Is there a difference in blood glucose after three meals for diabetics? What to watch out for?
The standard of glycemic control after three meals is the same for diabetics, and there is no difference between morning, midday, and evening meals.It is generally recommended that postprandial blood glucose (2 hours after a meal) be controlled within 10 mmol/L for diabetic patients.This criterion is clearly recommended in the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, and the recommendations on this point are the same in the 2013 and 2017 versions of the guidelines.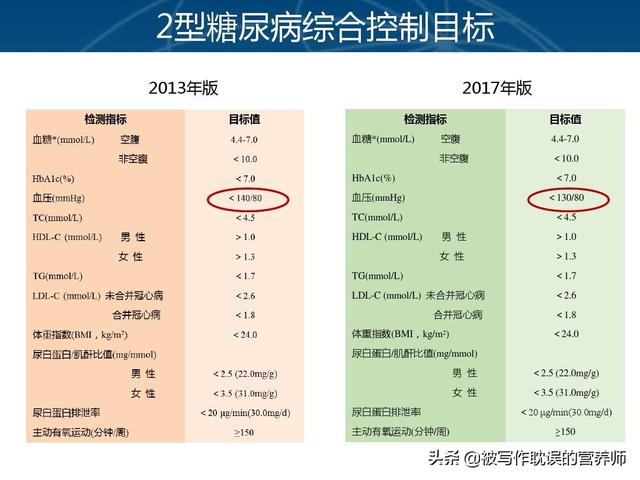 (Screenshot of "Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes")
(Screenshot of "Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes")
However, for some of the older and longer-term diabetic patients, the postprandial blood glucose control target value can be appropriately relaxed to about 12mmol / LIn contrast, for new-onset patients with a short course of disease, it is recommended that the control criteria in the chart above should ideally be met.
Because controlling postprandial blood glucose as well as fasting blood glucose is an important part of preventing and controlling diabetes complications, it needs to be given adequate attention.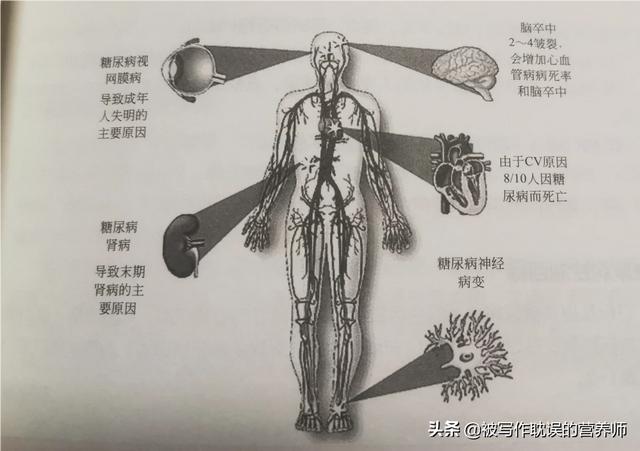 ((Common complications of diabetes)
((Common complications of diabetes)
In addition, people with diabetes should also pay attention to their blood pressure, blood lipids, glycated hemoglobin and other indicators, good control of them is also conducive to reducing the risk of complications, here focus on diabetes combined with hypertension:
For patients with diabetes mellitus, blood pressure is recommended to be controlled at 130/80 mmHg in patients with new onset of the disease and no history of hypertensive disorders, whereas the blood pressure control target for elderly patients with diabetes mellitus can be appropriately relaxed to within 150/90 mmHg.
This is because high blood pressure increases the risk of kidney disease, eye lesions, and heart disease and strokes.
Dietary advice for people with diabetes:
It is recommended that every diabetic should consult and study the Chinese Dietary Guidelines for Type 2 Diabetes online.This is the definitive dietary guide, written by clinical experts as well as nutritional experts, which details the daily dietary considerations regarding diabetes.
It is recommended because diabetes is a lifelong, chronic disease, and patient self-management largely determines glycemic control.Drugs, insulin and doctor's orders are all means to help blood sugar control, while their own diet management, exercise and lifestyle habits are very important, personally I have come across many sugar addicts who drink and eat meat while zapping insulin.Relying exclusively on medication without dietary control can be very detrimental to the progression of the disease.
Finally, I'd like to share a small summary of diabetic meal suggestions:
- Eat three regular meals, vegetables first and then main meals
- 1/3 to 1/2 of your main meal should be roughage
- Eat enough vegetables to cover 500 grams per day
- When blood glucose control is stable, add about 150 grams of fruit between meals, split between morning and afternoon.
- 1 egg per day
- Plain milk/unsweetened yogurt 1 cup per day
- Meat in moderation (about 2 taels), preferably lean fish and poultry meat
- No alcohol, no smoking
- Light and less oily cooking
- Maintain your water intake by drinking healthy beverages such as green tea in moderation.
Thanks for reading, I hope this helps.
There is no difference, both belong to the postprandial blood glucose, the difference is the amount of sugar intake, which may lead to a change in the measured value.
Diabetic patients' blood sugar is generally high, so in the daily diet need to strictly control the intake of sugar, for some sugar high food and carbohydrates need to be strictly controlled, it is recommended that the use of coarse fiber-rich grains and vitamin-rich vegetables, and with protein to use, pay attention to small meals, pay attention to low-salt, low-fat, low-sugar diet, and also need to pay attention to, high energy food, high starch content food also need to pay attention to eat less or not eat. Energy-rich foods and foods with high starch content should be eaten sparingly or not at all. Yam, lotus root, taro, carrots, garlic, etc. eat less in addition to walnuts, sunflower seeds, peanuts and other high-calorie foods, reduce the intake of fine grains with high sugar content food, to control blood sugar problems.
I hope my answer helps.
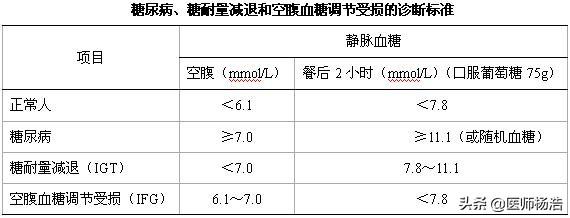
For diabetic patients' blood glucose test, it is divided into fasting blood glucose, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose, random blood glucose, and fasting blood glucose is fasting state 8 hours without food, between 6-8 o'clock is more appropriate to measure, after 8 o'clock a variety of glucose-raising hormones will be secreted, the detection of blood glucose is slightly affected, the reference range of 3.9-6.1 mmol/L; and 2 hours after meal Blood glucose refers to the three meals, the standard is the same, the normal value <7.8mmol / L is appropriate; and random blood glucose control in the 7.8mmol / L below relatively good, and the elderly standard can be appropriately relaxed, control in the 10mmol / L below relatively good, in addition to the detection of glycated hemoglobin and so on, and at the same time, try to avoid hypoglycemia occurs.
When it comes to diabetes, we are certainly not unfamiliar with it. As one of the common chronic diseases, the incidence of diabetes has been increasing in recent years, and it is gradually showing a trend of rejuvenation, which is a serious threat to the health of human beings.
Is there a difference in blood glucose after three meals for diabetics? What to watch out for?
Like hypertension, high blood pressure, high blood cholesterol and other chronic diseases, in fact, diabetes itself is not fatal, but the complications induced as a result can jeopardize the patient's life. According to statistics, the complications of diabetes are up to more than 100 kinds, which is the disease with the most known complications. Therefore, for diabetic patients, the key is to control the stabilization of blood glucose in order to prevent complications and improve the quality of life of patients.
Diabetic patients know that the monitoring of blood glucose mainly includes fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose. And research shows that our countrymen's genes and the characteristics of beta cell function and so on make me over diabetic patients mostly show postprandial blood glucose elevation. Statistics show that about 82% of diabetic patients in China are characterized by elevated postprandial blood glucose. Especially in the early stage of diabetes.70% of patients do not necessarily have high fasting glucose, but high postprandial glucose.And up to 47% of diabetics have simply elevated postprandial blood glucose with normal fasting blood glucose. Therefore, postprandial glucose monitoring is crucial for diabetics.
So when do you test your postprandial blood sugar? It is generally accepted that postprandial blood glucose testing needs to be done two hours after a meal. And the initial time of meal is counted from the first bite when you start eating. Under normal circumstances, blood glucose will slowly return to normal 2 hours after a healthy person has eaten a meal, while the blood glucose of diabetic patients will not drop. Therefore, in general, postprandial blood glucose is not differentiated between breakfast, lunch and lunch, because as long as eating causes blood glucose to rise, the patient's blood glucose control can be assessed. Some patients may have different blood glucose after three meals, such abnormalities have no specific clinical value, if there is not much difference, do not worry too much.

In clinical practice, when postprandial blood glucose <7.8 mmol/L, it predicts normal blood glucose; postprandial blood glucose between 7.8-11.1 mmol/L predicts reduced or impaired glucose tolerance, i.e., preglycemia; postprandial blood glucose ≥11.1 mmol/L with two consecutive tests on different days predicts diabetes mellitus.
In addition, it is important to note that for diabetic patients, especially those with elevated postprandial blood glucose, three numbers should be kept in mind: 10.0, 7.8, 4.4. Specifically, this means that the regular target value of postprandial blood glucose is <10.0mmol/L; for newly diagnosed patients with a shorter course of disease and younger age, the target value is <7.8mmol/L, otherwise it will increase the risk of complications; strict control of blood glucose while at the same time It is also necessary to guard against hypoglycemia, i.e., it is required that blood glucose should not be lower than 4.4mmol/L.
I am Pharmacist Wang, insisting on spreading the knowledge of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases with simple and easy-to-understand words, and dedicating my own small efforts for a healthy China. If you think my answer is helpful to you, please leave a like! In addition, if you still have questions related to postprandial blood glucose test, welcome to leave a message, we will discuss together.
Is there a difference in blood glucose after three meals in diabetics?
Postprandial blood glucose reflects the highest level of our blood glucose (fasting blood glucose reflects the basal level of our blood glucose), and postprandial blood glucose is influenced by a number of factors, which are related to our early phase of insulin secretion, pancreatic glucagon secretion, as well as insulin sensitivity of muscle, liver and adipose tissue, as well as preprandial blood glucose levels, the type and time of eating, digestion and absorption, etc., so that either after breakfast, after lunch or after dinner can be used to reflect this. However, it should be noted that the general is to test the blood sugar two hours after the meal, that is, from the time you eat the first mouthful of food to count, test two hours after the blood sugar value, normal people is below 7.8mmol / L, diabetic people is above 11.1mmol / L, in 7.8~11.1mmol / L although not reach diabetes, but suggests that blood sugar has been abnormal, there is a development of diabetes.
Why does it cause an increase in blood sugar after a meal?
Current research suggests that elevated postprandial blood glucose is the result of inadequate production of our own insulin, impaired utilization of blood glucose by peripheral tissues (liver, muscle, and fat, etc.), and abnormalities in hepatic glycogen output.
What are the dangers of elevated postprandial blood sugar?
Nearly half of our diabetic patients only have elevated blood glucose after meals, and the harm of elevated blood glucose after meals is no less than the fasting blood glucose damage to our body. Elevated postprandial blood glucose is prone to cause an increase in the secretion of various cytokines and inflammatory factors, increasing the body's oxidative stress response, leading to damage to the vascular endothelial function, thereby increasing the risk of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, kidney disease, retinopathy. Therefore, it is also very important to control postprandial blood glucose, which is conducive to reducing the fluctuation of blood glucose and making the glycated hemoglobin reach the standard, so as to reduce the occurrence of complications.

What should I look for in elevated postprandial blood sugar?
Postprandial blood sugar must be controlled and needs attention if you want to make blood sugar control smoother:
1. Diet should include vegetables before the main food; the main food should include 1/3 of coarse grains; eat more vegetables; chew slowly.
2. If your blood sugar fluctuates a lot, you can eat smaller meals.
2. Regular postprandial exercise helps to lower postprandial blood sugar.
3. Diabetics with predominantly postprandial blood glucose can use glucose-lowering drugs that reduce postprandial blood glucose under the guidance of a doctor, such as acarbose, voglibose, repaglinide, and nateglinide.
4. Pay attention to monitoring blood sugar two hours after meals. (Many people only measure fasting blood glucose but not postprandial blood glucose, which is wrong)
Welcome to like, forward, leave a message, I am physician Yang Hao, focusing on common diseases, multiple diseases diagnosis and treatment, chronic disease management, health science. If you want to know more about medical knowledge, welcome to pay attention to this headline!
Diabetic patients have varying degrees of elevated blood glucose after all three meals. In addition to the intervention of medication for postprandial blood glucose, the metabolism of energy consumption through exercise should be enhanced to stabilize blood glucose.

Diabetes is not at all strange to many people, China has more diabetic patients, as of the end of 2019, China's diabetic patients have reached 110 million, in addition, there are 140 million people with reduced glucose tolerance, which means that on average, one in every 11 people has already suffered from diabetes. Diabetic patients should pay attention to their blood sugar, and blood sugar, it is divided into fasting blood sugar and postprandial blood sugar, relative to fasting blood sugar, postprandial blood sugar has a higher reference value, is there any difference between the postprandial blood sugar of three meals?
For three meals of postprandial blood glucose diabetic patients control standard is the same, breakfast, lunch and dinner does not differ. Generally we recommend measuring postprandial blood glucose, postprandial blood glucose refers to the blood glucose value two hours after the meal. And two hours after the meal does not mean that after eating a meal to start counting time to two hours, but from the first bite of food to start timing, to two hours after the end of the end of the blood glucose value that we come to measure.
The normal value of two-hour postprandial blood glucose is less than 7.8 mmol/. If the postprandial blood glucose is between 7.8 and 11.1 mmol/, you can be diagnosed with hypoglycemia or impaired glucose tolerance. Diabetes is diagnosed when postprandial blood glucose is greater than 11.1 mmol/. For older diabetic patients, the target value of postprandial blood glucose control can be appropriately relaxed to 12mmol/.
Postprandial blood glucose is strongly influenced by diet, so diabetics should pay attention to the order of meals and other foods when eating. Diabetics should choose foods rich in dietary fiber, such as coarse grains and vegetables. These foods contain dietary fiber can slow down the rise of blood sugar, inhibit the body for cholesterol absorption, is conducive to diabetic patients to control blood sugar.
People with diabetes should not only focus on postprandial blood glucose, but also on glycosylated hemoglobin. Glycated hemoglobin fasting effect can see the last two or three months since the blood sugar a change in the situation, more conducive to blood sugar control.

The blood glucose standard after three meals is the same for diabetic patients, but my monitoring data show that the blood glucose level after breakfast is usually about 7.2, the blood glucose after Chinese meal is the highest in a day, sometimes up to 12 or so, usually 8.8 or so, and in the evening to do a larger amount of exercise, the postprandial blood glucose is 7.0 or so, the fasting glucose level is usually 6.0 or so, and the glycated hemoglobin is 6.6, which is actually a high level of postprandial glucose after the Chinese meal. Should be often exceeded, now the amount of Chinese food changed to two, to reach 8.0 or less is not easy, now I have stopped taking medication for 26 days, the body feels more comfortable, I now feel that dietary control to strictly adhere to the rules of diabetic patients diet, can not be less, can not be more, the quality of the high quality, variety, teeth should be protected, drink enough water, soak your feet, the quality of sleep should be good, to maintain a good mood, conducive to physical health.


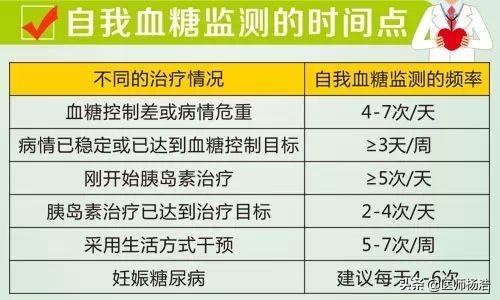
Blood glucose after all three meals is informative. Sugar lovers who have stable blood glucose also need to measure their blood glucose profile one day a week (fasting + two hours after three meals). Pay attention to timing from the first meal. If your blood sugar is unstable, you need to measure more frequently.
Hello! Diabetic patients' blood glucose standard is based on the pre-meal and post-meal as the standard, that is, focusing on two indicators, that is, the pre-meal fasting blood glucose and the 2-hour postprandial blood glucose as the practical significance, and is not based on the three meals as the diagnostic standard. Therefore, the diagnostic index of three meals for diabetic patients is the same, there is no difference.
First of all, fasting blood glucose refers to the blood glucose measured after fasting overnight, at least 8-10 hours without food, so the so-called preprandial blood glucose refers to the overnight fasting blood glucose value, fasting blood glucose mainly reflects the secretion function of the basic pancreatic islet β-cells, the blood glucose of the people every day with the food, activities and other circumstances vary, will fluctuate, only in the fasting blood glucose level is the most constant, so the general normal value for the Therefore, the normal value is 3.9-6.1mmol/L. The blood glucose value measured in this way can show the defective degree of β-cell function or insulin secretion.
Secondly, postprandial blood glucose is the blood glucose value detected 2 hours after eating, its clinical significance lies in a certain degree of response to insulin secretion and the body's sensitivity to insulin, which is usually used to do the glucose tolerance test, so that hypoglycemia can be detected from it, generally postprandial blood glucose between 7.8-11.1mmol/L for hypoglycemia. The normal value is <7.8mmol/L.
Therefore, the standard blood glucose value after three meals is the same for diabetics.

What to look for?
1, for the first incidence of general monitoring of blood glucose is more diligent some, blood glucose is more stable, can slightly reduce the number of monitoring;
2、Don't deliberately change your previous eating habits because of blood glucose measurement, so that the measurement will not be accurate;
3、Measuring postprandial blood glucose should be calculated from the time of the first bite of food, not from the time after eating;
4、Since postprandial blood glucose generally reaches its peak in 1-2 hours, you can measure 1-hour postprandial blood glucose and 2-hour blood glucose at different times to avoid inaccurate testing;
5. Before the test, it is best to stay calm, do not exercise, drink alcohol, or take diuretics, etc., otherwise all will affect the results.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.