Are there any after-effects after gastric diversion and any other harm to the body?
Obesity is gradually becoming an epidemic that is spreading globally. Some data say that there are nearly 1 billion overweight patients and 470 million obese patients in the world, and the number of obese people in the world is still increasing.

The prevalence of diabetes among overweight and obese people in China is 12.8% and 18.5% respectively, and the proportion of overweight among diabetic patients is 41% and the proportion of obese is 24.3%.
Epidemiologic studies have shown that weight loss in overweight or obese patients can help to reduce insulin resistance, leading to better glycemic control and reducing the risk of complications such as microvascular and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, in addition to traditional medical treatment, weight loss in diabetic patients is essential for the alleviation of the disease.

There are many ways to lose weight, including diet control, exercise, drug intervention, etc. However, obese patients usually have very poor compliance, and traditional medication is difficult to effectively reduce weight and sugar in the long term. Many people look to weight loss surgery.
Gastric diversion as one of the weight loss metabolic procedures
Currently bariatric metabolic surgery is really a very effective treatment modality that allows diabetics to achieve long-term weight loss and diabetes remission as well as improvement in complications.

Bariatric surgery has a history of more than 60 years now, and its surgical approach has been improved several times, with gastric diversion now becoming the more widely used procedure today.
Gastric diversion surgery simply involves cutting out most of the stomach and anastomosing it to the small intestine via the remaining stomach, thus, limiting food intake and reducing nutrient absorption to achieve weight loss.
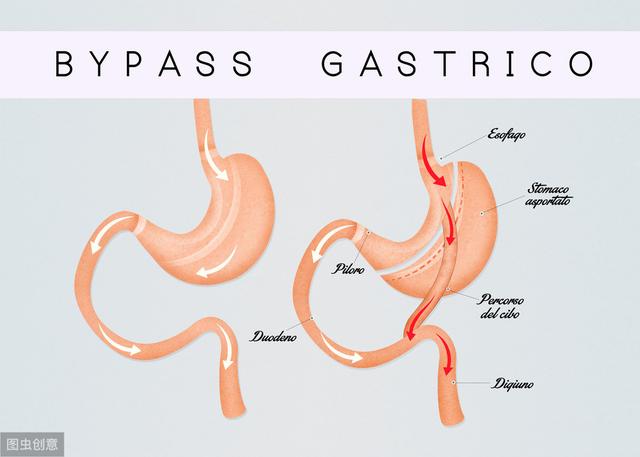
After weight loss, the patient's insulin resistance decreases. What's more, the hormone secretion of the gut-insulin axis in the intestines changes after gastrointestinal reconstruction, which improves the metabolic process in the body and is able to reduce diabetes. According to data from a study of more than 20,000 people, it was confirmed that 84% of patients with type 2 diabetes were completely reversed after surgery, and the majority of patients discontinued oral hypoglycemic drugs and insulin therapy upon discharge from the hospital, while the rest had a significant reduction in the amount of medication they were taking. The degree of fatty liver and atherosclerosis also improved.
Who are the patients for whom bariatric surgery is appropriate?
Now that you've read here, for those of you thinking about surgical weight loss, calculate your own BMI!
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ height (m) squared
If you have a BMI over 27.5 and are a combined diabetic, then you may want to consider metabolic surgery. If your BMI is over 32.5 and you have no stamina, can't resist the temptation of good food, and are lazy and don't want to be active at all, then you may only have to opt for metabolic weight loss surgery.
As a relatively mature surgery, gastric diversion does have certain efficacy for obese patients. However, changing the patient's normal gastrointestinal physiology through surgery is to counteract metabolic abnormalities with artificial abnormalities in the structural state of the organ, which will bring some new problems while reducing weight and sugar.
Patients who should never undergo metabolic weight loss surgery
This is why it is very important to carry out a rigorous selection of suitable patients. These patients should never undergo metabolic weight loss surgery:
- For patients with a clear diagnosis of type 1 diabetes
- Patients with type 2 diabetes who have largely lost islet B-cell function
- Combined with coagulopathic diseases, cardiopulmonary function can not tolerate the operation.
- People with diabetes who have a BMI of less than 28 and are able to control their blood sugar with medication or insulin.
Diabetes mellitus may bring about a number of postoperative complications, which is a great concern for clinicians and patients.
Postoperative complications of metabolic surgery include both immediate and long-term complications.

Recent Complications:Recent complications are similar to those of other gastrointestinal surgeries, mainly anastomotic fistula, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism, and wound infection.
Distant Complications:Malnutrition is the most common long-term complication of metabolic surgery and can occur with any type of procedure. Malnutrition includes disorders of nutrient metabolism such as proteins and vitamins and deficiencies of micronutrients such as iron, zinc and selenium.
Because postoperative complications are more common with metabolic surgery and can greatly affect the outcome, postoperative management and follow-up are very important.
Postoperative management of metabolic surgery
Several domestic and international guidelines state that postoperative metabolic surgery requires lifelong follow-up of the patient by a team of bariatric surgeons and endocrinologists and dietitians familiar with the field.

In postoperative managementDietary GuidelinesIt is an important part of ensuring the efficacy of surgical treatment, avoiding postoperative long-term complications, and improving the patient's postoperative discomfort. The aim is to form new eating habits to promote and maintain the improvement of glucose metabolism, while at the same time replenishing essential nutrients. The main principles are to apply sufficient amount of fluids, eat enough protein, and supplement essential vitamins and minerals.
With the rapid rise in the incidence of obesity and its complications worldwide, weight loss and metabolic surgery has grown rapidly in recent years, and almost every clinic visit is filled with obese patients inquiring about weight loss and metabolic surgery. Although I am not a great advocate of weight loss surgery because many patients cannot be treated with diet and exercise first, they want to opt for this immediate measure.
"Choose the lesser of two evils", metabolic surgery not only has the curative effect on obesity and diabetes itself which cannot be reached by traditional internal medicine, but also has good improvement and alleviation effects on a variety of obesity and diabetes comorbidities and complications, such as metabolic syndrome, sleep apnea syndrome, diabetic nephropathy, etc., which has an important clinical value and therapeutic It has important clinical value and therapeutic status.
In summary: For obese diabetic patients, the choice of metabolic weight loss surgery may be a better option, not only to reduce the abnormal state of glucose metabolism, but also to reduce the various comorbidities associated with obesity. Surgery may bring some immediate and long-term complications and requires a rigorous selection of indications. The postoperative period of metabolic surgery also requires the concerted efforts of the surgeon, endocrinologist, dietitian, patient and family to maintain the favorable outcome of metabolic surgery.
Hi, based on your question as an endocrinologist I'll answer your question. You are 27 years old and still young. With a height of 156cm, weight of 80kg and BMI of 32.9, you are indeed obese. You mentioned gastric diversion surgery is a kind of weight loss surgery, some people weight loss effect is also very good. At present, there are mainly the following kinds of weight reduction surgery: (1) laparoscopic sleeve gastrectomy. (2) Gastric bypass. (3) Laparoscopic adjustable gastric banding. Gastric bypass surgery is equivalent to the 2nd type of surgery, where the intestines are rerouted. It is not a very risky procedure in terms of the surgery itself, but there are risks. In addition to the risks of the surgery itself, it can lead to nutrient deficiencies in the long term, and sometimes a person may also experience hypoglycemia. I think that if you are able to lose weight through diet and exercise, you should try not to resort to surgery. I don't know if you have other diseases in combination, such as hand diabetes, already through the basic treatment of blood sugar is still difficult to control, a lot of complications and so on. There are many reasons for obesity, related to genetics, lifestyle, dietary habits, mental factors, etc. Most people are still able to control their weight through dietary changes and exercise, and traumatic treatments are always put on the back burner unless your benefits are much greater than the risks associated with obesity to consider this approach, which needs to be evaluated by a specialist.

The digestive tract has been remodeled, what more damage do you need? What kind of era is this, and you still believe in gastric reflux? Look at the experts. Do you still believe?
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.