My blood sugar is 7.5 two hours after dinner and 15 in the morning on an empty stomach.
If a diabetic patient has high fasting blood glucose, it is important to review what the patient ate the night before to see if he/she ate more or consumed too much fatty, protein/sugar-rich foods, as the process of converting these foods into sugar for absorption will be slower and can be prolonged until the next day's fasting and result in higher blood glucose.
Also eating for a longer period of time when eating out the day before, and continuing to eat over a relatively long period of time, may also result in a sustained rise in blood glucose, which can also affect fasting blood glucose the next day.
There is also the phenomenon of Sumuje, you need to observe whether the patient has nighttime hypoglycemia, such as patients applying too large a dose of drugs, hypoglycemia in the early hours of the morning, because the patient can not be perceived while sleeping, the body out of the protective effect will lead to an increase in the secretion of glucagon, resulting in fasting hyperglycemia in the patient in the morning.
So if poor fasting glucose control occurs, be sure to monitor glucose values at 0:00 a.m., 2:00 a.m., 4:00 a.m., and 6:00 a.m., and do so several times.
At the same time, to address the causes of high fasting blood glucose, timely adjustments to the diet and exercise program, if necessary, under the guidance of the doctor to adjust the medication program.
By testing blood glucose can be found, many diabetic friends after dinner blood glucose is okay, but in the morning it is found that the fasting blood glucose is higher, like this friend, found that his blood glucose after dinner 7.5mmol / L, fasting blood glucose in the morning is up to 15mmol / L, many diabetic friends are very incomprehensible, this is how?
They asked.
Dr. Sun, isn't it true that postprandial blood sugar is higher than preprandial blood sugar?
Isn't fasting blood sugar the blood sugar without eating? How come my blood sugar is high even though I didn't eat?
This is relatively common in clinical practice and something that is very confusing to many people who present with diabetes.
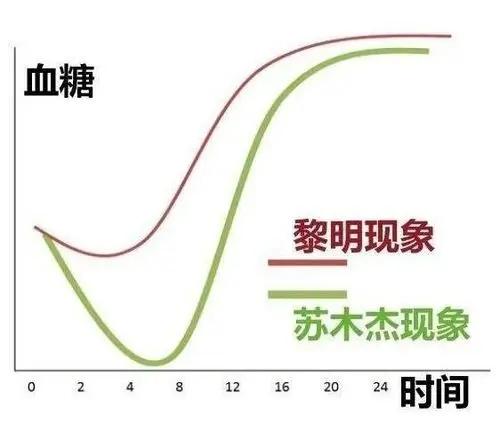
This most common reaction is called "Sumuday phenomenon", which means that the patient's blood glucose control is still good, but in the morning there may be an abnormal phenomenon of much higher blood glucose than usual, mainly because of hypoglycemia during the night. The patient's blood sugar drops, the body will secrete adrenaline, pancreatic glucagon and other substances, which can counteract the glucose-lowering effect of insulin, so that blood glucose increases, but due to the loss of control of blood glucose regulation mechanism of diabetic patients, the role of these hormones to make the body's blood glucose rises too quickly, there will be a blood glucose than the nighttime glucose and the usual glucose to be higher than the case of blood glucose. It becomes"The Sukkot Phenomenon", is one of the more common clinical causes of fasting hyperglycemia.
Patients with this condition usually experience panic, sweating, dizziness, poor sleep at night, etc. If the blood glucose test is performed, it will be found that there is a tendency for blood glucose to drop, and the symptoms will be relieved by consuming some sugary foods, and the blood glucose in the morning will not fluctuate too drastically if the amount of food eaten is appropriate. However, very often patients do not have conscious symptoms, or sleep after these symptoms are not easy to detect, you can not understand the occurrence of hypoglycemia, or after dinner did not carry out a blood glucose check, simple fasting blood glucose check found that blood glucose is high, without detailed clinical analysis, it is hastily considered that the patient's dosage of glucose-lowering drugs is not enough, and the direct addition of medication may make the patient's blood glucose drop even more pronounced, and even the emergence of hypoglycemic coma or even the possibility of life-threatening. At this time, the blood glucose change curve shows a downward and then upward curve, and the treatment is to reduce the dosage of medication before dinner or bedtime.
The dawn phenomenon can also be characterized by an increase in fasting blood sugar. Substances such as growth hormone and adrenaline are secreted during the night, and these raise blood glucose, leading to a gradual rise in blood glucose in the early hours of the morning, which then leads to a condition of elevated fasting blood glucose. Blood glucose monitoring shows a gradual curve of elevated blood glucose, and in this case the medication needs to be increased to lower the blood glucose, which is not the same as the management of the Sumuje phenomenon.
Of course, there are also some patients due to too little dinner or too much activity, there will be night hunger, then the patient to eat their own meals, without blood glucose checks, there will also be a higher blood glucose before breakfast, of course, this is not the fasting blood glucose value, but the blood glucose after the meal, will be with the calorie of the food he ate, the blood glucose will be high and low changes.
Therefore, it is very important to carefully analyze the reasons for the changes in the patient's blood glucose, especially when there are abnormal changes in blood glucose, and it is important to ask the patient in detail about the symptoms, medication, diet, medication, etc., to monitor blood glucose, and, if necessary, perform ambulatory blood glucose monitoring, in order to understand the changes in the patient's blood glucose.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
The normal value of blood glucose has different standards depending on different people, and different meal status. Fasting blood glucose for the general population should be between 3.9 and 6.1 mmol/L, one hour after a meal between 4.7 and 10.1 mmol/L, and two hours after a meal between 4.7 and 7.7 mmol/L.
And the diagnostic criteria of diabetes mellitus, mainly to observe whether there are symptoms, if there are typical symptoms of three more and one less, the patient has thirst, drink more, urinate more and weight loss, there is this typical symptom, if the random blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol / L, or fasting blood glucose ≥ 7 mmol / L, or after the screening of glucose tolerance, that is, in drinking sugar water to do glucose tolerance screening, two hours after the meal > 11.1 mmol / L, all can be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus, and the patient has a high blood sugar content. L, all can be diagnosed as diabetes mellitus.
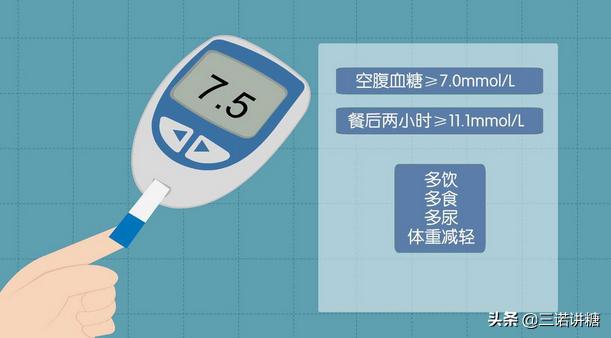
Your postprandial blood glucose is at 7.5, and your morning fasting reaches 15. The first step is to determine if it is a true fasting blood glucose. Fasting blood glucose is a fast that is to be taken overnight, at least for 8-10 hours, without eating any food but drinking water should be excepted, and the value of the blood glucose that is tested before breakfast is called fasting blood glucose.
Then after repeated confirmation, fasting blood sugar is always high, and you have not been diagnosed with diabetes, you must go to the hospital to confirm the diagnosis, so as not to delay treatment.
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, such fasting blood sugars are also classified as very unsatisfactory.
The main reason may be that the amount of meal in the evening is too much and the calories are too high, which leads to the blood sugar not being controlled in the normal range. You need to control the dinner diet, try to eat more light vegetables, do not eat too much staple food, as well as appropriate activities and exercise after meals to help reduce blood sugar.
If glucose-lowering drugs are applied, it mainly means that the dosage or type of glucose-lowering drugs is not appropriate, and the situation of not controlling blood sugar well, the dosage of glucose-lowering drugs needs to be increased, or the type of glucose-lowering drugs needs to be readjusted.
Thank you for reading this article, if you agree with the views expressed in the article, please give me a like, follow {Sano Sugar}, and if you have any questions, please invite me to answer them!
Two hours after dinner blood glucose refers to postprandial blood glucose, normal half an hour after meals and 1 hour blood glucose does not exceed 10 mmol / L, two hours after meals blood glucose does not exceed 7.8 mmol / L; morning fasting blood glucose refers to fasting overnight before breakfast blood glucose, normal fasting blood glucose should be less than 6.1 mmol / liter. From the results, your fasting blood sugar is high, and postprandial blood sugar is normal.

What does a high fasting blood sugar and normal postprandial blood sugar mean?
Fasting blood glucose reflects the ability of one's own insulin secretion, and postprandial blood glucose reflects the body's ability to produce additional insulin after a glycemic load.
There are three main reasons for having high fasting blood glucose and normal postprandial blood glucose:
One is the use of insulin, especially short-acting insulin preparations, because this insulin is fast-acting and acts quickly after a meal, so that postprandial blood glucose is a normal range; the second is that some patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus may have excessive insulin secretion and delayed peaks, and that high blood glucose values after a meal can stimulate the secretion of insulin and contribute to the reduction of blood glucose, and thus lower blood glucose occurs after a meal.
Third, patients may also experience elevated fasting blood glucose when they use insufficient amounts of intermediate-acting insulin at night resulting in poor fasting blood glucose control.
In summary, if you have been diagnosed with diabetes, you need to check whether your medication is reasonable, whether diet and medication can maintain balance, if it is not reasonable need to go to consult the doctor for medication change or reduce or add treatment; if you are not diagnosed with diabetes now, high fasting blood glucose indicates that fasting blood glucose has been impaired, the ability of their own insulin secretion is reduced, while the postprandial hematocrit is in the normal range. When this happens, then it is a state of impaired fasting blood sugar. At this point it is not yet possible to diagnose diabetes. In order to further confirm the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, it is recommended to go to a regular hospital to do an OGTT test to know the range of postprandial blood glucose to be able to finally confirm the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus.

What is the OGTT test? What does it do?
For people who have elevated blood glucose but do not meet the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, further testing is needed to figure out their glucose metabolism, and an OGTT screening test is needed here.
The Oral Glucose Tolerance Test, abbreviated as OGTT, is a method of checking blood glucose after an increased glycemic load (after eating sugar) to increase the detection rate of diabetes.The glucose tolerance test should be performed on an empty stomach. Before taking sugar, fasting blood sugar is drawn, then 75 grams of glucose powder dissolved in 300 ml of water is taken within 5 minutes, and blood is drawn to check blood sugar at 30 minutes, 1 hour and 2 hours after taking sugar to diagnose or rule out diabetes.
There are four types of OGTT test results, including normal glucose tolerance, impaired fasting glucose, decreased glucose tolerance and increased glucose tolerance. Patients should not perform strenuous activities before the test and should ensure sufficient rest. If patients experience symptoms such as fainting and pallor during the test to stop the test.
Impaired fasting glucose interventions are treated as follows
1. Control your diet and reduce your total calories.
Patients with impaired fasting blood glucose should adhere to the principle of light diet and balanced nutrition, and eat low-fat, low-sugar and low-salt foods. Eat more fresh vegetables, coarse grains, etc. Avoid sweets, fried, cholesterol-rich foods. For example, animal offal, all kinds of pastries, chocolate, carbonated beverages, etc. It is best to eat white meat, such as fish, duck, chicken, etc., as little as possible than red meat, such as pork, beef and mutton. And pay attention to coarse and fine food to match.

2. Reasonable exercise to reduce weight.
Exercise is an important means to improve the abnormal glucose metabolism, patients with abnormal glucose tolerance should insist on exercise, you can insist on daily brisk walking, jogging, playing gate ball, tai chi, tai chi sword, cycling, stair climbing, climbing hillside, etc..
3、Take medicine when it is time to take medicine
If your doctor suggests that you take medication, it is still important to follow the doctor's advice to do so. The dangers of diabetes should be known to everyone, so it is best to follow the doctor's advice to take medication to avoid complications of diabetes.
Finally, it is vital to keep a good mood.
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! Also, if you have family members who suffer from high fasting blood sugar related problems, please pass this article on to them!
Generally, the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is higher than the fasting blood glucose, but the following reasons can cause the fasting blood glucose to be higher than the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose:
(1) Reactive hypoglycemia
Early type 2 diabetes patients due to abnormal insulin function, there will be the arrival of the blood glucose peak, their own insulin secretion response is slow, the peak of postprandial insulin secretion delayed arrival, the peak of blood glucose in the front, the peak of insulin late, the two are not synchronized. This results in a significant rise in blood glucose within a short period of time after a meal, and a tendency for blood glucose to drop significantly 2 to 3 hours after the meal.
(2) Excessive hypoglycemic therapy
A portion of diabetic patients injected a large dose of premixed insulin before breakfast, and the peak of action of premixed insulin occurs 2 to 6 hours after injection, which happens to cover the time period from 2 hours after breakfast to just before lunch, and symptoms of hypoglycemia can occur if food intake is insufficient.
(3) Certain drugs and diseases interfere
- The direct effects of medications can lead to low blood glucose test results.
- An interaction between a drug and a glucose-lowering medication taken before or during a meal results in an increase in the blood concentration of the glucose-lowering medication, which is equivalent to an increase in the dose of the glucose-lowering medication.
- The effect of certain diseases on glucose metabolism, such as chronic liver disease. This condition usually results in a lower blood glucose value 2 to 3 hours after a meal than in the fasting state.
There are two steps to take if you want to prevent this:
(1) Good blood glucose monitoring
It is necessary to do a good job of real-time dynamic blood glucose monitoring, systematically grasp the characteristics of their own blood glucose fluctuations, and find the time zones where hypoglycemia is likely to occur. You can also strengthen blood glucose monitoring during the time when you are prone to cold sweats, dizziness and other uncomfortable symptoms according to your own characteristics to find a pattern.
(2) Developing recipes that suit your own characteristics
For diabetic patients are prone to low blood glucose before lunch, you can appropriate meal sharing, will be part of the breakfast to be placed in the morning around 9 o'clock to eat, while trying to avoid eating some of the absorption of the food too fast, so that not only can avoid a significant rise in blood glucose after breakfast, but also effectively prevent the next meal before the low blood glucose situation occurs.
For questions about postprandial glucose, see our column, "Lowering Postprandial Glucose from Scratch to Reverse Diabetes".
CONCLUSION: It may be necessary to monitor nighttime blood glucose, or to test liver function.

If you have started insulin therapy, there are three possibilities:
(1) Inadequate nocturnal insulin application;
② "dawnphenomenon": i.e., blood glucose control is good at night and no hypoglycemia occurs, but high blood glucose occurs only for a short period of time at dawn.Due to increased secretion of cortisol, growth hormone, etc. early in the morning--These hormones are blood sugar-raising hormones;
(iii) Somogyi effect: i.e., there had been hypoglycemia at night, which was not noticed during sleep, but led to an increase in the secretion of insulin antagonist hormone in the body, followed by rebound hyperglycemia after hypoglycemia.
Multiple measurements of blood glucose during the night (at 0, 2, 4, 6, and 8 o'clock) can help identify the cause of morning hyperglycemia, which can be performed by ambulatory glucose monitoring.
If you have not started diabetes treatment:
Fasting blood glucose represents the body's basal blood glucose value, reflecting the basal state of blood glucose maintenance through hepatic glucose output after an overnight period without food. Therefore, the main factor affecting fasting blood glucose is the breakdown of liver sugar.
At this point you should review your blood glucose, liver function and liver ultrasound several times, you should consider the presence of liver problems and start diabetes treatment (lifestyle and medication).
Follow @ScientistDr. Gen to learn more about medicine!
Hello, I am a medical worker Zhang, a practicing physician, can popularize health knowledge for everyone, if you know more, pay attention to me!
What is the reason for a blood sugar of 7.5 two hours after dinner and 15 in the morning fasting? Many people do not understand why the blood sugar after dinner is instead lower than fasting in the morning, today we will explain to you.

What is fasting blood sugar?
Fasting blood glucose is an important indicator of glycemic control in diabetic patients, and achieving fasting blood glucose is a good start for all-day glycemic control. For most diabetic patients, the expected goal of fasting blood glucose control is 4.4~7.0 mmol/L. For special circumstances, such as the elderly with multiple chronic diseases, the fasting blood glucose can be appropriately relaxed to 5.0-8.3 mmolL; pregnant women with gestational diabetes mellitus, the control of fasting blood glucose is more stringent, and it should be controlled at 5.3 mmol/L or less.
What about postprandial blood sugar?
A normal 2-hour postprandial blood glucose is a blood glucose measurement taken a full 2 hours after the first bite of a meal. Measurements should be taken at the same time and with the same dose of medication, insulin injection and meal as usual. Blood glucose 2 hours after a meal is affected by a variety of factors such as the type of food consumed, the speed of gastrointestinal peristalsis, the amount of exercise after the meal, and the level of preprandial blood glucose. Under normal circumstances, the normal value of 2-hour postprandial blood glucose ranges from 4.6 to 7.8 mmol/liter. Measuring 2 hours postprandial blood glucose can detect possible postprandial hyperglycemia. Many type 2 diabetic patients do not have high fasting blood glucose, but have high postprandial blood glucose. If only fasting blood glucose is checked, some patients may be missed. At the same time, the blood glucose value measured 2 hours after meal can better reflect the eating and the use of hypoglycemic drugs is appropriate, which is the fasting blood glucose can not reflect. In addition, the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose test will not affect the normal medication or injection, and will not affect the normal eating, so it will not cause the blood glucose to fluctuate greatly.
What's wrong with high blood sugar before meals and low blood sugar after meals?
1, excessive insulin secretion and peak delay Under normal circumstances, blood glucose will rise after eating, about 30~60 minutes blood glucose reaches the peak and then fall, plasma insulin level also rises to the peak in 30~60 minutes, for the basal value of 5~10 times, and then fall, 3~4 hours to return to the basal level. Therefore, although normal people's blood glucose rises after meals, it fluctuates within a certain range. patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus may have excessive insulin secretion (hyperinsulinemia) and delayed peak, insulin is maintained at a higher concentration and cannot return to the baseline level, and therefore, the phenomenon of lower blood glucose or even hypoglycemia occurs after meals.
2. Inadequate diet and excessive intensity of postprandial exercise Diet and exercise are two important basic measures in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Strict dietary control and appropriate exercise are conducive to weight reduction, improvement of hyperglycemia and reduction of hypoglycemic drugs. However, the diet program should be strictly and long-term implementation, and exercise should be regular. If the diet is insufficient or the intensity of exercise after meals is too high, patients may also have low blood glucose after meals or even hypoglycemic reactions.
3、Drugs Excessive dosage of hypoglycemic drugs, mismatch with diet, or simultaneous application of other drugs that enhance the hypoglycemic effect of hypoglycemic drugs may also lead to a significant reduction in postprandial blood glucose.
Why is fasting blood sugar higher in the morning than after a meal in the evening?
1, dawn phenomenon: fasting blood glucose mainly reflects the level of their own insulin, two hours after the meal blood glucose mainly reflects how the insulin reserve. Diabetic patients have low insulin level, so fasting and postprandial blood sugar are high. There is a glucagon hormone called adrenal glucocorticoid in human body, this hormone is secreted more from 4 o'clock in the morning, which makes the blood glucose rise gradually, which is called "dawn phenomenon" in medical science, for diabetic patients with insulin deficiency, the dawn phenomenon is more serious, so the fasting blood glucose may be higher than the one after dinner.
2、Sumu Jie reaction: Another possibility is that there is an unconscious hypoglycemia at night, which stimulates a variety of glucagon, reflecting as fasting blood glucose is higher than the post-dinner blood glucose, and medically, the reactive hyperglycemia after hypoglycemia is called "Sumu Jie reaction", which needs to be monitored for the nighttime blood glucose.
3, improper use of medication: there is a possibility that the oral hypoglycemic drugs taken or injected insulin belongs to the short-acting class, the power of the drug to maintain less than the early morning, to the second half of the night the drug can not keep an eye on the strength of the blood glucose rises higher than the day before after dinner.

Conclusion: dinner two hours of blood glucose lower than the morning blood glucose in the eyes of many patients are not normal, in fact, in the medical piece is also a phenomenon that often occurs, the specific how to do should go to the hospital to do a blood glucose monitoring observation, whether the dawn phenomenon and the phenomenon of Sumu Jie can be discharged, if it is not the two major phenomena haunted, then it may be the use of drugs is not appropriate to adjust the use of medicines again.
You have to take your long-acting insulin at night.
My personal shallow interpretation;
Two hours after dinner blood glucose 7.5 (may be the patient in the meal before the injection of insulin or oral sugar-control drugs, just in the time period of medication is also in the two to four hours to play a volatile effect), and the time of food dissolution in the stomach around 1:00 a.m. to start (by the bile, appendix fluid, gastric acid, pancreatic fluid into a putrefactive solution for digestion of food in the stomach, and at this time, pancreatic fluid has been replaced by the drug can not play a normal pancreatic islet Secretion of liquid function) food in the stomach after melting by the stomach and intestines to absorb the carbohydrates gradually penetrate and lungs, spleen, liver and kidneys to generate (gas) blood, at this time the pancreatic islets do not function also super-generated hemoglobin normal value (that is, the main component of blood glucose), so in the dinner for two hours to the morning test of fasting glucose basically has arrived at the 8 ~ 9 hours in the morning test of fasting glucose 15 should be This is the reasoning.
That's why the treatment of diabetes also goes to the root of the problem.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.