Why do some diabetics have foot pain?
Diabetics with foot pain may want to be aware that you may have diabetic painful neuropathy.
This kind of pain is really not ordinary pain, many people really drop is painful, they describe, like a knife cut, fire, etc., can you imagine what kind of pain that is!
With a prevalence of 60-90% and a gradual increase as the disease progresses, it is conceivable that many of our diabetic friends will eventually develop diabetic neuropathy.
But not all diabetic neuropathy is painful neuropathy; about 25% of patients experience pain. Many patients come to the clinic because of pain; they may not care when their blood sugar is high, but as soon as this pain appears, they have to come to the hospital.
This pain is mostly due to nerve impingement and is typically characterized by burning, cutting, pinching and shooting pains, accompanied by sensory abnormalities, usually worse at night.
Pain can be present at times or can be triggered to appear. It is accompanied by sensory hypersensitivity. The pain is increased by contact with the skin, e.g., wearing socks and shoes can make the patient's pain worse, and there is also hyperalgesia, abnormal sensation, etc.
Painful neuropathy can seriously affect a patient's daily life. When a diabetic foot develops, improvement will be significantly slowed, and even require amputation resulting in disability. Pain can present with psychiatric symptoms such as anxiety and depression, significantly reducing quality of life.
There are also cases where the patient has a skin breakdown or infection in the foot, in which case pain in the foot may also occur, but of course there may be no pain or no sensation at all. This is why it is very important for diabetics to have their feet carefully examined every day.
To summarize: diabetic painful neuropathy is a gradual progression of chronic disease that occurs on the basis of long-term unsatisfactory glycemic control. Smoothing out blood glucose is very important, and preventing the appearance of vascular and neuropathic disease in the lower extremities is even more important.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Thanks for the invitation. Diabetic foot pain is one of the common complications of diabetes mellitus and is usually an early manifestation of diabetic foot disease. It has two main causes, one is diabetic hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia caused by theDamage to peripheral nerves in the lower extremitiesThe other one is caused by hyperinsulinemiaMicrovascular sclerosis of the lower extremitiesInsufficient blood supply to the lower extremities. Such conditions are not always late manifestations of diabetes; many are present at the onset of diabetes.
Foot pain in diabetic patients is something that needs to be taken very seriously! Perhaps in the beginning, the pain is not obvious, but with the passage of time, the symptoms will worsen day by day, the later can appear foot ulcers, foot gangrene, serious cases have to be amputated! Therefore, diabetic foot disease in the early stage must be paid great attention to, prevention first.
While it is important to take care of the localized feet of diabetic foot lesions, the more important root of preventing further progression of the lesions is to control the hyperglycemic and hyperinsulinemic condition! Only by addressing this root can the risk of developing ulcers in the diabetic foot be fundamentally addressed. Welcome to my headline-Jiangsu Provincial Cancer Hospital Li Feng.
Foot pain in diabetic patients is an early warning signal of neuropathy, and neuropathy and vasculopathy are important risk factors for diabetic foot, signaling possible foot ulcers and gangrene. Since diabetic foot ulcers are difficult to cure and prone to recurring episodes, which may increase the risk of amputation, prevention of diabetic foot is more important than treatment, and reasonable interventions should be taken as early as possible.
Nervous tissue is widely distributed throughout the body and is a target organ often involved in diabetes. Nerve damage caused by diabetes mellitus is closely related to the duration of the disease and the control of blood glucose. In terms of the duration of the disease, diabetic patients with a disease duration of more than 10 years are prone to clinical symptoms of neuropathy, which may include limb pain, numbness, and burning sensation; cranial nerve injury such as facial paralysis, facial pain, and hearing impairment; and cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and respiratory systems of autonomic neuropathy. Therefore, diabetic patients with lower limb pain indicates that the current neuropathy has occurred, the more serious problem is that neuropathy is a risk factor for foot ulcers, foot ulcers occur even if they are cured, may also recur, and may increase the risk of amputation and death, some of my friends may not have a clear understanding of this, we may wish to look at a few sets of data:
High incidence: 8.1% of diabetic patients over 50 years of age have a 1-year incidence of first foot ulcer;
- High recurrence rate: the incidence of recurrent foot ulcers within 1 year in patients with healed foot ulcers is 31.6%;
- High amputation rate: A recent survey found that the amputation rate due to diabetic foot ulcers in China is about 19.03%;
- High mortality rate: the annual mortality rate of diabetic foot ulcers is about 14.4%, and the 5-year mortality rate after amputation is as high as 40%.
Therefore, diabetes mellitus should be highly vigilant when foot pain occurs. In addition to neuropathy, lower extremity vasculopathy is also a risk factor for diabetic foot ulcers and amputations. Diabetes is an important cause of atherosclerosis, with the prolongation of the disease, arterial stenosis may occur, lower limb arterial stenosis, can not meet the demand for blood supply during exercise, walking or exercise may be fatigue of the lower limbs, claudication and other symptoms. Of course, whether it is neuropathy or vasculopathy, before foot ulcers appear, by controlling blood glucose up to the standard, symptomatic treatment of neuropathy and vasculopathy can reduce the risk of ulcers. The most important measure for the treatment of diabetic neuropathy is to strictly control blood glucose to reach the standard, and at the same time should reduce the fluctuation of blood glucose, focusing on the smooth control of glucose; foot pain caused by neuropathy, can be used to improve the symptoms of anticonvulsants such as pregabalin, antidepressant such as duloxetine, etc., and the specific use of medication in accordance with the guidance of the specialist physician shall prevail.
Note to self:Simple neuropathy is a risk factor for diabetic foot ulcers. If a diabetic patient has developed foot ulcers, after symptoms such as worsening local pain, redness and swelling occur, he should be alert to the possibility of severe ischemia, aggravation of the infection, and needs to consult a diabetic foot specialist in time to clarify his condition.
In summary, diabetic foot pain is an early warning signal of neuropathy, which indicates a higher risk of foot ulcers. Smoothly controlling blood glucose to meet the standard is the most important measure for the prevention and treatment of diabetic neuropathy, and patients with significant pain can be given appropriate medication to improve their symptoms; at the same time, diabetic patients should also pay attention to the presence of symptoms related to vascular lesions of the lower limbs such as lower limb fatigue, claudication and so on, which is also an important risk factor for the development of diabetic foot. Before foot ulcers appear, controlling blood glucose to reach the standard, symptomatic treatment of neurological and vascular lesions can reduce the risk of ulcers occurring; patients with foot ulcers, foot pain aggravation should be alert to the possibility of exacerbation of the condition, and need to consult a diabetic foot specialist in a timely manner.
Thank you all for reading!
Please correct me if I'm wrong! Feel free to ask and share in the comments section!
Note: The content of this article is intended as health science only, and is not intended as medical advice or opinion, and does not qualify as medical guidance.
In fact, foot pain in diabetic patients is still relatively common in clinical practice. About 50% of patients with diabetes and about 13% of patients with impaired glucose tolerance are accompanied by neuropathic pain, which seriously affects our patients' quality of life and ability to work.
In trying to answer this question have you all thought about theWhat is pain? Why do we have pain in our feet? What can we do to prevent it?Let's go over some of them next.
What pain?
I'd like to start by asking you to think with me about the question why do we feel pain?
In fact, this involves a process of transmission of our nerves, we have a lot of micro-sensory nerves distributed under the surface layer of the skin, he can sense the subtle touch as well as strong stimulation, these actions will be neurons into nerve impulses in the form of electrical signals transmitted to the brain.
The brain categorizes different sensations according to the intensity of the electrical signals, and pain is one of the more intense impulses. In diabetic patients, inexplicable foot pain is likely to indicate that the nerves in our lower extremities may have been affected by the disease.
So why do people with diabetes feel pain in their feet? This pain is associated with peripheral neuropathy and painful neuropathy.
Peripheral neuropathy and painful neuropathy
1. Peripheral neuropathy
Peripheral nerves are the nerves that run through our skin, bones, joints and skeletal muscles. Peripheral neuropathy is one of the most common complications of diabetes. This somatic complication is mostly manifested as:
- Symmetric distribution of glove stockings ;
- The lower extremities are generally more severe than the upper extremities, with abnormal sensation in the limbs, and some people are unusually sensitive to pain,;
- In severe cases, nerve involvement and loss of sensation in the later stages of the disease can affect movement.
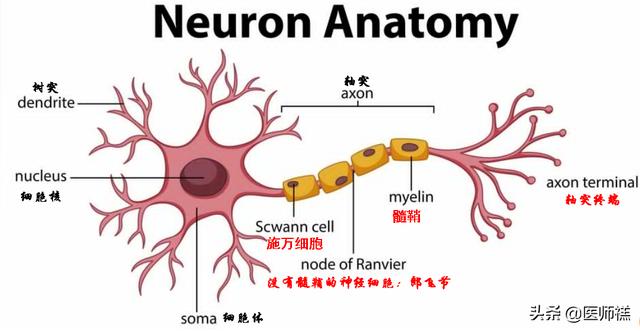
In order to explain this phenomenon to you in more detail, I retrieved an expert review published in 2019 by Tongji Hospital of Huazhong University of Science and Technology in the Chinese Journal of Pain Medicine, which gives us a good explanation of the pathogenesis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy.

In our peripheral nervous system there are cells calledSchwann cell, which are the most abundant cells in the peripheral divine system. They are responsible for wrapping synapses in peripheral nerves. Damage to Schwann cells is an important basis for neuropathy.
Whereas diabetics have high blood glucose, this high sugar state can shadow theSchwann cellThe internal production of neurofactors, which causes the supply of energy within the cell, can even promote the cell to secrete large amounts of inflammatory factors, which can lead to neuroinflammation, which is of course only the first step. The cells that cover the perisynaptic area affect the glia,axonalPass in neurotransmission and neurohomeostasis imbalances, causingAxons drag myelin sheaths, resulting in slowed nerve conduction.
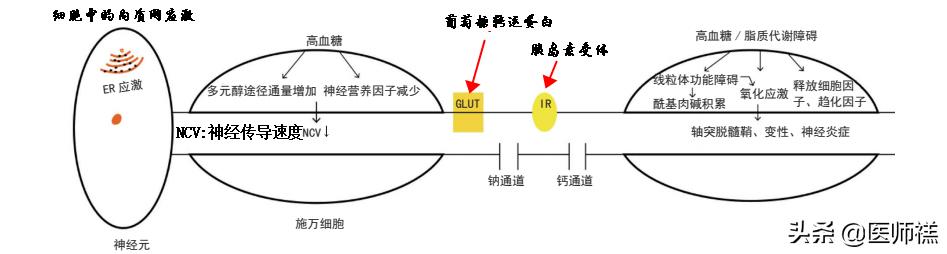
Insulin receptors in diabetics are insensitive to insulin, a phenomenon that exacerbates the degeneration of nerve axons, theLeads to axonal demyelination and myelin regeneration followed by axonal degeneration, which further promotes neuropathy and ultimately causes pain sensitization, and nociception in some patients.
2. Painful neuropathy
Painful neuropathy is a much more serious condition. This type of neuropathy presents with spontaneous pain that
Neuropathy occurs in up to 60% of all patients with type 1 or type 2 diabetes, and neuropathic pain occurs in >30% of these patients.
In the vicinity of our nerve cell bodies or within the periphery of small blood vessels exists anmicrogliaThe cells are activated in the presence of high levels of sugar. These cells are activated in the presence of high glucose, as shown in in vitro studies, and this activation lasts for more than 6 months.
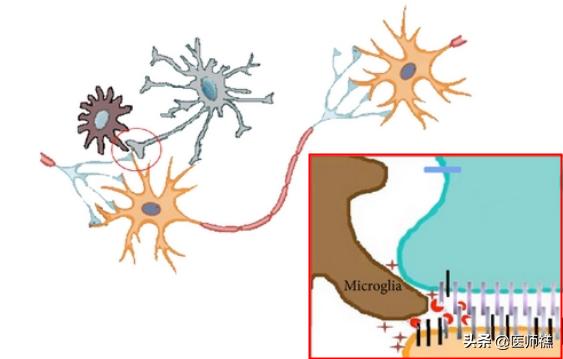
During the activation process, the body is activated with, for example, reactive oxygen species, nitric oxide, peroxynitrite, prostaglandins, and pro-inflammatory cytokines, which are neuromodulators and neuroactive substances involved in nociceptive sensitization and neuropathic pain in peripheral neuropathies.
This pain is characterized by nociceptive hypersensitivity, nociceptive hyperalgesia of unusually intense intensity or even accompanied by a degree of sensory loss, and is a challenge to control in the clinic.
The mechanisms of pain research in medicine are very complex, and these are just some of the mechanisms briefly given above.
In addition to the nerve damage that brings about peripheral neuropathy leading to numbness and even pain in the feet, diabetes also reduces blood flow to our lower extremities, depriving the feet of oxygen and nutrients. Healing of blisters, sores and wounds in daily life becomes more difficult, and sores and infections are likely to develop, which in severe cases may lead to gangrene and result in amputation.
Apart from clinical treatment, how should we protect our feet in our daily life?
1, always pay attention to their feet health, timely detection of abnormalities
Carefully check the crevices between the top of the foot and the toes for blisters and other infections. For people suffering from diabetic neuropathy because of pain sensitivity or even perception abnormalities it is even more important to seek help from family members.
2、Warm water bath feet, eliminate hot water scalding feet
This is because for the vast majority of patients with diabetic foot abnormalities, the sensory abnormalities may not be sensitive to heat, and in addition to preventing burns, there is more fear of localized sores or wounds that may be difficult to heal and cause the possibility of secondary infections. After washing your feet in warm water, you need to dry your feet promptly.

3、Choose comfortable shoes
Reduced sensitivity of the skin due to numbness, dullness or loss of sensation in the feet of diabetic patients can easily lead to skin damage. Therefore it is only important to choose a pair of shoes that fit well and are comfortable in order to avoid causing blisters that can lead to infections, and to buy well-fitting shoes or socks even when the slightest signs of redness or inflammation are present, as you may not be able to feel them when the situation worsens. So also check your shoes for rough seams, sharp edges or other items that could hurt your feet before you buy or put them on.

4、Keep your skin moist
When blood sugar is high, our skin is more prone to drying out and cracking, and cracked skin means that it is easier for bacteria to enter the skin and cause more healing infections. That's why it's essential to keep the skin on your feet properly moisturized by using a small amount of skin lotion every day. Try not to use lotion between your toes. Also keep your toenails neatly trimmed to prevent them from growing inward.
5, as far as possible to take the foot impact of small sports
Lighter foot impact, more recommended swimming, cycling, yoga and tai chi, etc. Firstly, these gentle exercises are suitable for diabetic patients, and secondly, the way of exercising with lower impact on the feet can better protect the health of the feet. However, patients with different conditions need to consult a medical professional for guidance before starting exercise.

6. The most important point to control blood sugar.
The best way to prevent neuralgia is to control diabetes properly. Clinically, people with type I diabetes and type II diabetes who take insulin injections and correctly administer medications to achieve strict blood glucose control can reduce the chances of developing peripheral neuropathy symptoms, and the associated tingling, burning, and even pain sensations can also be reduced.

8. Other measures
For people with diabetic neuralgia, the muscles may become very weak due to nerve damage. Supporting the foot with assistive orthotics can relieve pain.
Secondly, the length of time you have diabetes and the degree of control of your blood sugar determines whether you will suffer from diabetic neuralgia or not. Reasonable control of blood sugar, active control of blood pressure, blood lipids as well as proper diet, exercise and elimination of other factors such as bad lifestyle habits are also crucial to the prevention of diabetic neuropathy.
put at the end
Some diabetics have foot pain, some have numbness, and some even have more serious infections that can lead to amputation. Diabetic foot disease is one of the most common complications of diabetes. Correctly understanding the mechanism of pain, actively accepting treatment and doing a good job of prevention in daily life play a very important role in improving the quality of life of patients.
The above is an individual according to the literature and their own views on the more superficial answer, to help you at the same time also hope that you can by the way to forward the article to the people around you need (*^▽^*).

People with diabetes who feel pain in their feet are a complication of diabetes, academically called diabetic foot.
Little Medicine Man is sharing with you today three three reasons why diabetics can cause foot pain.
(1) It belongs to a vascular lesion where the small and medium arteries in the feet, the microcirculation is altered, resulting in insufficient blood supply to the feet. Your feet blood supply is not enough, your feet will have numbness, pain. Severe will be small wounds will not be able to close the mouth, more and more powerful, this blood supply is even more insufficient, forming a cycle. This is one of the main causes of foot pain.
(2) There is also the fact that diabetes can cause damage to the motor nerves in the feet. It is protective sensory nerve damage in the foot.
(3) Severe diabetes may cause some deformities of the foot, which can also cause foot pain
I hope the answer to the little medicine man was helpful!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.