What is the best time period to measure blood glucose, and is it better to do it on an empty stomach or after a meal?
With regard to blood glucose testing, new improvements were made just a short time ago, and most clinicians' knowledge is not currently up to date.
Testing blood glucose is a means of detecting and monitoring diabetes; high blood glucose indicates the presence of insulin resistance or diabetes.
Fasting vs. postprandial
Fasting blood glucose should be tested in the morning, 99 mg/dl or less is normal, 100-125 mg/dl is pre-diabetic, 126 or more is diabetic, for home use blood glucose monitoring then 80-130 mg/dl is normal, 130 mg/dl or more is diabetic.
Fasting blood glucose is not sufficiently sensitive; some diabetic patients have normal fasting blood glucose levels, so two-hour postprandial blood glucose testing is much more accurate, with a normal target of 180 mg/dl or less.
However, the two-hour postprandial glucose test is not well manipulated, so it is better to do the fasting glucose test first and then do the two-hour postprandial glucose monitoring when you need to confirm.
However, both fasting and postprandial are immediate, which is fine as a primary screening, and problematic for monitoring changes in blood glucose levels in diabetic patients, for whom it is important to look at blood glucose levels over a period of time.
A1C
Sugar binds to hemoglobin and red blood cells survive for an average of 3 months. by measuring the amount of sugar bound to hemoglobin, you can get an idea of your blood sugar levels over the past three months. the A1C is the best means of blood sugar monitoring. under 5.7% is normal, between 5.7-6.4% is pre-diabetic, and above 6.4% is diabetic.
In recent years it has been found that the A1C is also flawed because it is based on the average survival of red blood cells for 90 days, which is not actually the case - diabetics have a short survival time for red blood cells, normal people have a long survival time for red blood cells, and problems such as blood loss, suffering from anemia or sickle cell disease can affect the results of the test, resulting in false positives and false negatives. This problem also exists with fasting and postprandial blood sugar.
Fructosamine Detection
Tests the level of glycated proteins in the blood, which have a survival period of 14-21 days, so this test reflects blood glucose levels over the past 2-3 weeks and is independent of factors such as blood loss and anemia, making it particularly suitable for situations such as pregnancy where the body is changing rapidly.
Normal values were 205-285 mmol/L, 210-421 mmol/L in controlled diabetes and 268-870 mmol/L in uncontrolled diabetes.
How to test your blood sugar
If you are not a diabetic, just measure your fasting blood sugar during your physical exam.
Diabetic patients who are not taking hypoglycemic drugs can self-supervise with a blood glucose meter at home, but blood glucose meters are usually inaccurate and can only be a relative indicator. You should also go to the hospital every 3-4 months to test your blood glucose as follows.
It is not necessary for diabetic patients taking hypoglycemic drugs to self-test their blood glucose at home. They should go to the hospital every 3-4 months for blood glucose testing, including fasting blood glucose, A1C and fructosamine testing, so as to have a comprehensive understanding of the patient's blood glucose profile, and to test their liver and kidney functions and other metabolic indexes, in order to find out whether there are any serious side-effects from the medication and the progression of the diabetes mellitus.
Any fluctuating value needs to be measured multiple times and regularly, and blood sugar is certainly one of them.
Blood glucose values are not static. They are affected by many factors of daily life, including: diet, mood changes, exercise, climate, chronic constipation, insufficient water intake, and so on. When test results fluctuate, there is no need to panic and see if the above factors affecting the results are also changing. A good blood glucose testing record can help sugar lovers manage their blood glucose, which can make it easier to communicate with doctors about their condition and provide a basis for adjusting their treatment plan.
What is the best time to measure blood glucose?
It is important to know the correct time to monitor your blood glucose. The significance of blood glucose varies from time to time, so there is no such thing as a good time to measure your blood glucose.
Fasting blood sugar:It is an overnight blood glucose that is taken at 6-7 am and has not been eaten for 8-10 hours. Fasting blood glucose responds to basal insulin secretion and also responds to whether or not the medication administered the night before controls blood glucose into the following morning.
Pre-meal blood glucose:Refers to blood glucose before lunch and dinner. Pre-meal blood glucose reflects the persistence of the secretory function of pancreatic B cells. Meal blood glucose is required when blood glucose levels are high or when there is a risk of hypoglycemia.
Two hours postprandial blood glucose:It refers to the blood glucose after breakfast, after lunch, and 2 hours after dinner at the time of counting from the first bite of food. Mainly evaluates the effect of drug treatment as well as adjusts the drug treatment program.
Blood sugar at bedtime:It is the blood glucose measured at night before going to bed. It is used to determine the effectiveness of medication and the need for additional meals to prevent hypoglycemia from occurring.
Randomized blood glucose:Refers to blood glucose measured at any time other than those listed above. Randomized blood glucose captures changes in blood glucose at any time under special circumstances.
We measure blood glucose in a number of modes:
1. Measure blood glucose seven times a day (before three meals, two hours after three meals, and before bedtime).
2. Measure blood glucose 4 times a day (two options: before three meals + 2 hours after breakfast blood glucose, before three meals + bedtime blood glucose).
3. Measure blood glucose twice a day (various options: blood glucose before three meals + blood glucose two hours after three meals).
4. Random blood glucose monitoring (irregular and infrequent).
To summarize:
Only with proper monitoring of blood glucose, which is the foundation of all treatments, and with a correct and perfect foundation, the doctor will be able to adjust the measured blood glucose accordingly, so as to avoid diabetic complications and to control the blood glucose better.

Nutritionist Sugar to answer for you, blood glucose measurement does not exist what time period is good, but your condition, need to monitor which time period of blood glucose. In the end, should be measured fasting, or should be measured postprandial blood glucose, depends on what time period your blood glucose is prone to abnormalities, there is no when to measure better.
It is generally recommended that glucose lovers monitor their fasting blood glucose in the morning and their blood glucose 2 hours after meals. Because meals will have a greater impact on blood glucose, it is also recommended to measure preprandial blood glucose for some sugar users with unstable blood glucose. However, in general, sugar users do not need to monitor their blood glucose too often, except at the early stage of treatment, adjustment of the treatment program, and the combination of other diseases, which will require such frequent monitoring of blood glucose.

Here's an introduction to blood glucose monitoring and its significance at various time points for sugar lovers.
1. Fasting blood sugar:Measured on an empty stomach overnight for more than 8 hours, without food and without the use of medicationBlood Sugar Values. Fasting blood glucose reflects a person's blood glucose metabolism at rest during the night and theInsulin secretion levels.
2. Pre-meal blood glucose:It refers to the blood glucose measured before the three meals in the morning, midday and evening, mainly referring to the blood glucose before the Chinese meal and dinner. It reflects the blood glucose situation in the relatively fasting state before eating, and is mainly affected by the amount of food eaten at the previous meal and the efficacy of hypoglycemic drugs.
3. 2-hour postprandial blood glucose:Blood glucose measured 2 hours after a meal reflects the effect of the meal on blood glucose. However, there is a common misconception here that it is not the blood glucose 2 hours after eating, but rather the time from the first bite of the meal.
4. Randomized blood glucose:Blood glucose measured at any time of the day, mainly when feeling abnormal.
It is important for sugar lovers to understand that everyone's condition is different and so is the protocol for monitoring blood sugar. Follow your doctor's instructions to monitor and record your blood sugar in order to be able to judge the effectiveness of your treatment program.
For more sugar control knowledge, sugar lovers can follow us, click private message to send the keyword "blood sugar", to get professional learning materials and Concordia experts explain the complications of video Oh!
I hope Sugar's answer can help all the sugar lovers, if you think it is useful, why don't you click a like?
The time period chosen for blood glucose testing varies depending on the purpose.
Fasting blood glucose is primarily designed to assess nighttime fasting glucose metabolism and pancreatic islet function;
The three preprandial blood glucoses are primarily designed to assess blood glucose levels over a longer period of time after a meal when food affects metabolism and pancreatic islet function during starvation;
The two hours after the three meals were primarily designed to assess the effect of the amount and type of diet on glucose metabolism and pancreatic function;
Nighttime bedtime is to assess the bedtime glucose baseline to facilitate adjustment of the insulin dosage given;
When you are just starting the diabetes status assessment you will use the large profile test, i.e., fasting in the morning, blood glucose before lunch and dinner, blood glucose two hours after three meals, and blood glucose at night before bedtime, seven times;
This facilitates reassessment of glycemic status and islet function on top of diet and exercise;
When dietary exercise is relatively stable it can be adjusted to five measurements on an empty stomach, two hours after three meals, and then at night before bedtime;
When blood glucose levels are very stable based on diet and exercise monitoring and medication management they can be monitored once a day, slowly reduced to every other day, once a week and maintained.
Therefore, blood glucose monitoring depends on the stage of diabetes and whether it is stable or not. Close follow-up under the supervision of a doctor is required. A stable blood glucose has the least effect on the endothelium of the blood vessels.
 Many people will go to the hospital for blood glucose monitoring on an empty stomach, and very few will have their blood glucose checked after a meal. What is the difference between pre-meal and post-meal blood glucose, and which time of day is more accurate?
Many people will go to the hospital for blood glucose monitoring on an empty stomach, and very few will have their blood glucose checked after a meal. What is the difference between pre-meal and post-meal blood glucose, and which time of day is more accurate?
When most people go to the hospital for a blood sugar test, the doctor will ask if they have eaten. Fasting blood glucose refers to the value of blood glucose when it is about 8-10 hours from the last meal, and is most often done around 5:00 am or 6:00 am. The significance of measuring fasting blood glucose is mainly that it reflects the blood glucose level of the tester in a basal state without any dietary load. Fasting blood glucose is a good indicator of basal insulin levels and liver glucose output, and is an important basis for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.
Postprandial blood glucose is the blood glucose value measured two hours after eating, postprandial blood glucose can better reflect the patient's body pancreatic B-cell reserve function is an important indicator, that is to say, the detection of the person after eating food to stimulate the body's B-cells secretion of insulin ability. If we rely on fasting blood glucose alone, the diagnosis rate is high. Postprandial blood glucose is more troublesome to measure, and needs to be counted from the time the patient takes the first bite of the meal. However, postprandial blood glucose is the basis for early diagnosis of type II diabetes.
Blood sugar measurements are not just for fasting and postprandial blood sugar. To get a concrete picture of how your blood sugar fluctuates throughout the day, it's best to do 10-point monitoring of your blood sugar. They are fasting and postprandial, pre-lunch and post-lunch, pre-dinner and post-dinner, before going to bed, 3:00 a.m. and 5:00 a.m. blood glucose monitoring, and the different points of time for blood glucose test values also have different significance and role. The ten-point monitoring of blood glucose for three consecutive days can well reflect the fluctuation of blood glucose of diabetic patients, which is conducive to the development of personalized management methods.

If you have a good suggestion for this issue, you are welcome to leave a comment below!
I am Wang Guizhen, today's headline Wukong Q&A signed author, welcome to pay attention to [Wang Guizhen nutritionist] headline number, together to talk about health, so that we eat healthy, eat at ease!
Blood glucose values are different depending on when they are measured

So when is the best time to test your blood sugar?
Blood sugar at different times has different meanings:
The smallest error is of courseWhen fasting (8-12 hours in an unfed state)。
Fasting state:The absence of dietary influences on the pancreas at this time allows the patient to understand the strength of the basal function of the pancreas and to monitor the glucose control effects of glucose-lowering medications.
Postprandial blood sugar:In turn, it reflects the patient's ability to secrete insulin from pancreatic beta cells after food stimulation.
Postprandial blood glucose is significant in type II diabetes because early patients do not have high fasting blood glucose, but due to impaired pancreatic secretion, it is difficult to control blood glucose after eating and will show a significant rise.
The study found thatpostprandial glucoseIt is an important factor in the complications of diabetes.
Tests for blood glucoseNumber of times.groundPatient condition dependent
Recommended by the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Type II Diabetes Mellitus:
Patients with unstable blood sugar
If a patient is newly diagnosed with diabetes, has fluctuating blood glucose, is more severelySeven times a day.Blood glucose (before three meals, two hours after three meals, and at bedtime).
Blood glucose at control goal
The number of tests can be reduced, typically2-4th order/day(Pre-meal, post-meal, and bedtime blood glucose randomized).
Testing your blood glucose is a way to better monitor your health, theThe ability to make timely adjustments to treatment programs and diets accordingly.
For more on health, follow Kin On Life!
Feel free to like, share, and follow!
Blood glucose monitoring is one of the necessary measures to control blood glucose in diabetic patients. Proper blood glucose monitoring helps to detect unstable condition and abnormal fluctuation of blood glucose in time, so that the treatment plan can be adjusted at the first time to prevent the occurrence of complications.

What is the best time period to measure blood glucose, and is it better to do it on an empty stomach or after a meal?
With the emergence of blood glucose meters, patients can test their own blood glucose at home, but because of the different testing conditions, personnel, time, etc., it often makes the blood glucose test results have some errors.Blood glucose varies throughout the day, with different values measured at different times of the day.Proper testing should take into account a number of aspects, of which test time is particularly important.
1. Fasting blood sugar:Mostly refers to values taken in the morning before 8am after a night of fasting.for measuringinsulinsecretion and the duration of efficacy of the medication. Fasting blood glucose is alsoOne of the criteria for the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, which reflects the patient's basal blood glucose value. Normal between 3.9mmol/L-6.0mmol/L. It is suitable for patients who have been using hypoglycemic drugs for a long time.
2,Postprandial blood sugar:generally refers toA 2-hour postprandial blood glucose value, which can be 2 hours after breakfast, lunch, or dinner, is used to measure theInsulin secretion after eating, and the effects of pharmacologic and dietary interventions on glycemic control. For most people with type 2 diabetes, 2-hour postprandial glucose is even more important than fasting glucose because of their impaired insulin secretion, and postprandial glucose testing is more representative of basal blood glucose values. Note that 2 hours means timing from the start of the meal. Normal 4.4mmol/L-7.8mmol/L.

3. Pre-meal blood sugar:This refers to blood glucose measurement before lunch and dinner. Pre-meal blood glucose can reflect the secretion function of pancreatic islet cells, which can be used to help patients adjust their dietary intake and medication dosage before meals. Generally speaking, if you find high blood glucose before meals, you should pay attention to controlling the amount of food and drink.
4. Blood sugar at bedtime:Mostly refers to the time between 9:00 p.m. and 10:00 p.m., reflecting the pancreatic islet cells' regulation of blood glucose after dinner, which is used to help patients adjust the amount of medication or insulin injections during the night, and also to help patients determine whether they need to add a meal during the night.
5. Nighttime blood sugar:When high fasting blood glucose is found, if the blood glucose can be monitored at night, it will help to determine the time of occurrence of high blood glucose in order to determine whether the high blood glucose is due to the dawn phenomenon, insufficient insulin action at night, etc. You can choose to test your blood glucose at 0 o'clock, 2 o'clock, 4 o'clock and 6 o'clock.
6. Randomized blood glucose:Blood glucose measured at any time of the day, with no specified time. To avoid situations such as nighttime hypoglycemia or early morning hyperglycemia.
Hello everyone, I am Dr. Yang. I've actually talked to you a lot about when to test your blood glucose, but there are still a lot of diabetics who don't know when it's best to test their blood glucose, especially some of those who have just been discovered. So, let's talk to you about this again today.

What is blood sugar?
First of all, we need to know what blood sugar is. To put it simply, blood sugar refers to the level of glucose in our blood, which is the main and basic energy substance necessary to provide our body. So, if the blood sugar level is too low, our life is in danger. However, too high a blood sugar level can also be harmful to us, damaging our blood vessels, nerves, etc., thus leading to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases; it can also increase the risk of infections, make wounds not easy to heal, and even increase the risk of amputation as a result. Therefore, diabetics should monitor their blood glucose regularly, no matter how well their blood glucose is controlled.
Fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, glycosylated hemoglobin
These 3 indicators are the blood glucose indicators that we often need to monitor, and each blood glucose indicator represents a different meaning. The blood sugar control is mainly depends on these 3 indicators, no one can replace anyone, no one can be less.

fasting blood sugar
Fasting blood glucose, as the name suggests, is the value of blood glucose measured without eating, reflecting our basal insulin secretion. But no meal, not no lunch, no dinner, but refers to no breakfast, because fasting blood glucose requires at least 8 hours without food (can drink a small amount of water, but do not exceed 200ml). But don't go too long without eating, usually not more than 14 hours, because the hormonal changes in our body under starvation will make the measured blood glucose inaccurate. Therefore, the time to measure fasting blood glucose is usually in the morning 7~9 o'clock. Fasting blood sugar in diabetics is usually controlled at 4.4~7.0mmol/L.
2-hour postprandial blood glucose
It refers to the blood glucose value measured 2 hours after our first meal, which can reflect whether our insulin secretion function is impaired and whether the amount of food and medication is appropriate. Why measure blood glucose 2 hours after a meal? Can it be measured 1 hour or 3 hours after meal? In fact, you can measure blood glucose at any time after eating, only that the blood glucose at 2 hours after meal is the most meaningful, because most of us have the highest blood glucose at 2 hours after eating, and the blood glucose measured at this time is the most meaningful. Blood glucose measured at other time points is called random blood glucose, which also has some reference value. Diabetic patients in the non-fasting state of blood glucose measurement is generally controlled below 10mmol / L.
glycosylated hemoglobin
It refers to the product of hemoglobin, the main component of red blood cells in our blood, combined with glucose. Since the life span of a red blood cell is 120 days, glycated hemoglobin reflects whether the average blood glucose control in the last 2~3 months is up to the standard. The formation of glycated hemoglobin is a slow occurring process, so eating the time of day when the glycated hemoglobin is measured whether or not you have eaten does not affect the results. Glycated hemoglobin can be measured at any point in time. Glycated hemoglobin in diabetics is usually kept below 7%.
In addition to these blood sugars mentioned above, for diabetics who have a need for insulin, it is sometimes necessary to test thePre-meal blood glucose, bedtime blood glucose, which is used to guide insulin dosage and prevent hypoglycemia.
Well, today will say so much, if you feel that the speak can also point a praise chant ~ if there is a question you can pay attention to me to learn more about the health knowledge, thank you for reading.
"What is the best time period to test my blood sugar? Is it better to test on an empty stomach or after a meal?" This varies from person to person, some people are high on an empty stomach, some are high after a meal, or some are prone to hypoglycemia before a meal, so they should be monitored at those particular points. The purpose of blood glucose testing is to detect hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia in a timely manner, and then to continually adjust diet, exercise, and medication in order to bring blood glucose up to standard.
The body's blood sugar, which is constantly changing throughout the day, is shown in the chart below:
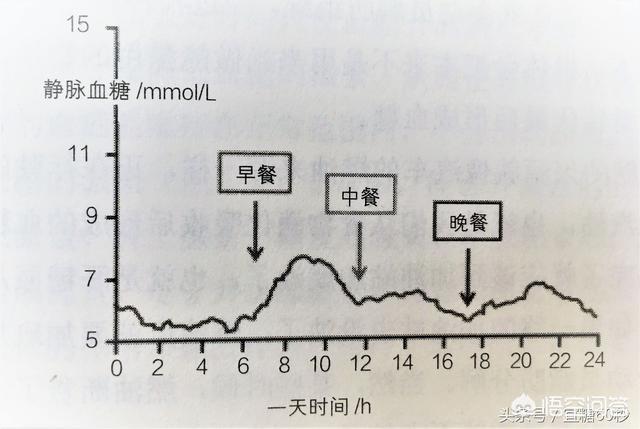 In healthy people, blood glucose is lowest at 2~3 a.m. and gradually rises after 4~5 a.m.. Blood glucose is greatly affected by meals. Blood glucose begins to rise 5 minutes after a meal, generally reaches its highest level 0.5~1.0 hours after a meal, then gradually declines, and basically returns to the pre-meal level 2~3 hours after a meal.
In healthy people, blood glucose is lowest at 2~3 a.m. and gradually rises after 4~5 a.m.. Blood glucose is greatly affected by meals. Blood glucose begins to rise 5 minutes after a meal, generally reaches its highest level 0.5~1.0 hours after a meal, then gradually declines, and basically returns to the pre-meal level 2~3 hours after a meal.
The reason for enduring the pain of taking a needle to measure blood glucose is to get valuable blood glucose to understand the effect of diet, exercise, medication, etc. on blood glucose so that adjustments can be better made. However, if the measurement is taken at the wrong point in time, then the shot is wasted.

So, how many times a day should you measure your blood glucose to better reflect your blood glucose levels? Which time point should be measured each time?
In fact, the frequency of measurement and the time point of measurement are different for glycosurgeons with different treatment regimens. Below is an example of the recommended regimen in the Chinese Guidelines for Clinical Application of Blood Glucose Monitoring (2015 edition):
Multiple insulin injections per day

Treatment with long-acting insulin
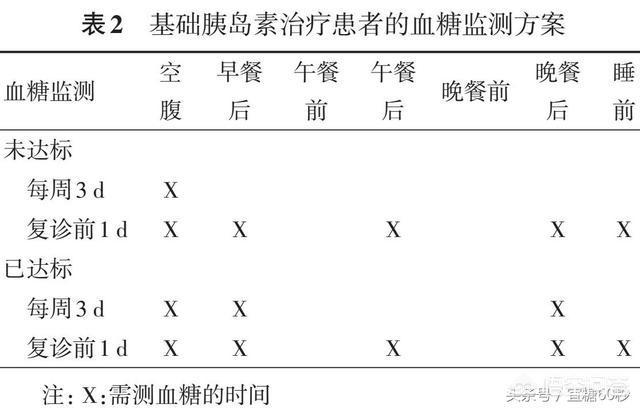
Pre-mixed insulin therapy twice a day
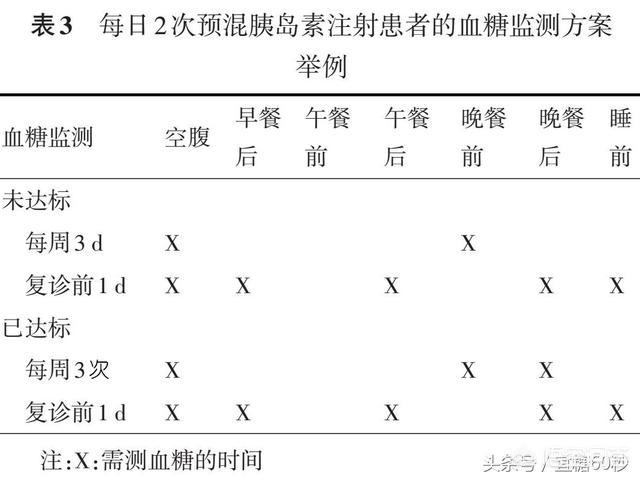
Oral medication users: short-term intensive monitoring
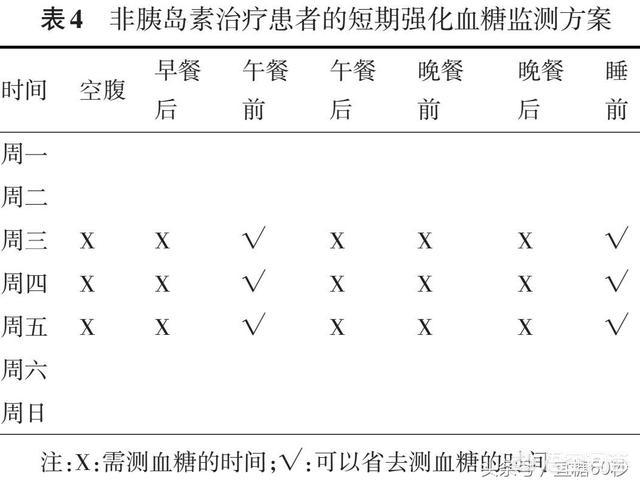
Oral drug therapy: alternate monitoring
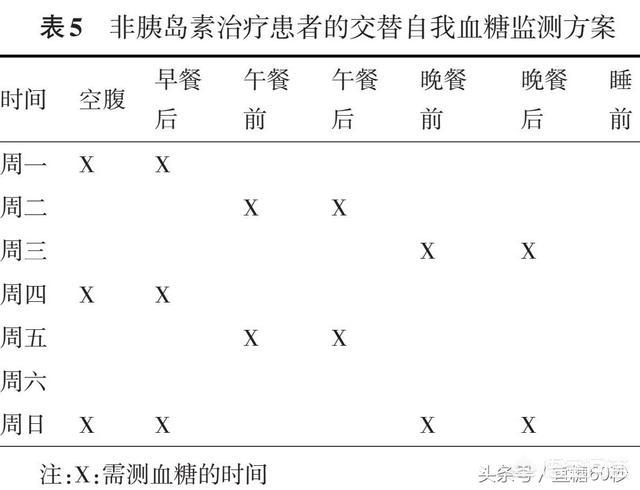
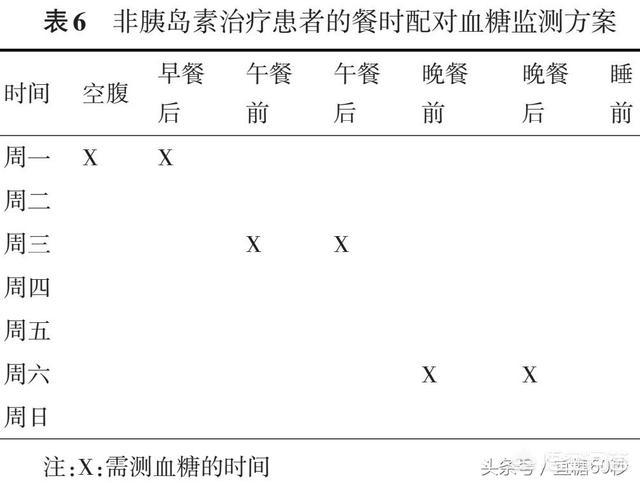
Oral drug therapy: the meal-pair monitoring method
[Yee Sugar in 60 Seconds] For more, read on:
Is it more accurate to use a second drop of blood to measure blood sugar?
Diabetes doesn't want to develop into uremia, these three indicators should be controlled!
She's 106 years old across three centuries, and the top five ways to live longer for a generation of wonder women!
Thanks for the invite!
Diabetic patients are divided into several kinds, one is high fasting blood glucose mainly, normal after meals, one is high blood glucose after meals, normal fasting, and the other is high blood glucose after meals and fasting. In fact, regardless of the kind, need to monitor fasting and two hours after meals blood glucose, observe the blood sugar changes and control, but also conducive to the next visit to the doctor to see easy adjustment of drugs. Especially insulin diabetic patients, especially to strictly monitor blood glucose, because you can adjust the dosage of insulin according to the blood glucose level to avoid hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia. Especially the occurrence of hypoglycemia, a single hypoglycemic event is a serious blow to a diabetic patient.
[Learn more about medical knowledge, please follow me to discuss oh
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.