Almost a month after the heart stent, but still have panic attacks, sometimes vague slight pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, upset, is this normal and what should I do?
I have encountered a lot of this situation in my work, you do not have to worry too much, this is the stage reaction after stenting, usually occurring within a few months after stenting surgery, the main performance are like stenting before the onset of coronary heart disease reaction.
Several male patients like you have come to the emergency room with angina-like symptoms within a month or two of stenting, and our EKG and cardiac enzymes were fine. Logically, the narrowed coronary artery has been dilated by the stent, and it is unlikely that angina will recur in the short term with regular oral medication.
The reason for this phenomenon I think is still related to the stent put in, after all, for the blood vessels, and then a good stent it also belongs to the "foreign body", it is not the body's own outgrowth, this thing is supported in the blood vessels will always be on the blood vessel wall and the cardiac nerves to produce some effect, but these effects will not be a big deal, or else no one would dare to do! Stents. Once the body adapts to the stent, the symptoms usually stop appearing in a few months to a year.
The above is just my personal analysis, because the patients encountered are nothing so did not too in-depth study of these manifestations do not need to be nervous, regular medication for a period of time will be good.
Hi everyone, I am a cardiovascular physician and I have encountered many of these patients in the hospital!
There are two simple cases: one is a problem with the heart itself, and the other is a non-heart cause.
I. Problems with the heart itself
Even if it's a cardiac cause, there are two types of cases: one is stent-related, or cardiovascular stenosis-related, and the other is not related to stents in any way, other cardiac problems.
1. Heart stent related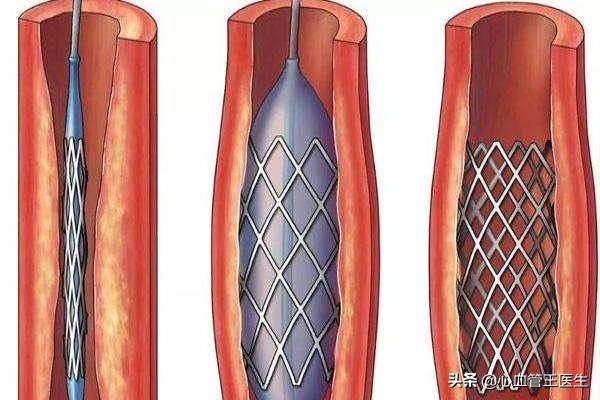
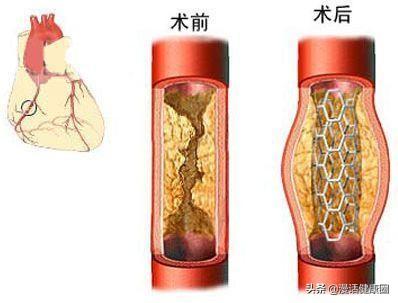
We should never feel that all is well after having a stent. The task of a cardiac stent is to shore up very severe stenosis and restore normal blood flow to a previously narrowed or occluded vessel. When the stent is implanted into the human blood vessel, the most basic task of the stent is also completed. Cardiovascular disease, on the other hand, will not be cured by the implantation of a stent because coronary heart disease cannot be cured at this time.
There are risks after stent placement itself, such as acute in-stent vascularization and in-stent restenosis, neither of which can be 100% avoided at this time.
The study showed the incidence of myocardial infarction, re-stenting or bypass, or death from heart disease within 5 years of stenting: 24.1% for implantation of bare-metal stents; 17.9% for first-generation drug-eluting stents; and 13.4% for second-generation drug-eluting stents.
Within 1 year of implantation of the most advanced stents available, 5.3% will have a myocardial infarction, have another stent or bypass put in, and die of heart disease; within 5 years, 13.4% will do the same.
Part of the reason for this outcome is the stent itself, and a large part is because the patient does not take their medication regularly, live a healthy lifestyle, or have regular reviews.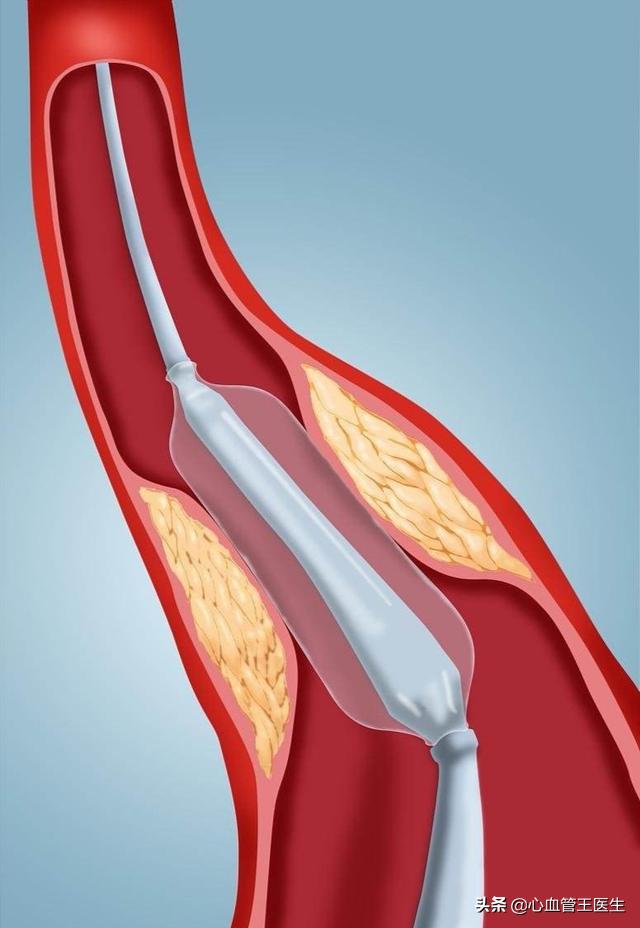
Aspirin and statin must be taken regularly for a long period of time, one year to one and a half years of tegretol or clopidogrel, as directed by your doctor.
Heart rate is controlled at about 60 beats, blood pressure is controlled at about 120/70, especially lipids, LDL is below 1.8, and blood glucose is normal;
Stop smoking and drinking, exercise properly, eat a low-salt, low-oil, low-sugar diet, control your weight, avoid staying up late, and reduce stress;
Regularly review routine blood tests, liver and kidney functions, electrolytes, blood glucose, lipid profile, creatine kinase, electrocardiogram and cardiac ultrasound.
Doing these 3 things will keep the blood vessels open and the stent clear.
So, first you have to rule out angina caused by the stent itself, which can be diagnosed just based on symptoms and an ECG.
2. Non-stented heart problems
Although the stent, but above we said the stent can only solve the serious cardiovascular stenosis, but the heart is divided into several departments: water, circuit, walls, doors and windows, etc.; stents only the water is not smooth repair, but the heart of the circuit can also cause panic symptoms, such as various arrhythmias; heart failure can also cause panic and other discomforts; so it is recommended to take a 24-hour dynamic electrocardiogram and do a cardiac So it is recommended to see if it is an arrhythmia or heart failure problem by taking a 24-hour ECG and doing a heart ultrasound. If it is arrhythmia, then treat it according to the nature of arrhythmia, and if it is heart failure, then treat it according to the formal treatment of heart failure.
If there is no arrhythmia and it's not heart failure, then it's another cause, a non-heart problem.
II. Non-heart problems
Panic, sometimes vague and slight pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, distraction, these manifestations, seemingly sound like a heart problem, just happened to have just had a stent, many people are more likely to think that it is caused by the stent. If you can rule it out by the above two points, you can prove that these symptoms are not caused by the heart itself. There are many reasons for panic attacks in the human body, such as vague pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, and restlessness; the most common ones are menopause, vegetative nerve disorders, insomnia, hyperthyroidism, and so on.
In short, after the stent heart panic, sometimes the heart vaguely slightly pain, fast heartbeat, upset. It doesn't mean that it is caused by the heart stent, and it doesn't even mean that it must be a heart problem. We have to find out the cause of the panic, sometimes vague and slight pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, and heartburn before we can know how to treat it.
So, first you have to inform your doctor about the symptoms in detail, get an ECG, or a 24-hour ambulatory ECG and a cardiac ultrasound.
Almost a month after the heart stent, but still have panic attacks, sometimes vague and slight pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, upset, please help? This question does represent a class of patients with coronary heart disease, especially patients with coronary heart stents put in, and many of them do have similar situations. So, how should we deal with these situations? Here's Dr. Zhang to give you a little insight into this issue.
In fact, for patients who still have symptoms of panic, vague pain in the precordial area, and fast heartbeat after cardiac stenting, you need to pay attention to 3 areas.
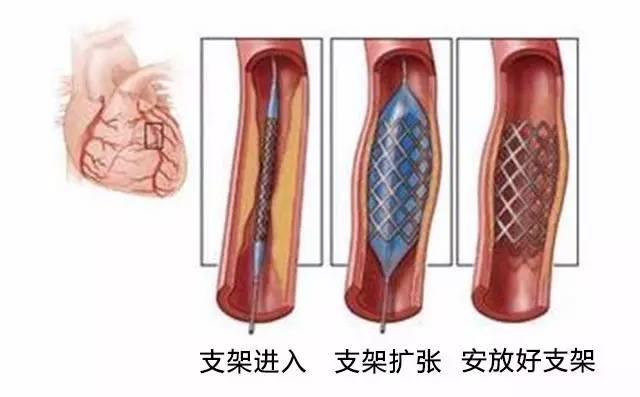
cardiac stent
1, pay attention to whether it is myocardial ischemia
For some patients after cardiac stenting who continue to experience discomfort such as panic and chest pain after the procedure, it is important to be aware if myocardial ischemia is occurring. Myocardial ischemia may be caused by restenosis at the stent site or ischemia at a site other than the stent. It is important to check the electrocardiogram (ECG) at the time of the discomfort to see if there is myocardial ischemia on the ECG. Of course, some people may not be able to have an ECG at the time of the attack, so they may need to have an exercise plate test, and some may even need a coronary CTA or coronary angiogram, depending on the specific situation.
2, pay attention to whether it is arrhythmia, especially to exclude malignant arrhythmia
For many people who have had stents put in their hearts, they are patients with coronary heart disease who have had myocardial infarction. For these people, special attention should be paid to regular postoperative Holter (ambulatory electrocardiogram) examinations, especially for patients with palpitations and rapid heartbeat, and even more attention should be paid to electrocardiograms and ambulatory electrocardiograms, in order to monitor the patient for the presence of malignant arrhythmias, such as atrial fibrillation, frequent short bursts of ventricular tachycardia, and other malignant arrhythmia occurrences. In severe cases of malignant arrhythmias, further specialized treatment, either by drugs or surgery, may be required.
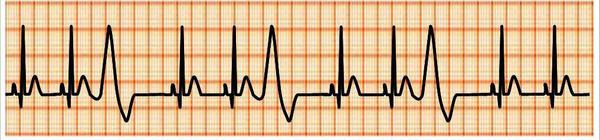
frequent premature ventricular contractions
3. Pay attention to heart function
For many patients who have had a stent put in their heart, whether it's a myocardial infarction or ischemic cardiomyopathy, many of them have impaired cardiac function, and that's when palpitations, chest discomfort, and in some cases, insufficiency of the heart may be the cause. Therefore, these people should regularly check the cardiac ultrasound, BNP test and monitor the heart function. If the heart function has been impaired, there is also a possibility that the medication regimen may need to be further adjusted.
In conclusion, for the majority of post-coronary stenting patients, it is important to pay special attention to the occurrence of some postoperative symptoms. The easiest way is to have an electrocardiogram at the time of the onset of discomfort, and in some cases a series of more tests may be needed to clarify whether there is a problem with this discomfort. For some people, after a series of tests have ruled out the existence of heart problems, there may also be excessive anxiety, muscle, nerve problems brought about by the discomfort, then you can go to the relevant departments in the consultation.

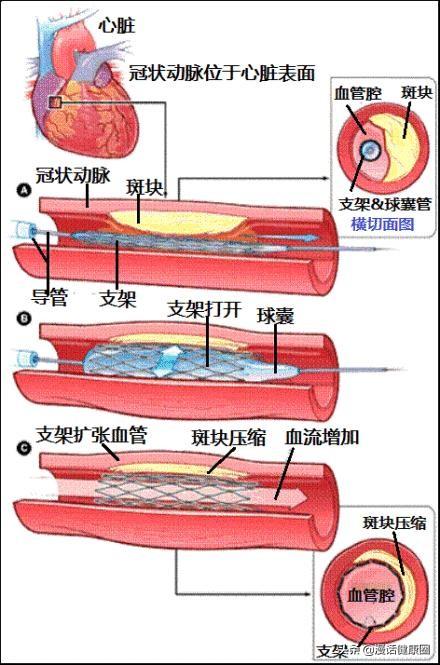
A cardiac stent can release the narrowing of the blood vessels in the heart and improve the symptoms of ischemia in the heart. But it does not treat a fast heartbeat. The most common cause of a fast heartbeat is arrhythmia. The common types of arrhythmia are as follows:

1, atrial fibrillation: atrial fibrillation is a disorder of the heart beat rhythm, is a kind of arrhythmia. In atrial fibrillation, the atrial frequency reaches 300-600 beats/minute, and the ventricular frequency is often fast and irregular, which can reach 100-160 beats/minute and is absolutely untidy. The atrium loses its effective contraction function, and cannot push the blood into the ventricle effectively. Atrial fibrillation will not only make the patient feel panic, shortness of breath, chest tightness, fatigue, and mental depression, which obviously affects his normal work and life, but also aggravates the existing symptoms of heart failure and angina pectoris; prolonged atrial fibrillation or frequent atrial fibrillation is also prone to lead to a stroke, resulting in hemiplegia.
2. Paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is a kind of intermittent episodes of fast and neat heart rhythm, referred to as "supraventricular tachycardia", which is more common in clinic, and is characterized by a sudden onset and sudden stop. It is characterized by sudden onset and abrupt cessation. During the onset, the patient feels that the heart beats very fast, as if it is going to jump out of the heart, which is very uncomfortable. The heart rate during an episode of paroxysmal supraventricular tachycardia is usually 150 to 250 beats per minute and lasts for a few seconds, minutes or hours, or even days.
3、Bradycardia or severe conduction block leads to a decrease in cardiac blood volume, vital organs and tissues, especially the brain blood supply is insufficient to produce a series of symptoms, which can be manifested as dizziness, blackout, fainting and other symptoms of insufficient blood supply to the brain; long-term bradycardia can also cause systemic symptoms, such as fatigue, palpitations, chest tightness, shortness of breath, double lower limbs or decreased mobility, and so on.
The question cannot be said to be positively abnormal!
The appearance or persistence of any abnormal symptom is an "abnormality" that must contain some pathological change or effect.
As for patients one month after stenting, the symptoms persist at this time, and the possibility of myocardial ischemia needs to be considered, and at this time, some patients may ask: "I don't all stenting and unblocking the blood vessels. The blood supply is restored, why is there still myocardial ischemia?
1, the body's blood circulation never relies on a single blood vessel, it often requires multiple blood vessels to work together. When a patient's blood vessels are stenosed and blocked, it refers to the stenosis of multiple blood vessels, and the stent resolves only one of them, or the most serious part of them, which also means that the stent does restore a certain degree of blood supply, but if the other blood vessels are too stenotic, it still will still be myocardial ischemia, so at this point the stent only improves the symptoms, not completely eliminates them.
2, in addition, there is another category of people in the clinic, their symptoms continue to be "self-seeking", they are delicate character like association, which is originally an advantage, but if the role of the disease is not good, because if the patient is in a long-term negative mental stress, it will make the nerves overly excited, blood vessel spasm contraction, further aggravate Myocardial ischemia, so for this group of people, even if the stent is done to expand the narrowed and blocked blood vessels, but because the blood vessels are still constantly spasmodic contraction, the blood supply will still be reduced, so there will be the emergence of related symptoms.
3, the patient may suffer from other diseases, many symptoms in the clinic are repeated with each other, so it is difficult to determine the disease by looking at the symptoms alone, if the patient suffers from other diseases at the same time, then even if the stent is done, but the other diseases are not treated, naturally there will still be related symptoms; and some of the diseases have an inducing effect, not only the same will lead to the patient to have panic attacks, chest pain, arrhythmia, and will aggravate Or even induce coronary heart disease, of which the typical is the spinal origin disease.

What should patients do at this point?
Words that never change:Before talking about treatment, you first need to confirm the diagnosis.
Used very appropriately here, any therapeutic intervention is not appropriate until the patient's problem has been identified and is likely to be counterproductive.
In this regard, the patient should first go to the hospital for a detailed diagnosis to determine the source of the symptoms, in order to be a good solution, do not believe in the advice given by some people off the cuff, it may indeed be possible, but the key is that it is impossible to determine, so it does not have any significance.

I hope my answer helps you!
If there's anything you don't understand, comment and private message me!
Recovery from stenting takes at least 3 to 6 months. Some of the postoperative sensations seem to be related to psychological factors. Listen to your primary care doctor, the doctor who put the stent in you has the best idea of the condition of the blood vessels where the stent was placed. So do your checkups, take your meds, live your life with an open mind, and don't worry about it. Live well and go to your doctor if you are sick.
Hello, I can tell you, my father-in-law the year before last in Shanghai East China Hospital to do heart stent surgery, good surgery in my home for six months, but in this six months time, he is often feel this stent is not support good ah, night recurrent insomnia, before and after the hospital review several times, the doctor also told him that the operation is very successful, but he is still insomnia, and even I have directly asked him to fear! I even asked him directly if he was afraid of dying, and he replied that he wasn't, but he still couldn't change his mind. Later returned to his hometown of Liaoning, back to his hometown with some of his friends to talk every day, not long after I called to ask him again, he said he had gained more than 10 pounds, lying down to fall asleep. It's been two years since his surgery, and he feels great now. In fact, after the surgery is done, there is a process of adaptation, mainly in the heart of this pass to pass. Don't doubt this and that. Everything will be fine if you have a good heart. In fact, how to persuade others are not useful, but also to mediate themselves. The main thing is to communicate with people, not online communication, appropriate exercise is essential. My father-in-law insists on a lot of road every day more than 5 kilometers.
Hi everyone, I'm Comic Book Guy and I'm happy to answer your questions!
Many people in the case of coronary artery blockage in the heart, will install stents, the operation results in good people, will be installed after the stent nothing, and there is no side effect, but there is also a part of the heart will be slightly hidden pain, heartbeat faster, upset and other phenomena, is this normal? Is this normal? I encountered such a case in the clinic.
XXX, male, 52 years old, 1 month after cardiac stent surgery. He complains of panic attacks with vague pain in the heart, a faster heartbeat, and occasional feelings of distraction. Meanwhile, taking aspirin and statins, which has been going on for a month, recently visited the outpatient clinic with the above self-report and asked the doctor if this is a normal condition.
I believe that many patients who have had cardiac stents have, to a greater or lesser extent, the concern that cardiac stents will have post-operative side effects.
In fact, if the patient is done with cardiac stent and can take the medication on time, there is a very good prognosis, but do not rule out that there will be an individual is the heart has a more serious lesions or stent-related problems, be alert to the following three situations:
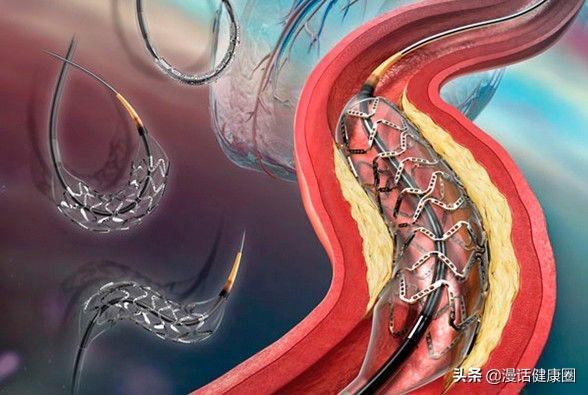
Clogged arteries from stents
The possibility of this kind of emergence is still relatively small, because the atherosclerosis caused by the blockage of blood vessels, resulting in the coronary artery blood is not good, and through the stent surgery, is to use internal medicine methods, in the narrow part of the blood vessels, put a special material made of stents, in general, put the stent is designed to expand the blood vessels, but once put the stent in a wrong location, there may be the possibility of arterial re-blockage.
myocardial ischemia
Many people think that all is well when a stent is installed. If the heart has symptoms of myocardial ischemia again, it is important to suspect that there is not the possibility of blockage of other blood vessels, and at this time there is the possibility of myocardial ischemia, and more importantly, in addition to the symptoms of myocardial ischemia, there is also the possibility of palpitations, heart pain, and other symptoms.
arrhythmia
After the stent procedure, further monitoring will be done, and if there is an arrhythmia in the heart, the accompanying symptoms are likely to be palpitations and heart pain. If this is the case, it is important to be aware that the problem is not due to the stent, but to other heart problems.
Excluding the above three reasons, we also have to understand that the heart stent may still be a foreign body to the body itself, installed in the blood vessels, or may cause the corresponding symptoms, the presence of this in the blood vessels, will stimulate the body to produce a certain response, which may trigger a "cardiac reaction", in fact, there is no great impact. In fact, there is no great impact, but in this case, we need to do some psychological guidance, especially after the operation, including before the operation, some patients may produce anxiety, which will invariably amplify the corresponding feelings.
Comic Book Review
If atherosclerosis occurs and the degree of severity is high, only when the heart stent will be considered, but after the heart stent is put in, the vast majority of people do not have obvious reaction, but do not rule out that there are individuals who have palpitations, heart pain and other side effects, if these side effects occur, you need to pay attention to whether there are other myocardial ischemia or cardiac disease related problems. In addition, after the installation of cardiac stents, it is necessary to follow the doctor's instructions, take medication on time, and not stop taking medication without authorization. It is also important to note that there is a need forTo low salt and low fat diet, eat more green vegetables, and actively participate in exercise. There is also the need to maintain a good state of mind, do not over-emotional.

Well, that's all for today's sharing, I'm Comic Talker, feel free to leave a comment and share if you have any questions.
Almost a month after heart stent, but still have panic attacks, sometimes vague slight pain in the heart, fast heartbeat, upset, please?
First of all, this is quite normal and, generally, this phase reaction occurs for a few months after the installation of a cardiac stent. Recovery from this type of surgery usually takes at least 3 months, and this may lessen when the condition stabilizes after some time.
On the other hand, after the installation of cardiac stents does not mean that all is well with the patients. It is important to know that there is no cure for coronary heart disease, and even after the installation of stents, within one year after the implantation of the most advanced stents, 5.3% of the people will suffer from myocardial infarction, have stents or bypasses put in again, and die of heart disease; and within five years, the above will happen to 13.4% of the people.
Apart from this, the occurrence of such a condition is also related to the habits of the patients themselves. If the patient does not take his medication regularly, does not live a healthy life, and does not have regular check-ups, then the chances of the above situation are very high.
After the stent surgery, you should also still follow the doctor's instructions, take your medication on time, stop smoking and drinking, pay more attention to rest in general, and have regular check-ups, so that you can avoid the risks as much as possible.
The Health Interface provides healthcare hotspots, policies, perceptions, opinions and interesting popular science content to 13 million healthcare practitioners and the broader health community every day, and looks forward to your every share and interaction.
There are a couple of special cases among the patients I have come in contact with that I would like to share with you in the hope that I can help you through their cases.
Case I;
He is a seventy-nine-year-old man, male, retired cadre, his home is living next to the Cardiovascular Hospital. One day near the Chinese New Year, the old man suddenly felt tightness in the chest and shortness of breath, and pain in the heart, the old man's family rushed to bring him to the hospital. Through CTA examination, it was found that the old man had thrombosis in his cardiovascular system, and an angiogram had to be performed immediately to see if it was necessary to put a stent. The old man and his family were very cooperative.
In the process of angiography, we found that the old man's blood vessels had three serious blockages and had to be put into stents. Considering the old man's age, we communicated with his family and put one stent in for the time being, and dealt with the other two blockages after the Spring Festival in two months. After the stent was put in, the old man first relieved the pain and shortness of breath, and the next day the old man was able to move around in the building, and there was no pressure on the old man from the outside.
Shortly after the Chinese New Year, the old man and his family came to the hospital again with the intention of putting down the stent on the two blockages. Through the whole body examination of the old man, we prepared to put the stent on the old man for the second time, and with the first experience, the old man was more frank this time. In the morning, after the surgery, the old man had to get out of bed, but in the evening, the old man had symptoms of discomfort, panic, premature heartbeat was very serious, but the important thing is that the old man's mind is very good, the mood is very stable not long before the old man's heart stabilized, and we observed the old man's heart for a night before he put it down. Later this old man has been quite stable.
Case 2
Zhang Mou, male. National cadres, fifty-four years old, health has been good with thirty years of smoking history. When Zhang came to the hospital, we were shocked when we saw him, his face was dark and he had chest pains one after another, seeing his condition we immediately carried out the necessary examinations on him and found that there was a blood vessel blockage. Through the contrast surgery, we found that Zhang's blood vessel blockage is not the root cause of his pain, mainly his heart has a small section of myocardial bridge, we suspect that it is this place is the cause. Sure enough after the stent although relieved his chest tightness, but still have irregular pain feeling. To later through the drug conditioning to a month later to control his pain feeling. Through the onset of Zhangmou completely quit smoking and have a good habit, is to insist on walking exercise every day. Now Zhangmou more than a year from no discomfort phenomenon, the drug has been reduced to two through various tests.
With these two pathologies, I want to tell you that a good mindset and the right exercises are a great help in curing the disease.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.