Is a positive urine sugar diabetes?
A diabetes specialist answers the question.
Recently, the medical insurance bureau experts for everyone to carry out the drug price cutting scene by the major portals crazy broadcast, a drug from 4.40 yuan because 4 too much, was reduced to 4.36 yuan of drugs, now you should know, that drug is dagliflozin, the trade name of the "Andadan" drug, its mechanism of action is to reduce the proximal curvature tubular reabsorption of glucose, can not be absorbed glucose is excreted in the urine. Its mechanism of action is to reduce the reabsorption of glucose in the proximal tubule, and the unabsorbed glucose will be excreted in the urine. This kind of drug is distributed by the medical insurance bureau "good drug card", the effect is really good in clinical use.

The reason for talking about this drug is because it relates to the question posed by the subject.
The mechanism of action of this drug is to excrete sugar, so it will appear in the urine a large amount of glucose, which is manifested in the urine routine, that is, positive urine sugar.
Of course it is diabetes that takes this medication, and people who are not diabetic can take this medication and have urinary sugar, which is determined by the nature of the medication.
Positive urine glucose without diabetes is seen in pregnancy, urinary tract infections, and renal pathology, where glucose leakage occurs due to increased permeability of the renal tubules.
A physiological type of urinary sugar is transient, present in the body for a short time and quickly returns to normal. For example, if we consume a large amount of sugar in a short period of time, exceeding the renal glucose threshold, we will have a positive urine sugar.
Transient positive urine sugar can be present in women with traumatic brain injury, emotional stress, strenuous exercise, and in the middle and late stages of pregnancy.
However, most of the urine sugar is pathologic, because the human body renal glucose threshold is 8-9 mmol/L. If the human body has positive urine sugar for a long period of time, that is, the blood glucose consistently exceeds this value, then the diagnostic criterion of diabetes mellitus is reached, and diabetes mellitus can be diagnosed.
Today's diagnostic techniques do not need to be based on urine sugar to determine diabetes; diabetes is diagnosed on the basis of blood sugar, not urine sugar. So when urine sugar is found positive in the urine, it is important to go to the hospital for a blood sugar test to determine if diabetes is a possibility.
Concerned about Dr. Sun talking about sugar, continue to learn about quality health knowledge, helpful please like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Urine sugar doesn't always mean diabetes, how is diabetes diagnosed?
Positive urine sugar does not necessarily mean diabetes.. It is important to realize that the currently accepted diagnostic criteria for diabetes is not defined by a urine test.The diagnosis of diabetes mellitus is made by drawing venous blood for fasting blood glucose (FPG), glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c), oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) 2-hour glucose, and random glucose, based on the results of their tests... According to the ADA guidelines for the management of diabetes, the specific criteria are as follows:
1. HbA1C ≥ 6.5%.
2. fasting blood glucose (FPG) ≥ 7.0 mmol/L. Fasting is defined as no caloric intake for at least 8 hours.
3. oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) 2-hour glucose ≥11.1 mmol/L. The equivalent of 75 g of anhydrous glucose dissolved in water was used as the glycemic load.
4. in patients with typical symptoms of hyperglycemia or hyperglycemic crisis, random blood glucose ≥ 11.1 mmol/L.
Diabetes can be diagnosed as long as several of the above indicators, one of which is met.

Why does urine sugar occur? What conditions may result in a positive urine sugar?
Why is urine sugar a positive laboratory indicator? In fact, when human blood passes through the kidneys, most of the water and metabolites (which includes glucose) pass through glomerular filtration, and then through tubular reabsorption to absorb useful substances, such as glucose into the blood, and useless metabolites, such as urea, through the ureter to the bladder, and then excreted in the urine.
Normal people's renal tubules can reabsorb most of the glucose in the glomerular filtrate back into the bloodstream, and there is only a very small amount of glucose in the urine, which cannot be detected by the general method, so normal people's urine glucose test is negative. HoweverThe reabsorption of glucose in the proximal tubule has a certain limit, when the concentration of glucose in the blood exceeds 9-10 mmol/L, the absorption of glucose by some proximal tubule epithelial cells has reached its limit, and glucose can not be reabsorbed in its entirety, and glucose is excreted in the urine and glucosuria occurs.The lowest blood glucose concentration at which glucose begins to appear in the urine is called the renal glucose threshold. Urine glucose begins to appear when the blood glucose concentration exceeds the renal glucose threshold.

The following are some of the conditions that may lead to a positive urine sugar:
1. Urine sugar occurs when a normal person consumes large quantities of sugary foods such as beverages, sweets, etc., and the blood glucose concentration exceeds the renal glucose threshold.
2. Diabetic patients with poor glycemic control above 10 mmol/L are more likely to have urinary glucose, but some older adults have an elevated renal glucose threshold and have negative urinary glucose even with poor glycemic control.
3. When you are in a state of stress such as infection, trauma, nervousness, excitement, etc., the body's glucagon is secreted rapidly, which may lead to an increase in blood glucose and cause urinary glucose.
4. Certain renal pathologies causing reduced renal reabsorption may result in positive urine sugar.
5. It is also the case that when you are in a state of pregnancy, the renal glucose threshold is reduced and you may have OK blood sugar and still have urinary glucose.

What do you need to be aware of when recurring positive urine sugars occur? What symptoms may indicate diabetes?
In case of recurring urinary sugar, it is advisable to check whether there is a possibility of diabetes or not, and to assist in the diagnosis by using the venous blood indicators mentioned above.
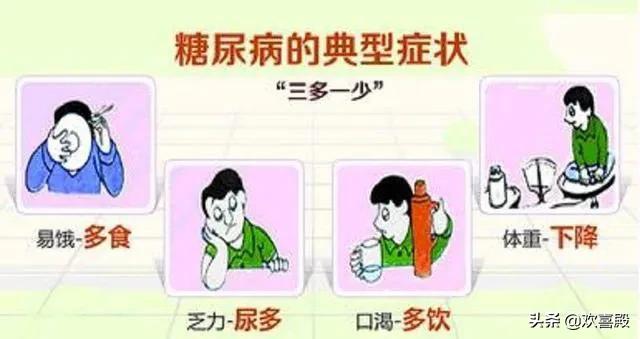
The more typical symptoms of diabetes are "three more and one less", i.e., excessive drinking, excessive urination, excessive eating and unexplained weight loss.
Polyuria: generally manifested in the urine volume of up to 3000-4000ml a day, or even more, this is mainly because the glucose in the body of diabetic patients can not be fully utilized by the cells, so a large amount of glucose can only be discharged from the body through the urine, the formation of osmotic diuresis.
Drinking a lot: This is because polyuria leads to a large loss of water in the patient's body, and the patient then feels very thirsty and drinks a lot of water.
Polyphagia: The patient often feels hungry and increases his dietary intake. However, despite eating more, the patient loses weight instead of gaining it because the body does not change its sense of nativity to utilize the glucose intake well.
However, not everyone with diabetes has symptoms, and studies have shown that 50% of the population may not have clinically significant symptoms. Such people may be detected during a physical examination. Others have some atypical manifestations early on, but ignore them.
What symptoms may indicate early diabetes?
If you experience a decrease in physical strength and fatigue; recurrent skin infections and urinary tract infections; unexplained vision loss; unexplained numbness of the hands and feet; alternating diarrhea and constipation; unexplained hypogonadism in men; and menorrhagia and amenorrhea in women, you need to be vigilant and seek medical attention as soon as possible to detect whether you may have diabetes.

Positive urine glucose is not a diagnostic criterion for diabetes mellitus. However, it suggests the possibility of diabetes mellitus, and it is recommended to complete the OGTT examination in the endocrinology clinic of the hospital to detect diabetes mellitus.
Normally, urine sugar is negative. It is only when blood glucose exceeds a certain level that glucose from the blood is excreted in the urine, forming urinary glucose. The blood glucose value that corresponds to a positive urine glucose level is the "renal glucose threshold", which is usually 8.9-10.0 mmol/L.
The presence or absence of urinary glucose and the number of plus signs depend on the level of blood glucose. When the renal glucose threshold is normal, urine glucose and blood glucose have the following correspondence:
Urine sugar "+" when blood sugar is 10.0 to 12.8 mmol/L;
Urine sugar "++" at blood glucose 12.8 to 15.5 mmol/L;
Urine sugar "++++" at blood glucose 15.5-17.8 mmol/L;
Urine sugar "++++" when blood glucose > 17.8 mmol/L.
1. Pregnant women and patients with nephrogenic diabetes mellitus can develop diabetes mellitus even when their blood glucose is normal due to the lowering of the renal glucose threshold.
2. Elderly and diabetic patients with blood glucose above 10.08 mmol/L (180 mg%) or even above 13.00-16.80 mmol/L (250-300 mg%) can be free of diabetes, which is due to an elevated renal glucose threshold.
3. Nephrogenic diabetes mellitus is characterized by the presence of diabetes mellitus with normal blood glucose and the absence of abnormalities in fat metabolism.

For more practical tips on diabetes
Want to read original diabetes education articles by doctors
Please pay attention to the online guidance sugar control pioneer - Micro Sugar
Positive urine sugar, not necessarily diabetes, there are many influencing factors, there is no direct relationship between each other, the diagnostic criteria for diabetes is based on blood glucose, glucose tolerance test examination, and also several times to confirm the diagnosis.
I. First of all, we need to be clear about two issues
1. Renal Glucose Threshold: It is the blood glucose level when sugar just appears in the urine, and it can also be said that it is the highest blood glucose value that the kidneys can completely retain the sugar so that it does not flow out. When the blood sugar exceeds 8.9-10mmol/L, urine sugar can appear, this blood sugar level, that is, the renal sugar threshold. When blood glucose is lower than 8.9 mmol/L, urine sugar is positive and is called a reduced renal glucose threshold.
2. Glucose tolerance: refers to the body's ability to regulate blood glucose concentration. Glucose tolerance test, a laboratory test to diagnose diabetes.
II. Transient diabetes: It is transient and temporary, and there are the following conditions
(1) Dietary Glycosuria: A transient elevation of blood glucose caused by the intake of large amounts of sugar in a short period of time, resulting in a positive urine glucose.
(2) Acute diabetes: traumatic brain injury cerebrovascular accident, emotional excitement, strenuous exercise and other situations, the central nervous system is stimulated, causing endocrine abnormalities, which leads to temporary positive urine sugar.
III. False-positive urine sugar
(1) Non-euglycemic glycosuria: most of the urinary glucose refers to glucose, but lactosuria can occur during breastfeeding in mothers with a false-positive reaction for urinary glucose.
(2) False Glycosuria: False-positive reaction to urine sugar after taking some drugs such as isoniazid, thiazide diuretics, morphine, and large amounts of vitamin C.

IV. Pathological diabetes
(1) Nephrogenic glycosuria: refers to normal blood glucose and positive urine glucose. This is due to renal disease, caused by renal tubular damage, glucose reabsorption function is reduced, the renal glucose threshold is lowered and the appearance of glycosuria, and has nothing to do with diabetes mellitus.
(2) Elevated blood glucose diabetes: In addition to diabetes, some other hormones that promote increased blood glucose, excessive secretion of endocrine diseases such as: hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma, anterior pituitary hyperfunction, etc., can appear in the urine sugar.
V. Summarizing
In summary, the changes in urine are with the changes of various factors, sometimes pathological and physiological test results are the same, just caused by different etiology, need to be analyzed on a case-by-case basis, positive urine glucose is an important clue, blood glucose and glucose tolerance test is the basis for diagnosis.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.