How do you determine the severity of your condition when you have had diabetes for many years?
From the point of view of the purpose of treatment, lowering blood glucose focuses on reducing diabetes symptoms and preventing acute complications in the near term, and on reducing islet cell damage and reducing chronic complications in the long term. Therefore, diabetic patients who have been ill for many years and have not achieved the above objectives indicate that their condition is relatively poorly controlled.
Whether diabetes symptoms are in remission
For most people with diabetes, the early stages of the disease are characterized by small increases in blood glucose and unremarkable symptoms. As the disease progresses, blood glucose rises gradually, and increased urination, increased water intake, increased eating, and weight loss may occur. Symptoms may be mild or severe in different patients, and some patients may even be asymptomatic. In addition to these symptoms, some patients may experience fatigue and weakness due to impaired utilization of blood glucose and insufficient energy supply; some women may experience itching due to irritation of the vaginal skin caused by urinary glucose. After reasonable glucose-lowering treatment, these symptoms will be gradually relieved. If the glucose lowering program is not reasonable, blood sugar control is not up to standard, even after years of illness, these symptoms can still reappear, especially when there is unexplained weight loss, after excluding other factors such as tumors, hyperthyroidism, anxiety, malnutrition, etc., it means that the current blood glucose control is not good, the disease control is not optimistic, and more need to use insulin to control blood glucose.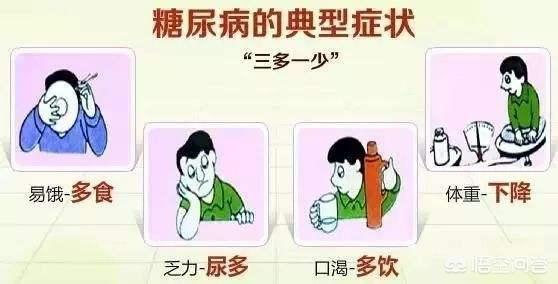
Whether acute complications occur
Acute complications of diabetes mellitus mainly include diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, the occurrence of which is related to the level of blood glucose. Diabetic ketoacidosis may occur when blood glucose reaches 16.7 mmol/L, and hyperosmolar hyperglycemia may occur when blood glucose reaches 33.3 mmol/L. The former is mainly manifested by acidosis, which may be characterized by deep and loud breathing, and the exhaled gas may have the smell of rotten apples; and the latter is mainly manifested by severe dehydration, and the amount of water lost may be as high as 15% of body weight. The occurrence of acute complications is related to infections, severe vomiting or diarrhea, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accidents and other triggers, but the main mechanism of the onset of the disease is still insulin deficiency, indicating that the current pancreatic islet cell damage is more serious, and not able to secrete enough insulin to lower the blood glucose, the condition is not optimistic. As diabetes is a progressive disease, with the prolongation of time, the difficulty of lowering glucose will increase, and the glucose-lowering program needs to be adjusted appropriately, so the irrationality of the treatment program is also the main reason for the development of acute complications.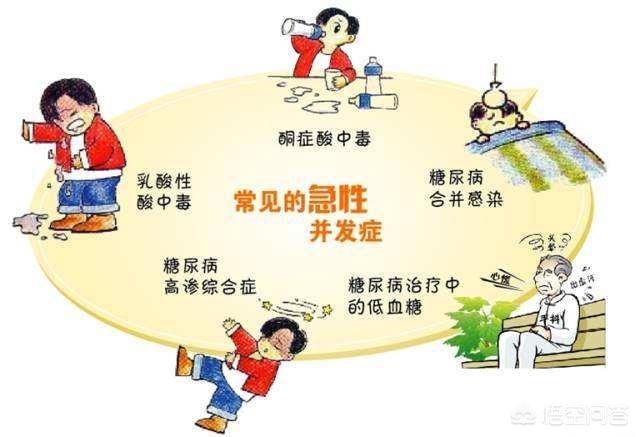
Whether chronic complications occur
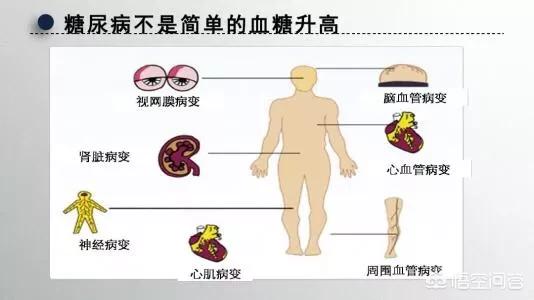
The target organs damaged by diabetes mellitus are cardiovascular, kidney, retina and nerve. Damage to cardiovascular, can be manifested as heart failure or myocardial infarction, etc. If there is heart fatigue and dyspnea after exercise, it means that the heart function has been impaired and the condition is more serious; if there is pain in the anterior region of the heart after exercise or emotional excitement, it means that the coronary stenosis is more serious, the risk of myocardial infarction is higher, and the condition is serious. Damage to cerebrovascular, diabetes disease duration of more than 5 years, the chance of occurrence of cerebral atherosclerosis is up to 70%, there may be headache, inattention, insomnia and other symptoms of neurasthenia, but also memory loss, impaired calculation and other symptoms of dementia, but the most serious for cerebral infarction. Kidney damage may present with foamy urine, elevated creatinine on renal function tests, and proteinuria on routine urinalysis. Retinal damage can be characterized by decreased visual acuity, flashing sensations, and in severe cases, blindness. Nerve damage may present with burning pain or numbness in the feet.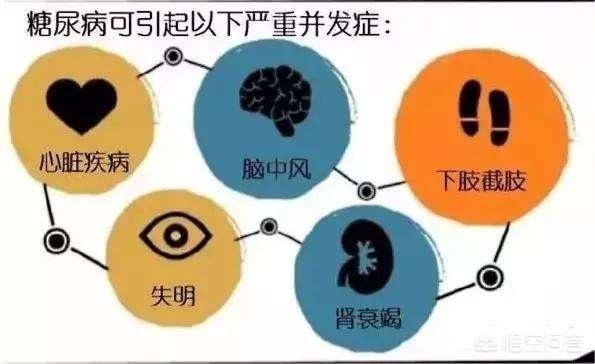
Whether it is the symptoms of diabetes, or acute and chronic complications, controlling blood glucose in the target range through rational glucose-lowering treatment can improve the symptoms and reduce the risk of complications, and can reduce the severity of the disease. Glycated hemoglobin below 7.0% is the glycemic target for diabetic patients, which can significantly reduce the risk of chronic complications. Some patients may ask: Why not control glycated hemoglobin below 6.0%? If the glycated hemoglobin is controlled below 6.0%, the damage to target organs can be further reduced, but compared with the reduction from 9.0% to 8.0% or from 8.0% to 7.0%, the magnitude of the benefit will gradually decrease; more importantly, the glycemic target is too strict, some patients may experience hypoglycemia, and the magnitude of the fluctuation of blood glucose is too large, which will still increase the risk of the occurrence of chronic complications. Of course, patients who can tolerate can control glycated hemoglobin with stricter indicators. Patients who have been ill for many years, when adjusting the treatment plan, glucose lowering follow the principle of lifestyle intervention - oral hypoglycemic drugs (1-3 kinds, according to the blood glucose control situation in order to increase) - insulin adjustment, when the oral hypoglycemic drugs increased to three kinds of drugs, the treatment of 3-6 months still can not control blood glucose up to the standard, should be initiated as early as possible to lower blood glucose with insulin, not only to delay the occurrence of chronic complications, but also reduce the damage to pancreatic islet cells.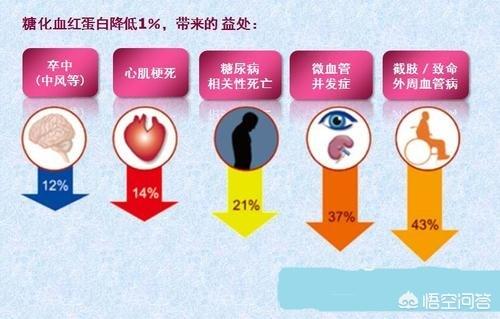
In summary, diabetic symptoms that have not been relieved, recurrent acute complications, or chronic complications that have developed indicate that the current condition is not optimistic. By adjusting the treatment plan, such as increasing the type of oral hypoglycemic drugs and replacing them with insulin to lower blood glucose, and controlling the glycosylated hemoglobin below 7.0%, the diabetes symptoms can be alleviated, the occurrence of acute complications can be prevented, the occurrence of chronic complications can be reduced or delayed, and it is conducive to the alleviation of the condition and the avoidance of exacerbation.
Thank you all for reading!
Please correct me if I'm wrong! Feel free to ask and share in the comments section!
Note: The content of the text is intended to be used as health science only, and is not intended as medical advice or opinion, and does not qualify as medical guidance.
This year 70 years old 35 years history of diabetes, did not take the control of blood glucose value seriously, so far did not do a glycation test, even can not say the name of the program. Feel that diabetes has little effect on the body, and even less to appreciate the diabetes process light and heavy.
Accidentally found diabetes in 86 years, when the preprandial blood glucose 22, in a small unit as a legal person, busy work has not been taken seriously, after more than 20 years, the weight gradually from 170 pounds down to 130 pounds, only so that there is no other disease, last year, check the liver, kidneys, blood lipid function indicators are normal.
My view on diabetes light and heavy is that it is important to maintain a normal weight, especially in the elderly, and with a normal weight, the organs are guaranteed nutrition. I sometimes take hypoglycemic drugs, eat the purpose is to maintain the current weight. To eat proper meat, it is essential to keep yourself hungry and healthy.
At the age of 70, people talk about death, but I have endless energy all day long, the same physical life as when I was 50 years old, walking 10 kilometers a day is the norm, the heart does not panic and do not gasp, and sleep through the night. I always feel that diabetes has been with me for 35 years, and I still can't see the end of the time between deaths. The severity of the diabetes process has little to do with the duration of the disease.
If you have diabetes and high blood fat, the danger is approaching, high blood fat is far more than the danger of diabetes, high blood fat will create a shocking thing, will let a person divided into seconds of yin and yang.
I have a friend with high lipids, the strange thing is that he knew hard that he wouldn't live long, did a cardiac stent and died after leaving the hospital, the love of his life died before and Dink, millions of dollars of family business no one inherited. One word miserable! Two words miserable!
There is no accepted consensus or guideline recommendation for such a judgment, but we can make a rough assessment in the following ways.
First of all, in terms of blood glucose, for newly diagnosed diabetic patients, according to the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists (AACE) guidelines recommended treatment path, if the glycated hemoglobin between 6.5%-7% can be used alone to control diet and exercise, for the glycated hemoglobin between 7%-8% can be used as a single drug to control blood glucose, for the glycated hemoglobin between 8%-9% recommended treatment with a combination of two or more drugs, for patients with glycated hemoglobin greater than 9% is recommended direct insulin therapy. A combination of two or more drugs is recommended for those with a glycated hemoglobin of more than 9%, and direct insulin therapy is recommended for those with a glycated hemoglobin of more than 9%. Therefore, such 4 ranges can provide reference for clinicians to differentiate between mild, moderate and severe blood glucose conditions.
Secondly, in terms of complications, for the existence of acute complications, the condition is certainly the most serious, while for the combination of chronic complications, the condition can be considered relatively moderate, but among them, if there has been renal failure for dialysis, or foot ulcers facing amputation, coronary heart disease requires the installation of a stent or bypass surgery, a large cerebral infarction resulting in limb movement disorders, fundus bleeds Those who are blind are relatively sick. Patients with no serious complications are generally considered to be in a less severe condition.
Again, from a lifestyle perspective, patients who do not have any awareness of healthy lifestyles are clinically considered to be more severely ill, but patients who are already aware of healthy lifestyles and have begun to make certain changes are clinically considered to be relatively less severely ill.
Other doctors will differentiate by age and duration of illness, with older, longer-term patients generally considered to be more severely ill, and younger, shorter-term patients mostly less severely ill.
To summarize, there is no uniform answer to the clinical judgment of diabetes, clinicians will be based on a number of dimensions (blood glucose control, complications, age, duration of the disease, lifestyle improvement, etc.) to carry out a comprehensive consideration, regardless of the severity of the disease, diabetic patients need to do is based on the improvement of the lifestyle, control of blood glucose, blood pressure, lipids, and other metabolic indicators, so as to prevent or delay the development of complications.
If you can keep your fasting blood glucose within 7.0, your postprandial blood glucose within 10.0, and your glycated hemoglobin within 7% over a long period of time, you can consider your condition to be well controlled. On the contrary, if fasting blood glucose often exceeds 9.0, postprandial blood glucose often exceeds 11.1, and glycated hemoglobin exceeds 8.5%, then it is considered that your condition is very poorly controlled.
It is recommended that glucose patients keep their blood pressure below 130/80 mm Hg, total cholesterol at <4.5 mmol/L, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) at <2.6 mmol, and triglycerides (TG) at <1.5 mmol/L. The condition is considered to be poorly controlled if the blood pressure and lipids are chronically much higher than these ranges.
Most of the myocardial infarction patients we often resuscitate have worse blood vessels if they have comorbid diabetes, because diabetes damages the blood vessels, often diffusely.
Diabetes is not a big problem if it is detected early and controlled properly, but if it is not detected early, or if it is detected and not controlled properly, then it is a real head-to-toe problem.
After years of diabetes, how can we tell if we are mild or severe?
First of all, the simplest and most preliminary judgment is whether the blood glucose is normal, of course, blood glucose includes fasting blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose, and most importantly, glycated hemoglobin, which represents the recent blood glucose situation.
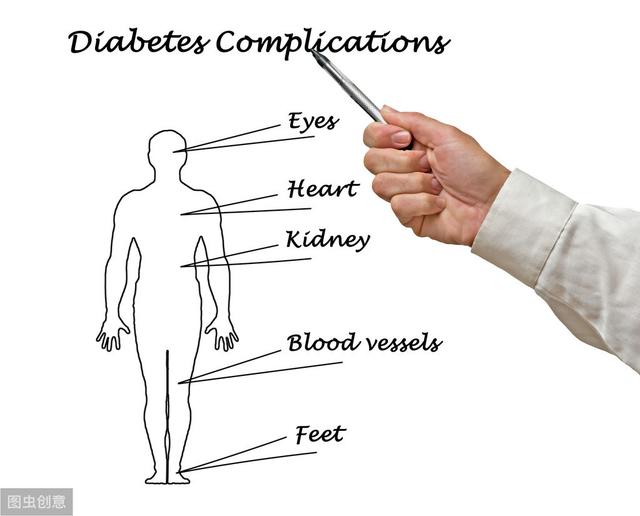
But because of the many years of diabetes, our main concern is that there is no damage to the target organs:
First, microangiopathy:
Check a urine routine, when found urine protein, must beware, this time has entered the diabetic nephropathy stage 3, slowly develop, late development of kidney failure. Pay attention to the adjustment of drugs, test blood sugar.
Check the fundus, blurred vision, retinopathy, cataracts are diabetes combined microvascular lesions, attention to early detection, attention to timely treatment. If there is blurred vision, and continue to worsen the situation, it is necessary to pay attention to perhaps diabetic retinopathy, the longer the course of the disease will be more likely, so diabetic people need to check the fundus of the eye once every six months.
Second, large vessel disease:
There is an unofficial statement, that is to say that diabetes is a coronary heart disease, there are some people because of diabetes sensory retardation, even if myocardial ischemia occurs, sometimes angina is not obvious, so diabetic patients with chest tightness, shortness of breath, panic and so on even if it is not a manifestation of pain, but also need to pay attention to, do not think that it is not angina pectoris. If necessary, the feasibility of plate test, coronary CT or coronary angiography and other tests. Can also limbs and neck ultrasound examination, to understand the limbs and carotid arteries whether there is plaque or stenosis.
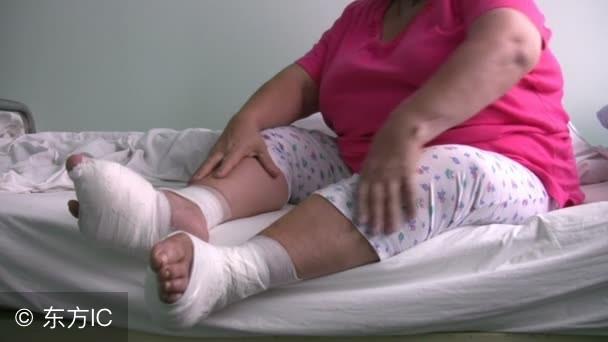
Third, diabetic foot:
Poor glycemic control, vascular nerve damage, non-healing wounds that are prone to rupture and can only get better with amputation!
Fourth, neurological lesions:
Some patients with angina or infarction do not know the pain, that is because of diabetic peripheral neuropathy, can appear limb numbness, sensory ataxia, can also involve the cranial nerves and spinal nerves. Early manifestations of limb numbness or sensory abnormalities, attention to timely medical exclusion of other neurological diseases.

Fifth, coma
Persistent hyperglycemia, after the loss of compensation phase, nausea, vomiting or abdominal pain, extreme thirst, urine volume increased significantly, etc., and often accompanied by headache, irritability, lethargy, deep and large breathing, expiratory odor such as the smell of rotten apples, cheeks flushed, mouth and lips cherry red. Complicated shock or cardiac and renal insufficiency. In the late stage, all kinds of reflexes are retarded or even disappeared, and eventually coma.
With more than 100 complications, diabetes is by far the disease with the most complications.
We must early prevention and early detection and early control of diabetes, or regret; we judge their own diabetes control, in addition to checking fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar, glycated hemoglobin, according to the individual situation also need to see if there are no complications, if there is that means that the situation is aggravating.
That's why diabetes isn't scary, it's our attitude of ignoring it that's scary.
[Copyright Dr. Cardiovascular Wang]
Comparing type 1 diabetes and type 2 diabetes, the condition of type 1 diabetes is generally heavier than that of type 2 diabetes because the pancreatic islet function of type 1 diabetes patients has been partially or completely exhausted, and they have to control their blood glucose with the help of external insulin injections. Type 2 diabetes patients can control their blood sugar with the help of lifestyle interventions and oral hypoglycemic drugs because they still have a certain amount of pancreatic function left in their bodies, and then resort to insulin to lower their blood sugar when their blood sugar is not controlled satisfactorily with the help of oral hypoglycemic drugs.
However, this is not absolute, if the type 2 diabetic patient does not actively control the condition, resulting in a variety of complications, while the type 1 diabetic patient due to the rational control of sugar, despite the disease for many years, there is still no complications, then at this time, the condition of this type 2 diabetic patient is heavier than the type 1 diabetic patient.
Patients with fluctuating blood sugar are sicker than those with persistent high blood sugar.
Persistent hyperglycemia indicates that the patient's blood glucose control is poor, and he or she is prone to chronic complications of diabetes, but these chronic complications occur on the basis of long-term hyperglycemia. The harm of blood glucose fluctuation will be even greater. Basic research has confirmed that: tissue cells have a certain adaptive ability to a stable high glucose environment, and when in a high glucose environment with repeated fluctuations, this adaptive ability is lacking, which leads to damage and apoptosis of vascular endothelial cells, and promotes the occurrence and development of vascular complications. Clinical studies have confirmed that repeated fluctuations in blood glucose can easily lead to frequent hypoglycemia during treatment, which increases sympathetic excitability abnormally, thus increasing the incidence of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases and mortality.
Finally to remind a point, do not rely on insulin injections to determine the severity of the disease, for newly diagnosed young patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, through the short-term insulin intensive treatment can effectively control the harm of glucotoxicity on the body, protect the pancreatic β-cell function, and to be stable after the blood glucose control, you can use the oral hypoglycemic drugs, and can not indicate that this case of the disease is serious.
One relatively simple criterion for evaluating the severity of your condition is this:
- If you need very little medication and have passing fasting and postprandial blood sugars, feel refreshed and energized, and have no serious diabetic complications and very few hypoglycemic episodes, you are in good control.
- And if you use many kinds of hypoglycemic drugs, but your blood sugar is still not good, sometimes high, sometimes low, and there are many complications or comorbidities, such as hypertension, hyperlipidemia, cardiovascular and cerebrovascular problems, numbness in the lower limbs, urinary albumin, retinopathy, and so on, it means that your condition is not well controlled.
Have diabetes for many years is to take stock of their condition, find out where to do right, conducive to the improvement of the condition, where to do not enough, must be strengthened as soon as possible, this is the significance of judging the severity of the disease.

However, if you think that since I am taking hypoglycemic drugs, blood sugar control is also passable, fasting blood sugar is less than 7, postprandial blood sugar is less than 10, then I can relax a little bit of life, such as New Year's Eve dinner time can eat more delicious food, enjoy a few days of relaxation, but that is really can not be done, because if you do, and then we have in order to adjust the period of time diet irregularities and lack of exercise brought about by the impact of blood glucose, need to pay more effort. The reason for this is that if we do this, then we need to put in more effort in order to adjust the blood sugar effects of irregular diet and lack of exercise during this period.
Managing diabetes over the long term requires the same effort as managing your health over the long term, but it is "hard work", but there are shortcuts. What can you do? You canTry to make friends with someone who is willing to live a healthy life, create a healthy circle for yourself, such people are willing to eat healthier at every meal, make an effort to do some exercise at least 5 days a week, and be sure to befriend a TA when you see one.
Diabetes mellitus is a very common chronic disease in our life, due to its blood glucose level is persistently elevated, with the elevation of blood glucose level, it will cause a series of tissue and organ complications in the later stage of the occurrence of diabetes mellitus, which need to be paid enough attention to us.
Diabetes mellitus can cause a series of complications to occur in the later stages as the disease progresses, so how to determine the severity of the condition of diabetic patients? If people's blood sugar control is stable and no complications occur, in this case, the disease control is relatively stable. If people's blood sugar fluctuates greatly, but instead, acute and chronic complications occur, then the condition control is poorer.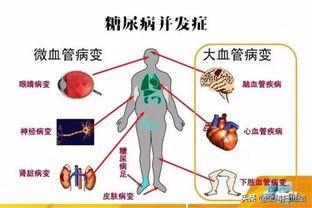
For diabetic patients, if people have acute complications such as hypoglycemia, ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar coma, etc., untimely treatment can lead to the occurrence of sudden death. And if long-term blood sugar control is poor, it can cause diabetic vasculopathy, peripheral neuropathy, gastrointestinal lesions, and in later stages can even lead to blindness, diabetic foot, coronary heart disease, strokes and other diseases.
Therefore, for diabetic patients, it is recommended that once diagnosed, they should actively standardize the treatment, pay attention to improving their lifestyle, achieve a reasonable diet, quit smoking and limiting alcohol, appropriate exercise, weight control, and under the guidance of the doctor reasonable use of medication, as well as pay attention to monitoring the changes in blood glucose levels and regular review, in order to stabilize and control the condition, reduce complications and improve the quality of life.
This article has been written by GP Sweeps and we hope it has been helpful. Please correct any deficiencies, the article is for reference only and is not intended as medical advice.
Diabetes is a slow disease that often lasts for many years, so how do you know how diabetes has gotten down over the years? Whether the development of more serious? Is a lot of sugar friends concerned about the problem, in fact, the length of time with diabetes, and the severity of the diabetes condition is not necessarily linked, some friends have diabetes problems, control is good, many years later the health status is still good, while some friends have diabetes problems, never go to the active control and management, but may be young complications, and even life-threatening.
Speaking of which, remembered an example around, years old friend's brother, from more than 30 years old when the problem of diabetes, the original has a job, live is also more energetic, blood sugar control is also good, and then because of a variety of reasons do not work, every day at home to smoke and play games, almost do not go out, did not take a few years, when the early 40s, retinal hemorrhage complications, resulting in severe vision loss The retinal hemorrhage complication occurred in the early 40s, resulting in a serious loss of vision, has been almost invisible, after surgery, although there is a certain recovery, but it is still very serious, and now at about 45 years old, has developed into renal failure, rely on regular dialysis to maintain such a situation, although the age of the disease is not too old, but this condition is definitely considered a serious situation, although since the emergence of these problems, has been more than the original attention to the control of blood glucose, but only then go to the control, is it not too late? ?
The development of diabetes, and the duration of diabetes has a certain relationship, but there is no inevitable link, diabetes is serious or not, and diabetic patients have no active early detection of high blood glucose, early intervention, early control, long-term smooth control of blood glucose has a close relationship, therefore, whether diabetes will develop into a more serious condition depends on the diabetic patient's own attention to disease and Therefore, whether diabetes will develop into a more serious condition depends on the diabetic's own attention to and understanding of the disease and respect for his or her life.
How serious is diabetes? Of course, the first thing to look at the blood sugar control, if the blood sugar control is not good, or the application of a variety of hypoglycemic drugs, can not effectively control the blood sugar, indicating that our pancreatic islet cell function has declined more seriously, the body's glucose regulation function has also become weaker, this situation, not only is prone to hyperglycemia caused by ketoacidosis and other acute complications, hypoglycemia will be more risky, hypoglycemia not only will cause palpitations, fatigue, tremor and other symptoms, hypoglycemia if it lasts too long, will also cause brain damage and life-threatening. Will cause palpitations, weakness, tremor of the limbs and other symptoms, hypoglycemia if the duration is too long, but also damage to the brain and life-threatening, severe hypoglycemia will also cause sympathetic nerve excitation, resulting in increased risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, therefore, if the blood sugar still can not be effectively controlled after the full application of hypoglycemic drugs, it means that our diabetic problem has been very serious.
Whether diabetes is serious or not also depends on the development of complications. The reason why diabetes is emphasized to be actively controlled is mainly to avoid the risk of complications brought about by long-term hyperglycemia. The complications of diabetes are multifaceted and are mainly divided into two major aspects: macrovascular complications and microvascular complications. Macrovascular complications generally refer to the harm of high blood sugar on cardiovascular health, triggering the risk of cardiovascular disease; while microvascular complications are diverse, peripheral neuropathy, diabetic renal impairment, retinopathy, diabetic foot and so on belong to the category of microvascular lesions.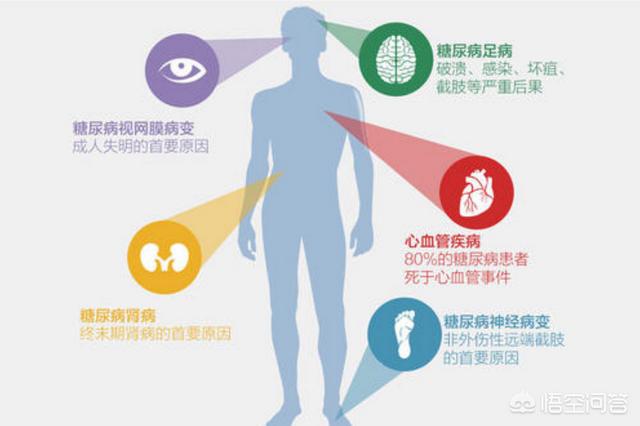
If long-term poor control of blood glucose causes cardiovascular events or life-threatening cardiovascular problems, this is a serious complication of diabetes; and if diabetes is poorly controlled, renal failure, retinal hemorrhages, foot ulcers and other serious complications occur, again, this is a sign of the seriousness of the diabetes condition.
Therefore, the severity of diabetes can usually be assessed by a combination of glycemic control, the risk of hypoglycemia, and the severity of diabetic complications.
Want to slow down the progression of diabetes, reduce the health risk hazards brought by diabetes, or request to emphasize that must be early detection, early intervention, early control of high blood sugar. Regularly check the blood glucose level, understand their own blood glucose situation, when the blood glucose appears to be initially elevated, should actively pay attention to, in the pre-diabetic period by strengthening the dietary management and exercise to control blood glucose level, when through the life conditioning can not effectively control the blood glucose level, in the life conditioning on the basis of strengthening the rational use of medication, if the full amount of two or more kinds of oral hypoglycemic drugs can not effectively control blood glucose, should also be combined with the situation, the timely start of the medication. When controlling blood glucose, it should also be combined with the situation, the timely start of insulin therapy, in short, smooth control of blood glucose levels, long-term control of high blood glucose is to prevent the progression of diabetes, reduce the occurrence of diabetic complications as well as to ensure the prognosis of the disease, to improve the patient's survival rate and life expectancy of the important aspects of the diabetes disease, if you wait for the emergence of serious complications or blood glucose difficult to control, and then think of ways to control blood glucose, it's too late. It is too late.
Checking blood sugar makes it easy to determine the disease status of a diabetic!
Glucose is now mostly measured by glucose oxidase or hexokinase methods. Venous whole blood, plasma, and serum glucose measurements are performed in health care facilities, and patients may use a small glucometer to self-measure capillary whole blood glucose.
One blood glucose measurement (fasting glucose, 2-hour postprandial glucose, or random glucose) represents only an instantaneous blood glucose level (spot glucose);
Multiple blood glucose measurements within 1 day (before and after 3 meals and at bedtime, 2 days per week, with additional measurements in the early morning hours if nocturnal hypoglycemia is suspected) provide a more accurate picture of glycemic control. Venous plasma or serum glucose is approximately 1.1 mmol/L (20 mg/dl) higher than venous whole blood glucose, and capillary whole blood glucose is the same as venous whole blood glucose during fasting and the same as venous plasma or serum glucose after meals.
1. Oral glucose tolerance test
People whose blood glucose is higher than the normal range but do not meet the diagnostic criteria for diabetes mellitus should undergo an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), which should be performed early in the morning after 2-3 days of unrestricted diet (with carbohydrate intake of at least 150g/day) and normal physical activity, and the use of drugs that affect glucose metabolism should be avoided. Drugs that affect glucose metabolism should be avoided, and fasting should be done for at least 8-14 hours before the test, during which time water can be consumed. After taking fasting blood specimen, subjects drink 250-300ml of liquid containing 75g of glucose powder (or 82.5g of glucose with 1 water molecule), and finish it within 5 minutes; children take 1.75g of glucose per kg of body weight, and the total amount should not be more than 75g. Blood specimen is taken 2 hours after taking glucose to measure plasma glucose.
2. Intravenous glucose tolerance test
Intravenous glucose tolerance test (IVGTT) is only indicated for post gastrectomy, post gastrojejunostomy, those with malabsorption syndrome and those with gastrointestinal dysfunction. The loading dose of glucose is 0.5 g/kg of standard body weight, prepared as a 50% solution, and injected over 2 to 4 minutes. Blood was collected before injection, and then blood was taken every 30 minutes counting from the start of the injection for a total of 2 to 3 hours; or any time between the start of the injection and the completion of the injection was used as the starting point, and blood was taken from the vein or capillary every 5 to 10 minutes for a total of 50 to 60 minutes.
The logarithmic values of blood glucose from 10-15 minutes to 50-60 minutes were plotted on a semi-logarithmic scale, and the time to fall from a given blood glucose value to its half value (t1/2) was calculated using the horizontal coordinate as time. The method uses the K value representing the percent decrease in blood glucose per minute as a diagnostic criterion for diabetes.
Diabetes mellitus is diagnosed in people under 50 years old if the K value is less than 0.9, and IGT if it is between 0.9 and 1.1.The K value is affected by the blood insulin level, hepatic glucose output rate, and sugar utilization rate of peripheral tissues, so the K value can be lowered in a small number of normal people. In normal people, the peak of blood glucose occurs at the completion of injection, usually 11.1-13.88mmol/L (200-250mg/ dl), and falls to the normal range within 120 minutes. 2-hour blood glucose is still >7.8mmol/L is abnormal.
Answer editor and reviewer: Dr. Li Shupeng (Headline), Master of Pediatrics, Beijing Children's Hospital
Follow the headline number of "medical catechism", more health Q&A easy to see!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.