Fasting blood sugar 12.6, can I get back to normal with late control without insulin and pills?
Thanks for the invitation. If your fasting glucose was tested in the hospital, you probably already know the answer, but are just fantasizing to find comfort, sorry, as a responsible and knowledgeable person, sugar really can't give you comfort.
Fasting 12.6mmol / L is the concept of what it is, the normal fasting blood glucose range between 3.9mmol / L-6.1mmol / L, 12.6 is already two times the normal high value, this is only fasting blood glucose, I do not know how much your postprandial blood glucose, the general Chinese residents of type 2 diabetes mellitus is usually based on the postprandial glucose increase, that is to say, your postprandial blood glucose may be even more high! I don't know what your postprandial blood glucose is!
What does high blood sugar mean? It means that every organ, tissue, and cell in your body where there are blood vessels is suffering from glucotoxicity, and most people are diagnosed with diabetes years before they even have complications, and if you're not an exception, your organism has been suffering from glucotoxicity for years!
And you still want to get back to normal through late control without insulin and pills, I can only lol! What does this kind of thinking mean? It's like a car with a tire that's about to break down and an engine that's about to explode, and the driver is thinking, "I'll see what happens to the car after I've run another 25,000 miles! And what is post control? How is post control? When is it? It's just the most common apathetic cop-out for sugar lovers!
At the early stage of diabetes diagnosis, timely use of medication or insulin intensive treatment, can be an early solution to high blood sugar "glucotoxicity" damage to the pancreatic islet function, to maximize the preservation of pancreatic islet function. Even with medication or insulin injections, dietary control and exercise, as the two cornerstones of diabetes prevention and treatment, should be carried out at the same time, and will continue to accompany diabetic patients throughout their lives. Even after regular active treatment, can only maintain blood glucose in the normal range, and normal people, but diabetes hat can not be removed for life!
Sugar man health network, a temperature control of sugar platform, welcome to pay attention to the questions and answers!
Hello everyone, I am Dr. Yang. Let me answer this netizen's question.
First of all, let me tell you what the concept of fasting blood glucose 12.6 mmol/L is.
If you have not been diagnosed with diabetes before and have not taken hypoglycemic medication, the normal fasting blood sugar is usually between 3.9 and 6.1 mmol/L; if the fasting blood sugar is between 6.1 and 7.0 mmol/L it belongs to the impaired fasting blood sugar; and if you have taken two measurements of fasting blood sugar that are both at 7.0 mmol/L and above, then you can be diagnosed with diabetes.
So, a fasting blood sugar of 12.6 mmol/L is already very high, more than twice as high as the average person! With such a high fasting blood sugar, even if diabetes was not diagnosed before, it is basically diagnosed now. Fasting is this high, after meals may be even higher, long-term, the occurrence of diabetes-related complications will only come early.
Can I get back to normal without pills or insulin?
I don't think anyone would do that. If you go to the hospital, there is no doctor who can see such high blood sugar and tell you that you don't need to take medication or insulin, and that you can improve your blood sugar until it returns to normal by living a healthy lifestyle, if there is one, it must be a liar, so beware of your pocketbook! (Sorry, can't understand what you mean by "through late control", I'll just assume it's a healthy lifestyle.)
In fact, a fasting blood glucose of more than 11.1 mmol/L requires immediate use of insulin, as recommended by our guidelines. Why is it important to use insulin immediately? There is only one purpose: to reach the target as early as possible!
If you don't, long-term high blood glucose will only keep violating your body. On the one hand, too much glucose will combine with the body's proteins to undergo glycosylation, leading to poor glucose uptake by organs such as the liver and muscles; on the other hand, it will also infringe on the walls of blood vessels, resulting in damage to target organs such as the heart, brain, kidneys, eyes, etc.; it will also continue to consume our own insulin; and it will even destroy insulin-secreting pancreatic β-cells, which will lead to insulin secretion disorders. Therefore, only by making blood sugar reach the standard as early as possible will this harm be reduced.
Then like fasting blood glucose 12.6mmol/L so high blood sugar, the best way at present is to use insulin on the basis of diet control, moderate exercise, weight control and other healthy lifestyle. As for whether to continue to use insulin in the future, whether to take hypoglycemic drugs, or can be completely stopped later, in fact, it is not good now, must be combined with the individual's insulin function, their own metabolic state and other comprehensive decision.
Well, I'll tell you so much, if you think you can still speak point a praise chanting ~ there are questions you can focus on me to see more related health knowledge, thank you for reading.
Dr. Duan's Q&A Online 🚀 Ways to control blood sugar 🚀
Fasting blood sugar of 12.6 will not cause very serious situation for a short time, of course, you can control it by non-drug first. However, judging from your current blood glucose situation, it is difficult to completely control your blood glucose to normal with only non-pharmacological treatment.

If, for example, blood glucose stays around 12.6 for a short period of time, there are no very serious emergencies or long-term complications immediately.
Emergencies with rapidly elevated blood glucose, primarily ketoacidosis and hyperglycemic hyperosmolar states, are associated with a dramatic increase in blood glucose, which must be at least 20 or higher, and often occur in the presence of a recent infection or in the presence of surgery or trauma.
Long-term complications of diabetes, such as fundus retinalis, renal, cardiac, and cerebrovascular, occur over a long period of time with elevated blood glucose, probably about 10 years, but of course the higher the blood glucose, the shorter the period may be.
So, for now, of course, you can start with non-drugs to control your blood sugar.
① Strictly control foods high in sugar (carbohydrates); ② Low-salt and low-fat diet; ③ Quit drinking; ④ Quit smoking; ⑤ Increase the amount of exercise; ⑥ Eat more vegetables, excluding foods high in starch such as potatoes, yams, and lotus root; ⑦ Moderate amount of protein, such as 2 taels of lean meat, 1 cup of milk, and 1 egg per day.

Based on your current blood glucose profile, it is expected to be difficult to control to normal range with non-pharmacological treatment
Fasting blood glucose is 12.6 and glycosylated hemoglobin should be above 11%. It is generally recommended that patients with first diagnosis of diabetes who have a glycosylated hemoglobin of 9% or greater consider preferring intensive insulin therapy.
If non-pharmacologic treatment remains >7% for a period of time (no more than 3 months is recommended), consider initiating pharmacologic therapy.

Dr. Duan specifically warned:
(1) Adhere to non-pharmacological treatment from start to finish, with or without medication.
(2) If your blood sugar is not controlled to normal after 3 months of adherence, then don't take any chances.
(3) Diabetes is the most important risk factor for the development of cardiovascular disease, so blood glucose compliance is the key to preventing complications.
👇 Follow Dr. Duan for health and wellness! 👇
Hello! Nutritionist regrets to tell you that getting back to normal is not possible, but it is possible to smooth out your blood sugar and stay away from medications with the right kind of sugar control.
1. Fasting blood sugar
Our normal fasting blood glucose level is 3.9-6.1mmol/L and more than 7.0mmol/L is diabetic level. Now your fasting blood sugar has gone to 12.6mmol/L, if it is not high blood sugar due to other factors, such as hormones, medications and other factors. Then your fasting blood sugar can be said to be high. If you don't use insulin or take medication at this time, it is definitely difficult to keep your blood sugar down.
2. Unable to return to normal
When you say you mean normal, I assume you mean back to normal. But Nutritionist is sorry to tell you that once diabetes is diagnosed, there is no cure. The good news, however, is that diabetics can have a good time if they can get their blood sugar under control. As of now, the ideal state for people with type 2 diabetes is to control their sugar through exercise and diet, as well as stay away from insulin and medication.
So what exactly should I do?
3、Correct way of operation
In fact, a case similar to yours was previously shared by Permaculture, in a similar situation to yours.
Zhang, 25 years old, was found to have diabetes mellitus when his fasting blood glucose went to 14.0 mmol/L, which is higher than your fasting blood glucose, in addition to strong positives for urinary glucose and urinary ketones.
Then the doctor suggested him to have intensive insulin treatment, with an insulin pump for more than a month, and then his blood sugar slowly improved. Then under the guidance of the doctor and dietician, he used a combination of medication, diet and exercise to control his sugar.
After insisting for half a year, Xiao Zhang found out a set of exercise and diet program suitable for him. Now Xiao Zhang has completely stopped using insulin and medication under his doctor's advice, and only needs to follow his exercise and diet program for smooth sugar control.
Therefore, the health care provider thought that if you to diabetes is detected early, the pancreatic islets have more residual function. Then it is necessary to carry out intensive treatment in the early days. Then under the guidance of doctors and dietitians, slowly through exercise and diet to control sugar. Although it can not completely cure diabetes, but as far away from drugs!
Finally, Nourish wishes you success in controlling your sugar!
I hope the above suggestions can help you, get more information about diabetes, please pay attention to the health care fine-tuning!
A fasting blood sugar of 12.6 is already diagnostic of diabetes. Normal blood sugar, fasting blood sugar is below 6.1. Fasting blood sugar between 6.1 and 7.0 is considered pre-diabetes. Above 7.0 diabetes is already diagnosed. In this case, diet and exercise alone is not highly recommended. It is recommended to first take hypoglycemic drugs to keep the preprandial blood sugar below 8.0, and then improve the lifestyle to bring the blood sugar to a normal level.

The basic principles of diet for diabetics are as follows.
First, eat regularly. 3+1 or 3+2.
The second controls total energy to keep your weight within the normal range. By normal range I mean a body mass index between 18.5 and 24. The formula for calculating BMI is weight divided by the square of height. Weight is measured in kilograms and height is measured in meters.

Third, increase the proportion of low-gi food in the staple food. Such as mixed grain rice, mixed grain porridge, whole wheat buns, whole wheat bread, cornmeal, corn ballast oatmeal millet, red beans, mung beans, kidney beans and so on. Reduce the intake of refined white rice and noodles, glutinous rice sticky rice.

Fourth, consume plenty of vegetables containing dietary fiber such as celery, amaranth, and turnip cherry with every meal. You can also consume more mushrooms and fresh legumes, such as shiitake mushrooms, fungus, string beans, and Dutch beans.
Fifth, meals have protein food, beneficial to postprandial blood sugar. Protein food preferred lean meat, fish and shrimp and eggs. You can also choose low-fat milk, low-lactose milk or dried beans, tofu.
Sixth, adjust the order of your meals by eating vegetables, protein foods, and staple foods in that order.
Seventh, choose low-gi fruits as an extra meal, not more than 200 grams per day. Such as apples, pears, peaches, cherries, grapes, grapefruit and so on.
Eighth, recommended olive oil, oil tea seed oil and other oils rich in oleic acid, less food containing lard butter, hydrogenated oil. Note that cooking oil diversity peanut oil, soybean oil, corn oil, sunflower oil, flax oil can be chosen.
Ninth, abstain from sweet drinks and sweets, and reduce salt and alcohol.
Tenth, scientific exercise helps lower blood sugar. It is recommended that at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week. Distributed over a minimum of three days in the Americas, and not more than two consecutive days without exercise.
Respondent Sun Jihong, licensed pharmacist, registered dietitian, member of the Chinese Nutrition Society, the fifth student of the nutritional special training class of the Hengdian Institute, and a second-level lecturer of the Nine Dimensions Health Management Institute.
Hyperglycemia is actually similar to hypertension in that we lower our blood sugar to normal through lifestyle interventions (dietary modifications + exercise) in combination with hypoglycemic medications, mainly due to medications. Diabetes is a chronic disease and it will keep progressing, exercise and medication can slow down the progress, but it is almost impossible to say that you can cure this chronic disease by taking medication.

Can I stop taking my medication after I get my blood sugar under control with exercise and glucose-lowering medication?
Even if the blood sugar is under control through exercise and hypoglycemic drugs, I do not recommend stopping the medication on your own, as it is easy to cause the blood sugar to rebound. If the blood sugar has been well controlled, you can try to reduce the amount of medication under the guidance of your doctor. During the reduction process, you should be diligent in measuring your blood sugar, so that you can have a clear idea of what you are doing.
Exercise, diet and glucose-lowering medications are all important in slowing the progression of diabetes, and the role of medications becomes more prominent the later the disease progresses. Late complications of diabetes such as retinopathy, diabetic nephropathy and diabetic foot can only occur later or even not at all if blood sugar is controlled. We are good enough if we can achieve no or slow progression of the disease.
I hope that my answer will help you! Give me a like if you like it!

 What level of blood sugar control? Opinions vary, and some patients have different views onHowever, according to the 2010 Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the goal of glycemic syndrome control is to control fasting blood glucose between 3.9 and 7.2 mmol/l, and non-fasting blood glucose needs to be controlled at a level of less than or equal to 10 mmmol/l;
What level of blood sugar control? Opinions vary, and some patients have different views onHowever, according to the 2010 Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the goal of glycemic syndrome control is to control fasting blood glucose between 3.9 and 7.2 mmol/l, and non-fasting blood glucose needs to be controlled at a level of less than or equal to 10 mmmol/l;
In addition to blood glucose, other indicators such as glycosylated hemoglobin need to be controlled at less than 7.0.
Body mass index needs to be kept below 24.
It can be seen that the fasting blood glucose in 12.6mmol / l that is certainly not qualified, this is only fasting blood glucose, that postprandial blood glucose? It's definitely higher. Such a state of affairs without taking medication is certainly not possible.
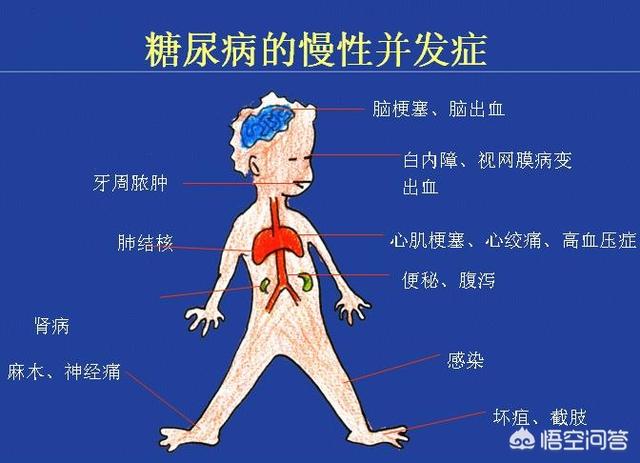
There are more than one hundred complications of diabetes mellitus, which is prone to various complications in long-term hyperglycemic states, and chronic complications can involve all vital organs of the body, in addition, diabetes mellitus is the leading cause of blindness, non-traumatic amputations, and a common cause of end-stage renal disease in our country. Compared to the non-diabetic population, diabetics have a much higher risk of all-cause mortality, cardiovascular death, blindness, and amputation than the general population.
Two common acute complications of diabetes are hyperosmolar hyperglycemic syndrome and diabetic ketoacidosis.
Chronic complications of diabetes are seen in the following broad categories.
1. Microangiopathy, microangiopathy can involve all tissues and organs of the body, mainly in the retina, kidney, nerves and myocardial tissues, of which diabetic nephropathy and retinopathy are particularly important.
Diabetic nephropathy is an important type of chronic kidney disease and is the most common cause of end-stage renal failure. It is the leading cause of death in type 1 diabetes.
Diabetic retinopathy, when diabetic patients have been ill for more than 10 years, is often combined with varying degrees of retinopathy and is a major cause of blindness.
2. Large vessel disease, atherosclerosis in the diabetic population have a high incidence, aortic atherosclerosis mainly violates the aorta, coronary arteries, cerebral arteries, renal arteries and limb arteries, etc., which can cause coronary heart disease, stroke, renal arteriosclerosis and limb arteriosclerosis.
3. Neurological complications, which can involve any part of the nervous system, are complex.
Central nervous system complications, such as altered mental status that can accompany severe diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or hypoglycemia; ischemic stroke; accelerated brain aging and dementia.
Peripheral neuropathy, included here are distal symmetric multifocal neuropathy, focal but neuropathy, fee symmetric multifocal neuropathy, and multiple radiculopathy.
Autonomic neuropathy, which is generally considered to have a poor prognosis in symptomatic autonomic neuropathy, mostly affects the gastrointestinal, cardiovascular and genitourinary systems. Gastroparesis, diarrhea, constipation, tachycardia at rest, upright hypotension, silent myocardial ischemia, prolongation of the QT interval, etc., can occur, and in severe cases, sudden cardiac death, urinary retention, impotence, pupillary changes, and abnormal sweating can occur.
4. Diabetic foot, which is one of the most serious and costly chronic complications of diabetes. It is the most important cause of non-traumatic amputation in diabetes.
5. Others, such as retinal maculopathy, glaucoma, cataracts, refractive changes and iridocyclopathy. Diabetic patients have an increased prevalence of certain cancers such as breast and pancreatic cancer, bladder cancer, etc. In addition, depression, anxiety and cognitive impairment are also more common.
Fasting blood sugar 12.6, can I get back to normal with late control without insulin and pills?
The normal fasting blood glucose range is 3.9 to 6.0 mmol/L.
The moment you see elevated blood glucose, people will immediately associate it with diabetes, diabetes can lead to diabetes, but the causes of elevated blood glucose in addition to diabetes, there are sudden cerebrovascular accidents, infectious shock, convulsions and other diseases, serious trauma or major surgery, long-term use of glucocorticosteroids or contraceptives and so on can lead to elevated blood glucose.
Stress or drug-induced blood glucose elevation, generally after the discontinuation of the drug and the removal of stress and the accompanying disease through the treatment and gradually return to normal blood glucose can return to normal, you can not need to play insulin, if the blood glucose elevation is serious, sometimes you need to consider the use of intravenous insulin, and when the disease gradually return to normal, gradually stop insulin, blood glucose gradually return to normal, generally will not develop into diabetes mellitus. The blood glucose will gradually return to normal and generally will not progress to diabetes.
If there is no previous diabetes, fasting blood glucose is 12.6, if there is also a combination of polyuria, drinking and eating, weight loss, thinness, itchy skin or blurred vision and other manifestations, then repeat a blood glucose measurement is still high, excluding stress or drug interference, it means that diabetes, if the fasting blood glucose is more than 11.1, it can be assumed that the patient's blood glucose will be even higher after eating through the diabetic diet and by exercise or activity to control blood glucose often also need to cooperate with medication or insulin to control blood glucose in the target range. Through diabetic diet and through physical exercise or activities to control blood glucose, often also need to cooperate with drugs or insulin to control blood glucose in the target range, of course, there are also some patients in the diabetic diet and exercise and cooperate with hypoglycemic drugs or insulin, can control blood glucose in the target range, a small portion of the patients through the late control can be no hypoglycemic drugs or insulin, and a considerable portion of the patients need to rely on the hypoglycemic drugs or insulin for the rest of their lives. A small number of patients will be able to control their blood glucose without taking glucose-lowering drugs or insulin at a later stage, while a large number of patients will need to rely on glucose-lowering drugs or insulin for the rest of their lives.

If diabetes has been diagnosed and there is an increase in fasting blood glucose, which may be caused by insufficient dosage of medication or the Sumuje phenomenon or the Dawn phenomenon, it may be necessary to adjust the dosage of glucose-lowering medication or control blood glucose by combining insulin with diet and exercise. Most diabetic patients who want to achieve glycemic control without medication or glycemic control without insulin are still relatively difficult to do so.
I tested my fasting blood sugar 10.5 on 3/15/19, after fasting fasted and dieting for dinner. I used to eat extra full for dinner and skip breakfast, after I started dieting and exercising, I only ate soup and vegetables for dinner and full for morning exercises. One month later, blood sugar dropped to more than 7 points, three months after the return to normal, and now I still adhere to the weight loss of more than 20 kg!
I'll answer this question from my own personal experience.
Let's start with me. when diagnosed with type 2 diabetes in 2007, fasting glucose was 17-18 and postprandial glucose was 25-33. age 51 at the time.
Through strict lifestyle management, I achieved a reversal (note: not a cure, just a reversal) of my type 2 diabetes.
For information.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.