What is a biopsy? What should I pay attention to?
Dr. Li is a gastroenterologist at a provincial tertiary hospital. Gastroscopy is part of my daily routine, just like a nurse's daily blood draw and injection. I think it is relatively authoritative for me to answer this question.
What is a gastroscopy biopsy?
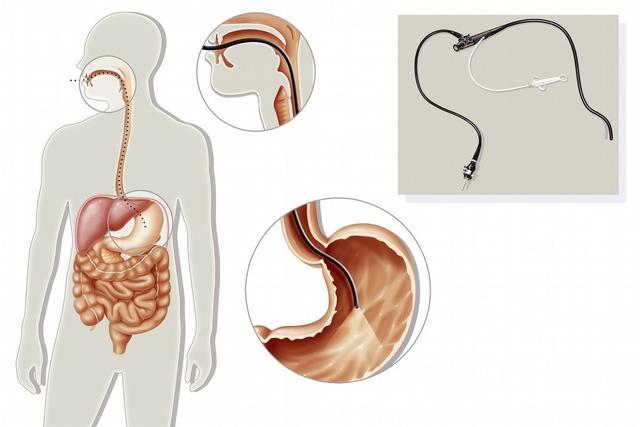
Stomach in the human body, we usually do the general examination can only see the appearance of the stomach, traits, functions, etc., just like a house we can only see its size, shape, color, appearance, etc. outside. Gastroscopy, on the other hand, leads us into the house of the stomach, where we can clearly see the layout, structure and the presence or absence of lesions inside the house.
Gastroesophageal reflux, gastritis, gastric ulcer, duodenal ulcer, upper gastrointestinal bleeding and other gastrointestinal diseases need to do gastroscopy, through gastroscopy, we can further clarify the cause of the disease as well as guide the treatment. When there is a suspicion of gastrointestinal tumor, not only to do gastroscopy but also to take a certain amount of gastric mucosa tissue for pathological biopsy, in order to clarify for the mucosa with or without cancer, for diagnosis and treatment are extremely important.
How is a gastroscopy done?
A gastroscope is a tube with a probe at one end that enters the stomach from the mouth or nose through the throat; the other end is connected to a large screen monitor to facilitate a clear view of the inside of the stomach.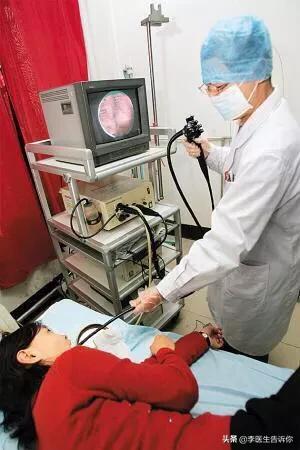

What to look for?
- Fasting. Fasting should be maintained for at least 6 hours prior to the examination. When the gastroscope enters the pharynx, it will cause normal physiological reflexes to stimulate and cause symptoms such as nausea and vomiting, and if the stomach is filled with gastric-digested food, it will be easy to cause accidental aspiration.
- No smoking. Nicotine is one of the main ingredients of cigarettes, and cigarettes can increase the excitability of the nerves in the stomach, which will increase the secretion of gastric acid, which will easily affect the results of the test. It can also avoid the pain caused by smoking and coughing when rubbing the back tube.
- Stay relaxed and happy, avoid excessive stress and cooperate with the examination. Gastroscopy is a fairly mature screening technique with little invasive damage and low risk.

Welcome to pay attention to Dr. Lee, to answer your medical problems, your likes are the biggest support to me.
During a gastroscopy you will often be told by your doctor that you need to do a tissue biopsy (also known as a pathology test), and many people who don't know about it will be confused as to how a pathology test is done. What can it do? What do I need to pay attention to during the examination? In the process of the examination, the doctor does not have much time to explain, on the one hand, because the examination time is tight, on the other hand, also because at this time the patient is lying on the examination bed (especially painless patients at this time in an unconscious state), not more than one minute of delay, the risk of increasing a. Therefore, it is important to understand the pathology examination in advance. Therefore, it is necessary to understand the pathology examination in advance, today we will look at the pathology examination inside the doorway it.
What is pathology?
Simply put, pathology is a method of making pathology slides of suspected diseased tissue retained during surgery or certain tests, and then using a microscope to further examine the lesions.

There can be many sources of specimens for pathology examination, the common ones are surgical removal of tumors and retention of the specimens for pathology examination, or endoscopy such as gastroscopy, enteroscopy and other endoscopes to clamp the suspected lesions and send them for examination in the course of examination. In addition, deep-seated lesions or tissues such as thyroid nodules, liver cysts, ascites, pleural fluid, etc. can also be extracted by ultrasound-guided puncture and sent for examination. After the tissue is extracted, fixed and stained, it can be observed under a microscope and a pathological diagnosis can be made based on its morphological characteristics and staining results.
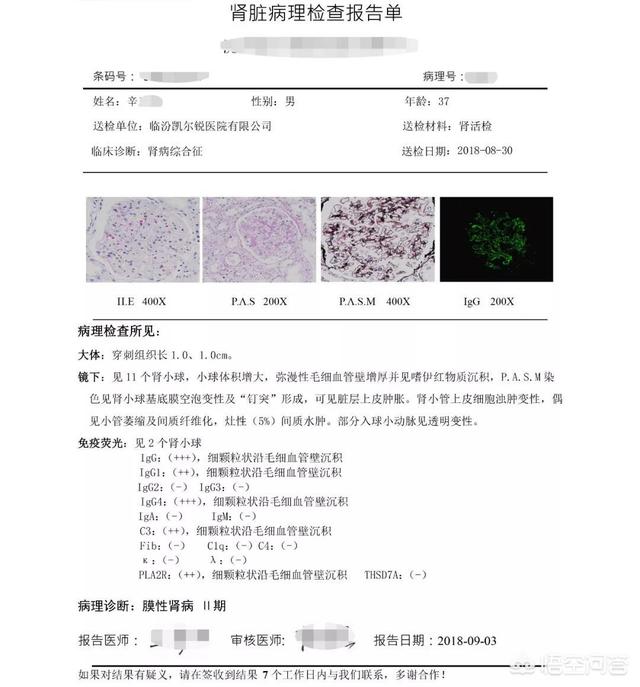
What's the use of pathology?
In clinical medicine, pathology is the "gold standard" for diagnosing the nature of a disease, which is also recognized as the most accurate diagnostic method in the industry. Therefore, if we ask what pathology examination can do, the simplest answer is that it can distinguish between "benign and malignant" lesions.
And through immunohistochemistry examination and flow cytometry in pathological examination, it is possible to make diagnosis and typing of some diseases, so as to formulate more accurate treatment plans. For example, in the formulation of treatment plan for lung cancer, the treatment methods for squamous carcinoma and small cell carcinoma can be said to be very different: small cell lung cancer is sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, which is its main treatment method, while squamous carcinoma is not considered to be sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and it needs active surgery to slow down the progression of the disease.This physician's use of pathology results to confirm cancer staging and guide subsequent treatment options is another important role of pathology testing.
What does a biopsy in a gastroscopy reveal?
Going back to the question of the subject, there are several important pieces of information that the doctor can get from the biopsy results during a gastroscopy:
1. Differentiation of gastric ulcer from early and progressive gastric cancer.Sometimes the microscopic manifestation of early gastric cancer or early gastric cancer is similar to that of ulcers, and there is also a tendency for the edge of gastric ulcers to become cancerous, so in such cases, tissue biopsy is the safest way to distinguish the benignness and malignancy of the lesions.
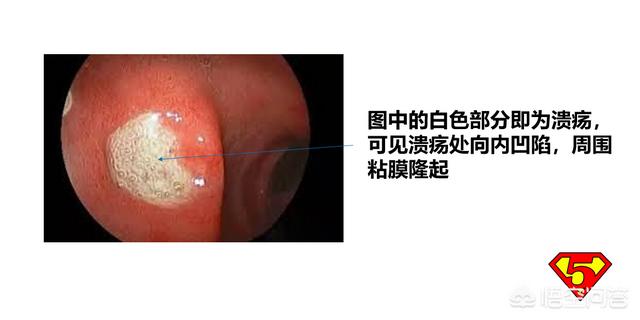
2. Diagnosis of atrophic gastritis.Under the action of H. pylori, atrophic gastritis is called "precancerous" because of its irreversibility after entericization and its tendency to become malignant. The diagnosis of chronic atrophic gastritis in the Kyoto Consensus is strict and needs to be supported by a pathologic diagnosis. The diagnosis is made when the results show atrophy or disappearance of the intrinsic glands of the gastric mucosa, intestinal epithelial hyperplasia or other heterogeneous hyperplasia. Pathologic examination is the "gold standard" for the diagnosis of atrophic gastritis.
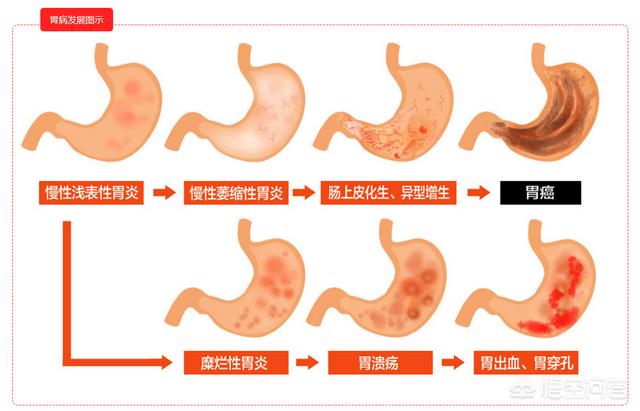
3. Testing for Helicobacter pylori.Rapid urease test on clamped lesion tissue can accurately determine the presence of H. pylori infection in the stomach, but because this test is invasive, requires high operational precision and is generally accurate, it has been slowly withdrawn from the stage of history after the application of the C14 blow test.

In addition to the routine gastroscopy precautions, there is a special requirement for biopsy tissue examination, that is, the patient has not taken aspirin and other antithrombotic drugs within a week, otherwise it will cause blood seepage at the biopsy, and in severe cases, it can cause anemia or even hemorrhagic shock. So when you or your friends or relatives want to have a gastroscopy before, you must be familiar with these precautions, otherwise it is very likely that the test will be canceled because of these details.
Attached are the precautions to be taken before a routine gastroscopy:
1. After 22:00 on the day before the examination and until the end of the examination, keep fasting on food and water during the period;
2. Patients with high blood pressure and diabetes should consult their doctors for timely adjustment of medication;
3. Have an EKG done to understand the condition of your heart and avoid accidents;
4. Through formal channels to understand the gastroscopy examination related information in advance, make good theoretical preparation and psychological foundation, explain to the accompanying personnel to cut polyps, take pathology and other decisions;
5. Remember to bring the report card with you if you have an early checkup, so that your doctor can compare your condition.
(END)
If it helps remember to follow Dr. Five, where you will get in-depth, data-driven medical and health science, as well as welcome private messages for questions and answers.
Usually, pathology is done for the purpose of making a definitive diagnosis and is used to determine the nature of the lesion (whether it is an inflammation or a tumor). If it is a tumor, it is also necessary to determine whether it is a benign or malignant tumor. In clinical practice, the pathology report is equivalent to a medical "judgment" on the nature of the lesion.
The results of pathological diagnosis are directly related to the clinician's choice of treatment plan, as well as the judgment of the prognosis of the disease. For example, when encountering patients with unexplained lymph node enlargement, the doctor will remove the lymph nodes and do a pathological examination. If the pathological diagnosis is "chronic lymphadenitis", internal medicine can be taken; if the pathological diagnosis is "Hodgkin's lymphoma", chemotherapy must be carried out immediately; if the pathological diagnosis is "metastatic adenocarcinoma", further examination is needed. If the pathological diagnosis is "metastatic adenocarcinoma", further examination is needed to find the primary lesion, and surgical treatment should be performed as far as possible. Therefore, pathological diagnosis is also called "final diagnosis".
Why can't pathology tests be "immediate"?
At present, the commonly used clinical pathology examination technique is paraffin-embedded sectioning. Usually, to make a set of pathology sections, it needs to go through more than 40 technical steps, taking more than ten hours, during which any part of the process is not handled properly, will affect the clarity of the sections, which in turn affects the accuracy of the pathological diagnosis results. In addition to the slice production cycle, the pathologist also needs to spend time under the microscope to carefully observe, in order to make a correct diagnosis, this process can not be replaced by any machine. Therefore, the pathology examination is different from ordinary blood tests, and cannot be realized "immediately". The corresponding Ministry of Health regulations on the time limit for pathological examinations are that the pathology department generally issues a report within 3 to 5 working days after receiving the specimen, with delays as appropriate in difficult cases.
Gastroscopy can actually be viewed in two parts: the first part is the procedure, that is, what the examiner sees with the naked eye during the examination; the second part, is that the examiner removes a little bit of tissue from the lesion seen with the naked eye with a special small forceps, and sends it to the Department of Pathology for the pathologist to look at under the microscope.
A gastroscopic biopsy, which is the second part of what the examiner is doing, is removing a bit of tissue from the lesion seen under the gastroscope for pathology.
Why the second step?
It is because our naked eye observation can only see the appearance of the diseased part of the stomach wall, is it inflammation and congestion, is it an ulcer, is it a polyp, or is it a tumor? These will have a gastroscopic visual impression, but what is the condition of the cells in these areas is not something we can distinguish with the naked eye, for example: are the cells on the ulcerated surface cancerous or not, and is the polyp a tubular adenoma or a villous adenoma? Are the tumor cells benign or malignant? And so on.
What can be done in this case? It would be necessary to remove a bit of tissue from the area and send it to a pathologist to look at it with a microscope and it would be clear.
Gastroscopy to take pathological biopsy, is a very important part of the examination content, but also the biggest advantage of gastroscopy, not only can see the lesions in the stomach, but also make a pathological diagnosis along with it.
This is not comparable to any imaging tests, including CT, MRI and even PET-CT, because all of these imaging means can only give an image judgment, but cannot take the tissues of the lesion site, and thus cannot give a pathological diagnosis.
而pathological findingsIt's the diagnosis.gold standard。
Of course, when you have a gastroscopy, sometimes it is done and no biopsy is taken, and this, congratulations, because the gastroscopist did not find any obvious abnormality in the stomach, and naturally, there is no need to take a biopsy.
▍大家好,我是西安大兴医院消化科主任/施海
QUESTION: What is a gastroscopy biopsy? What to look for?
(Audio Response(It's on my homepage, so you can listen to it directly)
---------- --------
Text Response:
(1379 words, approximately 2 minutes to read)Gastroscopy is one of the more common tests performed in gastroenterology and is the primary and most accurate test for diseases of the esophagus, stomach, and duodenum.It is still widely used in clinical practice.For example: reflux esophagitis, esophageal polyps, chronic gastritis, atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcers, gastric polyps, duodenal polyps, duodenal ulcers, and tumors of the stomach and esophagus are examined by gastroscopy.
So we often hear people ask during exams, "What is a gastroscopic biopsy?" I'm going to answer this question here, and I hope it helps.
➊What is a gastroscopic biopsy?
Gastroscopy biopsy is the use of a thin, flexible tube into the stomach to directly observe the stomach, esophagus and duodenum lesions, by removing part of the tissue from the suspected lesion area for biopsy, and then carry out pathological staining to determine the type of cells and some of the surrounding lesions for early diagnosis of whether it is a tumor or inflammation, or other diseases.
This is a more reliable way to diagnose gastric cancer, esophageal cancer or duodenal tumor in our clinic.
Then it can also make a definitive typing for some of the inflammation, is it inflammation OR incarnation? Atrophy or heteroplasia? By doing a gastroscopic biopsy to define the lesion, it helps to diagnose pseudo-pyloric glandular incarnation or some disease of the pyloric gland.
➋做gastroscopic biopsyWhat do I need to be aware of?
Diet: Two days before the test you should eat foods that are easy to digest, such as thin rice, noodles, milk, eggs, and foods with coarse fiber;
The day of the test is usually a six to eight hour fast and a four hour water fast;
Intravenous hypernourishment should be applied preoperatively in critically ill, frail patients, and patients with feeding difficulties;
No smoking: smoking is prohibited the day before the examination in order to avoid coughing during the examination which may interfere with the intubation. No smoking can also reduce the secretion of stomach acid and facilitate the doctor's observation;
Past history: If you have had fever, cough, nasal congestion and runny nose in recent days, you should postpone the examination and inform your doctor of your past medical history and drug allergy history before the examination;
Dentures (false teeth), eyeglasses, and other items should be removed before the examination to avoid interfering with the observation;
Anticoagulants such as warfarin and aspirin enteric-coated tablets and blood-activating drugs should be prohibited for a week before the test;
The patient has to work closely with the doctor;
The patient should make a trip to the restroom to empty the bladder before the exam.
Notes:Gastroscopic biopsy is contraindicated in the following cases
Severe cardiopulmonary patients, critically ill patients with suspected shock, GI perforation, those with psychiatric disorders who are unable to cooperate with endoscopy, patients with acute inflammation of the digestive tract (especially those with corrosive inflammation), patients with obvious or diagnosed thoracic and abdominal aortic aneurysms, and patients with stroke.
➌做gastroscopyWhat what do I need to be aware of?
- The patient should not drink water for half an hour after the examination, so as not to accidentally inhale into the windpipe and cause choking or aspiration pneumonia;
- If the examination is taken in the examination or removal of polyps after treatment, two hours after the operation can eat some rice soup, vegetable soup and other warm and cool liquid food, and at the same time to prohibit smoking, drinking alcohol, drinking strong tea or coffee, in order to reduce the trauma and stimulation of the gastric mucosa;
- After the examination, there may be pain in the throat, a foreign body sensation, and hoarseness, which usually improve three to five days after the examination;
- You should not do strenuous exercise for 24 hours after the examination, and you should take proper rest in conjunction with your physical condition, and you should not do activities such as driving or climbing;
- Three days after the examination, you should observe whether the color of the stool is normal or not, if there is a tarry black stool you should seek medical attention immediately.
➍做gastroscopic biopsyWhat are the adverse reactions and risks?
Some of the adverse effects and risks of gastroscopy have are mainly the following:
- Infection:Aspiration pneumonia may occur because of the long duration of the operation. Endoscopic treatment with injection of sclerosing agents, laser dilatation and other treatments may result in localized secondary infections. In these cases, antibiotics can be used for 1 to 3 days as prescribed by the doctor;
- Hypoxemia: Ventilation dysfunction due to endoscopic compression of the airway, or because the patient is nervous about holding his/her breath, may improve with a period of oxygenation after stopping the examination;
- Bleeding: Because of rough handling, biopsy trauma, or improper hemostasis after endoscopic treatment, manifestations such as vomiting blood or black stools may occur; if once detected, the physician should be informed immediately for hemostasis, or endoscopic hemostasis if necessary.
(ps: The report is usually available on the same day as the gastroscopy. If a biopsy is taken for biopsy histopathology, the case report usually takes about a week to get in hand.)
If my answer is helpful to you, remember to like it and keep it in your hand.
"Biopsy" is short for "biopsy histopathology". It has a history of about 100 years and is one of the most widely used, valuable, accurate and reliable methods in tumor diagnosis. Through biopsy (including extraction, cutting and excision), the material can be obtained directly from the lesion, made into sections, and the morphology and structure of the cells can be observed under the microscope, in order to determine whether it is a tumor or not. Is it benign or malignant? Which type of tumor is malignant? What is the degree of chemotaxis? It plays a great role in determining the diagnosis and choosing the treatment method, as well as anticipating the next evolution of the disease.
Biopsy is generally not difficult, for tumors on the surface of the body and some exposed areas (such as skin, cervical cancer, etc.), it is easier to obtain tissues; for deeper tumors, some special instruments (such as various endoscopes, etc.) can be used to carry out biopsy.
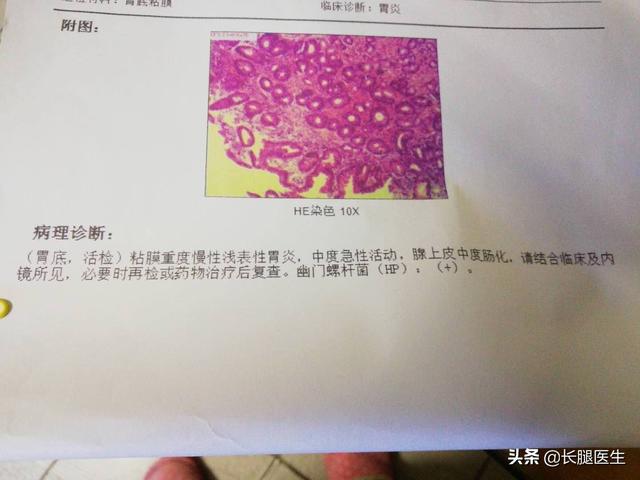
Gastroscopic biopsy is based on gastroscopy, when lesions or suspected lesions are found by observing the stomach, a small portion of tissue is taken by biopsy forceps for pathologic examination. In order to make a clear diagnosis, in principle, patients with general tumors or suspected tumors should strive for biopsy as much as possible. In addition to gastric diseases, radical mastectomy, radical cervical cancer, and radical intestinal cancer routinely require a clear diagnosis before surgery because pathological diagnosis is the gold standard and biopsy is relatively easy to perform.
Pathologic biopsy, generally doctors are very cautious, some patients have concerns about biopsy, in fact, biopsy will not bring harm to most patients. As long as the operation is meticulous, gentle, and the instruments are sharp, it will not cause the tumor to spread. On the contrary, if the correct diagnosis is made in time through the biopsy, the correct treatment can be obtained at an early stage, and the possibility of cure will be greater. The most common complication of gastroscopy biopsy is bleeding. The amount of traumatic bleeding is usually not big, but there is a very small number of patients with gastric cancer who may suffer from hemorrhage, so it is also necessary to listen to the doctor's instruction after the examination and arrange the diet reasonably, and do not eat blindly.
During a gastroscopy, the doctor first observes whether there are any lesions with the naked eye, and then performs a gastroscopic biopsy if necessary. Biopsy will be done in the following cases, such as chronic atrophic gastritis, gastric ulcer, gastric polyp biopsy clip removal, suspected intestinalization of gastric mucosa, gastric cancer pathology to confirm the diagnosis and so on. The biopsy is performed to further clarify the diagnosis, and after the biopsy, it is important to fast for 4 hours and follow up on the pathology of the biopsy tissue for further feedback to the doctor.
I hope my answer is useful to you.
Gastroscopic biopsy can be used to identify benign and malignant ulcers, can detect early gastric cancer, and can be used to detect Helicobacter pylori.
What do I need to pay attention to before the examination? First of all, relax, gastroscopy biopsy is a very common and safe method, if you have arrhythmia to tell the examining doctor, nervous people can take sedatives before the examination; fasting, the doctor will explain that the day of the examination should be fasting for at least 5 hours, fasting when the examination, otherwise the food in the stomach will interfere with the examination, the delayed gastric emptying of the stomach, fasting time is even longer; before the procedure will be given to the mucous surface anesthesia, and so on.
Biopsy is short for biopsy histopathology. Gastroscopic biopsy, that is, obtaining diseased tissue for observation, especially microscopic observation, through the gastroscope in order to make a clear diagnosis, is also known as gastric mucosa biopsy.
In general, gastroscopy biopsy is performed for those who have upper gastrointestinal symptoms such as dysphagia, epigastric pain, epigastric fullness, retrosternal pain or heartburn, and loss of appetite, but the cause is unclear; those who are suspected to have mucosal lesions or tumors that cannot be confirmed by barium X-ray; those who have upper gastrointestinal bleeding of an unknown cause and those who have a followup review of certain gastric disorders.
The results of gastric mucosal biopsy sometimes do not completely and accurately reflect the intragastric lesions, it is affected by a number of factors, which can be overcome if the patient and the physician can cooperate well. First of all, the patient should eat light food the night before the examination, avoid drinking alcohol and eating stimulating food. Do not smoke before gastroscopy, gastroscopy process follow the doctor's instructions to avoid too nervous and cause obvious nausea reaction. Secondly, due to the uneven distribution of chronic gastritis lesions, a biopsy of a piece of tissue can only understand the situation at that point, so it is necessary to take several times, multi-point biopsy, in order to make a comprehensive evaluation of the gastric mucosa.
For those who have intraoperative biopsies, eat a soft diet on the day of the procedure and do not eat overheated foods because of a small wound in the local mucosa. Very few patients may have active postoperative bleeding due to the abundance of local blood vessels or poor coagulation. This may be manifested by black or tarry stools, or blood in the vomit and stool due to heavy bleeding, and once bleeding is detected, immediate medical attention should be sought.
1~2 hours after the examination, only after the anesthesia effect disappears can we eat; 2 hours after the examination, we can eat liquid food, if there is no choking, we can eat congee and noodles; within 3 hours of the examination, we need to be accompanied by someone; after 4 hours, we can have a normal diet; on the same day, it is advisable to eat some soft, easy-to-digest, non-stimulating food; avoid eating food that produces a lot of gas.
If there is pain and discomfort in the throat or hoarseness after pulling out the mirror, you can contain medicine to gargle or mouth containing throat tablets, there may be pain or foreign body sensation in the pharynx, mouth containing iodine throat tablets, grass coral tablets, etc., the symptoms can be alleviated or disappeared.
Smoking, drinking alcohol, strong tea and coffee are prohibited after the examination to avoid inducing trauma bleeding.
Patients who have had a biopsy (especially the elderly) should eat a semi-liquid diet for 1~2 days after the examination, avoiding raw, cold, hard and irritating foods. If there is a large black color to be promptly asked the doctor to deal with.
On the day after the examination, you should not drive motor vehicles and work at heights, as well as work such as actuarial and logical analysis, and should not do excessive physical labor; stop taking all medications for 3 days after the examination to avoid stimulation.
Lastly, because pathologic diagnosis is influenced by the experience of the pathologist, it is best for the patient to have a gastroscopy performed by the same physician at the same hospital and have the results judged by the same pathologist.
Gastroscopy is mainly used for upper abdominal discomfort, pain, unexplained anemia, barium meal examination can not be diagnosed or suspected of upper gastrointestinal diseases need to carry out a necessary examination, but also is the main means of diagnosis of upper gastrointestinal diseases.
In the gastroscopy process can not determine the nature of the lesion, the severity and type of tissue, the need to clamp the lesion site of a small amount of tissue for pathological examination, with the important significance of the characterization of the lesion, so it is a very necessary examination, but also very safe, because the biopsy forceps is relatively small, only a small piece of the gastric mucosa clamping, the wall of the stomach itself will not occur damage and impact.
Before gastroscopy, you should learn from the doctor about the purpose, method and possible side effects of gastroscopy and contraindications (history of coronary heart disease, hypertension, stroke), and try to cooperate with the doctor to complete the examination. Before the examination, it is necessary to remove the movable dentures, prohibit food and smoking for 12 hours, do more abdominal deep breathing during the examination to reduce nausea, vomiting and other uncomfortable symptoms, and gastroscopy cannot be performed within 3 days after the barium meal examination.
Gastroscopy after the temporary do not swallow saliva, so as to avoid choking, such as the disappearance of anesthesia, you can drink a small amount of water, the day's diet to fluid, semi-fluid is appropriate, took a biopsy of the person's diet should be warm and cool, do not cough after the end of the examination, so as to avoid damage to the mucous membrane of the pharynx. If abdominal pain and bloating symptoms occur after the examination, you can massage the abdomen to promote exhaustion, and carefully observe whether there is any complication such as gastrointestinal perforation, bleeding, infection, etc. within 3 days. If abdominal pain worsens and other symptoms, go to the hospital immediately to exclude complications that may be caused by the examination.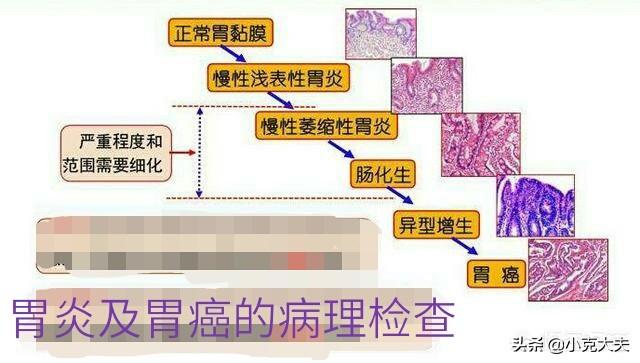
Follow Kirk for more health information.
Thanks for reading!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.