Glycated hemoglobin is 6.4%, is this normal?
Glycated hemoglobin is an indicator of the overall control of blood glucose. When glycosylated hemoglobin is elevated, it often indicates poor blood sugar control and is one of the indicators that diabetic patients need to monitor regularly. So, is a glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.4% normal? How is the blood sugar control? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze for you.
Glycated hemoglobin is the product of the formation of glucose in the blood and hemoglobin of red blood cells, mainly reflecting the control of blood sugar in the last 3 months, and its level is closely related to the level of blood sugar, the higher the blood sugar and the longer it lasts, the higher the glycated hemoglobin. On the contrary, if blood glucose is controlled within a reasonable range for a long time, the glycated hemoglobin will gradually decrease. The normal range of glycosylated hemoglobin is 3-6%, which may vary slightly from hospital to hospital.
Patients with a definitive diagnosis of diabetes require regular monitoring of glycosylated hemoglobin to guide the development and adjustment of treatment regimens:
Newly diagnosed patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who have a glycated hemoglobin ≥9%, indicating that the current average level of glycemic control is around 11.8 mmol/L, are severely hyperglycemic, and should be initiated directly on insulin hypoglycemia when formulating a glucose-lowering regimen;
- In patients with a previous diagnosis of diabetes mellitus, if the glycosylated hemoglobin is <7% after treatment, it means that the blood glucose control has basically reached the standard, and you can continue to follow the current glucose-lowering regimen. Therefore, the subject's glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.4% indicates that overall control of blood glucose is currently good.
Glycosylated hemoglobin <7% for the average diabetic patient, with slightly different control targets for young and elderly patients:
Young diabetics, with a short disease duration, less damage to target organs from hyperglycemia, and less frequent hypoglycemia, should have stricter control of glycosylated hemoglobin, preferably below 6.5%;
- In elderly diabetic patients with long duration of disease, if severe target organ damage has occurred, or frequent hypoglycemia, glycosylated hemoglobin may be relaxed to 7.5%, and to 8% in the elderly.
In summary, the glycohemoglobin control index varies among different diabetic patients, less than 7% for general diabetic patients, less than 6.5% for young diabetic patients, and some elderly diabetic patients can be relaxed to 7.5%, or 8% if necessary. Therefore, the subject's glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.5% indicates that glycemic control is possible.
Thank you all for reading!
We are looking forward to your attention and presenting more health knowledge to you!
Note: The images in this article come from the Internet, if infringement of copyright, please contact to remove. The content of the article is only as a health science popularization, not as a medical advice or opinion, and does not have the condition of medical guidance.
Glycated hemoglobin is the gold standard for glycemic control and an important tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes. In the treatment of diabetes, glycosylated hemoglobin levels are clinically important for evaluating overall glycemic control, identifying problems in treatment, and guiding treatment regimens.
If you are older than 70 and if you have long been diagnosed with diabetes and still under treatment, I give you a 70. Conversely being younger than 60 with no history of diabetes I can barely give you a 60. If you are under 50, overweight or obese, and have high blood pressure or away from bile international hyperlipidemia I can only give you a failing grade.
Although the glycated hemoglobin given by patients with sugar disease is less than 6.5% but normal people should be 4-6%, I always wonder: the vast majority of doctors, patients read the laboratory report is always concerned about whether the indicator has not exceeded the maximum value of the normal range. As if not exceeding the maximum value is normal and happy. Glycated hemoglobin 5.9 and 6 is not much of a difference, of course, when reading such reports, as long as it is above the minimum value, the lower the better!
Why is it that in modern society, where medical care is becoming more and more advanced, the number of patients with hypertension, hyperlipidemia, diabetes and pre-malignant diseases is increasing? The problem lies in the fact that doctors only take the report according to the guidelines to see the patient, and the awareness of disease prevention is seriously deficient, the indicators within the normal value: no problem, normal. Do not understand the importance of the difference between the highest and lowest values in the normal range. Some diseases show that the indicator is too low is not good, then it should be higher, but the vast majority is too high is not good should be lower is better. Whether high or low is close to a critical level it should be a warning.
So you ask me if a glycated hemoglobin of 6.4% is normal? If you do not have a history of diabetes, your three-month blood glucose value is on the high side as judged by the new diagnostic criteria for diabetes, and you are not far away from diabetes if your dietary structure and volume and exercise are not regulated and controlled. If you have a history of diabetes, then I think you should work harder to control the total calories eaten, HbAIc control is not good enough, has been close to the highest value of HbAIc 6.5%, the old patient dietary control tends to be better then increase the amount of exercise. If you are over 70 years old and have a history of diabetes for many years you can allow HbAIc to be at 6.5%-7%. over 80 years old you can relax to 7.5%-8%. Because of high blood sugar on the cardiovascular harm of less than ten years or more, people can live how many years, elderly people even the last fun in life to eat also hard to control off, live and how much value.
The Chinese Society of Endocrinology of the Chinese Medical Association released the "Expert Consensus on HbAlc Control Targets for Adults with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in China" in 2011
HbA1c level adapted population:
<6.0% of the population: newly diagnosed, young, no complications or concomitant diseases, no adverse effects of glucose-lowering therapy such as hypoglycemia and weight gain; those who do not require glucose-lowering drug interventions; diabetes mellitus comorbid with pregnancy; diabetes mellitus detected during pregnancy should be.
<6.5% of the population: less than 65 years of age, no diabetic complications and no serious concomitant diseases; diabetic planned pregnancies.
Remember that this is the highest value of the permissible range and not the target value! Glycated hemoglobin is lower than the average blood glucose value, but the average blood glucose value should not be compared with the fasting blood glucose menu blood glucose that we always check, that refers to the average blood pressure value of three months. And the unit of calculation is not the same, the conversion table is listed below for readers' reference.
2019.4.4
I went to the hospital the day before yesterday to do a glycated hemoglobin test, just 6.4% The doctor told me that this is not diabetes, just high blood sugar, to pay attention to! You can't eat sweets, you can't eat too much, just seven minutes of fullness, pay attention to nutrition, exercise every day, keep a happy mood, don't have a psychological burden, you don't need to take hypoglycemic drugs for the time being, and come over for a period of time to have a checkup. The doctor also gave me a dietary therapy to lower sugar. I followed the doctor's advice and did what the doctor asked me to do, and I will be fine if I come back for a review in two months. I have met a good doctor!

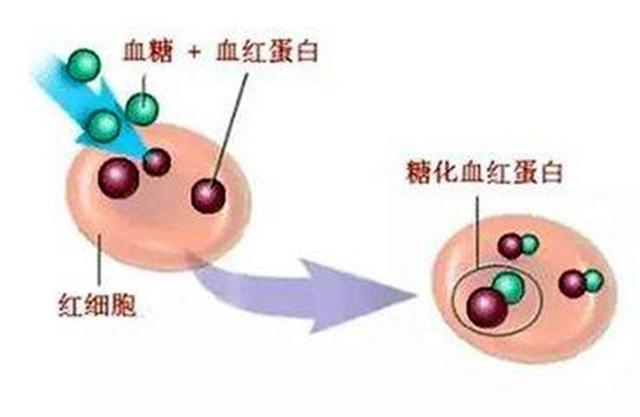
Glycosylated hemoglobin actually refers to hemoglobin (i.e., blood pigment) that has been glycated by glucose, and blood glucose levels are assessed by measuring the amount of glycated hemoglobin in the blood. When the concentration of glucose in the blood is high, the amount of glycated hemoglobin formed by the body will also be relatively high. The life span of red blood cells in the body is usually 120 days, and the level of glycated hemoglobin in the blood will also remain relatively unchanged until the red blood cells die. Therefore, the glycated hemoglobin level reflects the average blood glucose level in the 2-3 months prior to the test. The amount of glycated hemoglobin is independent of the time of blood draw, whether the patient is fasting or not, and whether insulin is being used or not. It is a good indicator for determining the long-term control of diabetes, and is considered to be the gold standard for measuring blood glucose control.

Diabetes itself is not scary, the scary thing is all kinds of complications, and the emergence of chronic complications is a long-term process, so we call diabetes "silent killer". Some studies show that every 0.1% higher glycated hemoglobin, the risk of complications increased by 5% -10%, so glycated hemoglobin is 7.1% -8.0% of the patient's risk of complications may be 50% more. So the closer the diabetic's blood glucose control standards are to normal, the lower the complication rate and the longer the life expectancy.

Glycated hemoglobin is 6.4%, is this normal?
In fact, glycated hemoglobin is not just a figure to look at, it is a stratified control depending on the patient's different conditions. That means there are different standards for different people. For young first-onset diabetics, diabetes mellitus combined with pregnancy, diabetes mellitus occurring during pregnancy, people with high blood glucose who do not yet need to take hypoglycemic drugs, and younger and lighter people with diabetes mellitus who have not yet developed any complications or concomitant diseases, the control of glycated hemoglobin for this group of people should be as strict as possible, and preferably controlled at 6.0 or less. For the elderly over 65 years old, glycated hemoglobin can be controlled at <7.0%; for those at high risk of hypoglycemia, those with malignant tumors and shorter expected survival, or those with cardiovascular disease, the control target of glycated hemoglobin can be further relaxed to 7.5-9%.

So whether glycated hemoglobin 6.4% is normal or not is something that depends on different groups of people. In addition, patients with hemoglobin abnormalities, such as long-term moderate-to-severe anemia, the results of the glycated hemoglobin test are unreliable, and should be based on fasting and postprandial blood glucose. Fasting blood glucose and postprandial blood glucose should be used. The results may also be affected if the specimen is high in lipids due to recent consumption of oily food. For those who test for glycated hemoglobin during a simple physical examination, if there is no previous history of diabetes mellitus and the hemoglobin is normal, a 6-7% level of glycated hemoglobin requires further fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and glucose tolerance tests to identify the presence of abnormal glucose tolerance or diabetes mellitus at the earliest possible time.
Hello! I am an endocrinologist and would love to answer this question!
Glycation of 6.4% with or without medication is basically the standard, and the diabetes guidelines recommend a diabetes standard of 7.0%.
However, there are individualized differences in the target of clinical treatment. Those with long duration of disease, old age, many complications or concomitant diseases, and poor pancreatic islet function with recurrent hypoglycemia are appropriately relaxed to 7.5 or even 8.0; however, for newly discovered diabetes mellitus, young, and obese patients, we set a more stringent target of 6.5 or even 6.0, and according to your own situation you can judge whether the glycation of 6.4 is appropriate or not.
Glycation is not blood glucose, it represents how well the blood glucose has been controlled in the last 3 months. If the glycation is up to standard you can review it at 6 month intervals, if it is not up to standard or if there is a change in the treatment regimen, review it at 3-4 months.

Please follow me! You can get a steady stream of professional and standardized knowledge and information on diet, exercise, fat and weight loss, as well as the prevention and treatment of metabolic diseases such as diabetes! Welcome to leave a message to discuss. Thank you!
Is a glycated hemoglobin of 6.4 normal? For someone who has been diagnosed with diabetes, this result is acceptable, controlled and normal. But for a person who does not know that he has diabetes, it is not normal. glycosylated hemoglobin
glycosylated hemoglobin
It is the product of hemoglobin in the red blood cells of human blood combined with blood sugar. It can reflect the patient's blood sugar control in the last two months. Glycation has several characteristics:1 The higher the blood glucose, the higher the glycation.2 Glycation is produced very slowly and is not affected by meals.3 Glycated hemoglobin is quite stable and is not easily broken down after it is produced.4 Glycation is the gold standard for the effectiveness of blood glucose control in a month or two. Based on these characteristics, glycation is the gold standard for glycemic control within a month or two. With a glycated hemoglobin of 6.4, your blood glucose level must be above 7. It can be concluded that you are a diabetic.
So I'd say I have to answer you this way when you ask if a glycation of 6.4 is normal or not. For diabetics, keeping the glycation under 6.5 will extend life considerably! I hope my answer helps you!
This question reminds me of a case of a 63-year-old Ms. Wang, who was overweight, with marked abdominal obesity and a BMI of 32, and the patient did not have the typical symptoms of diabetes mellitus of three more and one less, and was diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus after discovering by chance that her blood glucose was high. The patient's glycosylated hemoglobin was 6.4%, fasting blood glucose was 6.6-7.4 mmol/L, and postprandial blood glucose was less than 10 mmol/L. Does the patient need medication? Or just lifestyle modifications will do.
Glycated hemoglobin is the gold standard for measuring glycemic control and an important tool in the diagnosis and management of diabetes.Glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.4% is normal, and the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus state that the comprehensive control goals for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus are glycated hemoglobin of no more than 7.0%, and fasting blood glucose of 4.4-7.0 The above patients are therefore only required to undergo lifestyle management.
The guidelines state that different populations have different goals for control of theIn patients with type 2 diabetes who have a shorter disease duration, longer life expectancy, no complications, and no co-morbid cardiovascular disease, blood glucose should be controlled more tightly, with glycated hemoglobin below 6.5%。
Patients who already have cardiovascular disease or patients with very high cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease need to control their glycosylated hemoglobin below 7.5%; for patients over 65 years of age with an expected survival of 5-15 years, the control value of glycosylated hemoglobin can be relaxed to 8.0%; for patients with malignant tumors, an expected survival of no more than 5 years, and mental disorders and other patients, the control value of glycosylated hemoglobin The control value of glycosylated hemoglobin can be relaxed to 9.0%.
Glycated hemoglobin is a product of the combination of hemoglobin in red blood cells and sugars in serum, mainly formed through a slow, continuous and irreversible glycation reaction. The measured value mainly depends on the blood glucose concentration and the contact time between blood glucose and hemoglobin, and has no relationship with the time of blood draw and whether the patient is fasting or not.Stability is very good, but the price is a bit high。

Glycated hemoglobin is more stable, diabetic patients in the measurement of fingertip blood glucose, will feel that the two measurements have a certain degree of error, each time the value is not the same, which is normal, as long as the error is not very large.Then there is no need to worry too much. However, many patients are concerned about inaccurate measurements and will go to the hospital to have their glycated hemoglobin measuredGlycated hemoglobin values are not related to whether or not a meal is consumed, so they are very stable, but they are cumbersome to measure and must be done in a hospital.
Unlike monitoring blood glucose from fingertip blood, glycated hemoglobin does not monitor real-time blood glucose, but rather the patient's blood glucose level averaged over the last 8-12 weeksGlycated hemoglobin levels are important in evaluating the overall control of blood glucose. Therefore, in the course of diabetes treatment, glycosylated hemoglobin levels are very important in evaluating overall glycemic control, identifying problems in treatment, and guiding treatment regimens.
I am Pharmacist Wang, dedicated to helping you manage your body by explaining complex and difficult disease knowledge in plain words. Your praise is my greatest motivation! In addition, if your family members also have related troubles, please forward this article to them!
Glycated hemoglobin, as the gold standard for diabetes control, is now being taken more and more seriously, highlighted by the fact that more diabetic friends are being examined, more people are coming to inquire about glycated hemoglobin, and other sister departments are no longer focusing only on blood glucose, but are also gaining a deeper understanding of the significance of glycated hemoglobin.
glycosylated hemoglobin
Glycosylated hemoglobin is the product of glycosylation of blood glucose and hemoglobin, and is substituted as a percentage. Because hemoglobin has a lifespan of about 3 months, glycated hemoglobin represents the patient's average blood glucose level over the last 3 months.

Glucose control standards
The standard of glycemic control is based on a combination of the patient's disease type, disease duration, comorbid cardiovascular disease status, life expectancy and comorbidities. According to the recommendations of the Chinese Guidelines for the Prevention and Control of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, glycated hemoglobin should be controlled at less than 7%, but for those with a shorter history of the disease, no complications, and a combined pregnancy it should be controlled at less than 6.5%, which reduces the incidence of complications and ensures the health of both the fetus and the mother.
A glycated hemoglobin of 6.4% would say that the overall control is pretty good, and according to the estimated average blood glucose value of around 7.2 mmol/L, which is still very satisfactory.
Special attention needs to be paid:
Low blood sugar and high blood sugar many times repeatedly alternating conditions may also appear glycated hemoglobin performance is normal, because glycated hemoglobin as a whole is an average, like a student biased, 30 points one, 90 points one, an average of 60 points pass, but 20 points (low blood sugar) is a situation that needs to be vigilant. Because severe hypoglycemia can be life threatening.

summarize
Blood glucose monitoring and glycosylated hemoglobin tests should be combined, with glycosylated hemoglobin measured every 3 months and blood glucose measured at different times of the day, in order to maintain relatively stable blood glucose.
Concerned about Dr. Sun talking about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please click on the praise, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Glycated hemoglobin of 6.4% is already abnormal and elevated. Because the results of our population survey, the upper limit of glycated hemoglobin is 6.3%, 6.4% is obviously high. If ≥6.5%, then it meets a diagnostic criterion for diabetes.

Glycated hemoglobin is the average blood glucose level over the last 2 to 3 months; a high glycated hemoglobin indicates a high average blood glucose level.
In terms of glycated hemoglobin formation, this elevated level may be a little more closely related to high fasting glucose.
For patients with elevated glycosylated hemoglobin, it is best to screen for diabetes. If diabetes is present, then more attention should be paid to monitoring and usual control in terms of blood glucose.
Also, glycated hemoglobin reflects the average blood sugar level, and fluctuations in blood sugar can affect glycated hemoglobin levels. Some people with diabetes sometimes don't have as high a glycosylated hemoglobin level due to the hypoglycemia that can occur, and hypoglycemia can be risky for the patient, so it's even more important to be aware of it.
However, being normal is not exactly the same thing as needing pharmacological intervention.
This is because for the average adult with diabetes, a glycated hemoglobin control of about 6.5% is required as part of the criteria for blood glucose control. Therefore, 6.4% of glycosylated hemoglobin, even for diabetic patients, is still up to the standard, and can not be another intervention. In the case of elderly diabetics, the standard for glycosylated hemoglobin is even more relaxed and can go up to 7% or even higher.
This is because the damage that hyperglycemia does to the cardiovascular and other systems is a long-term, chronic process; whereas the damage caused by hypoglycemia is acute and immediate. Diabetics are at greater risk and more dangerous in the event of an episode of hypoglycemia. Therefore, the glycemic control of diabetic patients is relatively lax, intensive glucose reduction increases the risk of hypoglycemia, and patients do not necessarily benefit. Therefore, if patients have no special circumstances, they can continue to monitor and observe, and do not necessarily need medication.

Therefore, patients with a glycosylated hemoglobin of 6.4% should be screened for a definitive diagnosis of diabetes, well monitored, and whether pharmacologic intervention is needed depends on the patient's specific situation.
If the patient is young and obese, you can also take some metformin to increase the body's sensitivity to insulin, suppress appetite, reduce weight, generally do not occur hypoglycemia, safe and effective. At the same time, pay attention to improve the lifestyle.

Lifestyle intervention is an important aspect of controlling blood glucose levels in patients with disorders of glucose metabolism and diabetes. Whether diabetic or not, it is important to pay attention to, controlling diet, moderate exercise, weight loss in obese people, while paying attention to the control of metabolic abnormalities such as blood pressure, blood lipids, blood uric acid and so on.
For patients with a glycated hemoglobin of 6.4%, it is important not to deliberately diet thinking to control diabetes, and to prevent hypoglycemia from occurring when blood glucose is too low.
Glycated hemoglobin is the combination of hemoglobin and sugar substances inside the blood, the process is irreversible, that is, once the formation of glycated hemoglobin, can not be broken down into hemoglobin and sugar, and glycated hemoglobin metabolism is very slow, so theIt is used clinically as the gold standard for measuring glycemic control. It is also used as one of the tests to diagnose diabetes.
If you find it useful, can you support it by clicking follow?
The normal reference range for glycosylated hemoglobin is between 4% and 6%.
Its findings may be related to
①Blood glucose concentration

The higher the blood glucose, the more opportunity there is for hemoglobin to bind to blood glucose, and of course the more glycated hemoglobin you end up with.
(ii) the length of time that hemoglobin and blood glucose are bound to each other
This is a chemical reaction, we know that chemical reaction is affected by time, temperature, catalyst, etc. Temperature and catalyst can not be changed in the body, so the combination of the reaction time becomes a key factor, the longer the time, the more glycated hemoglobin will be produced, and vice versa!
③Time to draw blood
Generally at 3:00 am, 4:00 am blood glucose is at its lowest point, the most prone to hypoglycemia, but generally will not be lower than 3.3 mmol / l. Subsequently, the secretion of glucocorticoids increased, blood glucose will also slowly rise!
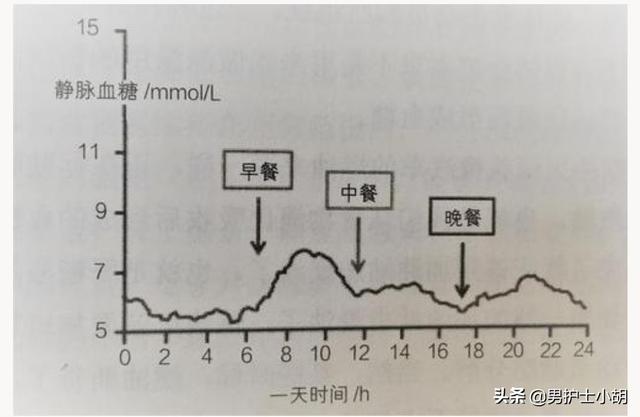
④Insulin use or not
Whether or not you use insulin is about blood glucose levels, and insulin and hemoglobin compete for binding to blood glucose. It also affects the overall glycated hemoglobin level!
Simple correspondence between glycosylated hemoglobin and blood sugar
it's worth noting that...Glycated hemoglobin and blood sugar are two different indicators.
Glycated hemoglobin is a measure of glycemic control over time, whereas blood glucose is real-time blood glucose at a point in time. There is a causal relationship between the two, but there is a difference between the two in their quantitative relationship. It can indirectly reflect the average blood glucose value over a short period of time!
The following chart shows the approximate relationship between glycated hemoglobin and average blood glucose
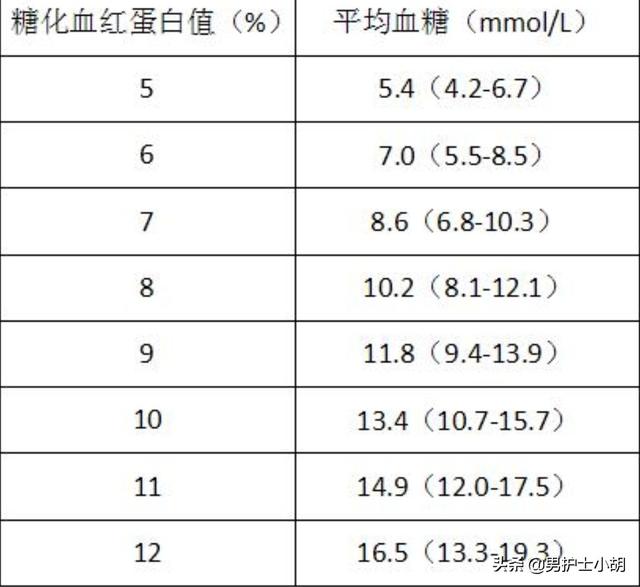
Glycated hemoglobin is 6.4%, is this normal?
Slightly high relative to standard normal values, but the deviation is not large, so it could be the result of the influence of external factors such as
Excessive consumption of sugar in recent times
One of the factors affecting glycated hemoglobin is the blood glucose concentration, which is affected by overeating, eating too many sweets, irregular eating, and prolonged hyperglycemia.
②Time to draw blood
Blood should be drawn in the morning on an empty stomach, without strenuous exercise, and without insulin, as far as possible, to ensure stable and accurate results!
Suggestion:Because it is slightly higher than the normal value of 6%, it is very likely that external factors interfere. Therefore, try to exclude the interference of external factors to re-measure, and record the blood glucose value during this period, so that it is easy to analyze and compare!

This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.