How high is normal blood sugar for a 73 year old?
Not normal, such fasting blood sugar value is already very high. It is recommended to control the diet, do some aerobic exercise exercise, you can consider dietary therapy to eat Changhong Moringa Seeds to regulate, can help the body to promote insulin secretion and regulate blood glucose, so that blood glucose will not fluctuate.
Are you asking, how much should a 73-year-old diabetic's blood sugar be controlled? Generally for the elderly blood sugar to be relaxed, fasting 7 or so, after meals 11 or so can, in principle, do not appear hypoglycemia. If you are asking about the blood glucose range for healthy elderly people, then this is the same as the standard for ordinary adults, and there is no age difference in the criteria for diagnosing diabetes.
[Professional doctor to answer your questions
First of all, in terms of the normal value of blood glucose, it is the same standard regardless of age, i.e., fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 4.4-7.8 mmol/L. Since the damage to the body caused by high blood glucose does not vary according to age, normal blood glucose for people in their seventies should also refer to this standard.
However, due to the aging of the body of the elderly, most of them will have certain diseases, so in the control of blood glucose should be individualized treatment. For example, people with cerebral infarction, due to the existence of cerebral vascular lesions can easily lead to a decrease in blood flow, the control of blood pressure should be relaxed in order to ensure that there is sufficient blood supply, the same reason blood sugar should not be too low, otherwise it will lead to insufficient supply of energy and exacerbate the cerebral infarction; for example, people who are physically weak and emaciated, the body's ability to utilize nutrients decreases, and if the blood glucose is too low, it is even more detrimental to normal If the blood sugar is too low, it will be more unfavorable to the normal physiological activities, and it is not advisable to be too harsh on the blood sugar.
More importantly, once hypoglycemia occurs in an old person, the already aging cells will be damaged or even killed or injured due to the lack of sufficient energy supply, which in turn will endanger their lives; coupled with the decline in gastrointestinal function of the elderly and the decline in the absorption of nutrients, the deliberate control of blood glucose may lead to the occurrence of malnutrition. In addition, the damage of high blood sugar to the body has a gradual and progressive process, and the life expectancy of the elderly is limited, to ensure that there is a high quality of life standard is more important, and there is no need to have too harsh requirements on blood sugar.
Therefore, it is ideal for older adults to be able to keep their blood glucose in the normal range, and it is acceptable if they can keep their fasting blood glucose below 7.0 mmol/L and their 2-hour postprandial blood glucose below 10.0 mmol/L.
I hope this answer can help you, welcome to click on the attention and leave a message, together to learn to understand more about health knowledge.
For diabetics, blood glucose control can be a learning curve. The need to keep one's blood glucose under control as well as the need to be aware of the prevention of hypoglycemia requires a reasonable glycemic control goal so that cardiovascular disease can be minimized. The glycemic control goal, in turn, needs to be a combination of the patient's age, comorbidities, and complications in order to live a healthier life. Here's a chat with you in relation to the above questions.

First of all, let's be clear with you about what the normal value of our blood sugar is
We usually assess whether our blood sugar is normal or not by fasting blood sugar, 2 hours after meal blood sugar and glycated hemoglobin. Except for the special period of pregnancy, the diagnostic criteria for normal blood sugar and diabetes are the same, and there is no relationship with age.
According to current standards, normal fasting blood glucose is 3.9 to 6.1 mmol/L, blood glucose 2 hours after a meal is not higher than 7.8 mmol/L, and glycated hemoglobin is 4.3% to 5.9% (glycated hemoglobin measurement may be subject to error due to variations in testing systems).
However, if it is higher than these normal values, it can not be said that it is diabetes, because the development of the disease has a process. Normal people need to go through the stage of pre-diabetes to develop into diabetes, if we can improve our blood glucose levels through lifestyle at this stage we can avoid developing diabetes, but unfortunately many people do not know if they are out of pre-diabetes.
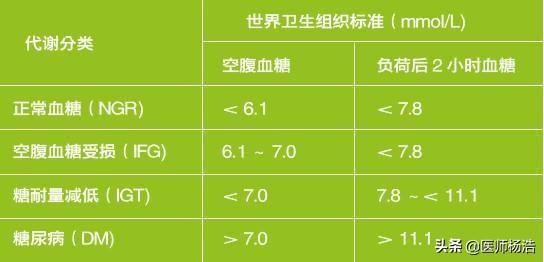
Prediabetes can be categorized as impaired fasting glucose and abnormal glucose tolerance
Impaired fasting glucose refers to a 2-hour postprandial glucose in the normal range and an abnormally elevated fasting glucose (6.1 to 7.0 mmol/L);
Abnormal glucose tolerance refers to normal fasting blood glucose and abnormally elevated 2-hour postprandial blood glucose (7.8 to 11.1 mmol/L).
Diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus
The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is either fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol / L, or 2 hours after meals ≥ 11.1 mmol / L. However, please note that if there is no typical "three more and one less" (thirst, drinking, urination, eating, unexplained weight loss), you need to review your blood glucose again on another day, and if it is still higher than these two values, then the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus can be confirmed. If it is still higher than these two values, the diagnosis of diabetes will be confirmed.
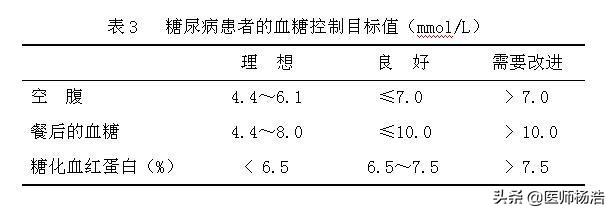
Now that you've been diagnosed with diabetes, let's take a look at how much you should keep your blood glucose under control
As mentioned earlier, the glycemic control target needs to be a combination of the patient's age, comorbidities, and complications. For the average diabetic, our fasting blood glucose usually needs to be controlled at 4.4~7.0mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose below 10mmol/L, and glycated hemoglobin below 7%. If the risk of hypoglycemia is high, for example, there has been a serious hypoglycemia, obvious microvascular or macrovascular lesions, serious comorbidities or diabetes has a long course, life expectancy is shorter, etc., then we can appropriately relax the blood glucose control target, fasting blood glucose does not exceed 8.0 mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose does not exceed 11.0 mmol/L, glycated hemoglobin does not exceed 8% are all. hemoglobin not more than 8% are acceptable.
However, this is only a principle of our blood glucose management, specific to the individual still need to be based on the patient's own situation. Some people who are 73 years old and in very good health, living like a 50 year old can follow the general diabetic target for strict glycemic control; while some people who are only 50 years old but are sickly and have serious complications can appropriately relax their glycemic control targets.
Having said that, I think you should see what I mean.
I am physician Yang Hao, specializing in the diagnosis and treatment of common and multiple diseases, chronic disease management, health science. Welcome to like, forward, leave a message, pay attention to this headline, let you live a healthier life!
Blood glucose generally refers to venous blood sugar, which is the main substance that maintains the normal physiological activities and energy metabolism of our organism. For a normal population, the normal blood glucose range of our organism is the same regardless of our age.
In other words, whether we are young people in our 20s, middle-aged people in their 50s, or older people in their 730s, we all have the same normal range of blood glucose, and exceeding this normal range is considered to be elevated blood glucose. Under normal circumstances, our organism's fasting venous blood glucose should be <6.1mmol/L, and two-hour postprandial venous blood glucose should be <7.8mmol/L. As we age, our organism's average blood glucose level increases accordingly, but regardless of the increase in blood glucose level, it should be fluctuating within the above normal range.
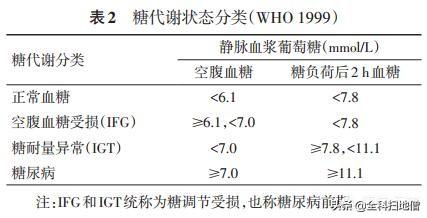
For the presence of typical symptoms of diabetes such as excessive eating, drinking, urinating and wasting, and fasting blood glucose ≥ 7.0 mmol / L or two hours after meal blood glucose (or random blood glucose) ≥ 11.1 mmol / L, should be considered as diabetes; if there is no typical symptoms of diabetes, the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus should be diagnosed by two measurements of blood glucose exceeding the above ranges on a non-same day. And if we when blood glucose exceeds the normal range, but has not yet reached the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, for pre-diabetes.
For patients with existing diabetes, we should actively seek medical treatment, follow the guidance of professional doctors, pay attention to improving lifestyle, achieve a reasonable diet, appropriate exercise, and at the same time, reasonable use of medication, as well as pay attention to monitoring the changes in blood glucose levels and regular review, in order to stabilize and control the condition, reduce complications, improve the quality of life, and improve the prognosis.
This article is answered by General Practice Sweeper, we hope that it will be helpful to you, copyright ©️, reproduced with permission. Please correct any deficiencies. The article is for reference only and is not intended as medical advice or medical guidance.
The normal fasting blood glucose of human body is 3.9mmol/L-6.1mmol/L, and the normal value of postprandial blood glucose is: 1, blood glucose of 1 hour after meal is 6.7mmol/L-9.5mmol/L, and at most it can't be more than 11.1mmol/L; 2, blood glucose of two hours after meal is less than 7.8mmol/L; 3, blood glucose of 3 hours after meal is back to normal, and every time the urine glucose is negative. . Generally blood glucose in the middle part of the normal value range is the most standard.
These two indicators are the same. For will lower the standard because of age, so normal is normal a level, fasting blood sugar between three point nine and five point nine, reach six point one is diabetes whether you are seventy-two or seventy-three. Then one hour after the meal is not greater than eleven, two hours of not greater than eight on it. Instead of thinking that the elderly, blood glucose can be a little higher than normal, on the contrary, as the age of the older

Body function will decline, can not be stabilized in the normal value, it will only become more and more serious aggravate the phenomenon of disease, so it is not to say that young people five point several okay, the elderly seven point several also okay is not so, but the difference between healthy people and people with blood glucose problems, on the contrary, the older the higher the blood glucose a little bit of damage are aggravated by some of them, it is a vicious cycle, such as young people's blood glucose for a moment a little bit higher, but also really nothing! It's a vicious cycle.

But the elderly only a little higher is a big problem, just like young adults to lift fifty pounds and the elderly to lift fifty pounds of the same, the elderly to increase a little can not afford, so look at the indicators according to the normal norms, do not think that this requirement will decline, on the contrary, the older the older, the more can not afford to change.

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.