What will be the result of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time?
I am a level III senior pharmacist and based on my experience in clinical medicine, let me answer this question.
Hypertension is currently the world's highest prevalence of a class of chronic diseases, what is high blood pressure, to say very simple, can be through the existing electronic sphygmomanometer or mercury mercury sphygmomanometer, through the repeated and correct measurements, if found that the systolic blood pressure more than 140mmHg, diastolic blood pressure more than 90mmHg, can be considered to exist in high blood pressure disease. Hypertensive disorders can be categorized etiologically into primary hypertension and secondary hypertension.
Primary hypertension is the main group of disorders, accounting for 90-95% of patients with hypertension, often with no detectable cause and requiring lifelong medication.
Secondary hypertension often occurs as a result of conditions such as kidney disease, endocrine disease, aortic disease, or poor sleep apnea, and the blood pressure can return to normal after the cause of the condition is removed.
What will be the result of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time?
Long-term use of antihypertensive medication inevitably has side effects, but it does not develop resistance; it is not like antibiotic medication, which carries the risk of resistance.
"Clinical antihypertensive drugs are divided into a total of five categories: the first category, diuretics, diuretics antihypertensive principle is to reduce blood volume, because the application of diuretics after the patient's urine volume will increase, the body's blood volume will be reduced, the blood for blood vessel pressure will be reduced, so the blood pressure will be reduced.
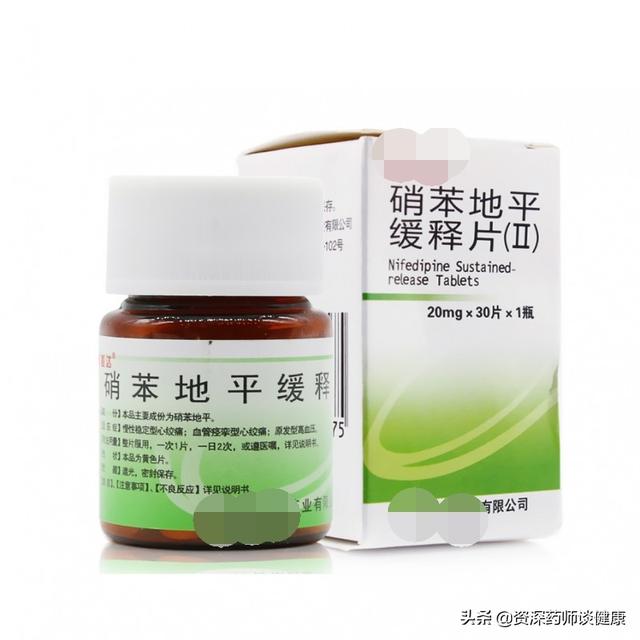
The second category, calcium channel blockers, such as nifedipine, the antihypertensive principle is to dilate blood vessels.
The third category, beta-blockers, treats hypertension on the principle of reducing sympathetic excitability.
The fourth category, ACEI class (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), the main representative of the drug for captopril, mainly through the inhibition of angiotensin-converting enzyme to play the role of lowering blood pressure.
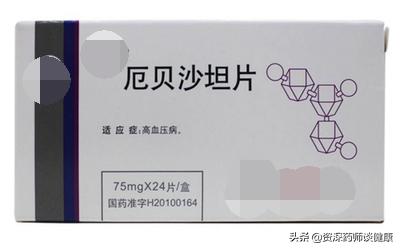
The fifth category, ARBs (angiotensin antagonists), such as irbesartan and valsartan, achieve antihypertensive effects primarily through angiotensin ll receptor antagonism.''
So these five main categories produce side effects, summarized below according to the clinic:
In the first category, thiazide diuretics are not suitable for hypertensive patients with combined gout because they may cause hyperuricemia. In addition, long-term use of thiazide diuretics may lead to water and electrolyte disorders, producing hyponatremia, hypochlorhydria and hypokalemia. Since thiazide diuretics can inhibit insulin release and glucose utilization, it can increase blood glucose, so it is more important to pay attention to blood glucose changes in hypertensive patients with diabetes.
In the second category, the common adverse effects of calcium channel blockers are dizziness and headache, followed by a feeling of fever, redness of the face, edema of the feet and fluid retention, which are actually widespread vasodilatory effects. Adverse reactions usually appear 1.2 weeks after the drug, and then gradually subside, usually side effects occur without stopping the drug. Animal experiments have potential teratogenic effects, so women of childbearing age are advised to use contraception during the medication phase. In addition, a few reports nifedipine can cause hepatitis, hyperglycemia and so on.
In the third category, beta blockers can cause insomnia, produce depression, make patients fatigued, gain weight, and can cause headaches, dizziness, and nausea.
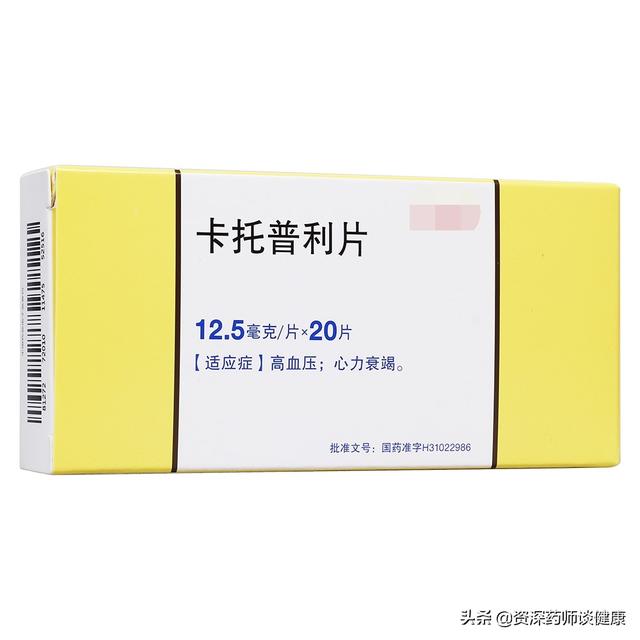
The fourth category, ACEI class (angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors), 1, and angiotensin Ⅱ, aldosterone generation is blocked side effects related to low blood pressure, transient proteinuria, hyperkalemia, sinus bradycardia, headache, etc., with the prolongation of the time of use of the drug, these side effects quickly disappeared, generally do not have to deal with. 2, and bradykinin, prostaglandin activation-related side effects of vasoneurotic edema, dysphagia The side effects related to bradykinin and prostaglandin activation include angioneurotic edema, pharyngeal discomfort, irritating dry cough, hoarseness, eructation, etc. Angioneurotic edema should be discontinued in time and irritating dry cough is common, which can be alleviated and disappeared with the prolongation of the medication time. Captopril contains sulfhydryl group can cause granulocytopenia, loss of taste or loss, allergic dermatitis, transient proteinuria, skin itching, fever and so on. Second-generation ACEIs such as elapril do not contain sulfhydryl groups have no side effects in this regard, alopecia, gynecomastia, teratology and so on, but they are rare.
The fifth category, ARBs (angiotensin antagonists) have common adverse effects such as panic, chest pain, bloating, constipation, myalgia, headache, insomnia, dizziness, dry cough, dyspnea, rash, anemia, and hyperkalemia.
Although long-term antihypertensive drugs have side effects, but people medicine weigh the pros and cons, if the efficacy of the medication is greater than the side effects of the medication, then it is necessary to take scientifically, to avoid the phenomenon of serious medication rebound. Even some side effects are not very influential, can be completely ignored, do not have to worry. Any problems go to the hospital in time to see a doctor, do not delay the condition.
These are my insights, please pay more attention to the senior pharmacist engaged in many years of clinical, remember to like plus attention! Thank you!
When it comes to long-term antihypertensive drugs, many hypertensive patients are more distressed, they always feel afraid of not eating if the blood pressure is out of control, induced complications, while eating is also worried about drug side effects. Although hypertensive patients have always been recommended to adhere to long-term medication, but the reality is that there are many patients, or because of the antihypertensive drugs appeared serious side effects , or obviously have been taking medication, but still failed to avoid the occurrence of complications. All these make hypertensive patients more confused.
What will be the result of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time?
In the clinic, often see such patients in the complaint, I am only 36 years old suffers from hypertension, now start taking antihypertensive drugs, will have to eat for several decades, by then will not die of disease, but instead of eating drugs to eat death! In addition, we often hear patients ask, long-term antihypertensive drugs will not hurt blood vessels, will not hurt the liver and kidneys, will not hurt the heart, etc., and so on and so forth because hypertensive patients are afraid of long-term antihypertensive drugs, think that long-term antihypertensive drugs are unimaginable consequences.

Why must people with high blood pressure take antihypertensive drugs?
Before answering the above question, it is important to be clear about the reasons why hypertensive patients must take antihypertensive drugs. At present, most of the clinical hypertension belongs to primary hypertension, accounting for more than 95%, that is, hypertension with unclear etiology, and because the pathogenesis of this type of hypertension is complex, the cause is complicated and difficult to find, so it is not possible to treat the cause, only symptomatic treatment.
The so-called symptomatic treatment can only lower the blood pressure through the use of medication, but can not eliminate the internal causes of blood pressure, and therefore can not cure high blood pressure. Symptomatic treatment refers to taking antihypertensive drugs to achieve long-term stability of blood pressure, to ensure that within the normal range of small fluctuations, so as to avoid high blood pressure on the target organ damage, and to prevent the occurrence of complications. However, the efficacy of drugs is limited, for antihypertensive drugs, even the most long-acting antihypertensive drugs, can only maintain the effect of lowering blood pressure for 24 hours, and after 24 hours, the drug is ineffective, blood pressure will soon rise again. Therefore, hypertension patients must adhere to the daily use of drugs, long-acting antihypertensive drugs once a day, medium-acting antihypertensive drugs twice a day, short-acting antihypertensive drugs three times a day.
What will be the result of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time?
In theory, the result of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long period of time must be good, because the drugs are used to save lives, and it helps patients to control their blood pressure and stay away from complications. However, it is a medicine that has three poisons, and drug side effects are one of the potential risks of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long period of time, while the wrong way of using the drugs is another possible risk. These two potential risks invariably increase the uncertainty of the outcome of long-term antihypertensive medication.
On the one hand, there may be some patients who are indeed intolerant to antihypertensive drugs, and to all antihypertensive drugs, and the consequence of this is that serious side effects may occur on long-term antihypertensive drugs, and even death may result, although this is extremely rare. Because the side effects of commonly used antihypertensive drugs on the market are clear and relatively mild, the incidence is low and most patients can tolerate them. Even if they do have an intolerance to one drug, there are other antihypertensive drugs available.
On the other hand, some patients may take medication for the sake of taking medication, only take medication without measuring blood pressure, do not manage their personal life, do not adjust their medication according to the progress of their condition, or take and stop taking medication and often forget to take it, all of which will result in the medication not being able to give full play to its effect, and will not be able to achieve the purpose of stabilizing blood pressure. The result can only be out-of-control blood pressure and invasive complications, a risk that occurs frequently and is the main reason for unfavorable blood pressure control in hypertensive patients.
Excluding these two outcomes, the consequences of long-term antihypertensive medication are inevitably good for most hypertensive patients. Moreover, the first risk is extremely rare, and the second is all in the hands of the individual patient. Overall, the benefits of long-term antihypertensive medication outweigh the disadvantages, which is why patients are required to take them.
It's worth looking at the other side of the coin to see what happens if high blood pressure results in no medication. This starts with the dangers of hypertension. The biggest danger of hypertension lies in its damaging effect on target organs, which in turn induces serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. We often hear of cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, coronary heart disease, heart attack, heart failure and renal failure and other malignant diseases are related to hypertension. High blood pressure is like a frog boiled in warm water, usually seemingly symptomless, but the harm has quietly begun. If you do not take medication, the result can only be that the blood pressure is out of control, complications attack. In this case, compared with the consequences of not taking antihypertensive drugs, the possible side effects of taking antihypertensive drugs are minimal. If you think about it this way, the result of taking antihypertensive drugs is what the patient can afford, while the result of not taking antihypertensive drugs is what the patient can't afford to avoid.
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! Also, if you have family members who are suffering from long-term antihypertensive drug-related problems, please pass this article on to them!
For people with high blood pressure, antihypertensive medication is a panacea. It's not an exaggeration at all. Let's look at a few classic examples.
1, Wang uncle, 56 years old, hypertension for more than 10 years, their own blood pressure, one day high, one day is not high, high when there is 180/100mmHg, low when there is 140/90mmHg, usually not much headache, dizziness symptoms, has always been happy, think high blood pressure is not a big deal, is not just a little bit higher, not always high ah, so not much to eat antihypertensive drugs, even if you take the medicine is to eat one meal, stop one meal. 2017-7-6 emergency to the hospital, hemiplegia, a check of the head CT, cerebral hemorrhage.
2, Li big brother, 49 years old, self-employed, hypertension for several years, did not pay much attention, do not see a doctor not take medication, socializing, often big fish and meat to eat and drink, the day is unusually dashing. 2017-12-1 suddenly fainted, coma, family members sent to the hospital, check the head CT, large cerebral infarction, soon herniated brain, death.
3, I have a college friend's father, 55 years old, the year before last, a brain stem hemorrhage, leaving serious sequelae. Repentance, because the home of the antihypertensive drugs are put into the expiration date, have not eaten much.
......
There are countless examples of this; many patients who have strokes and heart attacks have a history of high blood pressure, and often those who don't go about controlling their blood pressure properly are more likely to have a stroke, more likely to have a heart attack, and more likely to have kidney failure. Those who obey medical advice and take their lives seriously are often well protected.
1, Wang Auntie, 62 years old, some time ago when the clinic, took out a draft paper, figures densely packed, since they are their own three times a day blood pressure measurements, a cursory look, blood pressure is good, Wang Auntie laughed, said I can have to take medication, the doctor prescribes what I will eat. This is the attitude of treating hypertension. No wonder people with high blood pressure for 20 years, has not occurred obvious complications of renal insufficiency, no coronary heart disease, no diabetes.
2, Ma, 78 years old, hypertension for more than 20 years, a day a nifedipine extended-release tablets, spironolactone, betalactam has been a few years, blood pressure control is very good, to the present are still very hale and hearty.
......
All of the above cases, except the names, which are made up, are real cases.
Hypertensive patients, if not treated, do not eat antihypertensive drugs, do not exercise and diet control, then sustained high blood pressure will damage blood vessels, prone to atherosclerosis, which in turn may occur coronary heart disease, stroke, kidney failure and so on.
And if you take antihypertensive medication, you can certainly provide good protection against the above symptoms. Some people can just take one antihypertensive medication, while others have to take 3 or even more, but as long as the blood pressure is controlled at the desired level, then you can certainly prolong your life. This prolongation of life is relative to hypertensive patients who do not take medication.
Hypertensive patients, what other reasons do you have for not taking antihypertensive treatment? You think that once you take the medicine, you can't stop taking it, so you don't take it, what is this not stupidity? Hypertension is a chronic disease, it is not that you can not cut off the medicine, but this disease can not be cured, only long-term control, only long-term control, can be a long-lasting cure, otherwise, an inattention, a stroke, the light of the lack of speech, the focus of the paralyzed half of the body, and the heavier may be dead.
Dr. Wang you said that this antihypertensive drugs to eat for a long time, this every day to eat, I'm only 30 years old, this to eat for decades, did not die of old age, the results of letting the drug to eat death ......
The words are rough!
In fact, I can understand the patient's question and helplessness, but Dr. Wang can not help ah, hypertension is still a world problem, at least the formal sector has no cure, unless the small ads, you believe?
As for long-term medication, will not eat the body bad, this two say, theoretically drugs have toxic side effects, it is inevitable, but there is a sequence, not we have to take drugs to eat the body bad, but we have high blood pressure, and can not be other better ways to lower blood pressure, we have to take long-term antihypertensive drugs.
If you don't take your antihypertensive medication, you'll see what happens.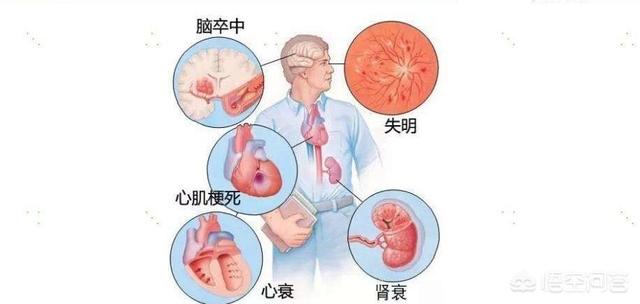
Prolonged blood pressure, if not effectively controlled, may occur: cerebral hemorrhage, cerebral infarction, coronary heart disease, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, heart failure, renal failure, aortic coarctation, and other malignant consequences.
It's not eating possible, and it's so likely that it's even a given that such an outcome will occur.
In fact, Dr. Wang especially understands what people mean, that is, they are afraid of the side effects of long-term medication, and everyone knows that medicine is bad.
But we need to make a comparison. The possible consequences of not taking antihypertensive drugs, which are irreversible and even disabling and fatal, are not many times greater than the possible side effects of antihypertensive drugs.
Just because most of the antihypertensive medications we take are lifelong, we need to be knowledgeable about the antihypertensive medications we are taking, and in addition to knowing when to take them, how much to take, and how many times to take them, it is important to know about the medication's side effects.
Side effects of commonly used antihypertensive drugs/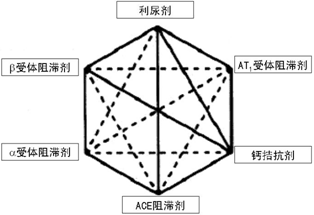
1), diuretics (hydrochlorothiazide, furosemide) Long-term application of large doses can lead to electrolyte disorders; hyperuricemia (gout); renal hypoplasia, the formation of hyperglycemia.
2) Calcium antagonists (XX diphenhydramine class) Common side effects: tachycardia, panic, gingival hyperplasia, flushing, headache, lower limb edema. Of course, the current diphenhydramine class of drugs has been developed to the third generation, relatively speaking, the side effects are gradually reducing.
3), Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors (XX Prilosec antihypertensive drugs) Common side effects: cough, edema, others include severe vomiting or diarrhea, swelling of the neck, face and tongue, etc., which may cause fetal malformation. If Prilosec side effects are found, bitartan can be replaced. Renal artery stenosis is contraindicated and is contraindicated in pregnant women.
4), Angiotensin II receptor blockers (XX sartan-type antihypertensive drugs) Common side effects: elevated blood potassium, may lead to hyperkalemia; renal artery stenosis is prohibited, pregnant women are prohibited.
5), XXazosin, XXolol, alpha-/beta-blockers Common side effects: alpha-blockers can cause postural hypertension (dizziness when standing up suddenly), edema; Beta-blockers may worsen asthma or other chronic lung disease, dangerous for people with breathing problems, aggravation of severe heart failure, slowing of heart rate, and ED in men.
The side effects of antihypertensive drugs need to be understood, but it is even more important to be aware of the dangers of high blood pressure and the importance of lowering it!
Taking antihypertensive medication for a long period of time to effectively lower blood pressure will make us healthier and reduce the occurrence of various potential complications!
We also need to detect and treat side effects of medications early!
But the good far outweighs the bad!
(For those of you who say you advertise antihypertensive medication, no one is forcing you to take antihypertensive medication, OK 👌!)
What is the outcome of long-term antihypertensive medication? This is a good question, and it is a question that many patients want to ask in the clinic. In fact, people who ask this question are more likely to ask: long-term oral antihypertensive drugs will not occur side effects? Dr. Zhang clearly tell you, if because of high blood pressure, long-term oral antihypertensive drugs, at the same time, blood pressure control is also up to standard, often patients in this case the benefits far outweigh the possible side effects. So what are the possible benefits of long-term oral antihypertensive medication?
longer life
Patients with high blood pressure, whose blood pressure still cannot be effectively controlled after rigorous lifestyle improvements, may then need long-term oral antihypertensive medication to control their blood pressure. In this case, as long as the blood pressure control is up to standard, the life expectancy of the patients in general will be substantially improved. This has been verified by many large-scale clinical trials.
Reduced incidence of cardiovascular diseases
Hypertensive patients, long-term oral antihypertensive drugs to control blood pressure. As long as the blood pressure control is good, the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases will be significantly reduced. Some patients because of long-term blood pressure control properly, even to the age of eighty or ninety years old, people are light and healthy, without any cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases.
Low incidence of kidney disease
Many patients with hypertension who do not control their blood pressure will eventually develop kidney disease. For example, renal artery atherosclerotic disease and so on. As long as the medication is taken for a long period of time and the blood pressure is well controlled, the incidence of kidney disease can also be drastically reduced.
As for the concern of whether long-term oral antihypertensive drugs will have side effects? This question is objectively possible. However, as long as it is handled properly, it will not lead to serious side effects. For example, coughing may occur with long-term oral Prilosec, so just adjust the medication and replace it with a beach-type antihypertensive drug. Every other side effect of antihypertensive drugs can actually be reduced or avoided by adjusting the medication, there is no need to worry too much.

Hello, I am a medical worker Zhang, a practicing physician, can popularize health knowledge for everyone, if you know more, pay attention to me!
Hypertension is one of the most common cardiovascular diseases, with a high prevalence especially in the elderly population, where almost 50% of the elderly suffer from hypertension. Hypertension is the most important risk factor for coronary heart disease, stroke and renal failure. Therefore, actively preventing hypertension is an important part of protecting the health of middle-aged and elderly people. The prevalence of hypertension in China is characterized by high prevalence rate, high disability rate and high mortality rate, and at the same time, there is a low awareness rate, low medication rate, and low control rate of the phenomenon of "three lows". With the dissemination of medical knowledge at all levels of medical care in recent years, the public has a new and more understanding of hypertension as a chronic disease. The treatment of chronic diseases is inseparable from long-term oral medication, but what will happen if you keep taking antihypertensive drugs?
What are the factors that influence high blood pressure?
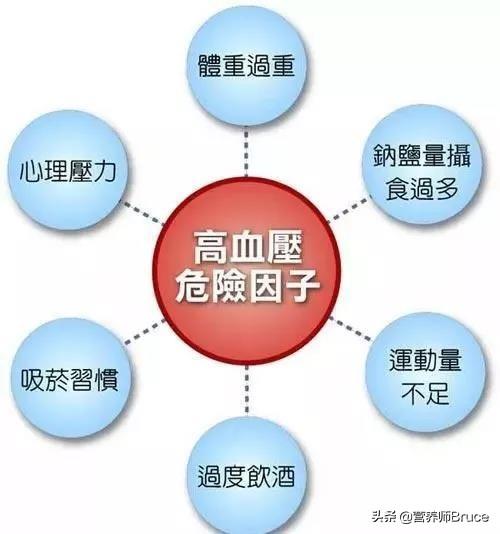
There are two types of hypertension: primary and secondary. Secondary hypertension has an obvious cause, for example, primary aldosteronism, pheochromocytoma, aortitis and other diseases can have high blood pressure, such that the increase in high blood pressure is only one of the symptoms of the respective disease. Such secondary hypertension accounts for about 5% of all hypertension and is treatable. The cause of primary hypertension is not yet fully understood, but we do know that there are some risk factors that predispose to hypertension, three of which have been proven in epidemiologic studies: overweight, high dietary salt, and moderate to high alcohol consumption. Other possible causes of hypertension include genetic predisposition, smoking, age, gender, work stress, hyperlipidemia, socio-economic and psychological factors.
What are some of the common symptoms that people with high blood pressure experience?
Dizziness (vertigo) is one of the most common symptoms of high blood pressure, most patients show persistent dullness and discomfort, but also for a transient. Dizziness can hinder thinking, memory loss, lack of concentration and reduce work efficiency. Long-term high blood pressure can lead to insufficient blood supply to the brain, which is one of the important causes of dizziness in hypertensive patients. Some patients with long-term high blood pressure have adapted to higher levels of blood pressure, and when the blood pressure drops too fast or too low after taking antihypertensive drugs, dizziness is also produced because of the maladaptation of cerebrovascular regulation. Blood pressure should be measured promptly when symptoms such as dizziness and headache occur in order to detect hypertension as early as possible and treat it as early as possible. If dizziness is accompanied by transient recurring neurological symptoms of cerebral ischemia, or if you feel that the sky is spinning, your body loses balance, or you cannot walk, you should consider transient cerebral ischemic attack, and you should take timely measures to prevent stroke.
2, headache Hypertensive patients are often accompanied by headache, mostly manifested as persistent dull pain or throbbing paroxysmal pain, usually occurs in the occiput and temples, especially when waking up, part of the higher nervous system dysfunction caused by no clinical specificity, but if frequent headache or headache is very strong, and at the same time feel nausea and want to vomit, you should pay special attention to the transformation of the condition, be alert to the emergence of the event.
3、Palpitations When the blood pressure rises in the early stage of hypertension, the neuromodulation is out of balance and the sympathetic nerves are over-excited. When the sympathetic nerves are over-excited, it will cause the heart rate to accelerate and the heart contraction force to strengthen, and the patient may feel palpitations at this time. It is generally believed that in the early stage of hypertension or mild hypertension, the occurrence of arrhythmia is mainly functional and related to sympathetic excitability, so there is no need to be overly nervous. However, the development of hypertensive heart disease can lead to structural remodeling of the heart, myocardial hypertrophy and myocardial ischemia, which can change the electrical activity of cardiomyocytes and produce arrhythmias. Hypertensive patients with arrhythmia belong to the high-risk group prone to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. Severe ventricular arrhythmia can lead to transient ischemic attack or stroke, which can induce angina pectoris or even sudden death, therefore, if a patient with hypertension feels palpitations, an ECG should be done for early diagnosis, so as to facilitate early treatment.
4、胸闷 胸闷可能是功能性自我感觉,也可能是心脏以外的因素引起的,从高血压病角度分析,胸闷可能是以下原因造成的:早期高血压在心脏代偿时期发生的胸闷,往往是神经性的,可能属于神经(官能)症,检查可能无明显异常表现;血压长期升高,增加心脏负担,心脏的结构和功能可能 Long-term elevation of blood pressure increases the burden on the heart, which may change the structure and function of the heart, gradually causing cardiac hypertrophy and insufficient blood supply to the coronary arteries, and the patient will feel tightness in the chest; when hypertension is combined with cardiac arrhythmia (e.g., premature heartbeats) or when heart failure occurs, the patient will feel tightness in the chest, shortness of breath, and palpitations in a state of quietness or in a state of activity. Hypertension is the most important risk factor for coronary heart disease. When hypertension is combined with coronary heart disease, symptoms such as chest tightness, discomfort in the precordial region, and even typical angina pectoris attacks often occur.
5、Numbness of limbs Hypertensive patients may appear numbness and stiffness of hands and feet, may also appear ants, most of these phenomena are due to hypertension vasodilatation dysfunction or arteriosclerosis and other reasons for the limbs of the local blood supply is insufficient due to, that is, usually spoken of as "qi and blood and", through the control of blood pressure and symptomatic treatment, generally can be gradually relieved and disappear. Through controlling blood pressure and symptomatic treatment, the symptoms can be gradually relieved and disappear. Hypertensive patients with numbness of the hands and feet should also consider the existence of other diseases, the most common are diabetes and shoulder, neck, waist and leg pain, diabetes control will cause peripheral neuritis and other lesions, will also appear numbness of the limbs, sensory abnormalities of the symptoms, should be vigilant and properly dealt with.
What are the benefits of taking high blood pressure medication for a long period of time?
1, high blood pressure can cause angina pectoris high blood pressure and coronary heart disease is closely related, hypertension patients with coronary heart disease incidence rate of normal blood pressure 4 times higher. Long-term high blood pressure causes serious spasm and hardening of coronary arteries, and accelerate the process of atherosclerosis, causing coronary artery stenosis or blockage, ultimately leading to angina pectoris. Hypertension is one of the most dangerous factors for angina pectoris.
2, high blood pressure can cause myocardial infarction Long-term high blood pressure causes serious spasm and hardening of the coronary arteries, but also accelerates the process of atherosclerosis, resulting in coronary artery stenosis or blockage, ultimately leading to myocardial infarction.
3, high blood pressure can cause hypertensive heart disease Long-term hypertension increases the burden on the heart, causing compensatory hypertrophy of the myocardium, called hypertensive heart disease. Left ventricular hypertrophy is an independent risk factor for hypertension and an important factor in the occurrence of cardiovascular events and death. Hypertensive patients with left ventricular hypertrophy not only have a significantly higher incidence of sudden death, but also have a significantly higher incidence of cardiovascular disease, mortality and arrhythmias.
4, hypertension can cause cardiac insufficiency Long-term hypertension increases the burden on the heart, the heart will gradually hypertrophy, enlargement, which is a pathological compensatory process, and ultimately compensatory failure, signs and symptoms of cardiac insufficiency.
5, high blood pressure can accelerate atherosclerosis triggered by stroke Stroke, including cerebral thrombosis and cerebral hemorrhage, etc., is the main cause of disability and death of the population in our country, the annual incidence of 120-180/100,000, mortality rate of 60-120/100,000, the incidence of stroke in our country is 4-6 times of myocardial infarction. The incidence of stroke in China is 4-6 times higher than that of myocardial infarction. The relationship between stroke and hypertension is extremely close, and clinical studies have found that: ① for long-term hypertensive people, elevated blood pressure of 9/5 mmHg leads to an increase in the incidence of stroke by 1/3; elevated by 18/10 mmHg increases by 50%, and a long-term average decrease in blood pressure of 5-10 mmHg reduces the number of strokes by 35% to 40%. (ii) Systolic blood pressure levels and pulse pressure difference are even more related to the risk of stroke. The risk of stroke in those with a pulse pressure difference of >80mmHg is 3-4 times higher than in those with a pulse pressure difference of >50mmHg; the relative risk of stroke in those with elevated diastolic blood pressure alone and normal systolic blood pressure is almost the same as that in those with normal blood pressure.
6. Hypertension can cause transient ischemia. Hypertension is the most important and common cause of transient ischemic attack. Transient ischemic attack refers to focal cerebral dysfunction caused by temporary insufficiency of blood supply to carotid artery or vertebral basilar artery system. Clinical manifestation is sudden onset, usually lasts for several minutes to several hours, and fully recovered within 24 hours, but it can be repeated. About 1/3 of the cases develop into cerebral infarction.
7, hypertension can cause kidney damage and renal failure The kidney is one of the important target organs of hypertension, hypertension causes renal arteriolar sclerosis, which ultimately leads to glomerulosclerosis and renal interstitial fibrosis, hypertensive kidney damage is one of the main causes of end-stage renal disease.
8, hypertension can cause diabetes blood pressure and diabetes are common diseases, the combined existence is very common. Hypertension combined with diabetes will accelerate the occurrence and development of cardiovascular disease, stroke, kidney, retinopathy, effective antihypertensive, hypoglycemic treatment is essential to control the development of the disease. Hypertension accelerates the development of diabetic nephropathy and aggravates diabetic nephropathy.
However, if you take antihypertensive medication for a long time, you can delay the arrival of these complications, and it is even possible that they will not come for the rest of your life, which is why it is necessary for people with high blood pressure to take antihypertensive medication.
What are the disadvantages of taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time?
The rational application of anti-hypertensive drugs can effectively control hypertension, which can improve the prognosis, reduce complications and improve the quality of life. However, some antihypertensive western drugs often produce some adverse effects while effectively lowering blood pressure. Drug side effects have become one of the most important issues affecting long-term continuous treatment and quality of life, and must be properly recognized and managed. The following is a description of the possible adverse effects of the four major classes of antihypertensive drugs and their countermeasures.
1, diuretic antihypertensive drugs: thiazide diuretics (dihydrochlorothiazide) main side effects for a low (low blood potassium), three high (elevated blood lipids, blood sugar, blood uric acid). (1) Tabs diuretics When taken in small doses, the body adjusts itself, and blood potassium is generally not significantly lowered, and additional potassium supplementation is not necessarily required; usually more potassium-rich foods will be sufficient. Blood electrolyte levels should be measured and electrocardiograms checked regularly. If hypokalemia occurs, potassium should be supplemented or combined with potassium-preserving diuretics, which should be used with caution if the blood potassium itself is low or renal function is poor. (2) Thiazide diuretics have adverse effects on glucose and fat metabolism, and should be used sparingly or not used in patients with high blood glucose and lipid levels and insulin resistance, and avoided in combination with β-blockers so as not to superimpose the effect of elevating blood lipids. It is forbidden to use in patients with diabetes mellitus and gout.
2, β-blockers: various types of β-blockers have different effects, and their side effects are not the same, should be selected and monitored according to specific circumstances. (1) β-blockers have negative heart rate, partial muscle strength and negative conduction. When taking them, heart rate and electrocardiogram should be checked frequently. Elderly hypertensive patients with slow heart rate should be observed more closely when taking them, and severe bradycardia, severe atrioventricular block and obvious cardiac insufficiency should be prohibited. (2) Certain beta-blockers have adverse effects on blood lipids and can also aggravate insulin resistance, and are contraindicated in patients with hyperlipidemia and diabetes mellitus. Selective? Thrive receptor blockers such as metoprolol (bethanechol) have less metabolic effects and can be appropriately applied. (3) Certain beta-blockers will induce vascular smooth muscle spasm and are contraindicated in people with a history of asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. (4) Hypertensive patients taking beta-blockers for a long period of time, especially those with coronary artery disease, should not stop taking the drugs abruptly, so as to avoid rebound overexcitation of the sympathetic nervous system, which may lead to a rise in blood pressure and deterioration of cardiomyopathy.
3、Calcium antagonists: different types of calcium antagonists in different diseases, different routes of administration and dosage when the response varies. (1) Calcium antagonists such as nifedipine significantly dilate blood vessels, which can cause headache and flushing, even unbearable, ankle edema is also more common. (2) Calcium antagonists such as nifedipine can reflexively excite the sympathetic nerves while lowering blood pressure, causing the heart to beat faster. (3) The use of short-acting calcium antagonists such as nifedipine can sometimes lead to a rapid fall in blood pressure and induce rapid heart rate and angina pectoris, so it is advisable to start with a small dose and gradually increase the amount. (4) Verapamil (isobarbital), diltiazem (Tenocardium), two calcium antagonists have negative heart rate, negative inotropy and negative conduction effects, and should not be taken by people with severe bradycardia, severe atrioventricular conduction block and cardiac insufficiency. Do not combine with beta-blockers to avoid exacerbating side effects.
4. Converting enzyme inhibitors: the most common side effect is coughing, and the exact mechanism of its occurrence needs to be explored. Generally disappear after stopping the drug, but will appear again after resuming the drug. Different varieties of converting enzyme inhibitors caused by dry cough effect degree varies. They should be used with caution in patients with significant renal insufficiency and should be contraindicated in patients with bilateral renal artery stenosis. Converting enzyme inhibitors, may appear high blood potassium, especially in the complication of diabetes mellitus and renal insufficiency, should pay attention to the changes in blood potassium, a few patients may appear rash, angioneurotic edema and other reactions.
Conclusion: high blood pressure for the harm of the population in a direct emergency (hypertensive crisis) is a small number of people, for most hypertensive patients the real danger of long-term high blood pressure will lead to atherosclerosis, making the liver, kidney, brain, coronary arteries and other target organs of the whole body vascular extensive lesions. If the blood pressure is not controlled for a long time, in less than three to five years these target organs will be damaged, followed by coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction, liver and kidney damage and other complications. Although long-term use of antihypertensive drugs does damage the liver and kidney function, but there is no way, do not take antihypertensive drugs the consequences will only be more serious.
This is a lot of friends worried about the problem, control of high blood pressure need to take long-term medication, and taking drugs have inevitable side effects, long-term antihypertensive drugs, will not be resistant to drugs? Will the body eat bad? Today we will explore this issue.
Can you develop resistance to long-term antihypertensive medication?
This issue is of concern to many people, but there is no need to worry. Unlike anti-bacterial and anti-viral drugs, which have the risk of developing drug resistance, antihypertensive drugs do not develop drug resistance.
Clinically used five major classes of antihypertensive drugs, angiotensinase receptor blockers (Prilosec), angiotensin II antagonists (sartans), calcium antagonists (diphenhydramine), β-blockers (Lol, carvedilol, etc.), diuretics (thiazides, spironolactone, furosemide, etc.), respectively, through a different mechanism of action, the action of the body to control blood pressure, such as Prilosec and sartans is mainly to inhibit the vasoconstriction, diphenhydramine dilate arterial vessels, Lol class to slow the heart rhythm, thiazide diuretics promote sodium excretion, reduce blood volume, etc. From these mechanisms of action, taking antihypertensive drugs will not produce resistance to vasoconstriction, diphenhydramine class dilate arterial vasculature, lorazepam class slow down the heart rhythm, thiazide diuretics to promote sodium excretion, reduce blood volume, etc. From the point of view of these mechanisms of action, taking antihypertensive drugs medication will not produce drug resistance.
Some friends take a drug has been good control of blood pressure, but with age, there will be poor control of blood pressure, if this situation is progressive, may be related to the aging of blood vessels and atherosclerosis degree of aggravation, you can consider co-prescription of other suitable antihypertensive drugs combined control of blood pressure, such as sartan or priligy + diuretics, sartan or priligy + diphenhydramine, diuretics + diphenhydramine, etc. are good choices. If there is a sudden onset of poor blood pressure control, you should seek medical attention to rule out the possibility of other diseases triggering uncontrollable elevation of blood pressure.
What about side effects from long-term antihypertensive medication?
Long-term use of antihypertensive drugs, many friends worry about another problem, is the problem of side effects of the drug. For the side effects of the drug, the correct understanding of it is very important, to give you the first two points:
1. All medicines have side effects, but they do not necessarily happen to everyone who takes them. For example, some people may have a strong dry cough when they take Prilosec, while others may not have a dry cough at all. Therefore, you should be aware of the side effects that are labeled in the instructions, but they should not be a mental burden because they may not necessarily happen to you.
2. To treat the side effects of drugs, it is best to look at the dialectic, in order to treat or control the disease, taking drugs, the therapeutic effect of the body's benefit must be greater than the possible side effects of the drug, if the side effects of the body can not tolerate the body or the body to cause greater harm, then this drug is not suitable for your drug. For hypertensive patients taking medication, if taking medication can be a good control of blood pressure steady, can effectively delay atherosclerosis, reduce cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, fundus and other diseases, which is very great for the body's benefit, for antihypertensive drugs may produce some side effects, is completely negligible.
A brief overview of the side effects of commonly used antihypertensive drugs for your information and understanding
Diphenhydramine- Hot flashes, rapid heartbeat, edema of the gums, edema of the ankles, and headaches;
Prilosec - do common side effect is dry cough, which is generally tolerated, if not should be changed, and also be aware of problems such as high blood potassium;
Sartans - Be careful to monitor blood potassium; hyperkalemia and angioedema are possible side effects of sartans;
Lorazepam - Bradycardia, which may affect lipid and glucose metabolism, and may also be sexually active males are affected;
Thiazide diuretics - hypokalemia, elevated uric acid, etc.
Hypertensive patients take antihypertensive drugs for a long time, of course, to stabilize blood pressure and avoid various complications, as well as to improve the quality of life, so that we can live a life like a normal person.
Once we are diagnosed with high blood pressure and start taking medication, we have to take it every day just like we eat, we can't forget and we have to take it every day
Take medication every day, which is the key to controlling blood pressure, some people always fish for three days and sunshine in two days, so that the blood pressure is high and low, very dangerous.
Among the hypertensive patients I manage, not many used to be able to adhere to long-term medication, but now more and more are.
I can also see that all these years of hard work have not been in vain, and people are starting to pay attention to their bodies and their blood pressure.
Of course, at present, the most crucial thing is still the blood pressure control to meet the standard stable or not, which is related to everyone's adherence to medication, regular monitoring of blood pressure and timely adjustment of medication.
With better medication adherence, we also need to see if the medication is working well in controlling our blood pressure and keeping it up to standard and stable.
If we can't, we need to adjust our medications in time to the point where we reach the most stable state.
Then we take our medication on time, follow up quarterly, and if we are up to standard and stable, we just carry out annual health checkups for heart, brain, kidneys, eyes, and so on.

With long-term medication for hypertension, we need to be aware of the side effects of the medication.
At present, the "Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension at the Primary Level" recommend a total of four major classes of antihypertensive drugs ABCD, compared with the therapeutic effect, their side effects are very small, for hypertensive patients, a kind of side effects of the drug, we can adjust the other antihypertensive drugs according to the actual situation.
1, Class A drugs include ACEI antihypertensive drugs and ARB antihypertensive drugs
- The ACEI class of antihypertensive drugs is the pulsatile class of drugs, and common adverse effects are cough, which occurs in 30% of people, elevated blood potassium, and edema.
- The ARB class of antihypertensive drugs, represented by the drugs sartans, has common adverse effects mainly edema and elevated blood potassium.
2. Class B drugs, beta-blockers
- Lorazepam is commonly used in clinical practice, and a common adverse effect is slowing of the heart rate, so a heart rate of less than 80 beats per minute is not recommended, as well as headache and dizziness.
3. Class C drugs calcium antagonists
- Commonly used clinical drugs include diphenhydramine, and common adverse effects include headache, tachycardia, ankle edema, constipation, and transient anginal attacks.
4. Diuretics
- Commonly used clinical drugs include furosemide, hydrochlorothiazide, and indapamidean, and common adverse effects are hypokalemia, hypotension, and electrolyte disturbances.

In the face of these side effects of drugs, we can combine drugs so that the side effects of drugs cancel each other out and improve the effectiveness of drug treatment.
- For example, if Class A drugs raise blood potassium and diuretics lower it, we can combine these two classes of drugs to achieve the therapeutic goal and offset the side effects.
- Another example is that the lorazepam slows down the heart rate and the diphenhydramine speeds it up, so is it much better when we use them together.
- There are also diphenhydramines that cause edema, which is eliminated by diuretics, so the combination may be more effective.

Hypertension is the key to lowering blood pressure to meet the standard, only in this way, our blood pressure can be stabilized, our quality of life will be high, but the long-term use of drugs, but also a yearly physical examination.
- Look for complications of high blood pressure, such as heart, brain and kidney lesions, and changes in the fundus.
- See if the medication has any effect on the liver. We know that medicines are poisonous, not to mention taking them every day, but nowadays high blood pressure medicines are causing less and less damage to the liver, but still there, so you need to check your body regularly to see how your liver functions.
- Compared to the therapeutic effects, these side effects of high blood pressure medications are very minimal.
- Therefore, the clinical use of hypertension drugs, according to the actual situation of the patient medication, choose to the patient effective, small side effects of the drug.

In summary: Adherence to medication for hypertension is the key to achieving stable blood pressure, and although there are some side effects, they are very minor compared to the effectiveness of the treatment, and we can adjust the medication through regular assessments.
I am your friend Xiaoxiao love health, this article is purely hand-typed, welcome to criticize and correct.
Hypertension is one of the most common chronic diseases, cardiovascular disease is an important factor leading to the death of our residents, and more than 50% of cardiovascular events are related to hypertension. China's primary hypertension (hypertension of unclear etiology) accounts for more than 90% of the total number of patients with hypertension, which means that the majority of patients with unclear etiology can only be treated symptomatically by taking antihypertensive medication, which can control the blood pressure, and the blood pressure will be repeated after stopping the medication. Therefore, to ensure that the blood pressure is maintained at a normal level, it is necessary for patients to take antihypertensive drugs for a long time.
long-term use of antihypertensive medication to maintain blood pressure at normal levels.It will reduce the damage of hypertension to the cardiovascular system and prevent the occurrence of various complications. Of course every drug has side effects, at present everyone common antihypertensive drugs are after a long period of time a large number of clinical research, to determine that these drugs for hypertensive patients benefit more than harm. And side effects do not happen to everyone, there is specificity, some patients take a long-term antihypertensive drugs, blood pressure control is stable, no adverse reactions, regular testing of liver and kidney function and other indicators are also normal, that proves that this drug for him is safe and appropriate. Therefore, patients with hypertension should insist on taking antihypertensive drugs for a long time, and after controlling blood pressure smoothly, they should not stop taking the drugs arbitrarily.
References:
[1] Committee on Revision of Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension. Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Hypertension (2010 Revision).
[2] Expert Committee on Rational Use of Medications of the National Health and Family Planning Commission, Hypertension Committee of Chinese Physicians Association. Guidelines for the rational use of medication in hypertension (2nd edition) [J]. Chinese Journal of Frontiers of Medicine (Electronic Edition), 2017, 9(7):28-126.
Author:Li Chunyu Unit:Clinical Pharmacy Department, Fengtai Hospital, Beijing, China, Member of Pharmaceutical Affairs Network
Drugs.com authoritative interpretation, unauthorized reproduction, plagiarism will be prosecuted
In recent years in China, the
The number of people with hypertension has exceeded 200 million and continues to increase by about 10 million each year.
And, high blood pressure isn't just limited to the elderly anymore.
The prevalence of hypertension has reached more than 10% in young people under 30 years of age.
There are statistics:Of the 3 million or so cardiovascular disease patients who die each year in China, 50% are related to hypertension

With such a high percentage of hypertensive patients, lowering blood pressure has become the only way for everyone to avoid some of the chronic diseases caused by high blood pressure
- However, many hypertensive patients encounter two bottlenecks inside lowering their blood pressure
First, the blood pressure won't come down;
Second, even though the blood pressure comes down, it doesn't stabilize.
The way to lower blood pressure, the current clinical mainly with western drugs to achieve the effect of taking western drugs, has been the traditional antihypertensive maneuver for hypertensive patients.
But long-term use of western drugs to lower blood pressure can be harmful, you know?
There is a consensus among many hypertensive patients who take blood pressure lowering medications:
Western drugs to lower blood pressure, although fast, but treat the symptoms but not the root cause, because there is no way to inhibit the deterioration of the condition, not only can not block complications, but will exacerbate the occurrence of complications.

- Main reasons
- (1) Antihypertensive drugs produce very high levels of drug-metabolizing toxins deposited on blood vessel walls
The more you take and the longer you take it, the more is deposited, which will eventually lead to hardening, thinning and brittleness of the blood vessels;
- (2) In addition, antihypertensive drugs are used to lower blood pressure quickly by strongly dilating blood vessels.
It will definitely make the already hardened blood vessels even more fragile, and it will be easier to damage the heart, brain, liver, kidneys and other important human organs, and exacerbate the occurrence of complications
- (3) The blood pressure we measure now is predominantly in the brachial artery
When a high blood pressure is found in the uterine artery, the blood pressure is actually already higher elsewhere in our body, such as the tiny blood vessels in the brain and heart. So although blood pressure is always monitored, many patients actually develop complications of hypertension
- (4) Make sure to adjust your lifestyle before taking blood pressure lowering medication
Remove the main cause of high blood pressure, so that the most fundamental direction
Do you suffer from this? Feel free to leave a message in the comments section
Like my content, welcome to follow the likes of forwarding, every day there will be health knowledge to share!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.