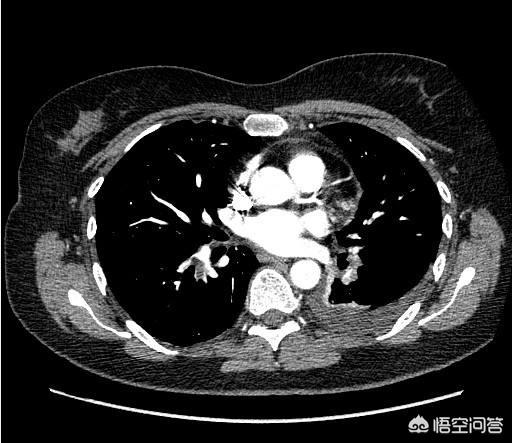
Of course, we should not ignore the physical examination and laboratory tests, which are much easier and more convenient to do. Especially the physical examination by clinicians can help you to detect some problems and then carry out targeted examinations.
In the end, I want you to be guided by your clinician to make targeted choices so that your benefits are better.
With the rising incidence of cancer and the increasing awareness of cancer prevention, many people are concerned about what tests can be done in the hospital to screen for cancer in a relatively effective manner.
Blood tests: tumor markers:
There are many kinds of tumor markers, such as gastrointestinal/respiratory/gynecological tumors, etc., which need to be tested selectively according to the health condition. Of course, all of them can be tested. It is important to understand that tumor markers only play a role in suggesting the presence of cancer, and when there are obvious abnormalities, further screening is required. However, abnormal does not necessarily mean there is cancer, and normal does not mean there is no cancer.
Lung Cancer Screening: Chest X-ray and or enhanced CT of the chest.
Chest X-ray is commonly used for medical checkups, which is simple, economical and fast. It is generally used for initial screening. For those who are over 45 years old, have a history of smoking, or have a family history of lung cancer, it is recommended to have a thin-layer spiral enhanced CT, which has a high resolution and can screen out small cancerous foci in the lungs. When lung nodules are found on chest X-ray, further enhanced CT is usually needed to clarify, and puncture biopsy is needed to clarify when lung cancer is highly suspected.
Thyroid Cancer Screening:
Ultrasound is commonly a neck ultrasound to find out the size of the thyroid gland with or without nodules; if the ultrasound suspects that the nodules are cancerous, a puncture biopsy or excisional biopsy is needed.
Screening for abdominal tumorsAbdominal ultrasound is mainly used to find out whether there is any space-occupying or other lesions in the liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, kidneys and other organs, or whether there is any solid tumor in the abdominal cavity. But ultrasound for abdominal gastrointestinal examination has limitations, affected by the gastrointestinal gas, easy to ignore, can do abdominal enhancement CT clear.
Pelvic organ tumor screening: Pelvic ultrasound can provide information about the bladder and uterus and ovaries (in women) and the bladder and prostate (in men). When ultrasound is suspicious, an abdominopelvic enhancement CT or MRI can be done to further define the size and possible nature of the occupancy. Ultrasound-guided puncture biopsy is needed if necessary.
Breast Cancer Screening: Breast ultrasound can reveal the presence or absence of breast lumps. Generally, ultrasound is used in conjunction with mammogram (molybdenum target) to screen for breast cancer. If cancerous breast nodules are suspected, an enhanced MRI is needed to further clarify the size, extent, and lymph node metastasis, and ultimately, a sex puncture biopsy is needed to clarify the nature of the tumor.
Esophageal, gastric, duodenal cancer screening and colorectal cancer screeningThe most direct and effective means are gastroscopy and colonoscopy. The location, size and shape of the lesion can be clarified, and more importantly, biopsy can be taken for pathological examination to clarify the nature of the disease; for example, the degree of differentiation of adenocarcinoma (highly differentiated, moderately differentiated, poorly differentiated, and indolent carcinoma, with the degree of malignancy increasing in the order of malignancy). However, sometimes there are some special cases, for example, biopsy does not pick up the tumor at one time, and most report chronic inflammation. In this case, there are two cases: one is that there is no cancer in the stomach, and it is indeed gastritis and mucosal ulcers; the other case is that there is cancer, but due to the accompanying inflammation and ulcers interfering with the results, or even the biopsy only took the inflammatory part of the mucosa and did not take the cancerous cells in the deeper part. Then, if the endoscopist thinks that the lesion is suspicious, he or she will advise the patient to take oral acid-suppressing drugs (proton pump inhibitors, such as omeprazole or pantoprazole, etc.) for 2-3 weeks, and then do the gastroscopy again and take a biopsy. It is always recommended to listen to the doctor's advice in this case, take the medication and take biopsy again.
Liver Cancer Screening: then ultrasound is sometimes slightly inadequate in the differential diagnosis, and powerful enhanced MRI is needed to save the day. The combination of a history of viral hepatitis and abnormalities of alpha-fetoprotein (a tumor marker specific for liver cancer) is also needed; if all three conditions are not present but liver cancer is highly suspected, ultrasound-guided biopsy is needed, which is the most powerful diagnostic basis.
Cranial Tumor Screening: Don't consider ultrasound, go straight to cranial CT or MRI for more clarity.
Cervical Cancer Screening: It is necessary to check for HPV infection, colposcopy, cervical biopsy, etc. Specific instructions from your gynecologist are needed.
[Dr. Zhang Chenghai] All articles are original, the pursuit of truth, objectivity, universal health knowledge, welcome to pay attention to and forwarding, and continue to provide useful medical health (tumor prevention and treatment) popular science and oncology work content.
One of my neighbors, 35, has a family history of cancer.My father and sister were diagnosed with lung cancer.And that became a problem for him.

Not long ago, he heard that a PET-CT examination (costing nearly 10,000 yuan) could detect even budding cancer, and he immediately rushed to the hospital and specified that he wanted to have a whole-body cancer prevention physical examination with PET-CT, but he was dissuaded by the doctor. It turns out that PET-CT is generally not recommended as a medical checkup for healthy people.

"Cancer screening" is a must.PET-CTWhat? - I don't know.
At present, some clinicians on our side have some misconceptions that PET-CT is so expensive that it must be able to diagnose lesions that are difficult to characterize by CT, MRI and other imaging means;
However, the advantages of PET-CT in predicting and characterizing cancer are not as obvious as one might think, and its greater value should be inTumor staging and efficacy monitoring。
Choosing the right cancer screening for you
carry outRegular specialized cancer screening, which is still the best way for human beings to ward off cancer, the key is to choose a medical check-up center or hospital with a series of services for examination, diagnosis and treatment for screening.

90% of cancers have no symptoms in the early stage, 90% of early cancers are detected by professional census, and 90% of cancer patients with self-awareness of symptoms are already in the middle or late stage when they arrive at the hospital for consultation, losing the best period for cure.
A one-size-fits-all medical checkup program may not be right for you.To prevent cancer, it's best to individualize each person's checkups。
People between the ages of 35 and 60 should have a cancer checkup once a year, while specific high-risk groups with a family history of tumors should have 1-2 checkups per year.
What are the priority groups for cancer screening?
(1) Heavy smokers or chronic smokers, chronic drinkers with an alcoholic habit;

(2) People who have been found to have pre-cancerous diseases and who have a family history of cancer in their family are also a major group at high risk of cancer.

(3) People exposed to or permanently working in the following industries: furniture manufacturing, smelting, rubber, pesticides, tar and soot, aromatic amines, alkylating agents, ultraviolet light, arsenic, nickel, chromium, cadmium, benzene, asbestos, and so on;

(4) Chronic schistosomiasis patients, overweight people, AIDS patients, people with cirrhosis of the liver, chronic hepatitis C, chronic hepatitis B;
Contents of Cancer Screening
The regular cancer screening test program includes the following:
(1) Regular program:Blood routine, urine routine, fecal routine, liver and kidney function, blood uric acid, blood lipids, chest X-ray, electrocardiogram, liver and gallbladder ultrasound, urinary system ultrasound.

(2) Endoscopy: It is an important means of tumor diagnosis and can be used for cavity organ and body cavity examination, which can detect precancerous lesions and carcinoma in situ in tissues and organs.
(3) Diagnostic imaging: Highly expensive tests like MRIs and CTs.
(4) Tumor Marker TestsThe following substances are produced by the tumor cells themselves or by the body in response to the tumor cells during the process of tumorigenesis and proliferation, reflecting the existence and growth of the tumor.
Cancer screening is not as good as more programs
The key to cancer screening is to be targeted。
Men should pay special attentionLung, stomach, esophagus, liver, colorectal and pancreatic cancersThe signs;
For women, it is important to checkBreast, cervical and ovarian cancer。
Common Tumor Screening Recommendations
(1) Breast Cancer
For women between the ages of 20 and 39. Recommended once a yeartactile examination。
For women 40 years and older, 1 time per year is recommendedPalpation examination + mammogram。
Increased frequency of screening is recommended for women who have high risk factors, such as a family history of cancer and a previous history of breast cancer.
tumor marker: CEA (cancer embryo antigen), CA-125, CA-153.
(2) Lung cancer
1 per year for those over 45 years of age with a long history of smoking, or working in confined environments for long periods of time, or working in environments with high levels of dust particles for long periods of time, or with family history ofLow Dose Spiral CTScreening for early lung cancer.
tumor marker: CEA, NSE (neuron-specific enolase), SCC (squamous epithelial cell carcinoma antigen).
(3) Stomach cancer
People with long-standing gastric ulcers, long-term chronic atrophic gastritis, or atypical hyperplasia detected by gastroscopy.1 gastroscopy per year。
tumor marker: CEA and CA72-4.
(4) Colorectal Cancer
Both men and women, but anyone who is over 50 years of age, has a family history of colorectal cancer, has frequent pain in the lower abdomen, has chronic colitis, has frequent bowel movements, and has blood or mucus in the stool. Should be followed:Colonoscopy, fecal occult blood test (performed once a year)。
tumor markerCEA, CA-199, and CA242.
(5) Liver cancer
People who have been drinking heavily for a long time, chronic hepatitis B patients, patients with cirrhosis of the liver, and people who have been working with chemicals for a long time are recommended to have this test once a year.echographyIf necessary, conductLiver-enhanced CT examination.
tumor marker: AFP (alpha-fetoprotein).
How can I save money?
Different risk factors are emphasized differently during the cancer checkup.

Before deciding to have a cancer checkup, it is important to explain your health history, family history of tumors, recent discomfort, etc. This will allow the checkup center to make a decision based on the situation.A personalized medical checkup program that meets the cancer screening needs of the examinee and is more affordable。
I'm Dr. Qi, a veteran TCM oncologist, and I'm happy to answer this question for you, and I hope it helps.
One of the scariest things about cancer for us is that there are no symptoms at the beginning, and by the time it becomes uncomfortable it is already in the middle or late stages, and it cannot be detected by ordinary medical checkups. Especially after the age of 40, the incidence rate rises sharply.

So what are the symptoms people need to be checked for? How can you get a medical checkup based on your condition? And what are the tests that correspond to the disease?
(1) Long-term smokers are advised to have a checkup once a year.
Screening focus: lung cancer
Physical Examination Program: Low Dose Spiral CT
If you find shadows or nodules on your CT lungs, it is recommended that you see an experienced doctor at a regular major hospital to see if you need a biopsy.

(2)Those who have a long history of eating barbecue, pickled foods, drinking alcohol, and chronic stomach problems are advised to have a checkup every 3 years if they are over 40 years old.
Screening Focus: Stomach Cancer
Physical examination: Gastroscopy
If you experience abdominal discomfort, vague pain in the precordial area, a feeling of fullness after eating, loss of appetite, weight loss, fatigue, frequent vomiting of overnight food, or black tarry stools, etc., do a gastroscopy promptly!

(3)Colorectal polyps, patients with enteritis, those who drink a lot of alcohol for a long time, and those who like to eat pickled food. It is recommended to have a colonoscopy every 3-5 years over the age of 40.
Screening focus: bowel cancer
Experience it: Colonoscopy
If you notice blood in your stool, don't assume it's hemorrhoids, consult your doctor and get a colonoscopy if necessary.
(4)Chronic alcohol abuse, late nights, hepatitis patients, hepatitis B carriers. Check once a year.
Screening focus: liver cancer
Experience the program: ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein screening.
(5)Women over 40 years of age, women with severe lobular atypical hyperplasia and lobular carcinoma in situ are recommended to have a breast cancer screening once a year.
Screening focus: breast cancer
Experience: X-ray Mammography, MRI and Ultrasound
X-ray mammography is more accurate, but should not be performed too frequently.

(6)Women over the age of 30 are recommended to be screened for cervical cancer every five years. Chronically immunocompromised and a long history of gynecological problems are also at high risk for cervical cancer.
Screening focus: cervical cancer
Experience Program: Cervical Cytology and HPV Testing

Note: If there is a history of cancer in the family, it is important to have regular checkups for all relevant cancers.
Regular medical checkups for timely detection and early treatment, and consult your doctor as early as possible once you notice any physical discomfort.
I'm Dr. Qi, and I've been dealing with cancer all my life, so if you have any questions about cancer, you can leave them in the comments section or private message me directly, and I'll do my best to respond to them all.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.