What fruits should I not eat with type 2 diabetes?
Hello everyone, I am very happy to be here to answer your questions and it just so happens that I have recently been reading a book "Food and Health: the Consensus of Scientific Evidence". It just so happens that it talks about the relationship between fruits and type 2 diabetes, and I'm sharing it with you here.
The most rigorous part of this book is that it is based on the collection of a large number of scientific research literature at home and abroad, food and health relationship research and evidence-based reference to the World Health Organization guidelines to develop a manual for evidence evaluation requirements and level evaluation, and conclusion of the recommended methodology in the scientific evidence-based and nutritional and epidemiological experts to discuss, put forward our country's food and health evidence evaluation methodology and conclusion of the recommended opinion.






Thank you for reading what I have filmed below, I believe some of you read it and some of you are not sure, so I can explain it to you here.
There are six studies mentioned here.
The first study, a systematic synthesis of studies of 187,382 people from a cohort of U.S. nurses as well as a cohort of health professionals, commenting on data after 18.5 years of follow-up, found that fruit intake reduces the risk of developing type 2 diabetes. Those who consumed fruit daily had a lower incidence of the disease, and an analysis of different fruit types found that increased intake of blueberries, grapes and apples significantly reduced the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
The second study, a dietary frequency questionnaire for 403,259 subjects, of which 27,940 were diabetic, showed a significant reduction in the risk of diabetes in the highest intake group compared to the lowest intake of fruit.
The third study, the Dietary Frequency Questionnaire, was conducted on 191,686 cases of sweetened fruit juices studied, and 137,663 cases of pure fruit juices, and fruit and 100% pure fruit juice intake were not associated with type 2 diabetes.
The fourth study, a prospective cohort study of 978 Japanese people aged 40-60 years, found that the incidence of retinopathy was significantly reduced with higher fruit intake in all cases after 8 years of follow-up.
A fifth study, of 16,154 control people and 12,403 people with type 2 diabetes, found that those with fruit intake of 103.7-316.9 g/d or more had a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes by consuming varying portions of fruit, every day, after an average of 11.7 years of follow-up.
In the sixth study, of 223,522 individuals, a systematic evaluation approach, no significant associations were seen between fruits and vegetables together, or fruits alone, and the risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
In summary, the results of the study showed that fruit intake is not significantly critical to type 2 diabetes, with a grade of recommendation of c. In other words, the credibility of fruits in reducing the incidence of type 2 diabetes is C. There are a large number of factors of individual differences, which have to be treated differently and cannot be generalized.
1. Choose the type of fruit diabetic patients can eat which fruit depends mainly on the GI value of the fruit itself, simply put, this fruit is eaten by us into the belly after the speed of blood glucose and the ability to rise, the higher the GI rise blood glucose faster. That we certainly want to choose low GI fruit is better, 55 < GI < 70 for the determination of the standard, 55 below the best, 70 above the most unsafe, the specific value of the figure to speak. So, we know that apples, pears, cherries, plums, grapefruit, apricots, more suitable for diabetics to eat; relatively speaking, watermelon, durian, jujube, mango, pineapple, lychee, these are less suitable for diabetics to eat.

2. The amount of fruit eaten, even if it is not suitable, is not to say that a bite can not be eaten. In life, diabetic patients have another misunderstanding, that is, either a bite does not touch, or nothing to worry about. No matter which kind of fruit, the sugar content is very high, is not suitable for a large number of people to eat, the intake should be less than the normal 200 to 350g, diabetic patients daily fruit intake should be kept within 200g, 100 to 200g is appropriate. Banana, pineapple, kiwi only eat a little less, will cause blood sugar fluctuations, so if you eat, less than 50g at a time, taste even! Although watermelon has a high GI value, it does not have as high an effect on blood sugar (GL) as bananas because of its high water content, so you can eat a small piece at a time.
4. Diabetic patients with blood sugar levels for eating fruit, there is another point is to look at the patient is in which stage of diabetes, if the blood sugar is relatively stable, outside the hospital intervention is expected, so that the choice of eating fruits are a little larger, if the blood glucose burst, hospital treatment, it must be careful and cautious, and must be strictly in accordance with the standard in the two meals, eat a small amount of low GI fruit!

Author: Zuo Xiaojing, Bachelor of Medicine, National Level 2 Public Nutritionist, Psychological Counselor, Member of Chinese Nutrition Society, Chief Nutritionist of Liaoning Nutritionist Office.
Popularizing Diabetes
type 2 diabetesIt is pancreatic islet resistance, where the pancreas secretes insulin, but high blood glucose levels in the blood vessels result from damaged receptors in the target cells that are unable to store the glycogen, resulting in hyperglycemia.
type 1 diabetesIt is due to the destruction of beta cells in the pancreas that causes the pancreas not to work properly and not to secrete insulin normally. Insulin regulates sugar metabolism and balances blood sugar. Due to the lack of insulin, blood glucose cannot be metabolized normally, which in the long run leads to the continuous rise of blood glucose and the formation of diabetes mellitus.
Managing Diabetes
Dietary management is an important way of controlling blood glucose, helping to reduce the burden on the pancreatic islets, achieve and maintain ideal blood glucose levels, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular complications.
Diet culture has a long history in our country. Scientific diet does not require patients to go hungry or give up their favorite foods, we just need to rationalize the types and quantities of food we consume daily to enjoy healthy food.

There is no fruit that a diabetic should never eat.
If you have to say anything, then the following fruits are high in sugar or calories, so be careful not to eat too much of them:
1. Cinnamon:
Lead to a rapid rise in blood sugar. Cinnamon is high in sugar content, fast digestion and absorption after eating, which can quickly lead to a rapid rise in blood sugar, which is not conducive to the control of diabetic patients.
2. Dates:
It may impair the digestive function of diabetics. Although jujube is rich in nutrients, the sugar content of jujube is very high, especially sun-dried jujube (over 20% sugar per 100 grams of fresh jujube, and 60%-70% for dried jujube), which will rapidly raise blood sugar after consumption. If diabetic patients with poor gastrointestinal function consume too much jujube, it will also damage the digestive function and cause gastrointestinal discomfort.
3, Kakiko:
It should not be consumed by people with poor blood sugar control. Persimmon is a fruit with high sugar content, after consumption will rapidly increase blood glucose, so diabetic patients must pay attention to consume persimmons do not overdo, otherwise it will aggravate the burden on the pancreatic islet cells. Persimmon contains a large number of persimmon gum, eating persimmon gum on an empty stomach will be with the stomach secretion of gastric acid in the stomach cohesion into a hard block; when the hard block more and more large, may lead to the inability to discharge, medically known as the "persimmon stone disease", so even if the consumption of food should not be eaten on an empty stomach.

4. Grapes:
It is harmful to diabetic nephropathy patients. Grapes have a high sugar content and are predominantly glucose, which can be quickly absorbed by the body and rapidly raise blood sugar, which is not conducive to blood sugar control. The fructose content of raisins is as high as 60%, which is higher than that of grapes, so diabetic patients should avoid eating raisins. Grapes are rich in potassium, especially not suitable for diabetic nephropathy patients.
5. Durian:
It is not conducive to blood sugar control in diabetic patients. Durian has high calorie and sugar content, while diabetic patients have impaired pancreatic function, relatively insufficient insulin secretion and reduced glucose utilization, thus diabetic patients will have elevated blood glucose after consumption.
6. Litchi:
Make blood sugar rise rapidly. Lychee pulp contains up to 20% sugar, of which glucose content accounts for 66% of the total amount of sugar, and the glucose in the body of diabetic patients can not be fully utilized, the consumption of lychee will make the blood sugar rise rapidly.
7. Bananas:
Reduce the potassium excretion capacity of patients with diabetes mellitus complicating nephropathy. Bananas contain high sugar content, diabetic patients will rapidly increase blood glucose after consumption, is not conducive to blood sugar control, so diabetic patients consume bananas must do a good job of food exchange portions. Bananas are rich in potassium, and patients with diabetic nephropathy have a reduced ability to excrete potassium, so they should not be consumed. Bananas that are not ripe contain more tannic acid, which has an astringent effect on the digestive tract, inhibiting the secretion of gastrointestinal fluid and inhibiting gastrointestinal motility.

8. Sugar cane: The sugar content is too high for blood sugar control. Sugar cane is the raw material for the manufacture of sucrose, so its sugar content is very rich, 18% -20%. And sucrose in the human body is easily converted to glucose, affecting the insulin secretion in the body of diabetic patients, so that blood sugar increases, so diabetic patients should not eat.
The principles of dietary management are total calorie control, maintaining body weight within a reasonable range, a balanced diet with a variety of food types, and regular eating.
Scientific Diet
A scientific diet should follow the 3 steps of diet: how much to eat? What to eat? How to eat?
Step 1: How much to eat?
Total daily calorie intake is related to gender, age, ideal body weight, and activity level. Standard weight needs to be calculated to determine whether you are obese, normal or thin.

Step 2: What to eat?
Tip: Diabetes Diet Mantra: "1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7"
"1" 1 pound of vegetables per day; "2" 2 taels of staple food per meal; "3" no more than 3 tablespoons of vegetable oil per day; "4 "4 two fruits per day; "5" 5 servings of protein per day (including 1 two fish, 1 two meat, 1 egg, 1 bag of milk, and 1 serving of soy products); "6" No more than 6 grams of salt per day; "7" No less than 7 glasses of water per day.
Step 3: How do I eat?
Species-rich, coarse and fine matching, small meals, 3 to 6 meals a day, regular and quantitative, rich in dietary fiber, low-fat and less oil, less sugar and less salt, limiting alcohol consumption, resolutely quit smoking.
Common dietary treatment tips:
√ Food cooking methods should be stewed, boiled, steamed, braised, and chilled, avoiding frying, deep-frying, and over-oil braising.
√ No more than 6 grams of salt per day, about 1 capful of 500ml mineral water. Don't neglect the amount of salt contained in soy sauce and hot sauce. Vinegar and lemon juice can be used instead of seasonings.
√ If you feel hungry during calorie control in diabetes, you can eat more low-calorie, high-volume foods in moderation such as 25 grams of rice can be replaced with 100 grams of yams or 200 grams of corn on the cob or 500 grams of pumpkin.
√ When blood glucose control is stable, you can eat a moderate amount of fruits such as apples, pears, grapefruit, strawberries and other fruits with low sugar content between meals.

Common dietary treatment myths:
* :: If you don't eat staple foods, your blood sugar won't rise
Just because carbohydrates are more likely to cause a rise in blood sugar than proteins and fats doesn't mean that proteins and fats don't cause a rise in blood sugar.
* :: No porridge for diabetics
You need to reduce the amount of rice, and at the same time, you can add some miscellaneous grains and vegetables into it, such as millet, oats, vegetable leaves, etc.. Do not boil porridge for too long, so as not to overcook it to cause a rapid rise in blood sugar.
* :: Sugar-free foods can be eaten at will
Sugar-free foods just use sweeteners to replace sucrose, fructose, etc. as additives, but still contain more carbohydrates, eating more can still raise blood sugar.

* :: The smaller the meal, the better for a diabetic.
A diabetic diet is not a starvation diet; it must fulfill the body's energy requirements for daily living. Starvation alone to lower blood sugar can also cause serious acute complications of diabetes such as hypoglycemia and ketoacidosis.
* :: Mixed grains are low in sugar and can be eaten more often
The sugar content of grains is not low, 1 two green beans or 1 two old corn sugar content is similar to 1 two rice. Therefore, miscellaneous grains can be eaten, but also to control the amount.
Let's start with the fruits you can eat:
Cherries, plums, peaches, apricots, apples, pears, blueberries, strawberries, grapes, poppies, mangosteen, oranges, tangerines, grapefruit, pomegranate, guava, dragon fruit, kiwi, mango, papaya, pineapple, watermelon, cantaloupe, cantaloupe, lychee, longan and others.
The above low-calorie fruits basically cover more than 80% of the amount of fruits consumed on a daily basis.
Let's take watermelon as an example, it has a glycemic index of 72 (Daily Fruit Glycemic Index table attached), which is already high among fruits. Its carbohydrate content is 6.8%, calories per 100 grams are 31 kcal, and the glycemic load GL is:
6.8*72/100=4.869.
A blood sugar load of less than 10 is a low GL food. Right now watermelon's GL is less than half that yet, at 4.869!
If people with high blood sugar are unsure, they can eat watermelon between meals, 50 grams at a time for a taste (it's just a big bite), and it has very little effect on their blood sugar.
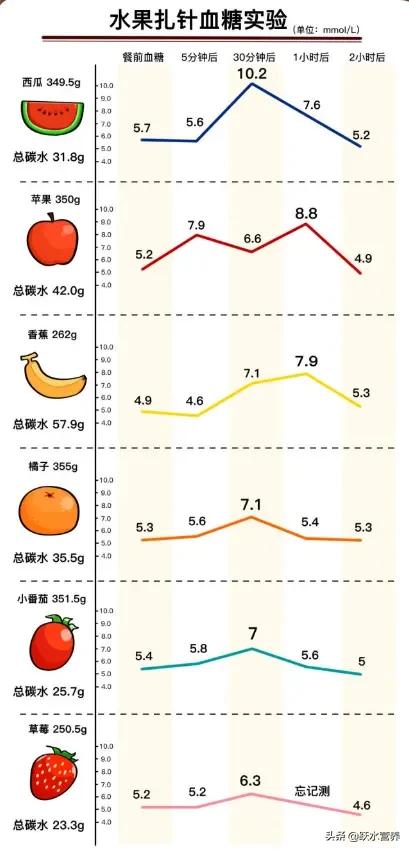
Some netizens measured the blood sugar response of various types of fruits, generally apples, pears, watermelon, etc. to eat to 200-300 grams, blood sugar will have more obvious adverse fluctuations.
This came as a surprise to the diabetic population who are entrenched inside the notion that they can't eat fruits!
Why is that? Because although watermelon is sweet, its carb content, at 6.8%, is only a quarter of that of rice, and it's eaten sparingly.
Fruits to be consumed with caution (in kcal/100g):
Bananas 93, plantains 115, pineapple nectar 105, fresh dates 125, and pretty much any fruit juice.
Bananas and plantains, because of the amount of starch they contain, can be used as a staple food for diabetics to replace some of the rice and pasta staples.

Several of the above foods are relatively high in calories. Pineapple honey, for example, has 25.7% of carbohydrates, a sweet taste, and a glycemic load per 100 grams that must not be low!
Fruit juices are digested and absorbed very quickly and are easy to drink in large quantities; if you add sugar, it will be very unfriendly to your blood sugar.
Fruits that are basically not considered for consumption:

Avocado 160, Coconut 241, Dried Cinnamon 277, Orange Cake 371, Persimmon Cake 255, Dried Mulberry 298, Sea Buckthorn 120, Dried Apricot 338, Dried Dates 276, and all other kinds of dried fruits.
The above fruits, calories are super high, diabetic people, or do not eat for good.
Sugar lovers can consume 50-100 grams of daily fruits at a time, no more than 3 times a day, provided that their blood sugar control is relatively stable. It is generally recommended to consume it when blood sugar is low, between meals or after exercise while monitoring blood sugar.
Fruits taste good and are a good source of plant compounds, minerals, vitamins, and dietary fiber, which are indispensable in the recipes of sugar lovers!

We first need to make one thing clear: diabetics can actually eat all the fruit, just the amount of more or less of the problem, there is no fruit that can not be eaten, unless the normal people can not eat, then let me answer for you in detail!
In order to facilitate the explanation, first to popularize the concept of glucose generation index (GI), must be a lot of sugar friends have heard, have not heard of me in passing, because glucose is the strongest ability to raise blood sugar, we will see it as 100 points, other foods through the glucose and glucose comparison, you can get the corresponding score, that is, their own glycemic index, we usually eat rice, pasta, and other staples GI value in about 80, and common fruits are far below this value, specific you can own Baidu, so as long as you can eat the staple food, you must be able to eat fruit, can eat any fruit!
At the same time, it should be noted that everything must have degrees, although the fruit can eat, but do not eat more, in order to be safe, try to choose the GI value of the fruit is relatively low, specifically what are the fruits, the phone on the map is not very convenient, we know Baidu!
Finally, we remind all the sugar users, usually try to read some regular websites and more authoritative public numbers, do not be deceived by some specious articles!
Impaired Islet Cell SecretionThe number of human islet cells is fixed from birth and cannot be regenerated, if damaged apoptosis occurs.
The remaining cells will have to take on more secretion tasks, like three people to complete the workload of five people, can not guarantee the secretion of sufficient insulin, and may continue to have apoptosis, the number of pancreatic islet cells continue to decline, diabetes continues to worsen.This type of diabetes is commonly known as type 2 diabetes.
What are the symptoms of type 2 diabetes?
1、Multiple urination, irritable thirst, and excessive drinking
Due to diabetes, urine osmolality increases and tubular reabsorption of water decreases, urine volume increases. Patients urinate frequently, more than one day and night can be more than 20 times, many times at night to get up, affecting sleep. Not only each time more urine and urine frequency, the total amount of urine a day is often more than 2 to 3L, occasionally up to more than ten liters. Due to polyuria and water loss, patients suffer from thirst, drink more water and the number of times, can be directly proportional to the concentration of blood glucose and the amount of urine and loss of sugar; when the lack of insulin and ketoacidosis, sodium and potassium ions back to the absorption of the more difficult, aggravated by polyuria; often plasma concentration, affecting the osmolality, which can be brewed into a hyperosmolar coma and other serious consequences.
2、Hungry and hungry
Due to the loss of sugar, sugar is not fully utilized, accompanied by high blood sugar to stimulate insulin secretion, appetite is often hyperactive, easy to have a sense of hunger, the staple food is sometimes up to 1 ~ 2 pounds, more than double the dishes than the normal, can not be satisfied. However, if the patient's appetite suddenly decreases, attention should be paid to whether there is infection, fever, acidosis, or ketosis has been induced and other complications. Polyuria, polydipsia and polyphagia are often clinically referred to as "triple polydipsia".

3. Fatigue, weight loss, weakness
As a result of metabolic derangement, decreased energy utilization, negative nitrogen balance, loss of water and electrolytes, and worse in ketosis, patients feel fatigued and weak. Especially in young (type I) and severe (type II) patients wasting significantly, weight loss can be up to tens of pounds, the labor force is often weakened. Young children with chronic disease have inhibited growth and development, short stature, yellowish face, less shiny hair, and weak physical strength. However, patients with type II mild disease above middle age are often obese due to overeating.
4、Itchy skin
Most common in women, due to urinary sugar stimulation of the local cause. Sometimes complicate Candida albicans and other fungal vaginitis, itching is more serious, often accompanied by leukorrhea and other secretions. Dry skin after water loss can also occur generalized itching, but less common.
5. Numbness of hands and feet
Diabetes can cause peripheral neuritis, which is characterized by numbness, pain, and a burning sensation in the hands and feet, as well as the sensation of walking on cotton. The incidence of peripheral neuritis is higher in the later stages of diabetes.
What fruits should I avoid if I have type 2 diabetes?
1. American Raisin
In fact, raisins for ordinary people, the nutritional value is very rich, you can eat a little more, but for diabetic patients, is determined not to eat, because raisins sugar content is high, ten raisins calories equivalent to the calories of two rice, so diabetic patients must not eat.
2、菠萝, 芒果
Pineapple and mango are common tropical fruits, but they are high in sugar, and although they are rich in vitamins, they are not recommended for diabetic patients, but they are more likely to cause allergies, so allergy sufferers should eat with caution. Pineapple and mango macerated in salt water and eaten, and can not reduce the chance of allergies, but only to improve the taste.
3、Chilean Chelsea
Sugar, rich in sugar, protein, vitamins and calcium, iron, phosphorus, potassium and other elements, the amount of iron in the fruit in the top, is iron, good for the brain, diabetic patients should not be greedy.
4. Dragon Fruit
Rich in vitamin b1, b2, b3 and vitamin c, carotene, anthocyanins, and contains calcium, phosphorus, iron and other trace elements and soluble dietary fiber, can prevent constipation, help laxative, also as "weight loss fruit". However, due to the natural glucose contained in easily absorbed, diabetics should not eat more than one meal. Have gastrointestinal dysfunction, easy to diarrhea people, should also eat less.
5. Sakya
Each 100 grams of Sakya can contain 15.3% to 18.3% of total sugar and 265mg of vitamin C. Due to the sweet taste of Sakya, the sugar content is high. Diabetic patients should eat with caution.
6. Durian
It is not high in protein or fat. The raw glycemic index is about 42, which is not very high, but 2/3 of the ingredients contained are sugar. For people with high blood sugar, high or low blood pressure, poor cardiac function, gastrointestinal ulcers, eat durian still need to be cautious, it is best to reduce the amount of meals before eating durian, so as not to intake of calorie overload, aggravate the original disease.
Extended reading: daily life in the control of blood sugar, I hope you do the following points~
I: Eat foods with selenium often to lower sugar and prevent complications
Selenium can protect and repair pancreatic islet cells from damage and maintain normal insulin secretion. Medical experts remind: Nutrition, repair of pancreatic islet cells, restoration of pancreatic islet function, so that it regulates its own blood sugar is the fundamental treatment of diabetes.
Which daily foods have selenium? Exposure to all kinds of seafood, animal liver, red meat, etc., a small amount of nori, kelp, mushrooms, but also, but selenium content of meat, offal, etc. to eat more than one is very easy to cause gout three high symptoms, so you also need to avoid.
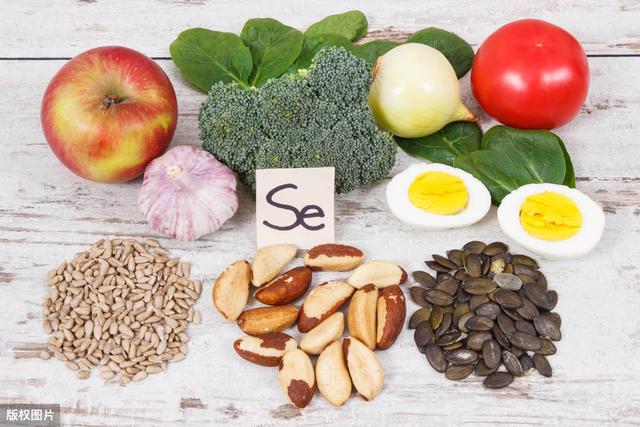

So you can also choose some crops from our selenium-enriched areas, such as selenium-enriched rice, selenium-enrichedZiyang! Hair! SharpWait a minute.
Eat some when you cook or put some in your drinkZiyang! Hair! Sharp, are simple and high in selenium, plus there are many fakes on the market, the best ones to drink are certified by National Landmarks.
Two: It's important to eat right
regularity of meals
Eat regularly, especially breakfast must be eaten. Eating breakfast is a great way to control your blood sugar. For breakfast, choose whole grain breads, yogurt, and low-fat cheese.
If you do not eat breakfast is easy to trigger hypoglycemia, because people a night metabolism, about 8-10 hours without myopia, blood sugar is at a low level, this state of activity blood sugar continues to fall, easy to fatigue, cranky, unresponsive and so on.
Secondly, skipping breakfast will lead to eating too much at lunch, which is not favorable to blood sugar control, and at the same time, it is easy to lead to obesity.

Eat your food before you eat.
One study showed that people with type 2 sugar, or pre-diabetes, who drank two tablespoons of vinegar before eating their main meal (i.e., carbohydrates) had a lower postprandial blood sugar rise.
Eating some vegetables before eating also helps with blood sugar control.

Eat less fast food
In a survey of 3,000 18-30 year olds, it was found that those who ate fast food more than twice a week gained at least 6 pounds.
In other words, people who eat fast food on a regular basis are prone to obesity and are equally prone to diabetes.

Three: Exercise in moderation, don't be lazy!
Studies have shown that people who are sedentary for long periods of time have a two times higher risk of diabetes, heart disease or premature death than those who are active.
Therefore, moderate exercise can prevent and delay the onset of diabetes.
Exercise guidelines for diabetes control recommend following the "1357" principle:
Specifically, no less than 30 minutes of exercise on 1 occasion and no less than 5 times per week;
The intensity of exercise should be warm, sweaty but not profuse, and the pulse rate should be controlled at: (170-age), so that the exercise is effective and safe.
Exercise for diabetics is best done by walking, preferably 1 hour after a meal.

Four: Don't stay up late and make sure you sleep
Staying up late can lead to endocrine disruption, abnormal biological clocks, and lowered body immunity.
Moreover, staying up late can also lead to increased fluctuations in blood glucose, which is a cause of increased blood pressure, increasing the burden on the heart and blood glucose, thus inducing the production of diseases.
Those with high blood sugar are more likely to get enough sleep to promote the body's repair function.

V: Get regular checkups, don't ignore
Sugar lovers, in addition to self-monitoring of blood glucose changes, should also do some related tests, such as fundus examination, insulin, glycated hemoglobin, etc..
A lower extremity vascular nerve detection test is also performed: stimulation of the toe bellies of the toes with a nylon wire can screen for neuropathy.
Regular checkups will help to detect complications early and treat them early with better results.
We still have to correct a point of view, there is no food that diabetic patients can not eat, it is only to grasp a degree! Fruits with a low glycemic index and glycemic load, we can eat a little more, and fruits with a high glycemic index and glycemic load we can eat a little less. As shown in the picture below, you are welcome to forward the collection!
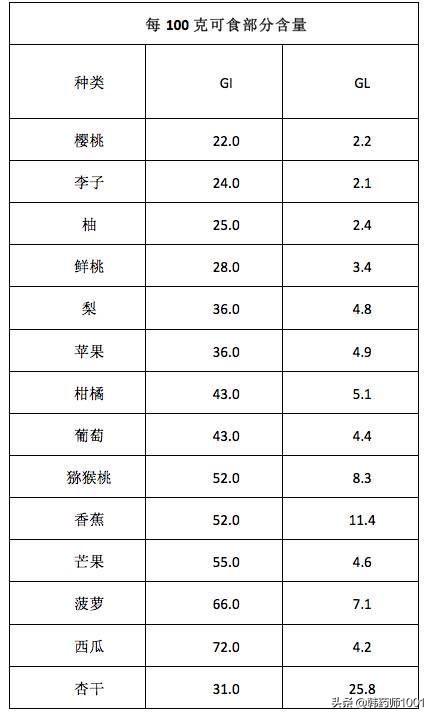
It lists the glycemic index and glycemic load of our common fruits!
What is the glycemic index? It is important to know that the speed at which carbohydrates in fruits can be absorbed and utilized by the human body is determined by the rate of digestion in the gastrointestinal tract, as fruits contain both polysaccharides and monosaccharides, and the former need to be degraded to monosaccharides in the digestive tract before they can be absorbed and utilized by the human body. In turn, blood glucose levels affect the body's insulin levels after the food has been ingested by the body, so how do we go about studying and determining the effects and relationship between the two?

In 1891, the concept of the 'glycemic index' (GI), which is is the rate at which carbohydrates reach the bloodstream, was introduced by Jenkins to address these issues.

The glycemic load (GL) is also derived from the glycemic index. When people refer to the glycemic index of different foods, they often overlook the fact that the degree of blood glucose elevation after eating is also related to the total amount of food intake, as the latter determines the total amount of carbohydrates consumed by the body. Therefore, medical experts have introduced the concept of 'glycemic load'. When we calculate the glycemic load, we have to consider both the glycemic index of the food and the amount of food consumed, which leads to the following formula
GI×absorbable carbohydrate÷total intake≈GL
In conclusion, the major difference between the glycemic index and glycemic load is that the former can only indicate the rate at which a food raises blood glucose, whereas the glycemic load measures both the type of food as well as the amount of food consumed, and it can indicate the extent to which a food raises blood glucose.

To summarize: like cherries, plums, grapefruit, cactus, pears, etc., these fruits have low glycemic index and glycemic load and can be eaten appropriately and more often, but like watermelon, pineapple, mango, etc. have high glycemic index and should be eaten less or not eaten! We recommend fruitsConsumed between meals, this will not cause blood sugar to rise too high and is in line with our principle of smooth sugar control!
Purely handwritten, I hope my answer was helpful! If you think the writing is okay, please like and follow!
Fruit is a very common food in daily life, it is very important for human health, not only can replenish trace elements, water, vitamins and other nutrients, but also the effect of beauty and skin care. As we all know, there are many varieties of fruits, suitable for most people to eat, but some fruits have high sugar content, type 2 diabetics are not suitable for consumption.

In general, diabetics have certain dietary requirements, and type 2 diabetes, also known as adult-onset diabetes, mostly develops after the age of 35 to 40 years, accounting for more than 90% of diabetics, and the control of sugar content is even more so. If you have type 2 diabetes, there are some fruits that are not suitable to take, as follows:
I. Raisin. Raisin skin and raisin seeds contain antioxidant substances, cardiovascular disease has a preventive effect, but its sugar content is high, ten raisin calories are equivalent to the calories of two rice, diabetic patients should not eat more.
Second, pineapple, mango. These are common tropical fruits, high glycemic index, diabetic patients should not eat more, the two belong to the same allergenic food, allergic people just touch the peel, may also be allergic.
Three, dragon fruit. Universal micronutrient deficiencies, can be used to reduce constipation, but the sugar in it is easily absorbed, diabetics a can not eat more.
Fourth, durian. 2/3 of its content is sugar, for people with high blood sugar, high or low blood pressure, poor heart function, gastrointestinal ulcers, eat durian still need to be careful.
In short, perhaps most people think that because the fruit is sweet, they dare not eat, can not eat, but if the blood sugar control in 7.8 mmol / liter can be eaten, but pay attention to control the amount. In daily life, diabetics should also develop a good habit of eating less sweets, snacks and more exercise in order to help alleviate the condition.
Follow "Family Doctor Online" headline, more health Q&A easy to see~~~~
Dr. Duan Q&A Online 🔑Diabetics, the right way to eat fruits 🔑
Many diabetic patients will think: fruit so sweet, certainly rise blood sugar particularly fast, can not eat. In fact, this point of view is not right. Diabetic patients can eat fruit, any fruit can, but to pay attention to certain ways and means, both do not raise blood sugar and can eat the fruit.

Diabetics, the right way to eat fruit:
①Fruit is eaten when blood sugar control is stable. Because if the blood sugar control is not stable, you do not know whether the fruit is appropriate to eat, should eat, can eat how much, need to add or subtract hypoglycemic drugs and so on. In order to better guide the use of medication, you should start to eat fruit after blood sugar control is stable, and then according to blood sugar, to see which and how much fruit is most suitable for you to eat, which will have the least impact on blood sugar.
② Eat fruit between meals, such as around 10 am and 3 pm. This is so that you don't eat the fruit right after the meal, which makes your blood sugar too high after the meal and affects the amount of main food.

③It is better to eat a quantitative amount of fruit every day for better blood sugar control. We take different amount of fruits as one portion and can only eat one portion per day, for example, the amount of fruits eaten per day is 500g of watermelon.
④Different fruits, because of the different sugars they contain, are eaten in different amounts every day. For example, 500g of watermelon = 300g of strawberries = 250g of oranges, pears = 200g of apples, pineapples, peaches, plums, oranges and kiwis. Such a serving of fruit will probably provide the body with 90kcal of energy, which is equivalent to eating 25g of rice.
⑤ It is best not to replace fruits with fruit juices, because fruit juices usually have the dietary fiber removed from them, and instead do not have the nutritional value they are supposed to have.
(6) It is best to choose fruits that are in season, so that they contain more water and have less impact on blood sugar.

Dr. Duan specifically warned:
(1) Fruits are rich in nutrients and are actively recommended for diabetic patients.
(2) I met a diabetic who purchased a kitchen scale for himself, and the food he ate every day was calculated. This level of meticulousness may not be possible for many people, but at least you can get a general idea, and it's okay to be not too far off from the standard.
👇 Follow Dr. Duan for health and wellness! 👇
Most fruits are high in sugar and are recommended to be eaten sparingly. If you usually have poor blood sugar control, it is recommended that you try not to eat them. In the case of better blood glucose control (glycated hemoglobin less than 7.5%, fasting blood glucose control in the morning between 5 to 9 mmol / L, 2 hours after the meal blood glucose control below 12 mmol / L, can be recognized as a relatively good situation) is allowed to eat some fruit. Fruits should not be consumed immediately after meals, but are recommended between meals to prevent postprandial hyperglycemia and to relieve fasting hypoglycemia. The types of fruits are recommended to prefer cucumber, pear, kiwi, strawberry, lemon, plum, hawthorn, olive, poppy seed and other fruits that have less impact on blood sugar. Persimmons, red dates, and dried cinnamon are recommended to be best avoided. Lychee and banana are also fruits that have a greater impact on blood sugar, with about 3 taels producing calories equivalent to those produced by 25g of rice (90 kcal, 1 unit, about half a bowl of porridge). Eat 2 to 3 lychees and half a banana at a time. You can have one intake in the morning and one in the afternoon. Peaches, apples, tangerines, oranges, grapefruit, apricots , grapes, guavas, etc. about 8 taels produce calories equivalent to 25g of rice. Apples can be eaten 1/4 to 1/3 at a time, twice a day.
In addition, some people will treat nuts as fruits. Most of the nuts contain high fat, calories are relatively, it is recommended to try not to eat. 15g of walnuts, almonds, peanut rice, pistacchio, macadamia nuts produces calories comparable to 25g of rice, calories are higher than rice. 25g of sunflower seeds (shelled) calories are comparable to 25g of rice. 40g of watermelon seeds (shelled) calories are comparable to 25g of rice. That means eating 3 walnuts is equivalent to eating half a bowl of porridge. So nuts should be eaten less, if you want to consume, the main food should be reduced accordingly, to maintain the stability of the day's calorie intake.
The authoritative interpretation of Pharmaceutical Affairs, unauthorized reproduction, plagiarism will be punished.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.