How often do you get complications from diabetes?
Diabetes mellitus is the number one metabolic disease in China and is a chronic disease that needs to be prevented and treated in middle-aged and elderly people. Treatment of diabetes focuses on reducing target organ damage and delaying the onset of chronic complications in order to improve quality of life and reduce the risk of death at a later stage. How long does it take for diabetic patients to develop chronic complications? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze it for you.
Diabetes mellitus can cause a variety of target organ damage, the damage to the cardiovascular and cerebrovascular mainly manifested as atherosclerosis, increasing the risk of myocardial infarction and stroke; the damage to the kidneys in the early stage of increased urinary excretion of protein, increasing the risk of chronic kidney disease; the damage to the retina in the early stage of the main manifestations of vision changes, and in some cases, can be blinded; the damage to the nerves to the peripheral neuropathy is the main, can be pain, numbness, burning sensation; the impact on the feet can not only appear nerve damage, but also vascular damage, increasing the risk of foot ulcers, in some cases, can cause amputation. The damage to the nerves is mainly peripheral neuropathy, which can cause pain, numbness and burning sensation; the effect on the foot can not only appear nerve damage, but also accompanied by vascular damage, which increases the risk of foot ulcers, and in severe cases, can cause amputation. Therefore, patients with diabetes can have multiple organ and tissue involvement. Once diagnosed with diabetes, they should lower their glucose reasonably, and at the same time screen for diabetic complications regularly, in order to treat them early, avoid the continuous aggravation of target organ damage, and prevent the occurrence of acute myocardial infarction, stroke, renal failure and other highly disabling and fatal complications, so as to improve the quality of life in the later stage of the disease.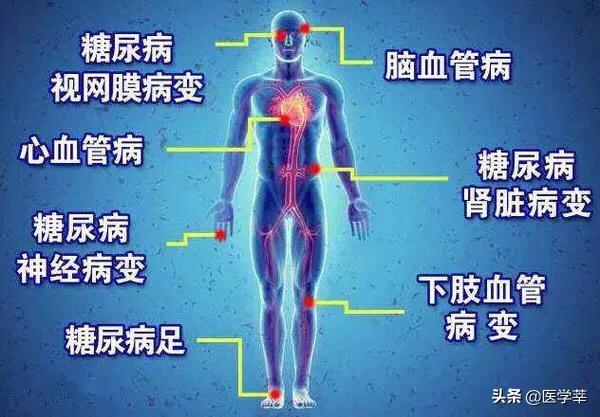
Most people are concerned about how long it will take to develop complications after a diagnosis of diabetes. There is no clear answer to this question. When some patients are diagnosed with diabetes, target organ damage has already occurred, such as damage to the endothelium of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular vessels, kidney damage, etc. However, the degree of damage in the majority of patients is relatively mild, usually with no significant symptoms, and is far from complications such as myocardial infarction, stroke, kidney failure, etc. Some complications may not appear until ten years later, such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy, usually with no significant symptoms. Some of the complications may show significant symptoms only after ten years, such as diabetic peripheral neuropathy, which usually shows significant clinical symptoms in patients with more than ten years of disease duration. Therefore, for the clarification of diabetic complications, it is necessary to regularly improve the relevant examinations, such as screening for diabetic nephropathy, it is necessary to regularly improve the urine routine and urine protein creatinine ratio, glomerular filtration rate, etc.; screening for diabetic retinopathy, it is necessary to improve the comprehensive examination of the fundus; screening for diabetic foot, it is necessary to regularly improve the vascular and nerve examination. Some of you may ask, how long is the so-called regularity? Generally, the screening is once every 1-2 years, and for serious lesions such as diabetic retinopathy, the screening is once every 3-6 months.
In summary, target organ damage has already occurred in some patients when they are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus, but in most patients the damage is mild and not easily detected at this time; some of the complications may appear significant clinical symptoms only after ten years. Therefore, the onset of diabetic complications varies from person to person and from target organ to target organ, and regular screening is important for early detection and early intervention.
Thank you all for reading!
Please correct me if I'm wrong! Feel free to ask and share in the comments section!
Note: The content of this article is intended as health science only, and is not intended as medical advice or opinion, and does not qualify as medical guidance.
Thanks for the invitation. Diabetes mellitus refers to an endocrine disease in which blood glucose is elevated due to a dysfunction of the pancreatic islets and a decrease in the quantity and quality of the insulin they secrete. Diabetes itself is not scary, but the most scary thing is the complications. The most common complications are related to atherosclerosis. For example, blindness caused by arteriosclerosis of the fundus of the eye, kidney damage caused by renal vascular sclerosis, coronary artery disease caused by coronary arteriosclerosis, and stroke caused by arteriosclerosis of the neck.
Preventing atherosclerosis is critical for people with diabetes! Why does atherosclerosis occur in diabetics? Simply put, it is the damage to the inner lining of the arteries caused by high blood glucose and hyperinsulinemia! This damage naturally leads to the development of atherosclerosis, which in turn leads to complications.
Therefore, when complications occur after the diagnosis of diabetes is closely related to the patient's control of blood glucose and hyperinsulinemia control status, blood glucose, hyperinsulinemia control properly, naturally there will be no complications, on the contrary, complications are inevitable. There are a lot of discussions about how to control blood glucose and hyperinsulinemia in my headline articles, welcome to pay attention to my headline number-Jiangsu Provincial Cancer Hospital Li Feng.
How often do you get complications from diabetes?
People are afraid of diabetes, more mainly because of the fear of complications, common complications are rotting feet, that is, the breach does not heal, blindness, kidney failure, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, neuropathy, etc., which complications are very scary, so diabetic patients, are trying every possible way to prevent the emergence of complications.
Some doctors will tell diabetic patients that as long as they can keep their blood sugar stable, they will not develop complications. The blood sugar stability mentioned here means that the blood sugar value in the blood is at a reasonable level, because some diabetic patients have taken the way of eating less carbohydrates, increasing the amount of exercise, and taking hypoglycemic medication, so as to make the concentration of sugar in the blood remain stable, but the reality is not so optimistic, and there are some diabetic patients who have kept their blood sugar stable for many years, but still developed complications. stabilized, but still developed complications.
This is because only to keep the surface of the blood sugar stabilization, did not solve the problem of no sugar in the cells, the sugar are discharged in advance, or no sugar intake at all, no sugar in the cells, the person has no energy. But people in what state to consume energy, no sugar, can only be replaced by the body's stored protein, protein is less and less, people become thin. Without protein, wounds are difficult to heal. Kidney protein is getting less and less, there will be kidney dysfunction. Therefore, the superficial lowering of sugar is very dangerous.
As for the timing of complications, it is related to each individual's maintenance, dietary habits, improved lifestyle, emotional state, immunity and other factors.
Dietitian Sugar is here to answer your questions.
When you have diabetes, how long before you develop complications? This actually depends on the condition of each person and there is no standardized criteria. Generally speaking, complications of different degrees will appear after 5 years of disease, especially eye complications and kidney lesions, and basically all kinds of complications will appear after 10 years. Of course, if the blood sugar control is better, it is possible to have no significant complications for ten years.

So how much blood sugar do you really need to control to stay away from complications?
It is generally recommended that diabetics keep their fasting blood glucose within 7.0, postprandial blood glucose within 10.0, and glycosylated hemoglobin within 7.0%. Of course, the control standard is different for different ages and disease duration. The younger ones with shorter disease duration should have stricter control requirements, and it is recommended to control blood glucose according to the standard of normal people, i.e., within 6.1 for fasting, within 7.8 for postprandial, and within 6.5% for glycated. For those with longer disease duration, tendency to hypoglycemia, and more serious cardiovascular disease, the control standard can be relaxed as appropriate.
It's not just about controlling blood sugar to keep complications at bay
Many diabetics only focus on blood sugar, that blood sugar control is good, but ignored the control of blood pressure, lipids, uric acid, creatinine and other indicators. Because the three highs often accompany each other and affect each other, so diabetics should pay attention to comprehensive control. Regular checkups of various body indicators are very important, and it is worthwhile to spend some money on checkups to buy health at a later stage. It is recommended to check hemoglobin, blood pressure and blood lipids every 3 months, and check the fundus and kidney once a year, early detection and early treatment is the way to health.
I hope Sugar's answer can help friends, more diabetes encyclopedia knowledge we share in the later Q&A!
Diabetes isn't scary, it's the complications that are scary, and I'm sure many of you are familiar with this saying.
Indeed, diabetes is usually more typical symptoms are "three more and one less", that is, eat more, drink more, urinate more, weight loss. Some diabetic friends do not take these symptoms seriously, and can not afford to eat, nothing to do, drink tea and look at the phone ah! Drink more, don't you urinate more? Weight loss. I'm trying to lose weight!
See, isn't that the mindset of many of our diabetic friends who have just been diagnosed with diabetes.
However, there are also many diabetic friends who have no symptoms at the onset of the disease, found when checking the body, was diagnosed with diabetes after a bewildered face, how could I have diabetes? I don't feel anything!
There are also some people with diabetes who do not have either of these conditions and come to the hospital because of complications. For example:
Eye lesions:Some people are diagnosed with diabetic retinopathy when they have blurred vision, decreased vision on examination, hemorrhages in the fundus, or even blindness, and when they are examined, they are found to have high blood glucose, high glycosylated hemoglobin, and the presence of various lesions of the retina.

Kidney lesions:Some diabetic friends have symptoms such as swollen eyelids, acidity and weakness, and upon examination, positive urine protein, high blood sugar and high blood pressure, diagnosed diabetic nephropathy. Some of them even have serious problems with kidney function, manifesting to the point of uremia or even the need for dialysis.
Skin infections:It is very sad that some people whose skin incisions continue not to heal or even become infected, or even show gangrene of the foot, come to the clinic and find high blood sugar, and need amputation treatment if they are diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. However, such patients can also be seen in the clinic.
In addition, such as diabetic neuropathy caused by limb numbness, plantar sensation, foot sensory abnormalities and so on. Many old people show chest tightness, panic, dizziness and other cardiovascular lesions, these are the complications of diabetes.
Diabetes is known as the silent killer, and it's scary because it attacks your body organs without a word, making your body sick without you even realizing it.
In fact, many times diabetes is not without some signs, but some people are not willing to pay attention or face it. For example, maintain a healthy diet, moderate exercise is certainly beneficial to the body, but can not resist the desire, not willing to adhere to, resulting in higher and higher weight. If you have high risk factors for diabetes, you are not willing to have regular checkups. If you have some symptoms of diabetes, you are not willing to go to the hospital for checkups, and you have a lucky break, thinking, "Maybe it's not," or "How could it be?"
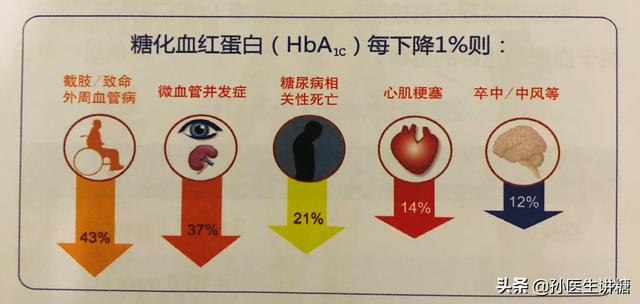
Prolonged poor glycemic control increases the chance of complications. Generally, there is a period of 8-10 years between the diagnosis of diabetes and the onset of complications, and if blood glucose can be kept relatively stable, the chances of complications are significantly reduced. Studies have shown that every 1 percentage point drop in glycated hemoglobin can result in a 43% decrease in the chance of amputation or peripheral blood cobalaminopathy, and a 37% decrease in the chance of microvascular complications such as eye and kidney. Therefore, controlling blood glucose is very important!
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
[Professional doctor to answer your questions
There is no standard answer to this question. In reality, we often see people in their forties and fifties or even earlier due to various complications caused by diabetes that seriously affect their lives and even lose their lives; some people can live a long life to eighty or ninety years of age, and these people do not have no complications, but only occur later or are not so serious, and the reason for this is actually very clear.
First of all, it is important to realize that diabetes is a progressive disease, which means that complications will eventually occur as the disease grows older, but when they occur is determined by the effectiveness of interventions to treat diabetes. Research has confirmed that complications occur after about 3-5 years in untreated cases, while in people with active interventions such as smooth blood sugar control, complications occur after 10 to 20 years or more.
Secondly, we should know that the occurrence of diabetic complications first from small vascular lesions, such as peripheral vascular lesions damage to nerve endings of peripheral neuropathy is often the earliest complications, followed by diabetic fundus lesions, diabetic renal damage and lesions, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease and other vascular disease occurs later, but the most threatening to life. Of course, there is no clear boundary between the various complications of diabetes, and they may occur at the same time, just with different degrees of severity.
Thirdly, we should know that although diabetes is mainly manifested by high blood sugar, in fact, the body's sugar metabolism must be abnormal, which will cause systemic metabolic disorders, such as blood lipids, elevated blood pressure, etc., and these factors together together to cause damage to the blood vessels, and ultimately triggered the occurrence of multi-tissue organ disease, in fact, all the complications of diabetes are the root of the vascular pathology of the results.
To sum up, when complications will occur, the key is to see the importance of diabetes, whether to establish a good lifestyle based on timely treatment under the guidance of the doctor to ensure that the indicators really control up to standard, in a word, to minimize the harm of diabetes rely on the doctor more rely on their own.
Now take a look at yourself and see if you are in control of these indicators that are most critical in the development of diabetes complications!

- Fasting blood glucose: ideal control is less than 6.1 mmol/L and should be at least 7.0 mmol/L or less
- 2-hour postprandial blood glucose: ideal control is less than 7.8 mmol/L, and should be at least 10.0 mmol/L or less
- Glycated hemoglobin: ideal control is less than 6.5% and should be at least 7.5% or less
- LDL: Ideal control is less than 1.8.mmol/L and should be at least 2.6 mmol/L or less
- Blood pressure: the ideal control goal is less than 120/80 mmHg and should be at least 130/80 mmHg or less
In addition, special care should be taken to avoid severe hypoglycemia, knowing that a single episode of severe hypoglycemia will offset years of control of high blood sugar and can even be life-threatening.
I hope this answer can help you, welcome to click on the attention and leave a message, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge.
How often do you get complications from diabetes?
There's no according body timetable for when this is, but you're going to have poor blood glucose control and there's a risk of complications. So controlling your blood sugar is the key.
Complications can occur very quickly with excessive restriction of staple foods and overuse of hypoglycemic medications. The United States in 2010 released statistical data line under the current sugar-lowering treatment, the probability of the disease ten years of complications is 98%! So you can't blindly lower your sugar!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.