Is a blood sugar of thirteen very high?
[Professional doctor to answer your questions

It can be said with certainty that blood sugar thirteen points more is certainly not normal, but not very high but can not make a clear answer, why? Because the human body in different physical conditions, high and low blood sugar as well as the magnitude of the rise and fall is different, how to understand it? Take a look at the law of change of human blood sugar.
After a meal, the first food will enter the stomach to be ground, the stomach has no absorption function, so there will be no change in blood glucose when the food is in the stomach; after about 15-20 minutes, the food in the stomach which has been ground to be minced is discharged into the small intestine, and the small intestine is the most important organ for absorbing nutrients, and the blood glucose starts to rise rapidly with the entrance of the food, and the peak of the absorption usually occurs in the 30-60 minutes after a meal. The peak of absorption usually occurs 30-60 minutes after the meal, at which time the magnitude of blood glucose elevation will reach the highest value; thereafter, more and more less food is discharged into the small intestine, the magnitude of blood glucose elevation will fall back to 2 hours after the meal, the vast majority of the food has passed through the small intestine, the nutrients basically absorbed, and there is almost no exogenous glucose reentering the bloodstream.
Based on this pattern of change in blood glucose after a human meal, medical science has chosen points in time when the vast majority of people are in the same state to test their blood glucose, respectively:

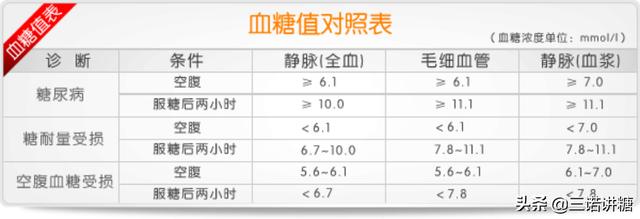
- Fasting blood glucose This is blood glucose measured 8-12 hours after a meal, during which time you should not eat any food except for a small amount of water.
- 2-hour postprandial blood glucose This is blood glucose that is measured 2 hours after the first bite of a meal.
- Mealtime blood glucose, i.e., blood glucose measured at any point within 2 hours of eating a meal.
At the same time, it also gives the standard of normal blood glucose at these three points in time, that is, fasting blood glucose 3.9-6.1 mmol/L and 2-hour postprandial blood glucose 4.4-7.8 mmol/L, and the maximum of meal-time blood glucose does not exceed 9.4 mmol/L. Note that these three standards should be reached at the same time in order to be called normal blood glucose.
Obviously, when the blood glucose exceeds the above normal value is elevated, but not as long as the elevation is diabetes, in the normal blood glucose and diabetes there is an interval is known as pre-diabetes, its blood glucose range is: fasting blood glucose 6.1-7.0 mmol / L or (and) 2 hours after the meal 7.8-11.1 mmol / L, and as long as the blood glucose of the two points of time have a blood glucose is in this range Prediabetes is defined as pre-diabetes.
Diabetes is diagnosed if blood glucose continues to rise beyond the upper limit of pre-diabetes, and the diagnostic criteria are: fasting blood glucose greater than 7.0 mmol/L or (and) 2-hour postprandial blood glucose greater than 11.1 mmol/L or meal-time blood glucose greater than 11.1 mmol/L.

In summary, to determine if your blood sugar is high? How high? It is important to know at what time the test was taken, and there are different criteria for judging blood glucose at different points in time. For example, this friend asked whether the blood glucose is very high at 13:00, if the result is detected during fasting, it is nearly two times higher than the upper limit of normal value, suggesting that the postprandial blood glucose may be even higher; if it is measured during meals, compared to the requirement of not higher than 9.4mmol/L, the magnitude of the high is not very much; if it is detected 2 hours after the meal, it has just exceeded the diagnostic standard of diabetes mellitus of 11.1mmol/L. The diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus are 11.1 mmol/L.
In conclusion, blood glucose testing should measure meaningful blood glucose, which is not only the need for monitoring blood glucose, but also the basis for judging the degree of blood glucose abnormality and formulating interventional treatment measures. Do you know how to measure blood glucose in the future?
I hope this answer can help you, welcome to click on the attention and leave a message, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge.
Dietitian Sugar is here to answer your questions. Blood glucose 13 points is relatively high, both fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose, it is over the standard. If the fasting blood glucose value has reached 13, proving that the condition is very poor at this stage, the patient has a higher risk of acute complications, and need to take timely interventions, can not be indulged.
We have encountered many similar questions, and we often have sugar lovers come to us and ask, "Is my blood sugar 20 high, can I not take medication?Many diabetics have no concept of blood sugar when they are first diagnosed, and always feel that they are not in pain, so their body should be fine.It is wrong to think this way. Because the erosion of high blood sugar on the body is chronic, a short period of time is not likely to make people have obvious discomfort, only after the long-term development of various organs of the body will appear lesions, and at this time many people are too late to regret.
Sugar lovers need to remember a few blood glucose values, first of all, normal people fasting blood glucose <6.1, 2 hours after the meal <7.8, if the control is strict, it can be completely according to the standard of normal people to control. The general blood glucose requirements for diabetic patients is fasting <7.0, meal two <10.0. If the disease course is longer and older, the control range can be relaxed to fasting <9.0, meal two <11.1. If the patient has a tendency to hypoglycemia, combined with serious cardiovascular disease, tumors, and life expectancy of the shorter people, but also can be relaxed a little more, the fasting control of 10.0 or less, meal control of 13.0 or less. In short, different people have different standards of blood glucose control, and detailed standards should be consulted with the doctor.
I hope Sugar's answer can help friends, more diabetes encyclopedic knowledge we continue to share in the next issue!
The blood glucose range for non-diabetic patients is 4.4-6.1 mmol/L. The range for diabetic patients is slightly more complex, and the standardization of blood glucose control is based on a variety of factors, including the duration of the patient's disease, age, complications, comorbidities, and life expectancy. Distinguishing between different conditions, a target range of blood glucose control of 3.3-10 mmol/L is possible.
Fasting blood sugar:
From the above statement, if the fasting blood glucose is 13.0 mmol/L, then it is very high, this blood glucose situation, the patient will have metabolic disorders, because it can not use the glucose in the blood to function for the body, it will consume the body's proteins and fats to function for the body, and this process produces ketone bodies, and the patient will have the symptom of acidity and weakness, and if there is an acidosis, there will be nausea, Vomiting, leading to further dehydration is evident and the patient may then become unconscious and comatose.
Long-term chronic elevation of blood glucose, the patient's fasting blood glucose at 13mmol/L, may not feel anything, but the patient will gradually lose weight. Due to the long-term elevation of glycosylated hemoglobin, the protein synthesis of the organs of the body is impaired, and various chronic complications will occur, such as lesions of the eyes, kidneys, nerves, blood vessels, etc., and the process of this lesion is irreversible.
Therefore, if you find a fasting blood sugar of 13 mmol/L, you should go to the hospital as soon as possible for examination and treatment, and the doctor will give a glucose-lowering program to correct the metabolic abnormality in the body, improve the symptoms, and slow down the progress of complications.
Postprandial blood sugar:
If blood glucose 13 is postprandial, then this blood glucose is also at a relatively high level, and for people with advanced tumors, various severe complications, and psychiatric disorders where glycemic control targets are particularly lax, target postprandial blood glucose is recommended to be controlled at less than 12 mmol/L. So it also needs to be well controlled.
If the patient's fasting blood glucose is basically normal, but the postprandial blood glucose is high, it is considered to be caused by the unreasonable amount and type of diet, such as consuming sugary food, thin paste-like food, fruits with large sugar content, etc., so it is necessary to adjust the diet properly. If the adjustment of diet still can not reduce blood sugar, can be combined with drugs such as acarbose, metformin, dagliflozin or short-acting insulin to treat.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Blood glucose mainly refers to our venous blood sugar, is the supply of human energy and maintain the normal physiological metabolism of the body must be substances, blood glucose levels are affected by a variety of factors, when various causes of blood glucose levels rise above the normal range, that is, hyperglycemia, and when the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus reaches the standard, that is, we need to actively standardize the treatment, so as to avoid the occurrence of a variety of complications.

Normally, our fasting blood glucose level is between 3.9mmol/L and 6.1mmol/L, and our two-hour postprandial blood glucose is between 4.4mmol/L and 7.8mmol/L. Hyperglycemia should be considered when our fasting blood glucose exceeds 6.1mmol/L and our two-hour postprandial blood glucose exceeds 7.8mmol/L, and diabetes should be considered when our fasting blood glucose exceeds 7.0mmol/L and/or or two-hour postprandial blood glucose exceeds 11.1mmol/L, it should be considered as diabetes.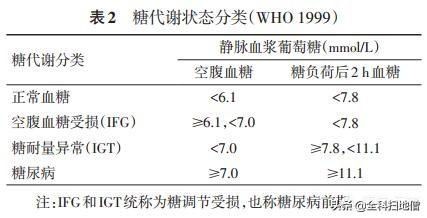
Therefore, for the subject's current blood glucose level of 13mmol/L, whether fasting or postprandial, has exceeded the normal range, and reached the diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus, need to pay enough attention, we are advised to actively seek medical treatment, pay attention to monitoring changes in blood glucose levels, and if necessary, can improve the glucose tolerance test or glycated hemoglobin test to clarify the diagnosis. Diabetes mellitus should be diagnosed if our fasting blood glucose ≥7.0mmol/L and/or two-hour postprandial blood glucose ≥11.1mmol/L and/or random blood glucose ≥11.1mmol/L are measured twice on non-simultaneous days, and diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed as long as one of the above criteria is met if the typical symptoms of diabetes mellitus such as polyphagia, polyphagia, polydipsia, and lethargy are present.
Once diagnosed, diabetes should follow the guidance of professional doctors, standardized treatment, in daily life should pay attention to: ① Reasonable diet, strict control of the total daily calories, three meals should be timed, eat more fresh vegetables; ② Appropriate exercise, mainly aerobic exercise, gradual, avoid strenuous exercise; ③ Weight control, obese (including abdominal obesity) should pay attention to weight loss; ④ Restriction of alcohol consumption, do not drink is best, it is difficult to give up alcohol need to strictly limit the amount and frequency; ⑤ Regular medication, medication should be individualized, if necessary, the use of insulin replacement therapy; ⑥ Monitoring blood glucose levels and regular review. Those who have difficulty in quitting alcohol need to strictly limit the amount and frequency; ⑤ regular medication, medication should be individualized, and insulin replacement therapy can be used if necessary; ⑥ monitoring changes in blood glucose level and regular review.
Overall, blood glucose 13mmol / L has reached the diagnostic criteria for diabetes, belonging to the higher level of blood glucose, need to pay attention to, and attention to medical consultation, clear diagnosis, and make targeted disposition.
This article is answered by General Practice Sweeper, we hope that it will be helpful to you, copyright ©️, reproduced with permission. Please correct any deficiencies. The article is for reference only and is not intended as medical advice or medical guidance.
The purpose of monitoring blood glucose is to detect diabetes at an early stage in order to give reasonable glucose-lowering treatment, reduce the occurrence of acute complications of diabetes such as diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, and delay the emergence of diabetic nephropathy, cardio-cerebral and cerebral vascular diseases and other chronic complications of diabetes. So, is blood glucose 13mmol/L high? Next, Medical Xin will analyze it for you.
Blood glucose measurements taken at different times of the day can be high or low. Under normal circumstances, blood glucose 1 hour after meal is high, blood glucose 2 hours after meal will gradually drop to 4.4-7.8mmol / L, fasting 8 hours or more blood glucose will drop to 3.9-6.1mmol / L, so blood glucose 13mmol / L has exceeded the normal range. So, can blood sugar 13mmol/L diagnose diabetes? The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is mainly based on the values of fasting blood glucose, blood glucose after 2 hours of glycemic load, random blood glucose, as well as the diagnosis of diabetes mellitus symptoms. If there are typical symptoms of diabetes such as polyuria, polydipsia, polyphagia and weight loss, fasting blood glucose reaches 7.0mmol/L and above, blood glucose after 2 hours of glycemic load reaches 11.1mmol/L and above, random blood glucose reaches 11.1mmol/L and above, and any of them can be diagnosed as diabetes; when there is no typical symptom of diabetes, if the blood glucose measured in the next day still reaches the above values, it should also be diagnosed as diabetes. In the absence of typical symptoms of diabetes, if the blood glucose measured on the next day still reaches the above values, diabetes should also be diagnosed. Therefore, blood glucose 13mmol/L is more likely to be considered as diabetes. Some of you may ask: Is blood glucose 13mmol/L serious? Any time of blood glucose abnormality, will damage the cardiovascular, cerebrovascular, renal, nerve, retinal and other target organs, the greater the magnitude of blood glucose elevation, the longer the duration of the disease, the more serious the damage to the target organs, if 13mmol / L for fasting blood glucose, more serious, need to give timely hypoglycemic treatment to reduce the toxicity of high glucose, to avoid further damage to the tissues of the insulin-secreting tissues; If 13mmol / L for two hours after the meal If 13mmol/L is 2 hours postprandial blood glucose, reasonable hypoglycemic therapy should also be given to reduce target organ damage and reduce the risk of complications.
In terms of treatment, 13 mmol/L either fasting blood glucose, or 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, should change the lifestyle, reduce the total daily dietary calories, control the intake of rice, noodles, steamed bread and other carbohydrate-rich foods, and appropriately increase the intake of coarse grains, dietary fiber-rich foods, dietary fiber has a satiating, delayed postprandial glucose elevation, quit smoking and limit alcohol, and adhere to the exercise for half an hour a day, and Reduce weight. In drug selection, if 13mmok/L is fasting blood glucose, insulin should be started as soon as possible to lower glucose; if it is 2 hours postprandial blood glucose, you can choose the drugs that inhibit carbohydrate absorption such as acarbose, miglitol, etc., and you can also choose to promote insulin secretion of drugs such as glargine, short-acting sulfonylureas, etc. Because metformin is the first choice of drug for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, patients with postprandial glucose elevation can also Metformin is the first choice for the treatment of type 2 diabetes, so patients with elevated postprandial blood glucose can also choose metformin to lower their blood glucose, starting treatment with 500mg per day and gradually increasing the dosage to 2000mg per day. So, what is the appropriate level of blood glucose control? Generally speaking, fasting blood glucose control at 7.0mmol/L or less is more appropriate, young people can strictly control the pointer, the elderly can appropriately relax the pointer, and the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose control at 10mmol/L or less is more appropriate.
In summary, blood glucose 13 mmol/L has exceeded the normal range, diabetes mellitus should be considered possible, if the fasting blood glucose, belongs to the higher level, insulin glucose lowering should be initiated in order to reduce the toxicity of high glucose, if it is the blood glucose of the 2 hours after meal, also should be reasonable lowering of glucose, to mitigate the damage to the target organs, reduce the risk of diabetic complications.
Thank you all for reading!
Hi, a blood sugar of 13 points is high.
If you have not been diagnosed with diabetes and your fasting blood glucose is 13 on a venous blood draw, then diabetes is very likely, and a normal person's fasting blood glucose is not that high. It is recommended that you do a regular glucose tolerance, and in addition check your fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar, and glycated hemoglobin.
You may wish to compare the table below to see that fasting blood glucose measured by venous blood sampling is out of the normal range when it exceeds 6.1, and generally does not exceed 10 two hours after a meal.
If you are already a diabetic, no matter what you measure is fasting blood glucose or postprandial blood glucose, blood glucose 13 is very high, if it is occasional high blood glucose, pay attention to controlling the diet, adhere to the exercise generally can still be lowered.
However, if long-term high blood sugar, and oral hypoglycemic drugs, adhere to diet therapy exercise therapy, blood sugar control is not good, you must promptly go to the hospital for examination, so as not to delay the condition.
High bar fasting in the present living conditions below 8 o'clock can be
Depends on whether it's before or after a meal, but it's pretty high before or after a meal, so watch what you eat, keep your mouth shut, and exercise in moderation.
This depends on whether you are fasting blood sugar or one hour after meal, two hours of blood sugar value. But no matter which is high, this value is not very high but is already a disease state, so you need to symptomatic examination and treatment, regulation, otherwise all kinds of diseases will come as promised. Fasting blood glucose value is between three point nine and five point seven, as long as it reaches six point one is diabetes, one hour after meal don't exceed ten point eight, we will say eleven, two hours after meal don't exceed seven point eight, we will say eight, so you this no matter which is

Fasting, one hour after a meal, two hours, are high, blood sugar is a physiological indicator of changes with diet. That is, one hour after eating to reach a peak value of no more than ten point eight, two hours at the peak is down, no more than seven point eight, so your thirteen points more than all the normal value of the indicators, you need to symptomatic examination and treatment, from diet, exercise, exercise, and medication for treatment and conditioning, because diabetes is a chronic disease.

Early development gives people the feeling of slow, no obvious discomfort, so will be ignored, later complications of various kinds of serious, is very serious, so early detection should be early treatment from the life of the diet, life avoidance, exercise exercise, medication, and other aspects of regulation and treatment to reduce complications and slow down the arrival of the disease, to prevent the disease from further development. Thirteen as a value is not too high but has been comprehensively missing, the normal value is like a flat top can be put on the round ball, and the value of the exceeding standard is slanting on the top can not be put on the round ball, the health will roll down can not be stabilized, will continue to accelerate the fall.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.