Must a diabetic's blood sugar be kept within the normal range? What happens if it's a little on the high side?
With the changes in dietary structure and lifestyle, our metabolism has also changed significantly compared to before, and elevated blood glucose is one of the more significant changes, dramatically increasing the incidence of glucose intolerance abnormalities and diabetes mellitus. After the diagnosis of diabetes, the first task is to control blood glucose, then, diabetic patients' blood glucose must be controlled within the normal range? Next, Medical Senlution will analyze it for you.
The purpose of controlling blood glucose in diabetic patients is twofold: one is to prevent acute complications caused by the rapid rise of blood glucose, such as diabetic pain acidosis and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state; the other is to prevent chronic damage caused by prolonged hyperglycemia to various tissues and organs, such as diabetic nephropathy, cardiovascular disease, cerebrovascular disease, diabetic retinopathy, diabetic neuropathy, and diabetic foot. For diabetic patients' blood glucose control, there is no requirement for diabetic patients to control their blood glucose in the normal range, but in the appropriate range.
So, what is the right amount to keep our blood sugar under control?
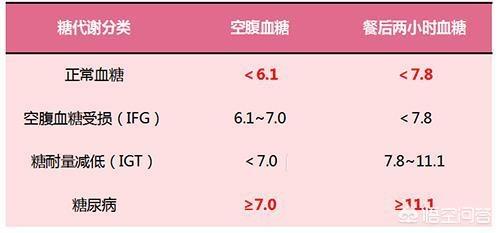
Normally, our fasting blood glucose range is 3.9-6.1 mmol/L and our 2-hour postprandial blood glucose range is 4.4-7.8 mmol/L.
For young diabetic patients with short duration of disease, no complications, long life expectancy, and no hypoglycemic episodes, fasting blood glucose control of less than 6.5 mmol/L, or even less than 6.0 mmol/L, and postprandial 2-hour blood glucose control of less than 8.0 mmol/L are required;
- For middle-aged diabetic patients with a long duration of disease, few complications, long life expectancy, and no or few hypoglycemic episodes, fasting blood glucose control of 7.0 mmol/L or less and 2-hour postprandial glucose control of 10.0 mmol/L or less are required;
- Fasting blood glucose can be relaxed to 8-10.0 in older diabetic patients with long disease duration, many complications, short life expectancy, and frequent hypoglycemic episodesmmol/L, with a relaxation to 12.0 mmol/L for 2-hour postprandial glucose.
So what happens when your blood sugar is a little high?
Our main goal in controlling blood glucose is to reduce or delay the occurrence of related complications and improve the quality of life in later stages. However, it should be noted that many diabetic patients have already developed related complications, such as kidney damage, coronary atherosclerosis, carotid atherosclerosis, lower limb atherosclerosis, diabetic neuropathy, etc., by the time diabetes is detected. Some patients were found early and intervened early to control their blood glucose in the appropriate range, which prevented the aggravation of the lesions or slowed down the progression of the disease; some patients were found late and even directly consulted with complications of diabetes mellitus, such as diabetic nephropathy, coronary heart disease and stroke. Therefore, if the blood glucose is higher than the required control range for a long time, the incidence of corresponding complications will be increased or the progress of complications will be accelerated at a later stage.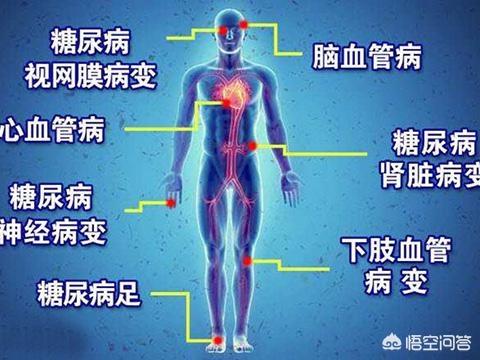
In summary, blood glucose is not meant to be controlled in the normal range; control in the appropriate range is appropriate for different populations, and hypoglycemia should be prevented while complications are prevented or delayed. If blood glucose is chronically high, it will increase or accelerate the progression of complications.
Thank you all for reading!
Welcome to learn more about medical senlution and health knowledge!
Note: The content of the text is intended to be used as health science only, and is not intended as medical advice or opinion, and does not qualify as medical guidance.
We usually emphasize that diabetes mellitus to control blood glucose standard, is due to diabetes mellitus long-term hyperglycemic state can easily cause damage to the important organs of the body can occur a variety of chronic complications, a variety of chronic complications, such as coronary heart disease, stroke and other cardio-cerebral vascular disease, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic peripheral neuropathy, diabetic foot, etc., these chronic complications serious impact on diabetes mellitus patient's quality of life, so the glucose control to meet the standard is to delay the occurrence of these chronic complications as much as possible. Therefore, the goal of blood glucose control is to delay the occurrence of these chronic complications as much as possible.
The exact value of so-called blood sugar compliance also varies from person to person and is not exactly the same.
The level of glycemic compliance is individualized and is assessed based on a comprehensive assessment of age, how many years the diabetes has been present, whether there is a combination of other organ diseases and the severity of diabetes-related complications, the expected duration of survival, and the occurrence of hypoglycemic reactions.
Glycemic control in most populations is recommended to be <7.0 mmol/L for fasting, <10.0 mmol/L for two hours after meals, and <7.0% for glycosylated hemoglobin.
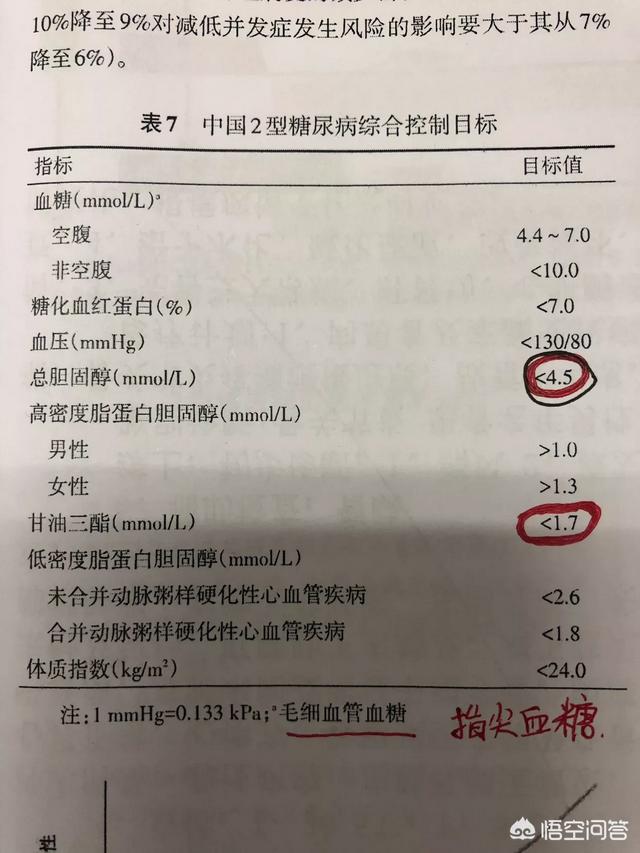
- If you are young, have a long expected survival time, have no diabetic complications or other organ pathologies, and have no hypoglycemic response, then tighter control of blood glucose levels is recommended, specifically, fasting blood glucose <7.0 mmol/L, two-hour postprandial blood glucose <10 mmol/L, and even the closer the blood glucose level is to normal, the better; and the indicator of the response to the level of long-term glycemic control, glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), is <6.5 percent.
- For those who are older, with comorbid diabetic complications and other cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, with a long duration of diabetes, with a short expected survival time, and with significant hypoglycemic reflections, then the glucose level can be appropriately relaxed, with a fasting glucose <10 mmol/L, a two-hour postprandial glucose <13 mmol/L, and a glycated hemoglobin <8.0%.

I am a medical doctor, a resident, specializing in the popularization of medical knowledge for the benefit of human health, if you want to know more, please pay attention to me, have questions can be left a message, will respond!
You must not know that November 14th is World Diabetes Day, which was established to tell people that diabetes has become a world problem, according to statistics, as of 2018, the estimated prevalence of clear and clinically diagnosed diabetes in a sample of adults aged 18 years and older in China is 11.6%, or about 113.9 million people, which means that there is one diabetic out of ten people. This shocking statistic tells us that diabetes has become a major public health problem in our country.
So many patients must ask: after diabetes, blood sugar must be reduced to the standard range?
- 1. It is of course best if the diabetic's blood sugar can be brought down to within the standard range:Blood sugar fluctuations are inevitable during our blood sugar control process. The purpose of our controlling blood sugar and lowering sugar is not only to simply lower the blood sugar, but also to slow down the progression of the disease as much as possible, prevent complications, and improve the quality of patients' survival. So for patients with different conditions, the standard for lowering sugar is different.
- 2. Patients at a younger age:Patients around 50 years of age and below, with relatively low age of onset, require strict adherence to standard glucose lowering. Fasting requirement is 6.1mmol/L or less, 2-hour postprandial blood glucose should be less than 7.8mmol/L, and peak blood glucose should be less than 11.1mmol/L. Because China's per capita life expectancy has reached more than 70 years old, and in some areas it has already exceeded 80 years old, the life expectancy of patients with younger ages is long, and strict glycemic control and delayed development of the disease will not affect the life expectancy of patients, and they may even live up to Ninety-nine is not a problem.
- 3. Patients with diabetes combined with other diseases:Some patients in addition to diabetes will be combined with hypertension, coronary heart disease, cerebral infarction and other diseases, this time the main focus on the treatment of the combined disease, can be appropriate to relax the blood glucose to fasting 7 mmol / L, 2 hours after the meal 9 mmol / L. Because of the main goal of these patients is to treat other diseases, blood pressure, prevention of thrombosis, lowering lipids, and other treatments for the combined disease is greater than the benefit of lowering the low blood glucose.
- 4. Elderly patients:Some elderly diabetic patients over 80 years of age, or a little younger, but has occurred heart, brain, kidney, vascular disease, can be fasting blood glucose can be relaxed to 9mmol / L, 2 hours after meals 12mmol / L. Even a little higher is acceptable, because the elderly patients are mainly to improve the quality of life is the focus of treatment.
Diabetes is dangerous mainly because of "high blood sugar", so what are the disadvantages of having high blood sugar?
- 1. Severe water loss:When high blood sugar causes the body to increase the amount of urine, the body will excrete more urine sugar, and a large amount of urine will cause the body to lose water.
- 2. Electrolyte disorders:In hyperglycemia, heavy urination not only loses water but also takes electrolytes out of the urine, disrupting electrolytes.
- 3. Brain dysfunction:Water flows from inside the cell to outside the cell during hyperglycemia, and this leads to cellular water loss, and when brain cells lose water it causes brain dysfunction, which clinically manifests itself as coma.
- 4. Wasting away:Since sugar in the urine increases during hyperglycemia, glucose is not well utilized by the body, so body fat and protein are broken down and as a result, you become thin and lose weight.
- 5. Multiple organ dysfunction in the human body:Elevated blood sugar can cause the body's vascular, nervous, and renal systems to develop give dysfunction, leading to kidney disease, hemorrhages in the fundus, and degeneration of nerve cells.
- 6. Multiple atherosclerosis of the heart, brain, and lower extremities:Hyperglycemia is often accompanied by hyperlipidemia, and atherosclerosis of the coronary arteries, cerebral blood vessels, and lower extremities occurs earlier and more severely than in normal people.
- 7. Distant complications:Examples include stroke, diabetes, coronary heart disease, and sudden death.
So how exactly is it best to control your blood sugar?
I. Keep your mouth shut:
1. Staple food should be rationed, coarse and fine to match, whole grains, mixed legumes accounted for 1/3.
2. Eat some vegetables and fruits in moderation, with a variety of types and colors.
3. You can also eat some fish and poultry, eggs and livestock in moderation, but limit processed meats.
4. But also to ensure that dairy beans every day, snacks plus meals reasonable choice.
5. Eat a light diet, drink plenty of water, and quit smoking and drinking.
II. Spread your legs:
In the absence of contraindications to exercise, it is recommended that at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise be performed each week, for example, you can exercise five days a week for 30 minutes each time. Moderate-intensity means exercising a little bit hard, with heartbeat and breathing accelerated but not rushed, for example: playing tai chi, cycling at a slow speed, playing table tennis or badminton. One hour after meals, do not exercise on an empty stomach, and can not participate in intense sports: such as speed running, jumping rope, skiing and so on.
III. Uncontrollable use of drugs:
If the blood sugar fluctuation is large, you can choose drugs reasonably under the guidance of the doctor to reduce the harm of blood sugar on the human body. At present, the new hypoglycemic drugs are sodium-glucose cotransporter protein inhibitors such as dagliflozin, which have good effects, and patients who are in a position to do so can choose to use them.
IV. Reduce your stress:
When you are stressed, the adrenal glands will secrete adrenaline, which causes the body to become excited, leading to a rise in blood sugar and increasing the burden on the pancreatic islet cells. Therefore, you should learn to reduce stress, for example, deep breathing is a simple and easy way to reduce stress. At the same time, a good mood is one of the secrets of stable blood sugar, if sugar users can maintain a calm and cheerful mind, it is very helpful to control blood sugar.
Final Summary: For blood glucose control, I advocate individualization, which means that every diabetic should keep their blood glucose within a range that suits them. And in addition to relying on medication, lowering sugar also requires dietary control and strengthening exercise. It is very simple to say the truth, but it is difficult to insist on doing it. I hope that every diabetic, can persistently adhere to the treatment, slow down the progress of the disease, and enjoy a happy life.
Purely hand-typed, it is not easy, if you feel that the writing can also be rewarded a praise, point a concern, if you have any questions can be left below ......
Hi, Speak Sugar Every Day is happy to answer your questions!
Do diabetics have to keep their blood sugar in the normal range?
The answer is no. A diabetic's blood sugar does not have to be strictly controlled within the normal range, but should be considered on an individual basis.
1. Fasting blood sugar
For young and middle-aged people with shorter duration of illness or younger age, the closer to normal the fasting blood glucose is, the better, the better to control 3.9mmol/L~6.1mmol/L; ② For middle-aged and elderly patients with longer duration of illness, the control standard of fasting blood glucose can be appropriately relaxed, and controlled within 7mmol/L as far as possible.
③ For older patients (over 60 years of age), this can be defined by dividing the age of the older glucose patient by 10. For example, if you are 80 years old, a control of about 8.0 mmol/L is sufficient.
2. Post-meal blood sugar
In general, postprandial blood glucose should be controlled below 7.8 mmol/L. This standard should be strictly enforced in patients who have not been ill for a long time and in young glycosurgeons.
For those middle-aged and elderly diabetics who have a longer course of disease or are older, and may have suffered from other chronic or acute complications, the criteria can be appropriately relaxed, and in the absence of hypoglycemia, it is recommended that postprandial blood glucose control is below 10.0 mmol/L.
Therefore, the standard of blood glucose is not fixed and should be relaxed appropriately according to the actual situation of the patient.
What happens if my blood sugar is a little high?
Regardless of age, it is not a big problem for all diabetics to have their blood sugar a little on the high side once in a while. Blood sugar itself is variable, but if it is a little high for a long time, and exceeds the normal range for a long time, then it is certainly not conducive to the control of the disease, and over time, it can also cause complications to come early.
To determine whether a diabetic's blood glucose is well controlled, it is important to look at whether the blood glucose is in the normal range (including fasting glucose, postprandial glucose, and random glucose), but also whether the blood glucose has remained stable.
Therefore, diabetics should try to keep their blood sugar within a certain range so that they can delay the onset of complications and live as long and healthy as normal people!
Blood sugar is essential to maintain the function of our body tissues and organs, and can play a role in raising energy and participating in metabolism. Normally, our blood sugar is within a fixed range, when blood sugar increases or decreases, it may lead to the occurrence of diabetes, hypoglycemia, etc. I hope you pay attention to it.
The normal blood glucose range of our body is: ① Fasting blood glucose: should be ≧3.9mmol/L and <6.1mmol/L; ② Two-hour postprandial blood glucose: should be <7.8mmol/L. Diabetes needs to be considered when we have fasting blood glucose more than 7.0mmol/L and / or fasting blood glucose more than 11.1mmol/L.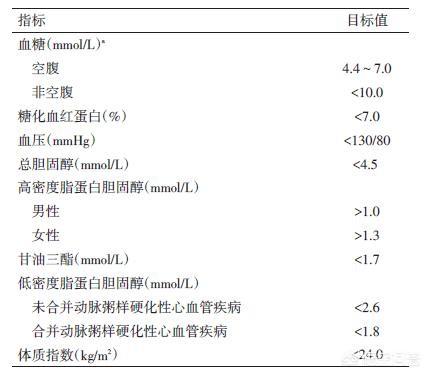
For diabetic patients, long-term high blood glucose level will cause damage to our tissues and organs, and in the long run, it may even lead to the occurrence of target organ complications such as kidney, eyes, blood vessels and nerves. Therefore, once diabetes is diagnosed, it needs to be treated actively and formally, paying attention to reasonable diet, appropriate exercise, weight control, and the regular use of hypoglycemic drugs, as well as paying attention to monitoring the changes in blood glucose levels and regular review.
We recommend that everyone should at least keep their fasting blood glucose to 7.0 mmol/L or less, and their two-hour postprandial blood glucose to 10.0 mmol/L or less. For younger, shorter disease duration, no complications, long life expectancy, and no hypoglycemic episodes in diabetic patients, the control goal will be more stringent. It may also be relaxed for diabetic patients who are older, have a long disease duration, many complications, short life expectancy or frequent hypoglycemic episodes.
If you have any questions, please feel free to leave a comment at the end of the article to discuss. Follow the author for continuous daily updates on health knowledge.
Diabetics are required to control their blood glucose within a certain range, which means that the standard of blood glucose control varies from person to person and is often referred to as the ideal range, the lax range, the
Establishing a glycemic control range is based on the principle of safety and also requires that the patient minimize the chance of complications within this glycemic range.
Whereas normoglycemia is the blood glucose standard for non-diabetics, that is, a fasting blood glucose of 4.0-6.1 mmol/L and a postprandial blood glucose of less than 7.8 mmol/L, for diabetics, this range is relatively narrow and difficult to achieve, and there is a risk of hypoglycemia.
So for diabetics, it is not required to keep their blood sugar in the normal range.
The ideal range for diabetic control is 4.4-6.1 mmol/L for fasting and less than 8.0 mmol/L for postprandial glucose.
This blood glucose standard is usually required for patients with shorter disease duration, younger, and without complications, because it is important to lower blood glucose as much as possible to maintain it in the normal range, so that the patient's chances of developing complications are smaller. However, for appeal reasons, according to the recommendations of the Chinese guidelines for the prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus, the patient's blood glucose control range is usually set as the ideal range, that is, fasting 4.4-6.1 mmol/L, postprandial blood glucose is less than 8.0 mmol/L, which indicates that the patient's blood glucose control is very ideal.
The relatively loose control criteria are 4.4-7.0 mmol/L for fasting and less than 10.0 mmol/L for postprandial glucose.
This blood glucose standard is the standard of control for most diabetics, and this blood glucose profile ensures that the patient's glycosylated hemoglobin is below 7%.
There is a misconception in the treatment of diabetes, and this is something that has happened to both patients and certain doctors. It is that if diabetes is detected, it's all about trying to get the blood sugar to normal levels.
What can you do to accomplish this, increase the dosage of your medication and tighten your diet.
But this has the additional consequence of hypoglycemia, which is actually far more harmful to the body than hyperglycemia. This is because if there is a chronic lack of blood sugar, it can cause damage to the organs. This includes brain cell damage, cardiovascular damage and so on.
Therefore, now for the early detection of diabetes, will ask the blood sugar control as far as possible to the normal level, because this case, usually the blood sugar is not particularly high, so through the diet and strengthen the exercise, and then with appropriate medication, it is possible to achieve a reasonable level of blood sugar.
In the case of diabetics with a longer history of the disease, this criterion is relatively relaxed.
There is also to be judged according to the state of the patient after the control of blood glucose, if the blood glucose control to the normal level after the obvious hypoglycemic reaction, even if the diabetic patient is just found, should not be excessive lowering of blood glucose, otherwise there are still adverse effects.
Glucose in the blood is known as blood sugar. Glucose, like oxygen, is an essential energy supplier for us to have enough energy for our cells to work properly. When hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia is monitored, it indicates that there is some dereliction of duty on the part of the pancreatic islets, the blood sugar command, and human intervention needs to be initiated.As long as our blood sugar remains stable, whether by the insulin officer or by our own behavior, oral hypoglycemic drugs or exogenous insulin, we are in a healthy state of blood glucose and will not harm our nerves or blood vessels. In other words, we have succeeded in getting rid of the "diabetes" label by our efforts.
There are many factors that make our blood glucose go up and down, including diet and glucagon that raise blood glucose, and exercise, self-insulin and exogenous insulin that lower blood glucose. The body's blood glucose homeostasis is like a balance, glucose-raising factors and glucose-lowering factors are like weights on both sides of the balance, when the weights on both sides are equal in weight, the balance is balanced, i.e., our blood glucose is in a stable state, and our blood glucose stays healthy.
We live a colorful life, eating, drinking and playing are essential, self-insulin, exogenous insulin, hypoglycemic drugs to help us cope with a variety of meals, plus meals, eating is the weights of sugar, self-insulin, exogenous insulin, hypoglycemic drugs and play is the weights of lowering sugar, the scales are all the time the dynamic balance of regulation.
Blood glucose values, curves are just the result of a balance, behind each blood glucose result there is a tug-of-war, that is, a confrontation between the weights of the sugar-raising weights and the weights of the sugar-reducing weights, when the abnormal blood glucose appears, first check the weights of our balance, which side is more, which side is less, and analyze the reasons for the victory or defeat of each confrontation. After finding the root cause, by adding or subtracting weights artificially, theBy mastering the skill of blood sugar balancing and rebalancing the scales, blood sugar is once again restored to a healthy state.
The weights on both sides of the scale change all the time, and blood glucose is always undergoing dynamic balance adjustment, combined with different people's gastrointestinal absorption speed is different, different food digestion and absorption time is different, and different people's insulin onset of action, duration of action is different, so postprandial blood glucose varies a lot, and blood glucose at a certain point is far from being able to represent the state of postprandial blood glucose.
Blood sugar health status is a macro-whole, not micro-point blood sugar, so we need to adhere to the regular monitoring of blood sugar, pay attention to the blood sugar compliance rate, high blood sugar, low blood sugar, average blood sugar, blood sugar fluctuations, from the five dimensions of the overall look at the blood sugar is good or bad.

For more practical tips on diabetes
Want to read original diabetes education articles by doctors
Please pay attention to the online guidance sugar control pioneer - Micro Sugar
Appropriately relaxed based on age, I am in control of myself by not going over the top on either end and never forcing myself by normal human standards!
Fasting is no more than 7, after the meal is no more than 11. If breakfast is late, one is to delay lunch, the other is to eat only vegetables and not the main course, and then eat again at dinner. In other words, two main meals a day, never take medicine (more than ten years as one day)!
Blood sugar control does not mean that you do not have complications, blood sugar control to relax a little, does not mean that you must have complications, the key to see can not recover, the original I also found out that diabetes, think the sky is falling, and then take drugs and injections have not been good, meal before all 18 disease, hair disease also have, in desperate times encountered a good doctor, I four months on the recovery reversal, I live a normal life, and I have to find a good doctor, I have to find a good doctor. I want to share this experience with you, it is important to find the right doctor, I hope it can help you.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.