How to prevent cardiovascular disease?
First, we should have a comprehensive understanding of cardiovascular prevention and treatment knowledge, correctly recognize the harm of cardiovascular disease, fully understand the harmful effects of smoking and alcohol consumption, and implement them into action. Second, reasonable nutrition, choose low-fat, low-sugar, low-salt, vitamin-rich and crude fiber food, and appropriately increase protein intake such as fish, lean meat, milk and so on. Third, to moderate exercise, to stay at the safety first, mainly aerobic exercise, exercise time to 30 minutes is appropriate, 4 to 5 times a week. The intensity of the exercise should not be strenuous to the extent that you do not feel tired. Fourth, if you have been diagnosed with coronary heart disease, high blood pressure, etc., to prepare first aid medicines, and at any time and any place can be taken. And prevent constipation, bath water temperature should not exceed 40 ℃. Fifth, to maintain a good and sufficient sleep.
Thanks for the invite:
Cardiovascular problems are on the rise as living standards improve and high oil and fat diets increase.
Cardiovascular disease is a general term for circulatory system diseases, the circulatory system refers to the organs and tissues that transport blood in the body, mainly including blood vessels, the heart, etc. Common clinical problems include angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, coronary artery disease, hypertension, etc. In fact, the etiology, pathogenesis, and so on, of these diseases are very similar, and they are all associated with atherosclerosis, and in severe cases, arterial stenosis, cerebral infarction, myocardial infarction, and so on. etc.
So the prevention of cardiovascular disease, mainly from the prevention of atherosclerosis and so on, to prevent the three high (high blood sugar, high blood fat, high blood pressure)
1. Quit smoking, the ingredients inside the cigarettes will make the blood vessels constricted, blood viscosity increased, and platelets will gather more easily, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis. At the same time, smoking is also harmful to the lungs.
2. Eat a light diet and drink plenty of water. Excessive intake of fats and oils will increase the cholesterol level in blood vessels, which will easily block arteries and cause hardening and narrowing of blood vessels. Eating more vegetables and a sensible diet can lower cholesterol. Drinking more water can also effectively ensure the total body circulation.
3. Proper exercise, exercise will promote the metabolism of lipids and reduce the accumulation of cholesterol, so that the risk of atherosclerosis will be greatly reduced.
4. Monitor blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids, regular annual physical examination. Timely monitoring of the above three, the value of abnormalities, especially to attract attention, timely adjustment of diet and lifestyle habits, if necessary, seek medical treatment. The probability of cardiovascular disease increases in people over the age of forty, so it is even more important to be aware of it.
Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs) are the leading threat to human life and health and have a high mortality rate, so reducing the incidence of CVDs is now a top priority in the prevention and treatment of CVDs.
However, not all cardiovascular diseases must be treated with medication at the beginning, Chinese medicine has long advocated that people strengthen the positive qi to ward off diseases through the following ways: such as moderate exercise, changing bad habits, regulating the spirit and so on.
moderate exercise
Proper exercise can make the body of the circulation of blood, joints, smooth, free of emotion, for resisting disease has an important role. Research also shows that obese people are prone to hypertension, high blood pressure, high blood lipids and high blood sugar and other symptoms, and after exercise to lose weight after blood pressure, blood lipids, blood sugar, etc. can have a certain degree of decline, and can even be reduced to the normal range.
Changing bad habits
Numerous studies have shown a close relationship between the development of hypertension and high sodium intake. Excessive smoking and drinking will increase the incidence of acute myocardial infarction and sudden death. Therefore, changing bad habits is of great significance to one's health and even life.
recuperate
In Chinese medicine, there are "all diseases are born in the gas", "anger is gas, joy is gas slow, sadness is gas disappear, fear is gas down, shock is gas chaos, thinking is gas knot", emotional stimulation can lead to the weakness of positive qi, so that the external evil can easily invade the human body and lead to disease. It can be seen that the state of mind is an important measure of a person's health. If the mood is comfortable, the human body qi and blood calm, qi and smooth, conducive to maintaining stable blood pressure, and the prevention of disease, occurrence and development of significant significance. On the contrary, modern medicine believes that long-term stress, anger, depression and other bad moods can cause changes in sympathetic nerves, plant nerves, endocrine, immune and other aspects of the changes will lead to aggravation of atherosclerosis, resulting in hypertension and other diseases. Therefore, regulating the spirit can strengthen the body's positive qi, ward off diseases and prevent illnesses, and is also one of the most important ways to prevent and treat hypertension.
Therefore, cardiovascular disease is not a single factor, but interlinked, such as the lack of attraction will cause physical obesity, physical obesity will lead to dyslipidemia and elevated blood pressure, increasing the chances of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, in the prevention of cardiovascular disease, the first step should be to strengthen physical activity. Generally speaking, moderate amount of physical activity on the cardiovascular protection of the strongest, large groups of muscle aerobic exercise has the best effect; second should be a balanced diet, according to the Chinese Society of Nutrition put forward by the Chinese adults balanced diet basic composition and structure, China's adults should be a daily intake of cereals 300-500 grams; vegetables 400-500 grams; fruit 100-200 grams; animal food 125-200 grams; dairy 100 grams; animal food 100 grams. Grams; dairy 100 grams; beans 50 grams; oils and fats 25 grams of the following; finally, should quit smoking, moderate alcohol consumption, and relaxation, which can effectively prevent cardiovascular disease.
There are countless articles on cardiovascular disease prevention on the Internet, but there are relatively few articles on cardiovascular disease from a physician's perspective. Next, I would like to introduce to you the clinical risk assessment of cardiovascular diseases from a clinical point of view, as well as how to take primary cardiovascular preventive measures from a macroscopic point of view.
Methods of cardiovascular risk assessment
I believe that the vast majority of us understand cardiovascular disease only in terms of the serious life-threatening risk it poses, but we know little about how to quantitatively assess our risk of acquiring cardiovascular disease in the future based on our personal lifestyle, age, and physical condition. There are countless tools for assessing cardiovascular risk throughout the world, but most of the methods are not suited to the basic conditions of our nation. Thus our country"Research group for the "15" research project on comprehensive risk assessment and intervention programs for coronary heart disease and stroke.With this, we have established a method for assessing the risk of ischemic cardiovascular disease that is suitable for our population, and I am going to show you how to use this method to make a simple assessment of the possibility of your future illness. Let's take an example of a person who is 45 years old, 1.70 meters tall, weighs 90 kg, has a blood pressure of 160/100 mmHg, cholesterol of 5.3 mmol/L, diabetes mellitus, and is a smoker.
There are countless tools for assessing cardiovascular risk throughout the world, but most of the methods are not suited to the basic conditions of our nation. Thus our country"Research group for the "15" research project on comprehensive risk assessment and intervention programs for coronary heart disease and stroke.With this, we have established a method for assessing the risk of ischemic cardiovascular disease that is suitable for our population, and I am going to show you how to use this method to make a simple assessment of the possibility of your future illness. Let's take an example of a person who is 45 years old, 1.70 meters tall, weighs 90 kg, has a blood pressure of 160/100 mmHg, cholesterol of 5.3 mmol/L, diabetes mellitus, and is a smoker.
Step 1: Gender-specific scores for each indicator
First rate each of the following points according to the scores in the chart below:
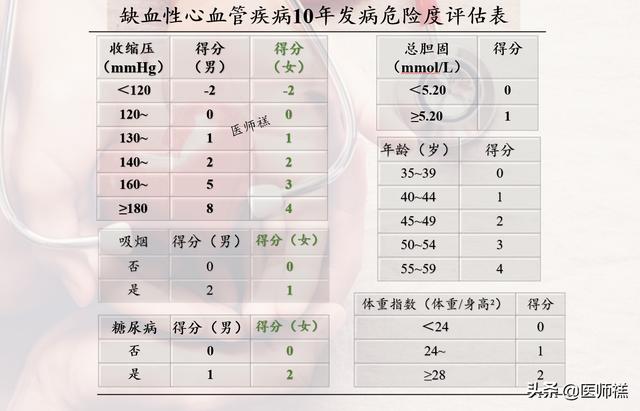
- Age: 45 years old, for example, with a score of 2 for both men and women;
- Blood pressure systolic: 160/100mmHg for example, 160 represents the size of the systolic down, the male equivalent score is 5, female score is 3;
- Body Mass Index (BMI): For example, for a height of 1.7 meters and a weight of 90 kg, the BMI is 90/1.7² = 31.1, with a score of 2. for both men and women.
- Total cholesterol: 1 for both men and women;
- Smoking or not: 2 points for men and 1 point for women;
- Presence of diabetes: 1 point for men with diabetes, 2 points for women.
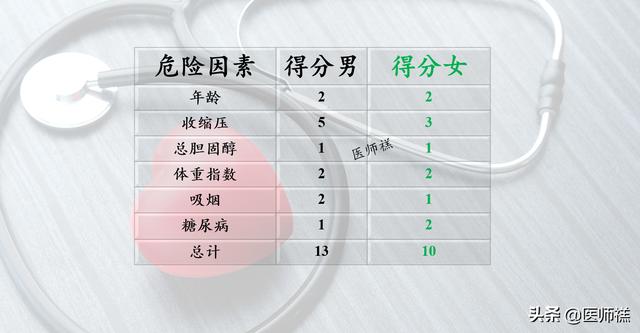
Step 2: Summarize the above scores according to the chart below:
13 points for men and 10 points for women
Step 3 Locating Absolute Danger
A score of 10 for women would be a 15.6% risk of ischemic cardiovascular disease in the next 10 years.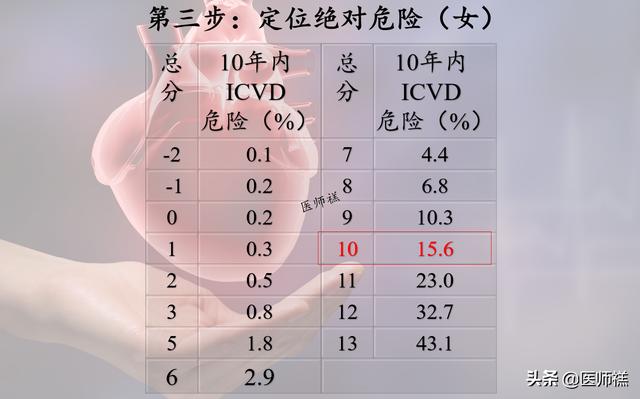
In contrast, a score of 13 for men corresponded to a risk of 21.7 for possible ischemic cardiovascular disease in the next 10 years;
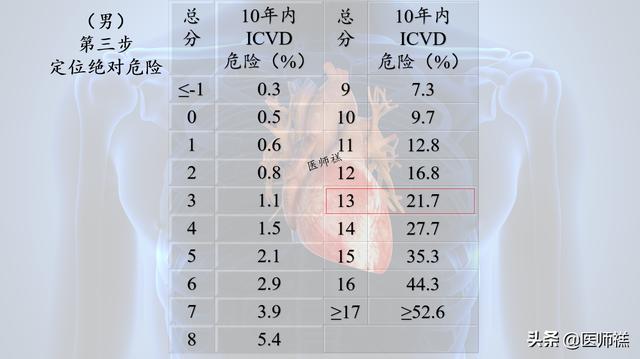
Assessing risk
Although the above risk for male and female prevalence based on numbers is not very high. However, according to the assessment methodology, relative to a healthy person of the same age (At age 45, the average risk level is 1.9 for men and 0.6 for women.(See Section 2.1.2.).
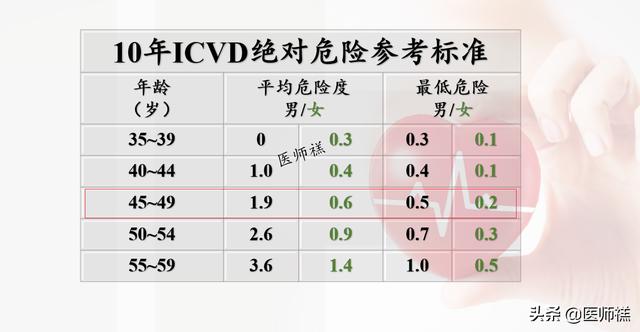
This 45 year old already exceeds 21.7/16= of healthy men his age in terms of blood pressure, cholesterol, diabetes, and bad smoking habits.11 timesand for females 15.6/0.6=26 times。
In other words, while the assessed scores and risk percentages may seem small, the risk of this disease is increased by several or even dozens of times relative to healthy people of the same age.
So our advice based on the risk assessment above is:
People over 40 years of age should have a risk assessment at least every 5 years, and it is best to have a risk assessment every other year if individuals have risk factors such as smoking, diabetes, hypertension, obesity, etc.
Macro cardiovascular as well as preventive measures
After assessing an individual's risk according to the nationally recommended risk assessment scale, a multiplier of risk relative to a healthy person of the same age is derived. We need to make macro adjustments to our life, diet, and exercise to positively face our risk of cardiovascular disease.As the saying goes, save for a rainy day and take primary prevention.
Cardiovascular risk factors currently recognized by the medical community include:
- Age, gender, family history;
- Hypercholesterolemia, diabetes, hypertension, abdominal obesity;
- Lack of exercise, smoking, lack of vegetables and fruits in the diet, mental stress;
For us as individuals except age, gender, family history and race are not modifiable. The other 8 traditional risk factors are all modifiable. In other words, cardiovascular disease can be prevented if these eight factors are treated and life improvements are made.
balanced meal
It is not necessary to emphasize here that lowering salt intake, reducing saturated fat, and increasing fiber intake from vegetables and fruits and sea fish and cereals can significantly reduce risk factors such as high cholesterol, diabetes, hypertension, and even abdominal obesity. Low salt, fruit and vegetable rich, low fat meals are vital.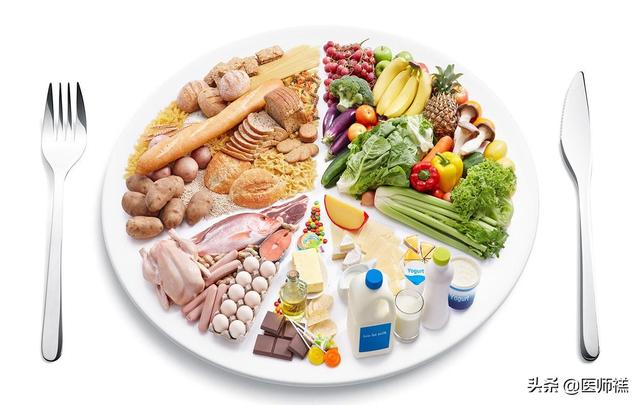
tobacco cessation
Smoking is an important causative factor of cardiovascular disease, and in principle the only causative factor that can be completely controlled. A large number of epidemiological studies, both domestic and foreign, have confirmed that there is an absolute causal relationship between smoking and cardiovascular disease. The cost of quitting smoking is much lower than the cost of future medication. Make up your mind to quit smoking now, it is the most cost-effective intervention to avoid cardiovascular deaths that can save you a lot of money.
regular exercise
Exercise is more recommended in the National Health Initiative for regular physical activity, both to reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease morbidity and mortality and to extend life expectancy. In particular, moderate-intensity aerobic exercise (including brisk walking, jogging swimming, hiking, various ball games, etc.) for at least 30 minutes a day, at least five days a week, is used in theLowering blood pressure, controlling blood sugar and weight, and improving cardiovascular function have benefits you never thought possible.
4. Weight control
Weight has always been a topic of major concern in the health community, especially in terms of overweight or even obesity with a BMI greater than 24. Controlling obesity is a key factor in reducing morbidity and mortality from chronic diseases. After 16 years of follow-up of 1 million healthy individuals, results show that overweight increases cardiovascular deaths by 1.5 times, and obesity increases cardiovascular deaths by 2 to 3 times.

5. Correcting emotions
Emotional stress is often closely linked to blood pressure, and excessive emotion is closely associated with the onset and development of coronary artery disease and cardiovascular events. In particular, personality traits characterized by irritability and emotional stress are second only to smoking as a risk factor for myocardial infarction.
In addition to irritability emotions that are closely related to cardiovascular include:
- apprehensive
- despondent
- panic attack
- hypochondriasis
- sleep disorder
- obsessive-compulsive thinking (OCD)
- Somatization sensory disorder, etc.
Staying emotionally stable and positive plays a big role in controlling cardiovascular disease.
summarize
Self-assessment of the risk of cardiovascular disease according to one's own characteristics and the multiplier of the risk in relation to that of a healthy person of the same age, in order to clarify one's state of health. Secondly, it is important to actively correct poor lifestyles. This includes
- cateringLack of vegetables and fruits, excessive amount of meat and fats, excessive salt intake, heavy alcohol consumption and other undesirableDietary patterns
- Smoking and stress
- lack of exercise

Winter is the high incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, once repeated dizziness, weakness of hands and feet, numbness and even fall, may be cerebral ischemia symptoms caused by cerebral vascular stenosis, to seek medical attention; prevention of cerebrovascular disease to ensure that the head, back and feet of the three parts of the warm.
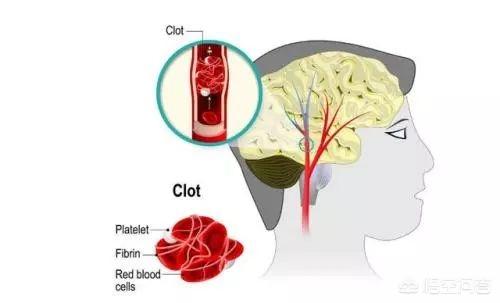
To prevent cerebrovascular disease in winter, we need to make sure that 3 parts of the body are warm. First, the head is warm.The human head is the seat of the nerve center, blood vessels and capillaries are many and thick, once the head is cold, can make blood vessel contraction, elevated blood pressure, capillaries are easy to harden, and even cause small arteries to continue to spasm, resulting in cerebral infarction, heart attack increased chances;Second, the back warmerThe back and the five organs are connected, if the cold attack, easy to cause back pain, cervical pain, while affecting the operation of qi and blood lead to blood stasis and induce cerebrovascular disease outbreaks;Third, the feet are warmOnce the feet are cold, the cold will be forced from the feet directly into the body, causing capillary contraction, inducing cerebrovascular disease.
Cerebrovascular disease refers to a group of diseases caused by rupture and bleeding or thrombosis of cerebral blood vessels, resulting in symptoms of hemorrhagic or ischemic injury to the brain as the main clinical manifestation.
Risk factors for cerebrovascular disease are categorized as non-interventable and interventable. Weather, age, and gender are non-interventable risk factors, but risk factors such as high blood pressure, heart disease, diabetes mellitus, smoking, alcoholism, and dyslipidemia are interventable.
At present, the risk factors for cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases in our population are rising rapidly, and there is a phenomenon of superposition of multiple risk factors. Research has confirmed that hypertension, diabetes, serum cholesterol levels and smoking have a direct relationship with the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, but it is worthwhile to emphasize that, so far, these major risk factors have not only not declined in China's population, but instead are rising at an "alarming" rate, so it is crucial to actively control various risk factors.
Risk factor 1: High blood pressure
The number of hypertensive patients in China is currently increasing rapidly and most of them have suboptimal blood pressure control, which is probably the most important reason for the high incidence of cerebrovascular disease. The main goal of treatment of hypertension is to improve the control rate in order to reduce the occurrence of stroke and other comorbidities, and it is equally important for patients to reach the standard of systolic and diastolic blood pressure, and a blood pressure level of <140/90 mmHg is appropriate.

suggestion: Take an active role in caring for your blood pressure. Adults over the age of 35 need to start keeping an eye on their blood pressure, and people with high blood pressure should measure their blood pressure more often to adjust their medication dosage. A healthy lifestyle is very important in preventing high blood pressure-
Weight loss Abdominal obesity ratio Body Mass Index BMI (kg/m2) remains at 20-24; salt restriction Under 6 grams per day.
Reduction of dietary fat
Daily consumption of 400-500 grams of fresh vegetables, 100 grams of fruit, 50-100 grams of meat, 50 grams of fish and shrimp, 250 grams of milk, 20-25 grams of cooking oil, 3-4 eggs per week, and less sugar and sweets.
Maintain appropriate physical activity; quit smoking, limit alcohol, alcoholics drink <20-30 grams per day for men and <15-20 grams per day for women.

Risk Factor 2: Heart Disease
The results of a study in the United States show that the risk of stroke is more than two times higher in people with heart disease than in people without heart disease, regardless of blood pressure level. Atrial fibrillation is an important risk factor for stroke, and its effective treatment can prevent stroke. Patients with non-valvular atrial fibrillation have a 3-5% annual risk of stroke, which accounts for about 50% of thromboembolic strokes.
Suggestions: regular medical checkups should be conducted above the age of 40 for early detection of heart disease; high-risk patients with coronary heart disease should take low-dose aspirin or other anti-platelet aggregation drugs under the guidance of a doctor.
Risk factor 3: Diabetes
Diabetes is a risk factor for cerebrovascular disease. In Europe and the United States, where the prevalence of diabetes is high, diabetes is an independent risk factor for ischemic stroke, and patients with type 2 diabetes have a twofold increased risk of stroke.
Recommendation:People with risk factors for cerebrovascular disease should have regular blood glucose testing, and fasting blood glucose should be <7mmoI/L. Mild diabetic patients should control their diets and strengthen physical exercise, and those whose blood glucose control is still unsatisfactory after 2-3 months should be treated with glucose-lowering medication or insulin according to doctor's instructions.

Risk Factor 4: Dyslipidemia
Eating a lot of greasy food, blood travels throughout the body with fat. Hyperlipidemia can increase blood viscosity and accelerate the process of cerebral atherosclerosis, which is associated with ischemic stroke. The risk of cerebral hemorrhage can be increased when serum total cholesterol levels are too low.
Recommendation:People with dyslipidemia, especially those with other risk factors such as hypertension, diabetes, and smoking, should first change their unhealthy lifestyles, choose lipid-lowering drugs if necessary, and have their blood lipids rechecked regularly.

Risk Factor 5: Smoking
Smoking affects the vascular and hematologic systems throughout the body, accelerating atherosclerosis, elevating fibrinogen levels, and promoting platelet aggregation. Regular smoking is a well-recognized risk factor for ischemic stroke, and its risk increases with the amount of smoking. Long-term passive smoking can also increase the risk of stroke.
Recommendation:Quit smoking; set up smoke-free areas in offices, conference rooms, airplanes, trains and other public places to reduce the harm of passive smoking.
Risk factor 6: Alcohol consumption
Alcohol intake has a direct dose-related effect on hemorrhagic stroke, and chronic heavy drinking and acute alcohol intoxication are risk factors for cerebral infarction in young and middle-aged adults.
Men who drink no more than 50 ml of liquor (alcohol content <30 g), no more than 640 ml of beer, and no more than 200 ml of glucose wine per day (women's alcohol consumption needs to be halved) may reduce the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases. The risk of cerebral infarction is significantly higher in people who drink more than 5 drinks per day (1 drink is equivalent to 11-14 grams of alcohol). Alcohol may increase the risk of stroke by raising blood pressure, causing hypercoagulability, cardiac arrhythmia, and decreasing cerebral blood flow. Alcohol may increase stroke by raising blood pressure, causing hypercoagulability, cardiac arrhythmias, and reducing cerebral blood flow.
Recommendation:Alcohol consumption must be moderate, do not abuse alcohol; men should not drink more than 20-30 grams of alcohol per day, women should not exceed 15-20 grams. For non-drinkers do not advocate a small amount of alcohol to prevent cardiovascular disease; pregnant women should avoid alcohol.

Cardiovascular disease is the first major killer of death of our residents, how to prevent cardiovascular disease is very important. Prevention of cardiovascular disease to do the following points, let's recognize and learn.
First, lifestyle interventions.
Almost all diseases require lifestyle interventions, and this is true for cardiovascular disease as well. Lifestyle interventions include smoking cessation, alcohol restriction, moderate activity, weight control, and regularity, among many others.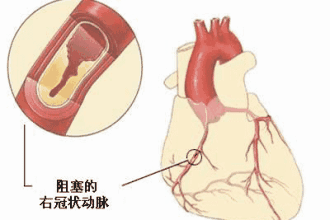
Second, control the primary disease.
Many diseases can induce and aggravate the emergence of cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes and so on, so actively controlling the primary disease can reduce the probability of cardiovascular diseases, and if not control the primary disease, then hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes and other diseases will induce and aggravate the development of cardiovascular diseases.
Third, a good mindset to face it.
Mindset is also very important for cardiovascular disease, for example, people with type A personality and type B personality, the former cardiovascular disease incidence rate is more than five times that of the latter, so a good state of mind and character for the prevention of cardiovascular disease is also very important.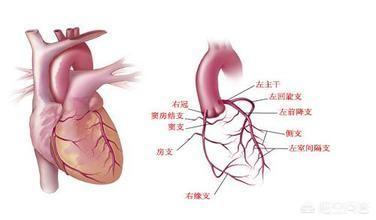
Fourth, avoid triggers.
If we these factors are intervened, but the patient is still a high-risk patient for cardiovascular disease, then we need to try to avoid the triggering factors to avoid the development of cardiovascular disease, common triggering factors for the development of cardiovascular disease are mainly infections, fatigue, anger and so on, to avoid the emergence of these factors, but also to reduce the occurrence of cardiovascular disease development.
Fifth, drug prophylaxis, if necessary.
Drugs for primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular diseases such as coronary heart disease are also very important. Primary prevention of cardiovascular disease is necessary if the patient is at high risk, and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease with drugs is necessary if the patient has already developed cardiovascular disease.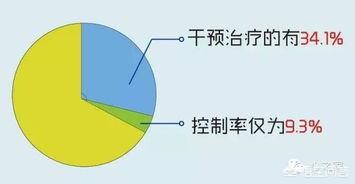
See what's going on? Follow us for daily updates on science, pushed to you.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a serious threat to human health. It is a common disease among middle-aged and elderly people over the age of 50, with high prevalence, disability and mortality rates, and is prone to recurrence. Although there are advanced and perfect treatment means, some survivors of cardiovascular accidents are still unable to take care of themselves. In addition to heredity, poor lifestyle habits are also a major cause of cardiovascular disease, so cardiovascular disease can be prevented by means of lifestyle modification.
How to prevent cardiovascular disease in daily life?
1、Control sodium intake
Studies have shown that the higher the intake of sodium in the diet, the higher the risk of hypertension and cardiovascular disease, and that reducing sodium intake can assist in lowering blood pressure. Hypertension is a high-risk independent factor for cardiovascular disease, and cardiovascular disease can be prevented by ensuring stable blood pressure.
Adults should not eat more than 6 grams of salt per day, cook food with less seasoning such as salt, chicken MSG and various sauces, etc. You may want to replace some of the seasoning with natural ingredients such as lemon juice, onion, ginger, garlic and mushrooms. Eating more potassium-containing foods such as fresh fruits and vegetables can counteract sodium ions and assist in lowering blood pressure.
2, away from saturated fatty acids
Stay away from high cholesterol foods such as animal offal, crab yolks and egg yolks, etc., daily cholesterol intake should not exceed 300 mg; daily saturated fatty acid intake should not be more than 10%, such as a variety of fatty meats and butter, etc., and should be appropriate intake of unsaturated fatty acids, such as nuts and vegetable oils, etc., which can reduce the chances of suffering from heart disease; stay away from high-sugar foods, and control the intake of energy from fat sources;
Eat less fine grains and foods made from fine grains, especially those containing fat, sugar and salt. Alcohol is a stimulant, and the more you drink, the higher your risk of high blood pressure, hemorrhagic stroke, and atrial fibrillation, so you should control the amount of alcohol you drink and try to stay away from it.

3. Drink coffee appropriately
The effects of coffee on cardiovascular disease have been the subject of much controversy in recent years. However, studies have found that daily coffee drinkers have a lower risk of cardiovascular death compared to non-coffee drinkers, and that drinking one to two cups of coffee per day is beneficial to cardiovascular health.
4. Exercise
Prolonged sitting does not increase the risk of cardiovascular disease and is also a high risk factor for fatty liver, type 2 diabetes and certain cancers. Adherence to aerobic exercise can reduce resting blood pressure, improve cardiopulmonary function and regulate nervousness. However, you should choose the right exercise program according to your own situation and interests. Having 30 minutes of exercise every day, up to 3-5 times a week, can effectively improve cardiovascular health; however, people over 65 years old should focus on training balance to prevent falls.
5. Refuse to smoke
The longer you smoke and the more you smoke, the higher your risk of stroke and high blood pressure and heart disease. Nicotine, tar and carbon monoxide in cigarettes can damage the endothelial integrity of blood vessels and promote the deposition of lipids in the walls of blood vessels, thus causing atherosclerosis, so you should stay away from cigarettes and secondhand smoke.

Spanish jasmine (Jasminum grandiflorum)
In addition to doing the above, you should also actively control your weight and keep your body mass index between 18.5 and 23.9. Learn to reduce stress, maintain a positive and optimistic mindset, sleep at least 7 to 8 hours a day and refuse to stay up late. In addition, stabilize blood pressure, blood glucose, blood lipids and various indicators such as weight and waist circumference, as well as go to the hospital regularly for relevant examinations.
If it has been clear that there is cardiovascular disease, then it is important to adhere to the medication under the guidance of a cardiovascular doctor; especially patients with clear angina pectoris and myocardial infarction; and never believe in small advertisements for health care drugs!
For people who just have high risk factors, it's important to quit smoking, control blood pressure, control blood sugar, and control lipids.
It is important to stick to moderate exercise, a balanced diet (eat everything, not too much of anything), and keep warm in the winter.
If you suspect you have symptoms of cardiovascular disease promptly get an EKG and see a cardiologist!
Those with a family history of this condition should be even more aware than others to seek prompt medical attention for symptoms such as chest tightness, breath-holding, pain or discomfort in the precordial area, palpitations, back pain, and so on.
It has been reported that cardiovascular disease has now become the number one killer of our national health. Cardiovascular problems have become a problem that many people who care about their health can't get around, so what should we do to prevent cardiovascular disease?
The development of cardiovascular disease does not happen overnight, it needs to accumulate over time, therefore, we should pay attention to it when it has not yet formed a climate and focus on prevention. This will have the best effect. When it grows into a big tree, we will have to use some extreme methods to remove the threat. In severe cases of cardiovascular disease, where the blood vessels are too clogged, we may need to use surgical bypasses, put stents in the blood vessels, and so on. And it's not a once-and-for-all solution. When a major blood vessel is blocked, other blood vessels are no better, and the patient's quality of life will be significantly affected.
How to prevent cardiovascular disease?
Perception:A correct concept of disease is a prerequisite for all prevention and treatment. Stop thinking that cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases are only a concern for the elderly, young people also need. Chronic kidney disease patients, even more need to be concerned!
Lowering of blood lipids:Elevated blood lipids, your doctor may give you lipid-lowering medication if you can't control it with your lifestyle diet.
Control blood pressure and blood sugar:Blood pressure should be less than 140/90mmHg and less than 130/80mmHg for protein greater than 1g. Some people have a strange attitude towards antihypertensive drugs, because they are afraid of dependence on antihypertensive drugs, and often have a meal without a meal. If it is high blood pressure condition needs, should continue to take regular antihypertensive drugs. Taking antihypertensive drugs is the condition needs, rather than your dependence on antihypertensive drugs lead to high blood pressure, this logic should be clear.
The use of antiplatelet drugs:For patients with pre-existing cardiovascular disease, doctors may recommend continuous low-dose use of antiplatelet medications such as aspirin or poliovirus as a preventive measure in order to prevent cardiovascular accidents, such as myocardial infarction and cerebral infarction, and other such problems.
Control of urinary protein, correction of severe anemia and disorders of calcium and phosphorus metabolism
Habits:This one is within the control of our generalized pain patients; smoking, lack of physical activity, overnutrition and malnutrition can all contribute to the development of cardiovascular disease. Therefore, smoking cessation, increased physical activity, overnutrition requires dietary restriction, and malnutrition requires correction of nutritional status, one by one, if these bad habits exist.
This is basic medical common sense, first of all, eat a light and balanced diet, moderate exercise, weight control, quit smoking and limit alcohol, and then the three high really good control, to meet the standard! Then there are regular checkups! It will be able to reduce the occurrence or development of most heart attacks, strokes and other serious cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.