What are the dangers of frequent hypoglycemia in diabetics?
Dietitian Sugar is here to answer. This is a good question, diabetics not only to prevent high blood sugar, but also to pay attention to and prevent hypoglycemia. Because the danger of hypoglycemia is no less than high blood sugar, even more fierce than high blood sugar. Diabetics have poor blood sugar regulation, and hypoglycemia can be fatal. In the hospital internship, we have seen a lot of hypoglycemic coma because of the diabetic patients were sent to the hospital for resuscitation.

When are diabetics prone to hypoglycemia?
1. Too little staple food.Staple foods are rich in carbohydrates, which are the basic substance for energy supply. When the intake of carbohydrates is insufficient, it is easy to hypoglycemia. Here it is recommended that sugar lovers to coarse grains and potatoes as the main food, such as - oats, buckwheat, potatoes, corn, etc., they are rich in dietary fiber, digested and decomposed more slowly in the body, the blood glucose does not rise quickly, not easy to occur hypoglycemia. On the contrary, if you eat too fine, such as eating a bowl of white rice porridge, not only the blood sugar soars fast, and when digested, it is also easy to hypoglycemia.
2. Inappropriate use of medication.For example, overdosing on medications and overdosing on insulin injections can cause hypoglycemia.
3. Excessive exercise.Or exercise at inappropriate times. The best time for diabetics to exercise is half an hour to an hour after a meal, which can reduce the peak of postprandial blood glucose, and is also not prone to hypoglycemia. And exercise in the fasting time, it is easy to have hypoglycemia, which is a taboo for sugar lovers.
4. Excessive alcohol consumption.Drinking alcohol will cause a decrease in blood glucose for a short period of time, but drinking alcohol is damaging to the pancreas and is not recommended for sugar users, especially if you drink on an empty stomach, which is more likely to lead to severe hypoglycemia.
5. Irregular diet.Too much time between meals is also an important factor that leads to hypoglycemia. Therefore, meals must be eaten on time, it is best to adopt a meal portioning system and learn to add meals between meals, which is an important measure to avoid hypoglycemia.
I hope that the answer to the sugar can help you, more diabetes diet and complications, welcome you to send us a private letter to the keyword "blood sugar", access to e-books and learning materials, you can also find a dietitian to help.
At one time or another in our lives, we will experience "low blood sugar", but if we can eat in time, we will not be left with any physical or intellectual disability. For diabetics, however, the dangers of hypoglycemia are different.It may cause convulsions, coma and even death, increasing the risk of death, and the dangers of hypoglycemia, as opposed to hyperglycemia, are quick and vicious, often measured in minutes or hours。Some experts believe that one severe hypoglycemia brings harm to the body of a diabetic patient will offset the benefits of a lifetime of controlling high blood sugar, which shows that the harm of hypoglycemia is much greater than that of high blood sugar. In addition, older diabetic patients are more likely to experience hypoglycemia than younger patients, so hypoglycemia deserves more attention from diabetic patients.For this reason, I have summarized some low blood sugar prevention and first aid methods for your reference.

I. Recognizing hypoglycemia
In normal people, blood glucose is maintained within a fairly narrow range through the regulation of the liver, nerves and endocrine system. Whether fasting or postprandial blood glucose, its low limit should generally not be lower than 3.3 mmol/l. Hypoglycemia occurs when the blood glucose value is lower than 2.8 mmol/l. However, it is worth noting that for diabetics, a blood glucose value of less than 3.9 mmol/L is hypoglycemia. Typical symptoms of hypoglycemia are mainly hunger and panic, profuse sweating, fatigue and weakness, pallor, lack of concentration, dizziness and headache, etc. If the blood glucose is even lower, or if the duration of persistent hypoglycemia is even longer, the patient will experience mental and consciousness disorders, such as not being able to find a place, not being able to recognize people, and even babbling, temperamental and violent tendencies, etc. If the condition is more serious, lethargy, convulsions, or even coma will occur and be life-threatening.

In addition, long illness, weak, unresponsive, long duration of diabetes, combined with a variety of diabetic complications, especially vegetative neuropathy, often reach the biochemical standard of hypoglycemia, but there is no detectable symptoms, or the symptoms are very mild and do not cause the patient's vigilance. And often asymptomatic hypoglycemia can not be handled in a timely manner, it is easy to induce life-threatening cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases, such as angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, stroke, and even more so in the sleep due to the lack of awareness and coma, so the long course of diabetes patients, especially those with a combination of multiple complications, should be equipped with a blood glucose meter, regular monitoring of blood glucose.
II. Prevention of hypoglycemia
For diabetic patients, the occurrence of hypoglycemia mainly did not grasp the three principles of diet, exercise and medication, such as not eating enough, when the time to eat did not eat, when the time to add a meal did not add a meal, or the use of medication is unreasonable, or increased exercise did not adjust the diet and medication in a timely manner, or drinking too much alcohol and so on, so all diabetic patients should provide their own blood glucose meter, regular monitoring of blood glucose. Therefore, all diabetic patients should have their own blood glucose meter and monitor their blood glucose regularly. In addition, some drugs are strong, such as eugenol or thirst-quenching pills containing eugenol, etc., which have strong hypoglycemic effect, which is their strength from the point of view of hypoglycemia, but the abuse of these drugs is one of the main causes of hypoglycemia. So in order to prevent hypoglycemia in diabetic patients, the specific methods are as follows:
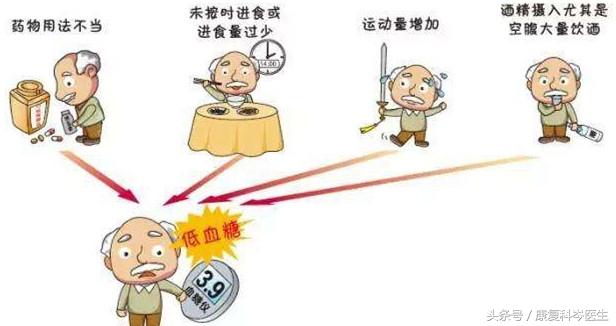
1、Provide your own blood glucose meter and monitor your blood glucose regularly: diabetic patients should develop the habit of monitoring their blood glucose on a regular basis, especially patients who apply long-acting or intermediate-acting insulin, oral long-acting hypoglycemic drugs should pay more attention to monitoring the changes in blood glucose, and it is best to record the occurrence of hypoglycemia or hyperglycemia of the specific time (specific to a few points of the time), the amount of food, types of food, exercise, the use of medication and so on. Find the pattern of change of their blood glucose, so as to be prepared.
2, diet, exercise, medication should be regular: diabetes treatment pay attention to the diet, exercise, medication and the regularity and mutual cooperation, should be regular and quantitative, can not be arbitrary. In addition, diabetic patients are best to eat on time, such as can not be best to eat some portable fast food or other food that can get energy, such as cookies.

3. Recognize symptoms of hypoglycemia: as in the previous section. In addition, hypoglycemia often occurs at the peak of the action of hypoglycemic drugs, after activity, before meals, before bedtime and at night. One should keep an eye out for symptoms of hypoglycemia, and can test blood glucose at these key points, and need to add meals appropriately and reduce the amount of activity if necessary.
4, be prepared: as the saying goes, "only a thousand days to be a thief, not a thousand days to prevent thieves", even if we do everything, hypoglycemia may occur, so usually diabetic patients are best to carry two things, in order to facilitate the treatment of hypoglycemia: one is a fast food or candy and water; the other is the patient card, the card states that I am a diabetic Patients, and indicate the name, age, home address and contact phone, usually use the drugs and hospitals, medical records, etc., and in the card can be made as follows: "I am a diabetic, if you find that I am behaving strangely or confused, may be the occurrence of hypoglycemia, please as soon as possible in my coat pocket candy in my mouth, and according to the address and phone number described on the card to contact the contact person, and try to send a low blood sugar, and also to send a low blood sugar. phone number with the contact person, and also try to send me to the hospital for first aid or call 120, thank you."

Third, low blood sugar how to first aid
Hypoglycemia will not only pose a threat to the patient's health and life safety, but may also cause rebound hyperglycemia, leading to fluctuations in the condition, so with hypoglycemia, it is important to detect and treat it in time. The details are as follows:
1, for the occurrence of general hypoglycemic symptoms of patients, should be measured blood glucose, if hypoglycemia, it should be quickly eaten any can make the patient quickly out of the symptoms of hypoglycemia of food, such as cookies, candies, bread, bread, honey, sugar water, sugar-sweetened beverages, or even white sugar and so on. If it still fails to relieve can be eaten again, if still can not be relieved, then need to immediately seek medical attention. It is worth reminding that people with diabetes need to control their diet throughout their lives, only when hypoglycemia occurs without control, do not be afraid of eating candy affect blood sugar, so that blood sugar increases. In addition, if you can not measure blood glucose due to conditions, whenever symptoms of hypoglycemia appear should be treated as hypoglycemia first.

2、For patients who have already experienced hypoglycemic coma, they should call the emergency number at the first time and seek medical treatment in time. Do not try to eat anything at this time, so as not to accidentally attract choking. Of course, if you are experienced, you can also put a small spoonful of sugar under the patient's tongue, or a piece of sugar cubes, but must be closely monitored to prevent accidental inhalation.
3、After recovering from hypoglycemia treatment, it is best to observe for a period of time while searching for the causes of hypoglycemia, and take preventive measures in a timely and targeted manner.
In conclusion, the danger of hypoglycemia is much greater than that of hyperglycemia, and it is an acute complication of the diabetes treatment process, which deserves vigilance and prompt treatment when hypoglycemia occurs.。
Reference: Internal Medicine, edited by Ge Junbo and Xu Yongjian, p757~761
Image source: Internet, please contact to remove if inappropriate.
Medical Health Gatekeeper is sharing this for you, ❤ Like, Follow, Retweet for more medical related knowledge, updated daily here!
First of all, we need to know what is hypoglycemia, clinically, the blood glucose value <3.9mmol/L becomes hypoglycemia, <2.8mmol/L is severe hypoglycemia. Hypoglycemia occurs mostly in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus or type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with insulin.
How do hypoglycemic episodes damage us?
- Transient hypoglycemia: Many hypoglycemic episodes are transient and can be cured soon after the episode, but such transient episodes can also lead to transient loss of cognitive function, which seriously affects our life and work, for example, hypoglycemia in drivers can easily lead to car accidents, and construction workers are prone to fall and injuries, and so on;
- Hypoglycemic cardiovascular and cerebrovascular damage: after an episode of hypoglycemia, the body will protectively secrete hormones that elevate blood sugar. The elevation of these hormones will lead to changes in the hemodynamics of the body, thus promoting the formation of vascular atherosclerosis, inducing myocardial ischemia, and even cardiac arrhythmia leading to death;
- Repeated hypoglycemia seriously affects our control of blood glucose, hypoglycemic episodes will make the body abnormal secretion of some hormones that elevate blood glucose, so that the usual glucose-lowering program can not be very good control of blood glucose; hypoglycemic patients will appear panic, palpitations and other manifestations, many patients because of the fear of hypoglycemia, and reduce the use of glucose-lowering drugs on their own, which increases the difficulty of blood glucose control;
- Hypoglycemic Brain Damage: Sugar is known to be the sole source of energy for the brain's tissues, and hypoglycemic episodes can lead to acute damage to brain tissue as well as cognitive dysfunction, and in severe cases, possible dementia;
- Continued unrelieved hypoglycemia may result in convulsions, coma, and even death;

These are some of my personal views on the dangers of hypoglycemia, I think that hypoglycemia is really harmful, so diabetic patients must do a good job of blood glucose management, monitor their own blood glucose, and strictly comply with the diabetes physician for us to formulate glucose-lowering program as well as dietary guidance program.
Hyperglycemia, diabetes is certainly not unfamiliar to everyone, but for hypoglycemia may not be so familiar with the most intuitive understanding is the occurrence of hypoglycemia will faint.
For normal people, the standard for hypoglycemia is <2.8 mmol/L. Patients with hypoglycemia are considered to be in the hypoglycemic category as long as their blood glucose value is ≤3.9 mmol/L.
Hypoglycemia is a common complication of diabetes and there are two types of hypoglycemia:
(1) Adrenal increase type.Often seen when blood sugar drops rapidly, this hypoglycemia is characterized by rapid heartbeat, profuse sweating, trembling or shivering, hunger, blurred vision, dizziness, weakness, and numbness of the mouth, lips, or tongue.
This is caused by the increased secretion of large amounts of stress hormones, especially adrenaline, after hypoglycemia, which is mostly perceived by the patient and can be determined by family members and friends with knowledge about diabetes.
(2) Central hypoglycemia.CNS manifestations include confusion, abnormal behavior, visual disturbances, rigidity, coma, and seizures. Hypoglycemic coma is often accompanied by decreased body temperature.
(3) Hypoglycemia in children.Hypoglycemia manifests itself differently in children than in adults, and it all depends on careful observation by parents. Pallor, cold sweat, weakness, inability to concentrate, disobedience, bedwetting, etc.
Hypoglycemia is harmful to the human body, especially to elderly patients, hypoglycemia is more harmful than high blood sugar
The main dangers of hypoglycemia are:
1. When hypoglycemia occurs, the glucagon hormones in the body, such as adrenaline, glucocorticoid, glucagon and growth hormone, increase, resulting in fluctuations in blood sugar and aggravation of the condition.
2, long-term repeated severe hypoglycemic episodes can lead to irreversible damage to the central nervous system, causing the patient's personality changes, mental disorders, dementia and so on.
3, hypoglycemia can also stimulate the cardiovascular system, promoting arrhythmia, myocardial infarction, stroke and so on.
4. Hypoglycemic coma left undetected for too long can be life threatening.
Therefore, you must usually eat on time, do not often insist on working on an empty stomach, and there is also the fact that the elderly need to be taken care of by their family members to prevent the occurrence of hypoglycemia fainting.
Diabetic hypoglycemia occurs when a diabetic uses insulin or medication to control the disease, which can easily lead to too much insulin and not enough glucose in the body.
The Dangers of Diabetic Hypoglycemia
Usually, hypoglycemia does not cause death.But if low blood sugar is ignored for a long period of time, it can cause a person to lose consciousness,Seizures, severe and potentially fatal. This is usually caused by the brain's inability to get enough glucose to maintain normal function.
The most important thing you can do to avoid the serious dangers of hypoglycemia is to recognize the signs of hypoglycemia and replenish glucose in a timely manner.
1. Signs of diabetic hypoglycemia include:
- Shudder;
- Sweating;
- Anxiety or nervousness;
- Hunger;
- Dizziness;
- Irritable or temperamental;
- Headache.
2. CautionNocturnal symptoms
Hypoglycemia may also occur during sleep, and patients may wake up with the following symptoms:
- Heavy sweating, resulting in damp bedding;
- Nightmares;
- Fatigue, irritability, waking up confused.
3. Serious symptoms
If diabetic hypoglycemia is left untreated, serious symptoms may occur:
- movementsClumsy or jumpy;
- Muscle weakness;
- Difficulty speaking or slurred speech;
- Blurred or double vision;
- Drowsiness;
- Confusion;
- Convulsions or seizures;
- Unconscious;
- Death.
How can I prevent and avoid the dangers of diabetic hypoglycemia?
- Don't skip or delay meal times.If you are taking insulin or oral medication for diabetes, try to keep the timing of each meal and the total amount of food consistent.
- Monitor your blood sugar closely.Regularly measure your blood glucose several times a week or several times a day as needed to ensure that your blood glucose is within the normal range.
- Follow your doctor's instructions, measure the dose of your medication carefully, and take it on time.
- If additional exercise is performedTimely adjustments to the dosage of medication and the amount of food need to be made. How much adjustment depends on the results of blood glucose tests and the type and duration of exercise.
- If you want to drink, remember to put some food on the table first.Drinking on an empty stomach can cause hypoglycemia.
- Record but your own reaction when you experience hypoglycemia.This can help you and your loved ones around you recognize low blood sugar in time to take action.
- Wear a card on your body that records information about your diabetes.So as to help the rescuer to take the right measures in case of emergency.
Because it may be difficult for patients to help themselves when they experience symptoms of hypoglycemia, it is also important to tell close relatives, friends, and coworkers about the symptoms of hypoglycemia and first aid so that they can get help in time.
Tip: Diabetics who are prone to hypoglycemia would do well to carry candy with them; have some fruit juice, honey or jam, glucose tablets, and glucose gel on hand.
The above content is edited and organized by "ask the doctor" for you, want to know more authoritative health knowledge, welcome to pay attention to us!
People with diabetes often experience hypoglycemia during treatment due to medications. Hypoglycemia is when blood sugar is lower than normal. For diabetics, hypoglycemia is diagnosed if the blood sugar is below 3.9 mmol/L. Of course there are some patients whose blood sugar may be higher than this value may also experience symptoms of hypoglycemia.
Symptoms and dangers of hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia can lead to serious discomfort and even life-threatening conditions, and is a significant barrier to achieving blood glucose targets. Repeated hypoglycemia may lead to long-term failure to achieve blood glucose standards, and patients may become fearful, eat a lot to prevent hypoglycemia or reduce the dosage of medication on their own, all of which are not conducive to blood glucose control.
The main symptoms of hypoglycemia areSympathetic excitatory symptoms and central nervous system depressant symptoms。
Sympathetic arousal symptoms are mainly characterized by panic, sweating, hunger, and anxiety.
Central nervous system symptoms include cognitive impairment, altered mental status, convulsions and coma, and even death.

A very famous saying in the field of diabetes treatment is:A single severe hypoglycemic event may offset the benefits of good long-term glycemic control.Therefore it is important to avoid hypoglycemia, especially severe hypoglycemia.
Stratification of hypoglycemia risk level
The hypoglycemia risk level stratification consists of three main tiers and they are:
1,Blood glucose less than 3.9 mmol/LThis value is a blood glucose alert value, in which case it is necessary to take sugar water and have the dosage of hypoglycemic medication adjusted by a doctor.
2,Clinically significant hypoglycemia, a blood glucose value of less than 3.0 mmol/L suggests severe hypoglycemia and is clinically significant.
3,severe hypoglycemiaThere are no specific glycemic thresholds, mainly because the patient will have severe cognitive dysfunction and will need to have measures to help recover from the hypoglycemia, which may be assisted by others or may require intravenous glucose or glucagon to elevate the blood glucose.
Causes of hypoglycemia in diabetic patients
1. The use of insulin or sulfonylurea and non-sulfonylurea insulin promoters can lead to an increase in the amount of insulin in the body. Insulin is the only glucose-lowering substance in the body, and under the action of insulin or drug-promoted secretion of insulin, hypoglycemia can occur if the drug dosage is too large and the amount of insulin secretion is high.
2, in the case of the use of stimulant drugs, if the patient did not eat in a timely manner or the amount of food is too small this, can also appear hypoglycemia.
3. Hypoglycemia can also occur when increased exercise promotes the consumption of ingested energy substances.
4, drinking alcohol can appear hypoglycemia, even severe hypoglycemia, especially some diabetics who drink alcohol on an empty stomach.

5, the application of hypoglycemic drug therapy, if the rate of blood glucose decline is too fast, the hourly blood glucose drop more than 6-8mmol / L, the patient will also appear obvious panic, sweating, etc., the emergence of these symptoms when the patient's blood glucose may not be low, may still be in a relatively high state, but there will be a hypoglycemic situation, which is known as hypoglycemia, insulin therapy to avoid the process of the situation.
To summarize: hypoglycemia occurs during medication, as a result of eating, exercise, incorrect use of medication, and medical personnel. Hypoglycemia may bring some serious consequences and lead to life-threatening situations. In the process of treatment, it is important to know the symptoms of hypoglycemia and how to deal with it, and to avoid the appearance of severe hypoglycemia, it is important to use medication regularly, and to eat and exercise at regular intervals.
I'm Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to learn more quality health knowledge, help please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
 For diabetics, keeping blood glucose as close to the normal range as possible is a lifelong endeavor, and a single severe hypoglycemic event in the process will potentially offset a year, five years, or ten years of hard work lowering blood glucose, and may even cost a diabetic his or her life in an instant, and here's why.
For diabetics, keeping blood glucose as close to the normal range as possible is a lifelong endeavor, and a single severe hypoglycemic event in the process will potentially offset a year, five years, or ten years of hard work lowering blood glucose, and may even cost a diabetic his or her life in an instant, and here's why.
We know that blood sugar is the body's life-sustaining energy substances, like people live must inhale oxygen, no energy supply, various tissue cells occur similar to the performance of 'severe hypoxia', especially the brain nerve is very sensitive to the lack of energy, once in a low-blood sugar environment, it will soon be damaged and function abnormally, the occurrence of dizziness, headache, sweating, trembling, palpitations, pallor, accelerated heart rate and other symptoms. The symptoms include dizziness, headache, sweating, trembling, palpitations, pallor and rapid heart rate. If hypoglycemia is corrected in a timely manner, and the cells will gradually die, drowsiness, loss of consciousness, coma until death, so severe hypoglycemic events are fatal to diabetic patients, much more harmful than simple hyperglycemia.
If hypoglycemia is corrected in a timely manner, and the cells will gradually die, drowsiness, loss of consciousness, coma until death, so severe hypoglycemic events are fatal to diabetic patients, much more harmful than simple hyperglycemia.
Some diabetics may say that diabetes is supposed to be a disease of elevated blood sugar, so hypoglycemia shouldn't occur, right? As a matter of fact, diabetics are more prone to hypoglycemia due to their lack of ability to regulate their own blood sugar:
- Restriction of islet cell function in diabetic patients delays insulin secretion, and patients tend to have preprandial blood glucose that falls considerably below normal.
- Diabetes is treated with insulin injections, too much insulin is used, or the injections are not followed by timely meals, resulting in a significant drop in blood sugar.
- Diabetic patients do not eat on time, their ability to break down glycogen is weakened, can not rely on their own blood sugar supplementation in a timely manner as normal people, thus leading to the occurrence of hypoglycemia. For example, normal people eat on time, hungry for a while on no hunger, because of their own blood sugar up, while diabetics this ability is weakened, can not replenish blood sugar in a timely manner, hypoglycemia symptoms will become more and more serious.

- In addition, it should be noted that diabetic patients due to the existence of long-term high blood sugar, tissue cells of this high blood sugar has produced tolerance, if the blood sugar drop too fast, the tissue cells too late to adapt, there will be symptoms of hypoglycemia, in fact, also belongs to the hypoglycemic reaction, the body will cause damage, should also be avoided.
In short, if the image is a little bit to say, high blood sugar like a slow knife slowly torture people, while low blood sugar like a fast knife will kill people, so diabetics must be strictly prevented from the occurrence of hypoglycemia.
- Diagnostic criteria for hypoglycemia in normal people: blood glucose less than 2.8 mmol/L
- Diagnostic criteria for hypoglycemia in diabetics: blood glucose less than 3.9 mmol/L
I hope this answer can help you, click on the attention of the daily listening to health, together to learn and exchange more health knowledge].
First, we need to know the criteria for hypoglycemia:
- For non-diabetics, hypoglycemia is diagnosed by a blood glucose of <2.8 mmol/L.
•Hypoglycemia is diagnosed in diabetic patients as long as their blood glucose level is ≤3.9 mmol/L
Brain energy supply: blood glucose, ketone bodies. The brain has no glycogen reserves, cannot utilize free fatty acids, and ketone bodies take time to produce, so it is dependent on blood glucose.Even when hypoglycemic, the CNS still requires 6g of glucose per hour.
Neurologic damage caused by hypoglycemia depends on: the degree of hypoglycemia, its duration, and the responsiveness of the body.
Short-term hazards of hypoglycemia:
(1) Mild to moderate hypoglycemia (2.8-3.9 mmol/L):
a. Severe hypoglycemia due to inadequate treatment;
b. Insufficient supply of energy to the cells of the body.
(2) Severe hypoglycemia (less than 2.8 mmol/L).
a. Causes impairment of consciousness;
b. Creates a risk of coma or even death.
Long-term dangers of hypoglycemia:
(1) Mild to moderate hypoglycemia (2.8-3.9 mmol/L)
a. Affects nerve function;
b. Affects vascular function.
(2) Severe hypoglycemia (less than 2.8 mmol/L).
a. Affects central nervous system function;
b. Cardiovascular effects.
So, it is important to prevent hypoglycemia.Prevention of hypoglycemia is more important than treatment, find the right cause and avoid it in time.
If you have any questions, you can leave them in the comments section and I'll respond when I see them.
The above answer is provided by Ms. Song Mingyue, a registered dietitian of MicroSugar

Hypoglycemia in diabetes: three common conditions, and the mechanisms behind them.
One, diabetics are most likely to experience hypoglycemia in the following three situations
First, insulin is injected and then not ingested in time to replenish blood sugar.
This is when a person is susceptible to a hypoglycemic reaction due to the sudden hypoglycemic effect of insulin.
Second, in strenuous exercise, physical labor
Because of the large amount of physical exertion, that is blood glucose depletion, when there is no timely blood glucose replenishment, the hypoglycemic reaction occurs.
Third, taking various hypoglycemic drugs inappropriately, leading to excessive lowering of blood sugar
Insulin sensitizing and secretion enhancing drugs, renal glucose reabsorption inhibiting drugs, and glucose uptake inhibiting drugs can induce a hypoglycemic response because of the direct lowering of blood glucose levels.
Second, the reason why diabetic patients are prone to hypoglycemic reactions
The first, ostensible reason is that diabetics require higher blood glucose levels than healthy individuals to maintain the body's physiologic activity needs.
Healthy people don't react to hypoglycemia until their blood sugar is below 2.8, diabetics can't do it below the very high level of 3.9, they have to go hypoglycemic. This is the body's need for higher blood sugar levels.
Various hypoglycemic measures can easily reach this threshold.
This is a message to all diabetics: it is not the lower the blood sugar the better. Blood sugar must meet the needs of the body to be good.
Second, diabetes requires the underlying cause of hyperglycemia: chronic stress-stimulated injury produces energetically high blood glucose levels, leading to reduced expression of the basal glucose transporter protein GLUT1.
This transporter protein is not insulin dependent like GLUT4. It is only dependent on blood glucose levels - if blood glucose is high, it transports more blood glucose to the cells of the body, and if blood glucose is low, it transports less blood glucose. After its expression is lowered, if blood sugar levels are low and it transports less, the cells in the brain, red blood cells, and other cells that depend on it to transport blood sugar can't function properly and a hypoglycemic response begins.
It may actually be a real target for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. But there is currently no way to regulate its expression.
Remember: with diabetes, high blood sugar is a need, not a harmful condition. It is important to prevent hypoglycemic damage with hypoglycemic treatment.
 Persistent hypoglycemia can be very harmful to the body
Persistent hypoglycemia can be very harmful to the body
1. What is hypoglycemia
The general plasma glucose, referred to as blood sugar, falls below 3 mmol/L, resulting in a clinical syndrome of glucose deficiency in brain cells that becomes hypoglycemia.
2. The dangers of hypoglycemia
The dangers of hypoglycemia are manifested in two main ways:

Dangers of sympathetic overexcitation: excessive sweating, trembling, weakness, palpitations, anxiety, pallor, hunger, salivation, and more;
Dangers of glucose deficiency in the brain: dizziness, poor mental acuity, sluggishness, blurred food, unsteady walking, hallucinations, up to coma and even death.
3. The dangers of prolonged hypoglycemia
If the short-term blood sugar is just a little bit lower, it may not be harmful because of the body's compensatory function;
Chronic hypoglycemia, in addition to the dangers of the two points above, can leave a person progressively weaker, malnourished, demented, and more.

I am Hang Chuan Medical Man, associate chief physician of internal medicine, and often post medical and health knowledge, welcome to follow.
(Note: The pictures not labeled in the article come from the Internet, such as infringement, please contact for deletion in a timely manner)
Copyright: This article is the author's original work, the copyright belongs to Hangchuan Medical Man, its content is protected by the Copyright Law; without permission, refused to reproduce.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.