Is carotid plaque dangerous? What damage can it cause to the body?
Is carotid plaque dangerous and what harm can it do to your body" is a question that so many people are worried about. Today we will talk about this issue.First of all, I would like to say that simply talk about the danger is not dangerous is not rigorous, is like asking you to drink a few glasses of white wine will be drunk almost the same question, because the wine has a soy sauce type, fragrant type, high, low and other distinctions, but also with the speed of the drink as well as the mood of the drink when the mood has a relationship. Similarly, the danger of carotid plaque also depends on what kind of plaque, plaque will not fall, the blood vessels blocked serious or not serious and other aspects related.I'm going to partially tell you about carotid plaque:
1, what is carotid plaque and what are the formation factors;
2, is carotid plaque dangerous and what harm can it do to the body;
3, how to find and treat carotid plaque it;
4, What are the preventive measures for carotid plaque.
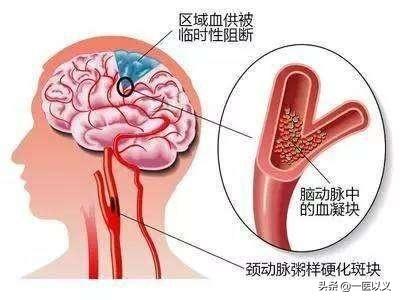
Human blood vessels are like roads on earth, responsible for the transportation of nutrients and metabolites to all parts of the body, all blood vessels have a certain life cycle, the optimal life of human blood vessels is about 40-50 years.As we age, just like a highway, blood vessels age, which means that atherosclerosis develops.
I. What is carotid plaque and what are the factors of formation
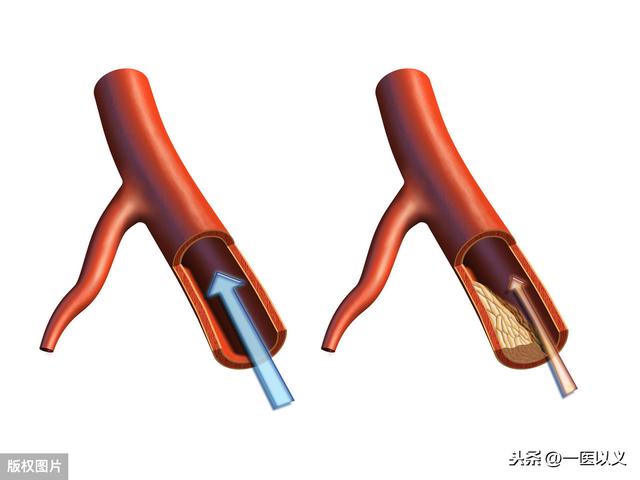
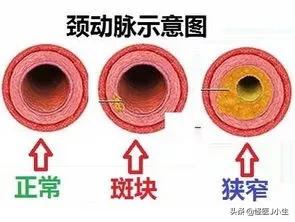
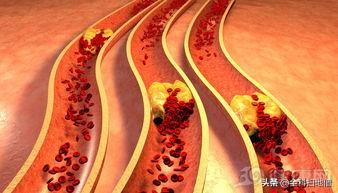
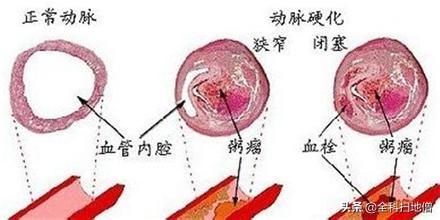
- First, understand what atherosclerotic plaque is.Its formation is a more complex process, with impaired lipid metabolism in the body as the basis of the lesion, theIt is characterized by the involvement of arterial lesions starting from the intima, the continuous accumulation of lipids and complex sugars in the vessel, and then the proliferation of fibrous tissue and the local deposition of calcium, resulting in the thickening and hardening of the arterial wall and the narrowing of the vessel lumen.
- It develops due to a number of factors.The main risk factors are hypertension, hyperlipidemia and heavy smoking, as well as diabetes, obesity and genetic factors. As people's standard of living continues to improve, the risk factors mentioned above are more common, and thus carotid plaque is also in many people's bodies.

Second, is carotid plaque dangerous and what harm will it do to the body?
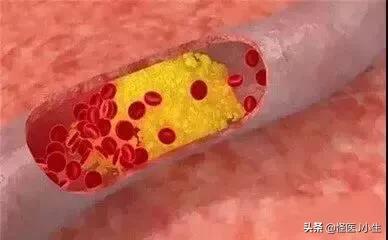
- Carotid plaque itself is not harmful, it is just a buildup of "waste" in the body.. But it can lead toNarrowing of the lumen of the blood vessel, which makes it more difficult for blood to pass through the narrowed area, thus preventing the supply of blood to distant tissues.. The human body relies mainly on the circulation of blood to carry out a series of activities, and if the blood flow is reduced, it is like a car without gasoline, it can not run properly.
- Reduced blood flow leads to symptoms of ischemia, the severity of which depends largely on the vascular lesion and the degree of ischemia in the affected organ.Coronary artery atherosclerosis patients, if the diameter of the narrowing of 75% or more, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, arrhythmia, or even sudden death, there will be activities after the transient post-sternal and precordial region of the boring pain or pressure; cerebral atherosclerosis can cause cerebral ischemia, cerebral atrophy, etc., there will be intermittent numbness of the hands and feet, weakness, vertigo or gait unsteady without intracranial pressure increase signs.
- Atherosclerosis of the renal arteries often causes nocturia, persistent hypertension, and severe renal insufficiencyMesenteric artery atherosclerosis can be manifested as abdominal pain after meal, dyspepsia, constipation, etc., and in severe cases, necrosis of intestinal wall can cause blood in stool, paralytic intestinal obstruction, etc.; atherosclerosis of lower limb arteries causes serious narrowing of vascular lumen, which can lead to intermittent claudication, disappearance of dorsal arterial pulsation of the foot, and in severe cases, even gangrene can occur.
- Mild stenosis can be managed to control further aggravation of symptomsModerate stenosis depends on the severity of the symptoms, with mild symptoms treated under observation and severe symptoms requiring further surgery. Severe stenosis requires surgical treatment, such as stenting or endarterectomy.
Third, how to detect and treat carotid plaque?
(1) How to detect carotid plaque
- We can go to regular hospitals for appropriate tests, such as blood tests, carotid ultrasound, TCD, CTA of the head and neck aortic arch, and cerebral angiography.Blood tests are performed to identify the internal components of our blood, such as blood cholesterol, triacylglycerol and HDL; carotid ultrasound and TCD are both non-invasive, radiation-free tests that can identify the degree of stenosis of the blood vessels as well as the speed of blood flow.
- Head and neck aortic arch CTA and cerebral angiography are used to visualize the narrowing of the lumen, the location and extent of lesions due to atherosclerosis.Compared to carotid ultrasound and TCD to be more accurate; and cerebral angiography is the gold standard for the diagnosis of cerebrovascular disease, as the saying goes, it sees most accurately, but need to receive a certain amount of radiation.
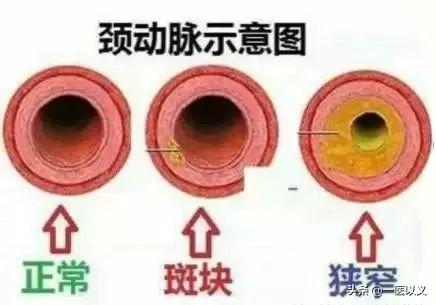
- First, the nature of the plaque and the degree of stenosis is further clarified by examination.Three cases: (1) stenosis less than 75%, there is no discomfort, then you can continue to observe, diet and medication control can be; (2) stenosis less than 75%, there are symptoms of ischemia, then there is a need for further intervention; (3) stenosis is greater than 75%, then you need to assess the situation for surgical treatment, such as carotid endothelial stripping or intervention. stenting.
(2) What's next?
- The treatment of atherosclerosis is divided into two areas. What about life?To control diet, increase exercise, maintain weight, etc.. Specifically: Eat a sensible diet; total calories in the diet should not be too high to prevent overweight. Significantly reduce the intake of saturated fats and sugars. Increase the intake of soluble fiber.
- Adhere to a moderate amount of physical activity, and set the intensity of activity according to your condition, activity habits, and heart functionThe most important thing to do is to control the risk factors of diabetes, including diet. If you have diabetes, you should control your blood glucose in a timely manner, including dietary control.

- What about drugs, let's ask the experts to give us the most professional guidance. For this atherosclerotic lesion, theThe most important are statins, like Rosuvastatin, Atorvastatin, Simvastatin, etc.These medications are able to lower LDL-C, the cholesterol we commonly call "bad" cholesterol. These medications are designed to lower low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), which is commonly known as the "bad" cholesterol, and the higher the LDL-C level, the more it contributes to increased atherosclerosis. Therefore, lowering LDL-C levels to normal levels is the goal.
- Of the many statins available, theThe best for lowering LDL-C levels is Rosuvastatin, a new generation of new aqueous statin, which is potent in lowering lipids while being safer.. In addition, some people have high triglycerides, need to use some other lipid-regulating drugs, such as Betaine, niacin drugs and so on, are able to reduce triglycerides. Of course, atherosclerosis patients, in addition to regulating lipids, but also with anti-thrombotic drugs, that is, we are familiar with aspirin or clopidogrel, these two generally use a can. When you have acute cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease, you need to take both.

- Ultimately, the most basic treatment for atherosclerosis is statin lipid modulation, and another is anti-platelet aggregation to prevent thrombosis.
- Anyone else care to know, I have carotid plaque, can I get better on medication?Medication is to regulate the internal components of the blood to regulate lipids and stabilize plaque.. Fully calcified and sclerotic plaques are very difficult to be relieved by medication alone, when theSurgical or interventional intervention is requiredthat mechanically enlarges the vessel lumen. Medication alone stabilizes unstable plaques that are prone to dislodgement, thus reducing the risk of stroke due to plaque dislodgement.
Fourth, what are the preventive measures of carotid plaque
- Primary prevention: promote a light diet rich in vitamin C (e.g., fresh vegetables, fruits and vegetables) and plant proteins (e.g., beans and their products).; do not smoke, do not drink strong alcohol; maintain an optimistic mindset and relaxed mood; 40 years of age and over the people adhere to at least once a year physical examination; from childhood onwards, that is, should not eat a diet high in cholesterol, high animal fats, but also to avoid eating too much, to prevent obesity.
- Secondary prevention: active treatment of diseases related to the disease, such as hypertension, obesity, hyperlipidemia, gout, diabetes mellitus, liver disease, nephrotic syndrome and related endocrine diseases, etc... Lifelong antithrombotic use of aspirin, long-term or lifelong use of statin lipid-modulating drugs, and active use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors.
- Therefore, when we find carotid plaque, don't worry too much, we should seek regular treatment and take medication regularly and improve our diet and lifestyle. The symptoms will be controlled and the risk of stroke will be reduced. Finally, it is recommended thatEat regularly, be active, stay healthy and be happy.

summarize
Carotid artery plaque formation itself is not harmful, because with the increase of age and the accumulation of underlying diseases, many elderly people suffer from different degrees of carotid artery plaque formation, but if the plaque is larger, the narrowing of the blood vessel is obvious, or plaque detachment occurs, there is a certain degree of harm to the body, and sometimes serious consequences such as cerebral infarction can occur.Therefore, it is important to detect the formation of carotid plaques at an early stage and then give targeted treatment and prevention to minimize the harmful effects of carotid plaques on the human body.
Hello, I'm medical worker Zhang, a practicing physician, can popularize health knowledge for everyone, if you want to know more, please pay attention to me!
Is carotid plaque dangerous? What are the risks to the body?
What is carotid plaque?
Carotid plaque is a manifestation of carotid atherosclerosis, which occurs at the bifurcation of the common carotid arteryIt is a non-inflammatory, degenerative and hyperplastic lesion of the carotid arteries, causing thickening, stiffening and loss of elasticity of the arteries, eventually leading to narrowing of the lumen, which is most common in the elderly.
Where exactly is the danger of carotid plaque?
The danger lies mainly in unstable plaques, that is, plaques that are not strong in the walls of the blood vessels and can easily fall off.When the plaque is dislodged in whole or in part it becomes an embolus in the blood stream and reaches the brain with the blood flow to block the cerebral arteries.
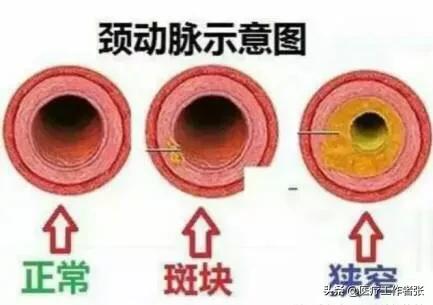
What harm does carotid plaque cause?
- When carotid plaque is not dislodged, resulting in carotid stenosis, theOften caused by ischemia and hypoxia of brain tissue, patients often feel dizziness, dizziness, poor memory, and a significant decline in thinking.
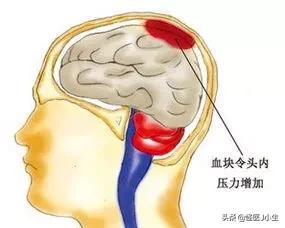
- If atherosclerotic plaque is dislodged from the hardened carotid arteries and travels with the bloodstream and blocks the cerebral vessels, theThis can lead to cerebral infarction, with stroke manifestations such as slurred speech, slurred speech, paralyzed limbs, and even life-threatening!
How is carotid plaque treated?
- Non-pharmacological treatment:Once carotid plaque is detected, regardless of the size of the plaque and whether or not it has caused a narrowing of the vessel lumen, lifestyle interventions should be carried out immediately, i.e., control of dietary intake, improvement of dietary structure, increase in physical activity, reduction of body weight, smoking cessation and restriction of alcohol intake.
- Active control of various cardiovascular risk factors:If you have high blood pressure or diabetes mellitus, you should also actively and reasonably control your blood pressure and blood sugar. Both high blood pressure and diabetes are important factors in the formation of carotid atherosclerotic plaque. Aggressive control of blood pressure and blood sugar under the supervision of a doctor can help to slow the growth of atherosclerotic plaque.
- Statin therapy:The need for Applatin therapy is determined on a patient-by-patient basis.
- If carotid plaque has caused significant stenosis of the carotid artery (≥50% stenosis), statin therapy is generally indicated;
- If the carotid plaque does not result in significant stenosis (<50% stenosis), the patient needs to be evaluated for the presence of cardiovascular disease or other risk factors for cardiovascular disease. The following scenarios are possible: 1) established coronary artery disease or ischemic stroke, with or without significant stenosis of the carotid arteries; 2) diabetes mellitus without coronary artery disease or ischemic stroke with hypertension; 3) diabetes mellitus with an LDL-C > 2.6 mmol/L; 4) chronic kidney disease (stage III or IV) with an LDL-C > 2.6 mmol/L; and 5) the presence of hypertension or other risk factors and LDL-C > 3.4 mmol/L.
- Aspirin therapy:The need for aspirin application is also determined on a patient-by-patient basis.
- If patients have significant carotid stenosis (≥50% stenosis), they should generally be given aspirin (75-150 mg daily).
- If a patient has only one or more plaques that do not result in carotid stenosis, or if the stenosis is present but <50%, the need for aspirin for primary prevention should be determined in the context of other cardiovascular risk factors present in the patient. Aspirin (75-150 mg daily) is recommended for these patients if they have ≥3 of the following risk factors: 1) men ≥50 years of age or postmenopausal women; 2) preliminarily controlled hypertension (blood pressure <150/90 mm Hg in hypertensive patients after treatment); 3) diabetes mellitus; 4) hypercholesterolemia; 5) obesity (body mass index ≥28); and 6) early-onset cardiovascular disease. family history (onset of disease in one or both parents <55 years for men and <65 years for women); 7) tobacco smoking
- Surgical treatment:Indications for surgery include: 1) symptomatic carotid stenosis with ≥70% carotid stenosis on noninvasive examination or more than 50% stenosis on angiography; 2) asymptomatic carotid stenosis with ≥70% stenosis on noninvasive examination or ≥60% stenosis on angiography; and 3) asymptomatic carotid stenosis with <70% stenosis on noninvasive examination but with angiography or other examination suggesting that the stenotic lesion those who are in an unstable state. Currently, the two most commonly used surgical procedures are internal carotid artery exfoliation (CEA) and carotid artery stenting (CAS).
In summary: There is no need to be overly nervous about finding carotid plaque, but it must be treated aggressively under the guidance of your doctor!
Welcome to leave a comment, think the writing is good, remember to point a praise oh! If you want to know other health knowledge, pay attention to me, private message for you to answer!
I am a medical doctor, a resident, specializing in the popularization of medical knowledge for the benefit of human health, if you want to know more, please pay attention to me, have questions can be left a message, will respond!
Is carotid plaque dangerous? What damage can it cause to the body?
I'm in the hospital, often come across the elderly have carotid plaque, which is mainly related to age and lifestyle habits, many people will also ask me what the harm is, people are very concerned about this issue, today I'll share the knowledge about carotid plaque.
1. What are the dangers of carotid plaque?
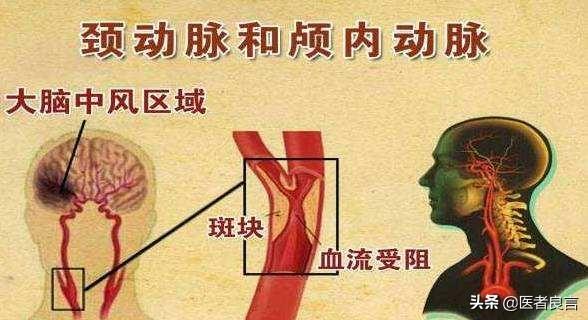
The degree of carotid plaque is in fact proportional to cerebral atherosclerosis, the carotid artery in the human body is considered a large blood vessel, and the coronary arteries of the heart, the cerebral blood vessels are relatively finer, more prone to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques; carotid artery plaque on the human body is mainly depends on the nature of the plaque and the degree of stenosis caused by the carotid artery plaques on the human body.If the plaque is a soft plaque, that plaque is very unstable, especially prone to diseases such as myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction; if the plaque is relatively large, it will lead to carotid artery stenosis, resulting in a reduction in the blood supply to the brain, theIt can cause symptoms such as dizziness, nausea and vomiting, and in more severe cases can cause chronic hypoxia in the brain, which can lead to sudden death;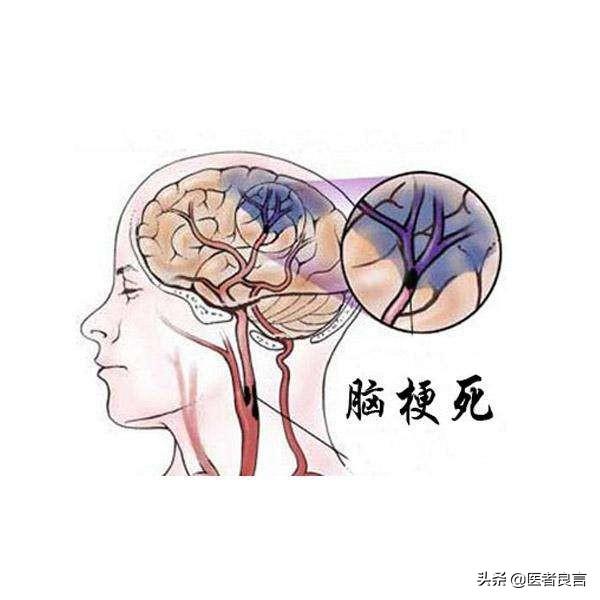
2. What should I do if I have carotid plaque?
- Complete the neck ultrasound:The nature of the carotid plaque and the degree of stenosis can be clarified; if the arterial stenosis has not exceeded 50%, it may be reversed or even regressed if treated aggressively; if the stenosis exceeds 70%, then surgical treatment will be considered;
- Take your medication on time:If the patient has no contraindications to aspirin and statins, they are required for life to delay carotid artery stenosis and prevent the formation of emboli;

- Control of blood lipids:If the patient is young and has no underlying disease, LDL can be controlled <2.6 mmol/L. If there is a combination of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, and renal impairment, LDL should be controlled <1.8 mmol/L;
- Regularly check the neck vascular ultrasound;
- Active treatment of high blood pressure and diabetes.
Final Summary: Carotid plaque is mainly prone to increase the risk of diseases such as cerebral infarction and myocardial infarction, and it can also lead to insufficient blood supply to the brain.
The above is my answer to the question, purely hand-typed, it is not easy, if you feel that the writing can be rewarded with a praise, if you have any questions you can leave a message below ......
I am Jiang Xiaosheng, I hope that through the opportunity of popularizing medical knowledge to let people better prevent diseases, understand diseases, and have a healthy and happy life habits. Interested friends can follow me. Let me answer about this question.
Is carotid atherosclerosis dangerous? What damage can it cause?
1. There is a risk, but not all plaques are at risk.
2. Under normal circumstances, there are two kinds of carotid plaques, one is stable plaque and the other is unstable plaque. Stable plaque is less dangerous and unstable plaque is the most dangerous.
3, in general, the plaque surface will be wrapped with a layer of fiber cap to protect the plaque. And unstable plaque in emotional excitement, strenuous exercise, alcoholism, cold and other circumstances, will cause elevated blood pressure, blood flow impact or vasospasm, this time the fibrous cap will rupture, plaque lipids and other substances out of the plaque leading to red blood cells, platelets, etc. The aggregation of thrombus, if blocked cerebral blood vessels, will lead to acute cerebral infarction.
Therefore, unstable plaque can be said to exist in the body of an "untimely bomb", as long as there are enough conditions for the bomb to detonate, it may explode and rupture at any time, triggering serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular events, endangering the lives of patients.

So does carotid plaque need to be treated?
The answer is yes. If atherosclerotic plaque is found in the carotid artery, it is possible that plaque may also be present in other parts of the body such as the coronary arteries and cerebral arteries. Therefore, once a carotid plaque is detected, it should be actively treated.
So how do you treat carotid plaque?
1. Non-pharmacological treatment: control diet, avoid greasy food, enhance exercise, reduce weight, stop smoking and limit alcohol.
2. Actively control blood sugar and blood pressure. Helps to slow the continued growth of atherosclerotic plaque.
3. Severe cases require long-term treatment with statins.
4. Long-term aspirin is also required if the patient has the following conditions: significant carotid stenosis (≥50% stenosis), age >50 years, hypertension, diabetes, obesity, hypercholesterolemia, and heart disease.
5. Patients whose plaques cause severe stenosis or even occlusion of the carotid arteries may also need carotid stenting or carotid endarterectomy, etc.
To summarize, if carotid plaque is found, there is no need to be overly nervous, but it must be actively treated under the guidance of a doctor.

The above is my answer. I am Jiang Xiaosheng, interested friends can pay attention to me, you can also click a like and then go chant. If there is any question you can directly invite me to answer, see will be back, back will be fast. Thank you for your support.

Carotid plaque is a common arterial disease in middle-aged and elderly people, and its occurrence and development are related to a number of risk factors, including age, gender, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, and alcoholism. So, is carotid plaque dangerous? What kind of damage will it bring to the body? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze it for you.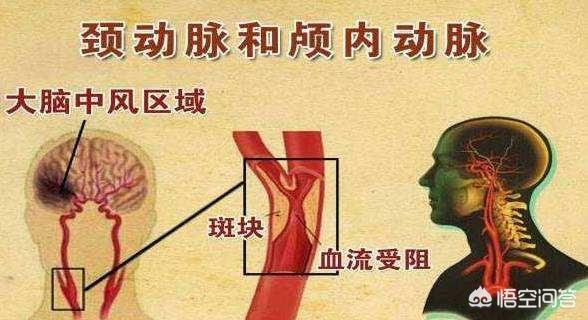
Carotid artery is the most important blood supply channel for the brain, due to the large blood flow of the carotid artery, under the impact of blood flow, the carotid artery intima-media has a higher chance of lesions, and it is one of the arteries that are often involved in atherosclerosis. Carotid atherosclerosis will lead to carotid artery stenosis and plaque formation, if the carotid artery stenosis is light, or plaque is small and plaque stability can be asymptomatic; however, if the carotid artery stenosis is heavier, plaque is larger or unstable, then it can produce related symptoms, such as cerebral ischemia, cerebral atrophy, or even cerebral infarction and other cerebrovascular accidents.
Cerebral ischemia.Carotid artery stenosis can lead to reduced blood supply to the brain. Early carotid artery can increase the blood supply to the brain through compensatory dilation, or the establishment of collateral circulation, but with the aggravation of stenosis, it will gradually enter into the period of loss of compensation, and symptoms of cerebral ischemia will appear, such as vertigo, headache, fainting and so on, these symptoms are the brain's signal of distress, and it should be timely to consult the doctor, and to review the carotid ultrasonography to understand the specific condition, so that the corresponding treatment can be given. Improve cerebral blood supply and prevent cerebrovascular accidents.
Brain atrophy.Prolonged ischemia of the brain can cause cerebral atrophy and vascular dementia. Due to the insidious onset and slow development of vascular dementia, it is not easy to be detected in the early stage, which can be manifested as mild cognitive dysfunction, such as mild decline in memory, inattention, and decline in learning ability, etc. With the progression of the disease, the above symptoms will gradually aggravate, and there will be serious memory loss, intellectual decline, etc., and even affective indifference, even symptoms such as emotional apathy, crying and laughing, and inability to take care of oneself in daily life.
Cerebral infarction.If the carotid artery plaque is unstable, plaque rupture and bleeding can occur, and the material inside the plaque exposed in the blood can easily induce platelet aggregation, form thrombus and block the cerebral artery, resulting in acute cerebral infarction, and the patient can have headache, vomiting, impaired consciousness, hemiparesis, hemianopsia, hemianopsia, aphasia and other symptoms, which not only have a high fatality rate, but also a high rate of disability, and it is the cerebrovascular disease that needs to be focused on the prevention of the middle and old ages. Therefore, all patients with unstable plaques should be given statin to stabilize plaques and even aspirin to prevent thrombosis.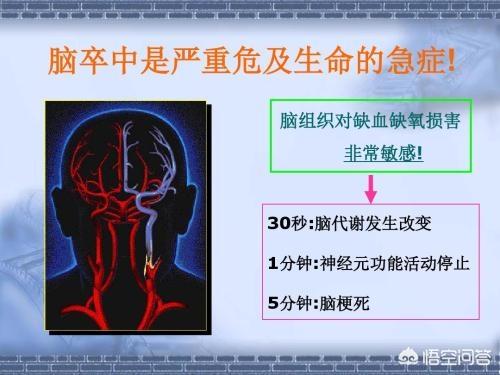
In summary, the occurrence of carotid atherosclerosis and plaque formation can lead to cerebral ischemia, symptoms such as dizziness, headache, fainting, etc.; cerebral atrophy can occur, symptoms such as memory loss, inattention, intellectual decline, etc.; plaque rupture can lead to cerebral infarction and other acute cerebrovascular events.
Thank you all for reading!
We are looking forward to your attention and presenting more health knowledge to you!
Note: The images in this article come from the Internet, if infringement of copyright, please contact to remove. The content of the article is only as a health science popularization, not as a medical advice or opinion, and does not have the condition of medical guidance.
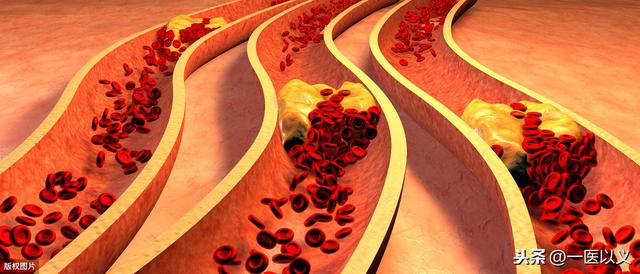
Carotid plaque is one of the manifestations of atherosclerosis, with the increase of age, our arteries gradually aging, and at the same time in the irrational diet, smoking and drinking, lack of exercise, obesity and other risk factors and hypertension, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidaemia and other chronic diseases, the incidence of arterial plaque is also increasing, with the progression of the disease, the arterial plaque can rupture or form a thrombus, and ultimately cause cerebral tissue Ischemia, hypoxia, and even necrosis occur, increasing the occurrence of stroke.
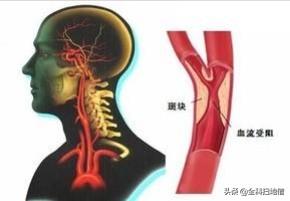
Carotid artery can be divided into stable plaque and unstable plaque according to the characteristics of plaque echo under color ultrasound, in which stable plaque is mainly calcified hard plaque, which is not suitable for rupture and has relatively high prognosis. Stable plaques are mainly calcified hard plaques, which are not suitable for rupture and have relatively high prognosis. Unstable plaques are mainly soft plaques, flat plaques and mixed plaques, which are relatively easy to rupture or surface thrombosis, leading to cerebral ischemia and even cerebral infarction.
For carotid plaque, we should pay attention to improve the lifestyle, to: ① reasonable diet, low salt, low fat, low sugar; ② do not smoke or quit smoking, avoid passive smoking; ③ limit the consumption of alcohol, do not drink alcohol is best, it is difficult to give up alcohol should be strictly limited to the amount and frequency of recommended to drink red wine; ④ appropriate exercise, aerobic exercise, talking about gradual and orderly progression; ⑤ control body weight, the attention of obese people to lose weight; ⑥ maintain a good state of mind and regular rest and relaxation. Weight control, obese people should pay attention to weight loss; ⑥ Maintain a good mindset and regular work and rest.
While improving our lifestyle, we should also actively treat underlying diseases such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, etc., to control blood pressure, blood glucose, and blood lipids up to standard. For unstable plaque, it is recommended to use aspirin to prevent thrombosis and statins to stabilize plaque while improving lifestyle. While we standardize the treatment, we should also pay attention to monitoring the changes and regular review.
This article is answered by General Practice Sweeper, we hope that it will be helpful to you, copyright ©️, reproduced with permission. Please correct any deficiencies. The article is for reference only and is not intended as medical advice or medical guidance.
Hello, I'm Dr. Yang, and I'll answer this user's question.
Carotid artery plaque tends to be uncomfortable unless it has caused significant narrowing of the carotid arteries which can cause symptoms such as dizziness and fatigue, but most people only find it during a physical examination.
Let's start by telling you what a carotid plaque is.
Arterial plaque can occur anywhere in the blood vessels, wherever there is an artery, and an attack in the carotid artery is called carotid plaque. If you compare a blood vessel to a water pipe, carotid plaque can simply be understood as the garbage in the water pipe. However, plaque is not simply deposited on the surface of the blood vessel wall. The blood vessel wall is originally smooth and elastic, but if the blood vessel wall is a little rough and broken and hardened due to various reasons, some components in the blood vessel will enter into the blood vessel wall through this "mouth", and thus gradually develop and grow to form arterial plaque. Therefore, the formation of arterial plaque is not simply attached to the surface of the blood vessel wall.
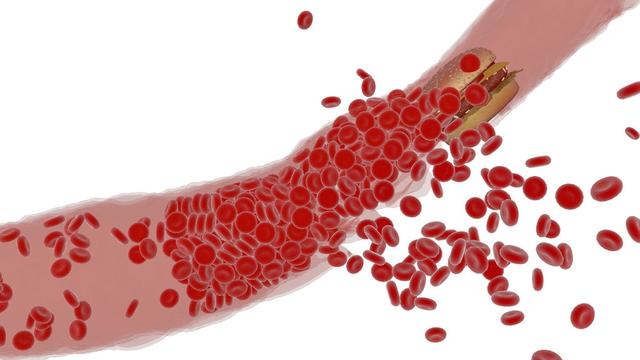
Is carotid plaque dangerous? What damage can it cause to the body?
Carotid plaque is not dangerous in itself if it does not cause significant narrowing of the carotid arteries or does not affect the blood supply to the brain, but its danger mainly comes from the possibility of dislodgment. Once dislodged, carotid plaque will enter the arteries of the brain with the flow of blood, thus blocking the blood vessels and inducing cerebral infarction, which may result in serious consequences such as hemiplegia, slurred speech, and may even jeopardize the life of the patient.
However, there is no need to be overly nervous as not all carotid plaques will dislodge. Whether carotid plaque is dislodged or not is related to the location, composition, size and shape of the carotid artery, as well as the general condition of the body and other factors. For people who have small dense hard plaques or hard plaques and have no other risk factors for cardiovascular disease, the likelihood of dislodgement is still very low.
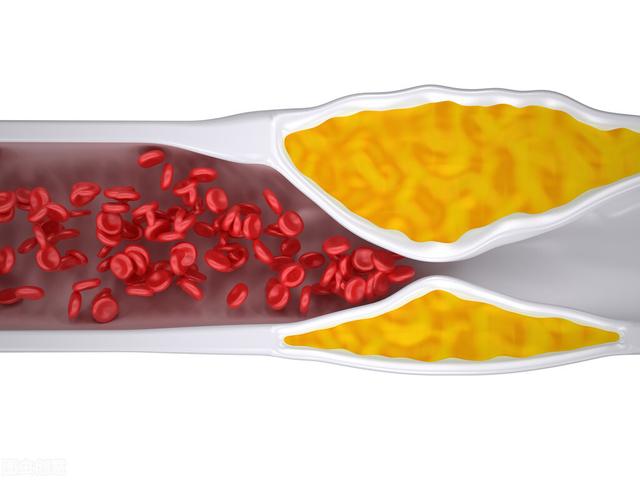
So the question is, what causes arterial plaque to form and how can it be treated?
The first is age. The older you get, the more likely your arteries are to develop plaque. basically everyone over the age of 70 has plaque forming in their arteries, and that's a natural law we can't change.
However, the formation of arterial plaque is not just about age, but is also closely related to an unhealthy lifestyle. Smoking will cause earlier hardening of blood vessels, unbalanced, high-calorie, high-fat and high-salt diets will also exacerbate vascular damage, lack of exercise is also not conducive to vascular health, and problems such as high blood lipids, high blood sugar, high blood pressure, high uric acid, and obesity will exacerbate vascular aging and result in the earlier appearance of arterial plaques. Among them, the elevation of LDL cholesterol in blood lipids is the trigger factor leading to the formation of carotid plaque. It is actually not uncommon for people in their 30s to be examined and found to have carotid plaque on an outpatient basis.
Therefore, a healthy lifestyle is the basic means of preventing and controlling arterial plaque, and controlling blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipid, uric acid and other indicators is also the key to preventing and controlling arterial plaque. Especially the control of blood lipids, if necessary, under the guidance of the doctor can use drugs for lipid regulation therapy, the most commonly used lipid regulating drugs for statins, such as atorvastatin, resuvastatin and so on. For carotid artery stenosis (usually ≥75% stenosis), stent implantation or endothelial debridement can be chosen after doctor's evaluation.

Well, that's all for today. If you think I've done a good job, just give me a like~ If you have any questions, you can leave a comment below. I am Dr. Yang, a general practitioner who focuses on blood pressure, blood sugar, blood lipid and uric acid management. Follow me to learn more about health.
As people's life expectancy increases and the level of medical diagnosis advances, the number of people with plaque found in the carotid artery increases. For carotid artery plaque, I believe that many people will ask the following questions: Why does plaque form in the carotid artery? Will this plaque bring me danger? Today Dr. Lee talks about his understanding of this issue.
Headline Healer Li Feng
First, it is important to understand the connection and difference between three terms: atherosclerosis, atherosclerosis and atherosclerotic plaque. Atherosclerosis refers to the arterial structure of aging, elasticity is weakened; atherosclerosis refers to the hardening of the arterial wall on the basis of damage to produce a gap, this gap needs to be repaired by lipids, that is, in the sclerosis on the basis of the accompanied by lipid deposition, atherosclerosis plaques refers to atherosclerosis lipid deposition to the lumen of the bulge.
In fact, tiny carotid atherosclerotic plaques start in some people from the age of about 5 years, the number of people who have plaques will gradually increase around the age of 40 years, and by the age of 60 years, almost 100% of people will have carotid plaques. It should be noted that among the carotid atherosclerotic plaques, the unstable plaques are the most dangerous ones, which are very easy to fall off, and such falling off can lead to cerebral thrombosis and thus symptoms such as numbness of limbs, speech disorders and hemiplegia. Currently, there is no reliable means to diagnose unstable plaques, except that ultrasound, MRI and CTA are helpful in the evaluation of unstable plaques.
In addition, carotid atherosclerosis also causes arterial stenosis. When the stenosis is <50%, patients basically do not experience any symptoms. However, when the stenosis exceeds 50%, insufficient blood supply to the brain may occur, such as dizziness, headaches, and memory loss. Once the stenosis exceeds 70%, surgery is often an option, and the more common procedures include internal carotid artery dissection and carotid stenting.
The cause of atherosclerosis in the neck is closely related to chronic inflammation in the body, which can be brought on by metabolic disorders, stress, sleep, and poor nutritional status. One thing I would like to emphasize here is the body's high insulin condition, which is the most common cause of chronic inflammation. Excessive intake of refined rice and flour, refined vegetable oils, and artificial sugars can induce hyperinsulinism and increase damage to the lining of the arteries (including the carotid arteries, naturally).
In fact, in our daily life, allicin in garlic, lycopene in tomatoes (cooked tomatoes), omega-3 unsaturated fatty acids in deep-sea fish, and vitamin K2 in fermented foods have a positive impact on reducing chronic inflammatory conditions and the formation of arterial plaque.
Feel free to follow my headline- Healer Li Feng. Also welcome to follow my watermelon video. Those who wish to communicate can join Dr. Lee's Hashimoto Discussion Circle for communication (not limited to Hashimoto).
Headline - Healer Li Feng
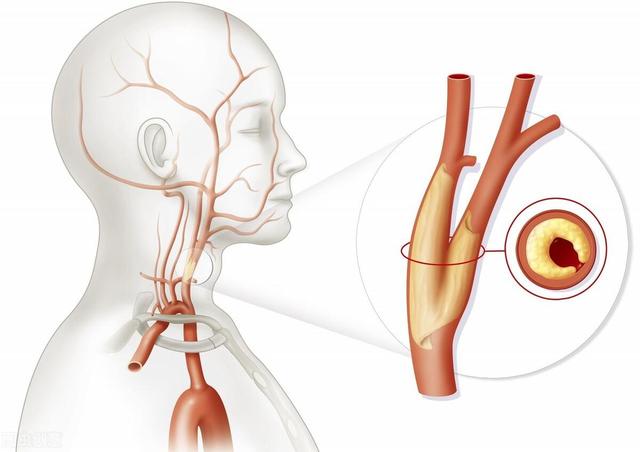
Is carotid plaque dangerous? What harm can it do to your body? Dr. Cardiovascular Xu is here to answer your questions.
The carotid arteries are relatively superficial arteries in our body and can be palpated by hand.
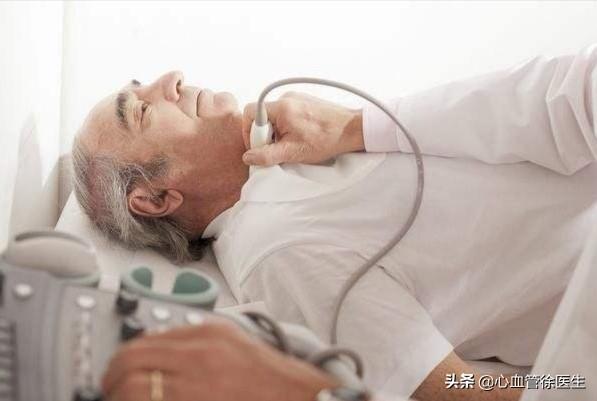
Carotid ultrasound can detect carotid plaque at an early stage. Carotid ultrasound is needed to assess atherosclerosis in people with high risk of cardiovascular diseases such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, coronary heart disease and cerebral infarction.
So if a carotid plaque is found on examination, is it dangerous? Is it dangerous to the body? It depends on the following two factors.
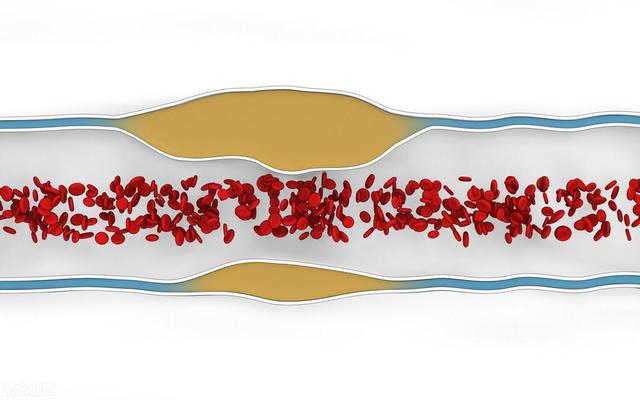
1. Carotid plaque size and degree of stenosis.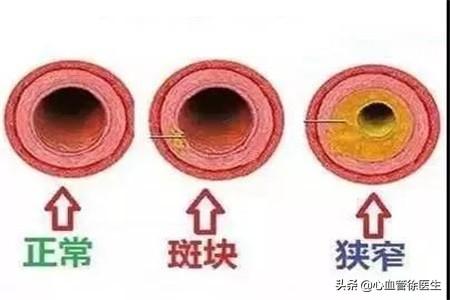
If the carotid plaque is not large and does not cause narrowing of the lumen or only mild to moderate narrowing, it has no effect on the blood supply to the brain. If the plaque is large and causes a severe narrowing of the lumen, the blood supply to the brain will be affected and the patient may experience symptoms of ischemia such as dizziness, blackout, or even fainting.
2. Whether the carotid plaque is a stable or unstable plaque.
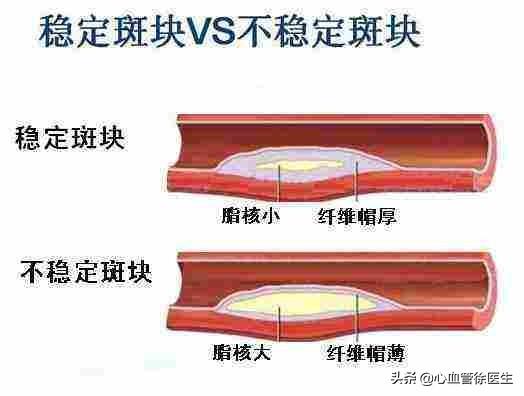
Whether the carotid plaque is stable or unstable depends on the description on the ultrasound report. If it is a hypoechoic plaque, it is considered to be an unstable plaque, which is prone to rupture, and some small plaques or blood clots will follow the blood flow to the cerebral artery, causing localized vascular blockage and acute cerebral infarction. If it is a strong echogenic plaque, it is considered to be a stable plaque, which is not prone to rupture and has little risk of causing a cerebral infarction.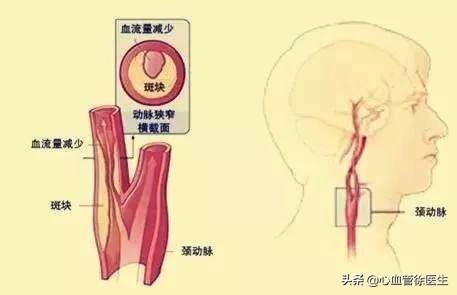
In conclusion, if carotid plaques are found, a comprehensive assessment should be made based on the size and stability of the plaque, combined with the patient's symptoms, and the combined cardiovascular risk factors, and an individualized treatment plan should be given.
If it is a relatively small strong echogenic plaque, the lumen of the blood vessel is not significantly narrowed, and there will be no physical discomfort, it is sufficient to take medication and adhere to a healthy lifestyle to avoid further development of the plaque.
If the plaque is large enough to affect the blood supply to the brain, it needs to be treated aggressively, with localized stent implantation to address ischemia, and long-term medication as well as maintaining a healthy lifestyle in the later stages to avoid recurrence of the problem.
If the plaque is an unstable plaque, statin stabilization therapy needs to be given aggressively to avoid rupture of the plaque causing a thrombus and resulting in a cerebral infarction.
Focus on health, focus on cardiovascular Dr. Xu!
In health checkups, carotid ultrasound is mainly used to observe the carotid artery, a relatively superficial arterial vessel. By evaluating the degree of atherosclerosis in the carotid artery, it is possible to determine not only the direct health effects of carotid atherosclerosis itself, but also to predict the degree of atherosclerosis in other important parts of the body, such as the heart, the brain, and the kidneys, or even the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular emergencies.
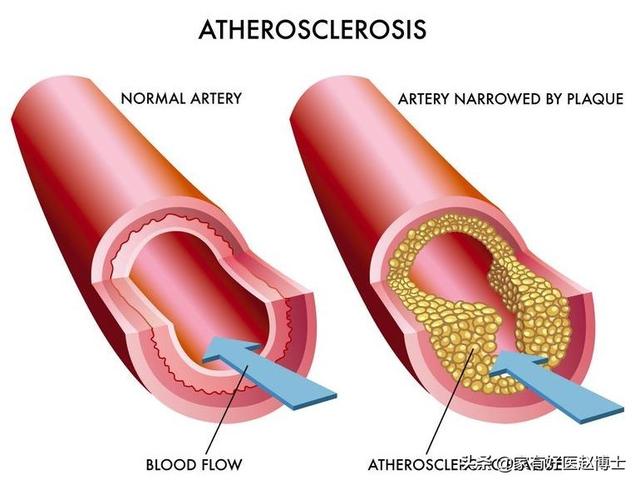
Atherosclerosis, as we often refer to it, tends to have several typical stages of development:
In the first stage, lipid deposits on the intima appear as "lipid striae";
In the second stage, the lipid pattern develops further, forming fibrous plaques;
In the third stage, the fibrous plaque progresses to an atheromatous plaque;
In the fourth stage, the atheromatous plaque is based on complications such as plaque bleeding, plaque rupture, thrombosis, and calcification.
In other words, when we clearly see plaque formation in the carotid artery lining through carotid ultrasound, it often means that the degree of atherosclerosis has already entered the third stage, and in the event of a fourth stage, it will often lead to serious clinical consequences. Therefore, carotid artery plaque is of course a clear danger, but due to the fact that the symptoms are often not obvious and the changes are very subtle, many people "throw away" the results of this test, in fact, there is a great risk.
Carotid plaque, whether stable or not, determines its harm and risk
The carotid artery is the "necessary route" for the heart to pump blood to the brain, and lesions of the carotid artery can often lead directly to brain damage:
- If the plaque in the carotid artery causes narrowing of the internal diameter of the carotid artery, then the blood supply to the brain will be affected, and symptoms and manifestations related to insufficient blood supply to the brain and transient cerebral ischemia can occur;
- Carotid artery plaque if rupture, in the rupture will quickly form acute thrombus, and these thrombi once dislodged, with the blood flow will "fall into" the brain, randomly infarction of brain tissue, resulting in ischemic stroke, asymptomatic cerebral infarction and other diseases.
However, this is not necessarily the case whenever plaque is found in the carotid arteries! Plaque in the carotid artery can also be "stable" or "unstable". The so-called "unstable plaques", also known as "vulnerable plaques", mainly refer to those carotid plaques that pose a higher risk of causing these damages.
Unfortunately, however, medical research has found that most of the carotid plaques that can be identified clinically by ultrasound or CT angiography are unstable plaques. In other words, once we see a carotid plaque on ultrasound, the odds are that the plaque is "unstable".
Increased overall risk of cardiovascular events in the presence of carotid plaque
The carotid artery is only a small segment of the arterial system of the whole body, but its detection can be regarded as a "sample survey" of the whole arterial system of the whole body. The detection of plaque in the carotid artery is often indicative of atherosclerosis in other parts of the arteries:
- People with carotid plaques have a high probability of detecting coronary heart disease because, while atherosclerotic lesions occur in the carotid arteries, there is a high probability that the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the heart, are undergoing similar changes;
- Similar to coronary artery disease, people with carotid plaque have a high probability of having atherosclerotic stenosis in the cerebral and renal arteries, so these people tend to be susceptible to ischemic stroke and chronic kidney disease as well.
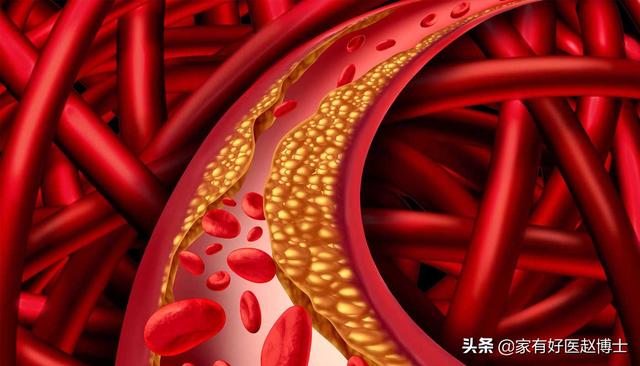
Acute myocardial infarction can be triggered by rupture of plaque and formation of acute thrombus in the coronary arteries, while acute cerebral infarction can be caused by sudden infarction of an important blood vessel in the brain. These acute and potentially life-threatening major cardiovascular diseases are what we often refer to as cardiovascular events. The presence of carotid artery plaque, without a doubt, suggests that the likelihood of a cardiovascular event is significantly higher.
Statin is the foundation of carotid plaque treatment
There are many people who are not familiar with the treatment of carotid artery plaque. Some of them think that once carotid plaque is formed, it is not easy to deal with, anyway, there is no symptom for the time being, so they will slowly forget about it; while some of them are very afraid when they hear that they need to operate or put stent in the carotid artery.
According to the opinion in the Chinese Consensus on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Head and Neck Atherosclerosis, the treatment of carotid plaque should be based on statin lipid-lowering drugs. The use of statin lipid-lowering drugs can help stop new plaque growth, stabilize existing plaque, and reduce the risk of cardiovascular events.
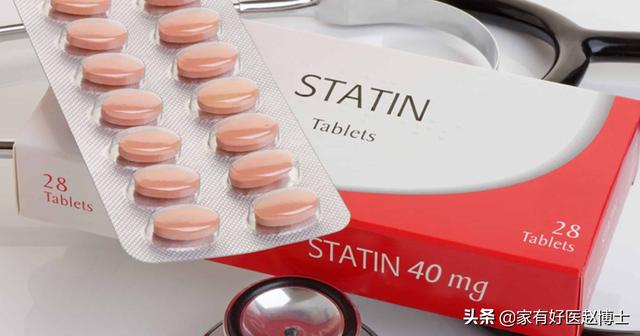
In addition to statins, high blood pressure, diabetes, and factors such as smoking, alcohol consumption, and poor lifestyle habits should also be controlled.
To summarize, carotid plaque is certainly harmful, and its own complications and can lead directly to problems such as stroke and cerebral ischemia. Not only that, but the presence of carotid plaque suggests an increased risk of cardiovascular events. The basic treatment to control carotid plaque is statin lipid-lowering drugs.
Okay, follow "Dr. Zhao, the Family Doctor", please share these medical tips with friends who need them!

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.