Is it safe for a diabetic mom to breastfeed her baby?
Diabetics can get through pregnancy and have a healthy, loving baby with good blood sugar control.
So how does a diabetic mom control her blood sugar during pregnancy?
Due to pregnancy, the current fasting blood glucose requirement for those who are pregnant is 3.3-5.1 mmol/L, and postprandial blood glucose is 4.0-6.7 mmol/L. As you can see from these values, blood glucose is much stricter in pregnant than non-pregnant individuals, and when it appears to be higher than this, gestational diabetes is diagnosed.
People with gestational diabetes have certain maternal and infant risks, such as miscarriage, preterm labor, intrauterine distress syndrome, infections, and developmental malformations; the mother may be at risk for gestational hypertension and eclampsia; and the risk of the mother and child developing diabetes later in life is greatly increased.
This is because if blood sugar is found to be elevated during pregnancy, it needs to be lowered to control it in the desired range. If the blood sugar cannot be brought down to the target range through diet and exercise, then pharmacologic intervention is needed to control the blood sugar in the desired range.
When diabetic patients combined with pregnancy or gestational diabetes mellitus apply medication to control blood glucose, the only medication available in our country is insulin. This is because no oral hypoglycemic drug has been approved for the treatment of diabetes mellitus combined with pregnancy or gestational diabetes mellitus in China. Because the small molecules caused by drugs may pass through the placenta and affect the fetus. While insulin is a large molecule, can not pass through the placenta, and the effect of lowering sugar is more accurate and reliable, safer.
Therefore, insulin therapy needs to be chosen for pharmacologic glucose lowering during pregnancy. If blood glucose does not return to normal after delivery and breastfeeding is planned, then insulin therapy still needs to be continued to smooth out the blood glucose because insulin is a large molecule, which is found in relatively small amounts in breast milk, and small amounts may be eliminated through the infant's digestive system. Oral hypoglycemic drugs, on the other hand, can affect the baby. Therefore, it is recommended to continue insulin therapy during breastfeeding.
Because about 2/3 of patients with gestational diabetes will continue to have diabetes or abnormal glucose tolerance, lactating mothers need to continue diet and exercise therapy after delivery.
Breastfeeding prevents the risk of type 1 diabetes and obesity in children, and mothers can promote the recovery of metabolic function, reduce stress, and help keep blood sugar stable.
Breastfeeding is therefore recommended for women with increased blood sugar.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Diabetes, a roadblock for pregnant and postpartum moms. This is because controlling blood sugar is an ongoing and difficult process.You cannot breastfeed if you had diabetes before you got pregnant and you still need glucose-lowering medication to control your condition after giving birth!
This is because glucose-lowering drugs can pass through the blood-milk barrier into breast milk and subsequently cause hypoglycemia or other illnesses in the baby. IfUse insulin to control your blood sugar, then instead you can continue to breastfeed your baby.
Diabetes that is detected after pregnancy is considered gestational diabetes. Gestational diabetes is usually transient, and after the placenta is expelled, anti-insulin levels drop and diabetic manifestations disappear. SoGestational diabetes can also be breastfed.
However, it is important to be alert to the development of gestational diabetes towards type 2 diabetes, as clinical statistics show that about half of mothers with gestational diabetes may develop type 2 diabetes between the ages of 40 and 60. Therefore, it is recommended that baby moms should have regular medical checkups, especially for blood glucose measurement and diet control.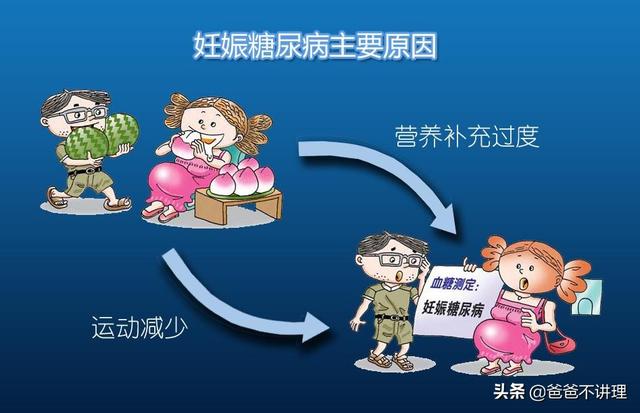
Gestational diabetes mellitus is mainly related to placental secretion of estrogen, progesterone and placental lactogen, which will lead to elevation of insulin resistance. In addition, a large number of foreign research evidence shows that the insulin resistance of female fetuses in utero is significantly higher than that of male fetuses, so mothers with female babies have a higher chance of developing gestational diabetes.
Whether you have diabetes before or after pregnancy, then you will have to do a glucose tolerance test at the 42-day postpartum review. 75g of glucose water to drink, if the review is still abnormal, then the doctor will arrange a treatment plan and daily dietary adjustments recipes, and combined with postpartum exercise to control blood sugar.
Summarize a sentence: postpartum need hypoglycemic control, can not breastfeeding; use insulin, can breastfeeding. If it belongs to gestational diabetes mellitus, usually after giving birth to a child blood sugar return to normal, does not affect breastfeeding. However, it is important to measure blood glucose regularly and control diet and weight.
Special reminder: if you are not feeling well feel free to visit your doctor for a diagnosis. Good luck! Please leave a message if you have any other questions.
Some mothers-to-be will experience high blood glucose during pregnancy, usually in the middle and late stages of pregnancy. On the one hand, it is related to the diet of the mother-to-be during pregnancy, due to excessive intake of high sugar and high oil foods, the weight gain is too fast, resulting in increased blood glucose levels; on the other hand, it is related to the age of the mother-to-be, with the older pregnant women having a higher incidence of illness, and experiencing high blood glucose at a much earlier time. Most of the mothers-to-be with high blood glucose in pregnancy can return to normal blood glucose level after delivery, which is not much different from normal mothers, and can breastfeed their babies normally, but there are some mothers who still maintain high blood glucose level after delivery, in which case, can they breastfeed their babies?
Can a mom with high blood sugar breastfeed her baby?
Mothers with high blood sugar must pay close attention to their glycemic index and try to keep it within a manageable range through diet and exercise. Bao moms in the daily diet must control the sugar, calorie intake, avoid high sugar and high oil food, cooking should be less sugar, use coarse grains instead of rice, eat more vegetables, reasonable control of fruit intake, each meal to eat seven or eight minutes full can be, and every day to maintain a certain amount of physical activity and exercise intensity, not only to control the momentum of the growth of the body weight, and it is best to also achieve weight loss and slimming, only in this way that can achieve the purpose of controlling or even lowering blood sugar.
If the mother can control her blood sugar through exercise and diet, she can breastfeed her baby without worry. Although the mother's blood sugar is higher than normal, these will not be absorbed by the baby through breast milk and will not affect the baby's blood sugar, and breastfeeding can help the mother to lower her blood sugar, so it is best for mothers who have high blood sugar to adopt breastfeeding to breastfeed their babies.
If the mother can not control her blood sugar through exercise and diet, she needs to inject insulin to control her blood sugar. During this period, she can still breastfeed her baby because insulin can not enter the breastmilk and it will not affect the baby, and breastfeeding can lower the blood sugar appropriately, but the mother must pay attention to the problem of low blood sugar. It is better for her to consult the doctor to determine the dosage of insulin and to eat moderately before and after breastfeeding.
concluding remarks
Most of the mothers with high blood glucose in pregnancy can return to normal blood glucose level after delivery, so they can breastfeed their babies normally, or breastfeed their babies if their blood glucose is still high and it will help them to control their blood glucose, however, they have to keep a close eye on the glycemic index and keep it under control through diet and exercise.
Breastfeeding has special benefits for mothers with diabetes:
1. Breastfeeding relieves stress, and the hormones secreted during breastfeeding make mothers more relaxed;
2. Studies have shown that breastfeeding reduces the risk of babies developing diabetes in adulthood;
3. The hormones secreted during breastfeeding and the extra calories consumed in the production of milk will reduce the amount of insulin needed by the mother;
4. Breastfeeding is effective in relieving the symptoms of diabetes, and many mothers experience partial or complete improvement in their condition while breastfeeding.
Insulin and breastfeeding are not in conflict because insulin's molecules are too large to penetrate breastmilk, while oral insulin is destroyed in the digestive tract and cannot enter the breastmilk, so diabetic mothers are perfectly capable of breastfeeding. It is important to note that because diabetics are susceptible to a variety of infections, it is important to pay extra attention to blood glucose levels, pay extra attention to personal hygiene, and protect the nipples from infection during breastfeeding.
Which group of people are prone to gestational diabetes Prone to gestational diabetes
Which are some of the people who suffer from this disease? Today the old official will share with you which category of people are prone to gestational diabetes. The specific answer is as follows; 1, the body is too fat. If the body mass index before pregnancy is more than 24 (body mass index = weight in kilograms / height in centimeters squared), should be more vigilant. 2, the age of 30 years old, especially more than 35 years of age of pregnant women. 3, the family has a diabetic patient, especially yi relatives (including parents and siblings) have diabetic patients, I have a significant increase in the risk of diabetes during pregnancy. 4, the urine routine examination during pregnancy Frequent fasting urine glucose positive. 5. Repeated vulvovaginal yin tract candidiasis (or mycosis fungoides) during pregnancy. 6. Repeated unexplained spontaneous abortions, intrauterine foetal deaths, and foetal malformations in previous pregnancies. 7. Delivery of a foetus weighing more than 4 kilograms. 8. Gestational diabetes mellitus in pregnancy. 9. Foetal growth in the course of the current pregnancy or excessive amniotic fluid. 10. Excessive amniotic fluid. The above explanation is that we should know more about their own body during the preparation for pregnancy is suitable for pregnancy, and the age of pregnancy on some of the control and physical examination during pregnancy, if it is a good job every time the obstetric examination, the doctor found some problems will give you timely feedback will have a large extent to avoid the emergence of diabetes.



Diabetes is an abnormality of glucose metabolism, but it does not interfere with the metabolism of other substances, nor does it affect the composition of breast milk, nor does breastfeeding cause the baby to develop diabetes, so it does not need special treatment, and normal breastfeeding is fine. Some people have abnormal glucose metabolism during pregnancy, you can control blood sugar through dietary adjustments, pay attention to regular activities, especially after meals, you can hold the baby and walk to the
Generally, mothers who are able to deliver are able to breastfeed, and diabetics are no exception. Although a diabetic's blood sugar is unstable, her milk is not sweet enough to cause diabetes in her toddler, so don't stop breastfeeding so easily. After all, formula is no better than your own breast milk.
2 And controlling diabetes with insulin will not affect normal breastfeeding because insulin is a large molecule, and when a young child consumes breast milk containing insulin, the insulin will be destroyed in the digestive tract and will not be easily absorbed, so it will not affect the quality of the breast milk, so diabetic moms can breastfeed your baby.
3 But if you usually take oral hypoglycemic drugs, you should pay attention during breastfeeding, because the drugs are likely to cause pancreatic β-cell proliferation in young children, making them prone to hypoglycemia. Therefore, it is not advocated that breastfeeding mothers take oral hypoglycemic drugs, and it is better to use regular artificial insulin.
It is safe for a diabetic mom to breastfeed her child.

Breastfeeding boosts baby's immunity
Nutritionally balanced breastmilk is the best natural food that a mother can give to her child, and breastfeeding promotes the healthy development of the baby and strengthens the immune system. Newborns of diabetic patients have low immunity and should be breastfed. Diabetes does not affect breastfeeding, as long as you control your blood sugar, you can breastfeed your baby.

Breastfeeding has benefits for mothers too
Breastfeeding is not only beneficial to the healthy development of the baby, but also to the mother, preventing obesity and reducing the risk of diseases such as breast and ovarian tumors.
It is recommended that mothers make good dietary arrangements and energy storage
It takes 945 calories to produce 850 milliliters of milk, which needs to be increased during breastfeeding and the use of stored fat from pregnancy to ensure milk production.

in a word
High blood sugar breastfeeding does not affect the fetus much, but it does affect me. If fasting blood sugar is high, active treatment is still recommended, and insulin treatment is still recommended during breastfeeding.
Mothers-to-be who suffer from gestational diabetes during pregnancy can breastfeed if their blood sugar is within the normal range after delivery. And there are a lot of mothers in the breastfeeding period, there will be symptoms of mastitis, if the inflammation is not very serious, there is no high fever, pus, pain unbearable symptoms, can also continue to breastfeeding.
insecurity
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.