What is the connection between diabetes and the fundus?
Some patients don't understand that
Dr. Sun, I just have high blood sugar, why am I blind?
This is often said that high blood sugar is not scary, the scary thing is complications ah! Can't see because of diabetes eye complications are serious ah!
Many people with diabetes come to the doctor with abnormal eye sight, both new diabetics and those who have had the disease for many years.
The first common symptom is blurred vision, and blurred vision is also a common symptom of prolonged and severe disease.
At the onset of diabetes, many of the main complaints are blurred vision. This is because the atrial fluid (a fluid in the eye) contains the same concentration of glucose as the blood. Thus, as blood sugar increases, so does the glucose in the aqueous humor. This simply means that you will definitely not see the same thing through sugar water as you do through water. After the blood sugar drops, many people feel like they can see much more clearly for this reason.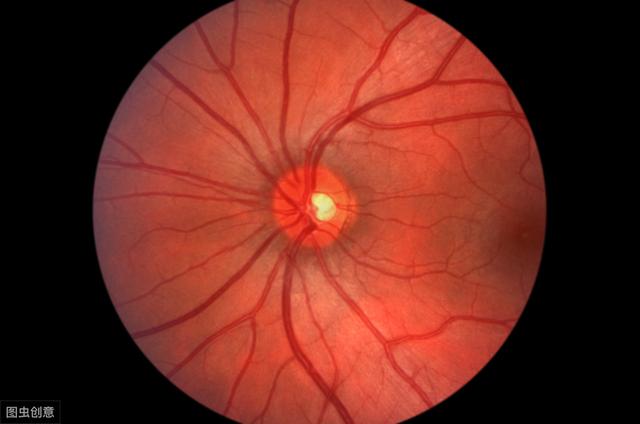
And later, as the disease prolongs and the blood sugar is poorly controlled for a long period of time, not only will you see things blurry again, but your vision will gradually decline. That is, diabetes causes lesions of the fundus, mostly the retina.
Retinopathy is the most common microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus
Clinically, retinopathy is the most common microvascular complication of diabetes mellitus. According to epidemiologic data, the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in the known diabetic population is 24-37%, and in the newly diagnosed diabetic population the prevalence of retinopathy is 3-13%. It is clear that the population with diabetes combined with eye disease is still quite large.
Diabetic retinopathy occurs as a result of a combination of many factors, such as increased retinal polyol pathway activity due to high blood glucose, non-enzymatic glycosylation of proteins, metabolic disorders of capillary wall cells, oxidation of free radicals, disorders of the coagulation-fibrinolytic system, an increase in pro-neovascular growth factors, and abnormalities of the local RAS system, on a hereditary basis.
Diabetes also causes increased intraocular pressure, open-angle glaucoma, and retinal arterial and venous occlusion, which are also more common in diabetics.
That is why it is important to perform regular fundus examinations in diabetic patients, which are now mostly performed with direct fundoscopy and, if necessary, fundus fluorography.
These lesions are often found in the fundus of the eye
These lesions are often found in the fundus with these tests:
microangioma
Small, reddish intraretinal lesions are seen at the posterior pole of the eye's retina, around the optic disk and macula. They occur primarily in areas of capillary nonperfusion, and microangiomas on fundus fluorescence angiography appear as fluorescein leakage. The more microangiomas there are, the greater the risk of progression to proliferative retinopathy. Microangiomas themselves do not diminish vision, but if the lesion is in the macula, even very small lesions can significantly affect vision.
rigid exudate
Hard exudates are waxy yellow spots or plaques formed by oozing plasma proteins, similar to microangiomas, which also occur early in retinopathy and usually do not affect vision unless they occur in the macular area.
retinal hemorrhage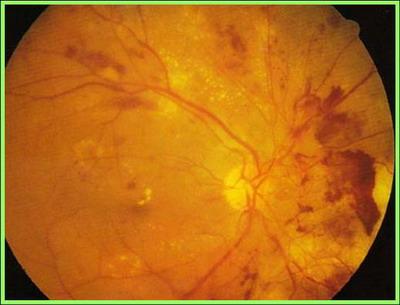
Retinal hemorrhages are caused by rupture of capillaries deep in the retina, which is deeper than the location of the capillaries that cause microangiomas. It manifests as hemorrhagic spots, flame-like hemorrhages in the nerve fiber layer of the retina, deep hemorrhages with irregular shapes, and large, black clusters of hemorrhages.
cotton wool spot
Cotton wool spots are often accompanied by pre-proliferative retinopathy, and when the number of lesions exceeds five, it suggests rapid progression of retinopathy.
Retinal neovascularization
Retinal neovascularization includes neovascularization of the retina and optic disc originating from venous vessels. Proliferative retinopathy usually results from growth factors released from the ischemic retina. The proliferating vessels are located in front of the retina, and between the retina and the posterior vitreous, so the pits can lead to pre-retinal or vitreous hemorrhage. Proliferative retina is more common in both type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes.
macular degeneration
Macular degeneration occurs in the retina at or near the central concave. It is clinically common. approximately 10% of the VADT study population had macular degeneration. Impaired vision usually results from macular edema and ischemia. Neither can be diagnosed by direct fundoscopy. Optical correlation tomography is currently the most important technique for assessing and monitoring macular edema. Macular ischemia can be definitively diagnosed by fluorescence angiography.
Severe diabetic eye disease is defined as vision loss due to proliferative retinopathy or macular degeneration.
Retinal blood vessel tear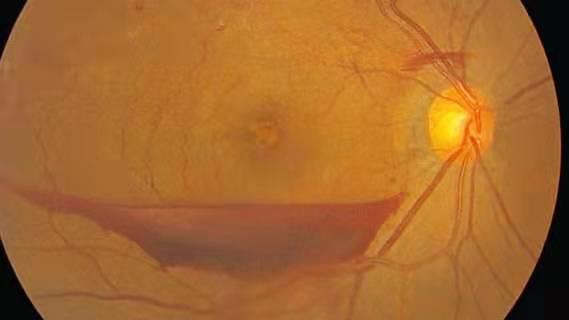
Retinal ischemia, common to all types of severe retinopathy, induces a vascular fibrotic response. The fibrous tissue in turn induces a traction effect, meaning retinal vascular avulsion, retinal detachment, and iris neovascularization.
Retinal vascular tears can lead to hemorrhages, including preretinal hemorrhages, which obscure the macula and may manifest as acute vision loss. Hemorrhages in other areas may present only as "floaters".
vitreous hemorrhage
Vitreous hemorrhages are usually large and result in acute vision loss. Spontaneous absorption of the hemorrhage and improvement of vision usually takes several months, and there is a risk of rebleeding.
Treatment of diabetic retinopathy
The main treatment for the appearance of the above lesions is laser photocoagulation. Laser treatment can reduce the incidence of severe vision loss by about 50%, but it is a destructive treatment, so patients need to understand that this treatment only stabilizes, not improves, vision. It usually requires 2,000 or more retinal burns per eye (how scary it is to think about), usually in 4 quadrants, and it takes 4 sessions to complete to achieve good results. And there are strict requirements for the condition of the patient and the skill of the doctor.
Some drugs are now gradually applied in clinic. Ranibizumab is a neovascularization inhibiting drug, which can be injected through the vitreous cavity to inhibit the growth of intraocular neovascularization, and it is mainly used in wet macular degeneration, retinal vasoproliferative lesions and other conditions. It can improve patients' symptoms and maintain vision, but it is more expensive and requires a certain level of skill.
How to slow or avoid diabetic retinopathy
The scary thing is that the loss of vision occurs gradually, like boiling a frog in warm water, and by the time you feel the loss of vision, it may be irretrievable. Moreover, when diabetic eye disease develops to a certain extent, it will get out of the diabetic trajectory and develop towards serious eye disease on its own. That is, a drop in blood sugar to a plateau won't undo the consequences of severe vision loss.
Diabetic eye disease experience instrument should be a kind of wake-up call for patients to educate the better. Experiencing blurriness when vision is still good, a very simple or very rudimentary instrument, speaks volumes, and I wonder if diabetics will then be able to control their blood sugar carefully without letting themselves gradually slide into a world of darkness?
Proliferative retinal changes in patients with type 2 diabetes are associated with severe coronary artery disease. Screening for heart disease in these patients is therefore required, as well as a high level of comprehensive diabetes management.
Thus patients with diabetes alone do not present to the diabetes clinic with many ophthalmologic complications, many patients present to the ophthalmology clinic with vision loss, and those who do present to the ophthalmology clinic have a higher prevalence of microvascular and macrovascular complications and are more likely to be smokers.
The DCCT study confirms that blood glucose is the most significant, and possibly the only, contributing factor to early retinopathy in type 1 diabetes, whereas for type 2 diabetic retinopathy, comprehensive multifactorial management is essential.
The DCCT study showed that glycated hemoglobin control at 7% slowed the rate of progression of background retinopathy, and the same result was obtained in the intensive intervention group of patients with type 2 diabetes in the UKPDS study. Clinical outcomes can be reduced in patients with type 2 diabetes with only mild to moderate retinopathy, but when progression to proliferative retinopathy is achieved, even good blood glucose is unlikely to produce a slowing of progression.
The ACCORD Eye study shows that for all diabetics, especially those with type 1 diabetes, it is essential to stop smoking, as smoking is severely associated with proliferative changes and impaired vision.
To summarize:
Diabetes and retinopathy are closely related, almost all diabetic patients have retinopathy 10 years after the onset of the disease, effective measures should be taken at an early stage to stabilize blood glucose, diabetic patients should quit smoking, an annual examination of the fundus for early detection and early treatment, the emergence of background retinopathy should be carried out as soon as possible to the photocoagulation of the laser treatment for the protective treatment of vision. When the eye disease develops to the proliferative stage lesion, when the vision loss is obvious, there are almost no effective drugs and treatment means.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Hi, lesions in the eyes are one of the most serious complications of diabetes, so it is important to make sure that if you have diabetes, you have your vision checked regularly every year.
What happens to the fundus of the eye
Diabetic retinopathy affects different people in different ways.
For example:cataracts, glaucoma, eye movement disorders.

And the longer a person has diabetes, the greater the chance that they will develop retinopathy.
Because diabetes causes damage to the walls of retinal capillaries, the blood can become hypercoagulable, resulting in thrombosis and hemosiderosis, or even blood vessel rupture.
take precautions against
The disease is a consequence of diabetic microangiopathy, which is characterized by damage to the retinal capillary walls due to diabetes, coupled with hypercoagulability of the blood, which predisposes to thrombosis and hemosiderosis, and even vascular rupture.

Also take care to have yearly checkups, and the sooner you intervene in the event of fundus lesions, the better.
Diabetes has become a serious problem that jeopardizes human health globally, changes in people's living standards and lifestyles, heredity and some unspecified reasons have become the cause of the high incidence of diabetes, listening to diabetes and the fundus seems to have nothing to do with it, in fact, most of the diabetic patients in the later stages of the systemic small-vessel pathology, and retinopathy is one of the most serious complications of microvascular disease Retinopathy is one of the most serious complications of microvascular disease.
Retinopathy is caused by long-term chronic hyperglycemia, the initial vision can not be affected, no feeling, with the development of the disease, can cause different degrees of vision loss, visual deformation, etc., if the lesion to the proliferation of the stage can be neovascular hemorrhage to the vitreous body and even blindness.
Hello, as we all know, the terrible thing about diabetes is not in the diabetes itself, but in its complications. Long-term high blood sugar in diabetic patients will cause damage to the heart, brain, kidneys, nervous system, feet, eyes and so on, among which diabetes damage to the fundus of the eye is another common and frequent complication.
Diabetic fundopathy is related to the duration of the disease and the degree of control. Diabetes can cause lesions in the conjunctiva, lens, retina, nerves and other parts of the eye, the most common of which is diabetic retinopathy, which often results in blurred vision, reduced visual acuity, and in severe cases, blindness. According to statistics, 50% of diabetic patients who have been suffering from the disease for about 10 years will develop this lesion, and the incidence of patients who have been suffering from the disease for more than 15 years will reach 80%.

Diabetic fundopathy is divided into six phases, the symptoms of the first three phases are often mild, and active intervention and treatment in the first three phases can prevent the further deterioration of the eye disease to a certain extent. However, the symptoms of the first three phases are relatively not very obvious, and some of them may not even show any symptoms, and if they are not detected in time, there may be the risk of fundus hemorrhage or even blindness.
Therefore, diabetic patients should pay attention to go to the hospital regularly to check their eyes. The treatment of eye diseases should be based on different periods of medication, laser or surgical treatment, and the earlier the treatment, the better the recovery will be.
In addition to remind the patient, in daily life should pay attention to do a good job of prevention, the first is to control the blood sugar, which is to reduce the premise of complications, especially diabetes with high blood pressure, high blood fat patients, and secondly, pay attention to eye hygiene, avoid overuse of the eyes, pay attention to eye protection, eat some bright food, etc., and go to the hospital on a regular basis for medical checkups.
I hope you find it helpful.
Diabetes is known abroad as "The Silent Killer", meaning that diabetes, which is not dangerous in itself, can lead to a variety of complications that can kill and maim because of the state of hyperglycemia, and diabetic complications often develop slowly without the person realizing it; it can take years to develop complications, but once they have developed, they are difficult to deal with and reverse.
The hyperglycemic state first affects a person's macrovessels and microvessels, and the inside of a person's eyes and kidneys are filled with microvessels and capillaries. From appearance to threatening force, diabetic eye lesions are a gradual process over a relatively long period of time. At the very beginning of ocular lesions, because the capillaries are blocked by excess sugar, gradually in thefundus of the eye (containing the choroid, retina, optic nerve etc)This location will appear similar to such as blood spots, microaneurysms, hard oozing, etc. With the development of time, patients gradually develop blurred vision, mosquito, and other perceptible symptoms. Ocular lesions appear in the early stage, if the patient does not pay attention to it, and does not improve blood sugar in time, symptomatic treatment, then it will eventually develop into irreversible ocular lesions, and the final result is, blindness.
As can be seen from the above, ocular pathology is a long process and some symptoms are first seen in thefundus of the eye (containing the choroid, retina, optic nerve etc)appears, but it is invisible to the human eye and difficult to be perceived by the patients themselves, which requires them to go to the hospital for regular checkupsfundus of the eye (containing the choroid, retina, optic nerve etc)Are there signs of lesions. It is important to note that diabetic eye lesions are in the pre-diabetic stage, it is controllable and reversible, and the vast majority of patients can improve or even reverse their condition with treatment.
Here are the most common eye lesions in diabetics: retinopathy
Retinal blurring may be what we call diabetic retinopathy, so there is no specialized ophthalmology to look at the fundus of such a result, because diabetic patients are generally older, many people have more eye problems, some of which are associated with diabetes, that is to say, there is no diabetes will also get.
For example, cataracts: older people without diabetes can get them. For example, vision presbyopia, you don't have diabetes, old age can also presbyopia, and glaucoma, which are non-diabetic can get, so, not diabetes specific complications, only diabetes fundus retinal microangiomas or microangiomas after spreading we call the fundus hemorrhage, this is diabetes retina specific complications, that is to say, only diabetes only can get the disease. So I understand that he asked this, then we must look at the fundus to see if there is a retinal microangioma, if there is a microangioma should take some medication accordingly, and then in the exercise to prevent the increase in intraocular pressure, the tumor ah, the pressure will bleed. So generally speaking, the old saying that diabetic patients should regularly go to the ophthalmology department to look at the fundus, especially if you have symptoms, already blurred, more to go to see, is not it.
Diabetes is very easy to lead to eye type of disease, in the hospital 60% of blind people are related to high blood sugar concentration, let's take a look at the eye disease caused by diabetes, divided into three kinds of conditions, the first kind of it, known as glaucoma, the onset of the attack, let's say that it has the two most obvious characteristics, the first one, it is seven or eight o'clock in the evening, go to the street lamp, you will see that the street lamp, it is no longer a bulb, it has a halo around it like a rainbow, known as the rainbow circle. Or look 50 meters away from the place of the building windows and doors and windows, found that the line is not vertical, but twisted, this is the manifestation of glaucoma, that the second case is more, diabetes-induced cataracts, that is, as if a layer of hairy glass in the world, vision is very blurred, the beginning of the time it feels as if mosquitoes in front of the eyes in the fly, but with the hand to drive away the time to find that there is no mosquitoes, this is called flying mosquitoes, this is called the mosquito. Mosquitoes, this is called flying mosquitoes, or see the light tears, etc., then the future of a long time, it will be easy to lead to cataracts, there is a kind of it, called retinopathy, retinopathy has a non-proliferative type, this is not easy to cause blindness, there is also a proliferative type, is more likely to cause blindness, so it is recommended that sugar friends to do fundus test regularly!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.