Is there a link between periodontitis and diabetes? Why?
I am Dr. Sun, pay attention to Dr. Sun talk about sugar, continue to provide you with quality health knowledge, help please click on the like, have questions please leave a message, will reply!
Periodontitis is a chronic infectious disease of the periodontal supporting tissues caused by microorganisms in plaque, resulting in inflammation and destruction of the periodontal supporting tissues, mainly in the form ofPeriodontal pocket formation, progressive attachment point loss and alveolar bone resorption, which is highly prevalent in diabetic patients and is therefore considered one of the chronic complications of diabetes.
Diagnosis of periodontitis
The diagnosis of periodontitis consists of gingival inflammation, bleeding, periodontal pocket depth and attachment loss.
It can be categorized into 3 degrees based on severity:
Mild gingivitis: there is inflammation of the gums, which bleeds on probing.
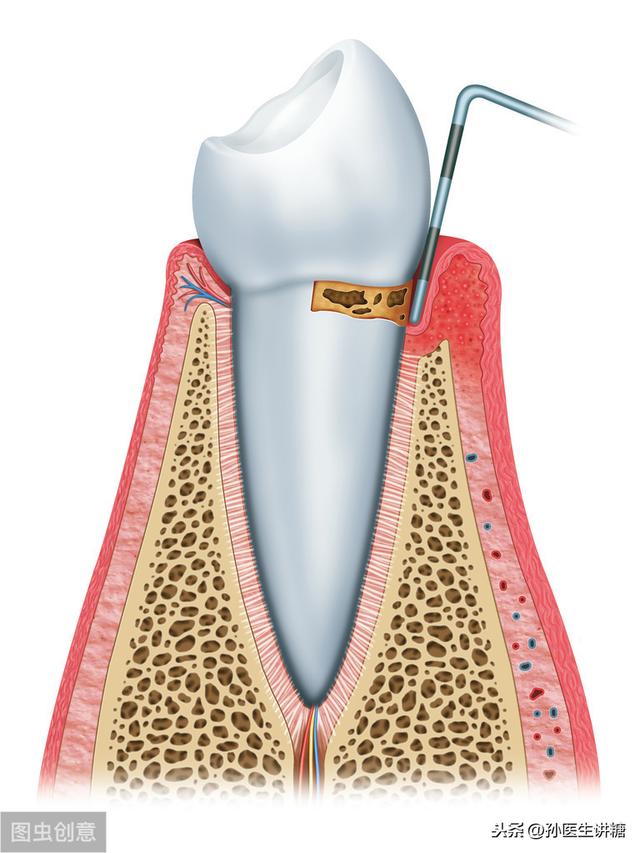
Moderate periodontitis with inflammation of the gums, bleeding on probing, purulent discharge, and mild loosening of the teeth.
In severe periodontitis, the inflammation is more pronounced or a periodontal abscess occurs, and the tooth is more likely to be loose.
The intricate relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease
High prevalence of periodontal disease in diabetic patients
The prevalence of oral diseases among diabetic patients is highest in periodontal disease and tends to be heavier. The health checkup of more than 30,000 people in an enterprise found that the prevalence of oral diseases among diabetic patients was significantly higher, with periodontal disease being the most prevalent, accounting for nearly 40%. A foreign study showed that the risk of periodontal disease in diabetic patients is 4.8 times higher than that of healthy people. The prevalence of periodontal disease is significantly higher in both type 2 and type 1 diabetics than in healthy people.
Periodontal disease may lead to diabetes
Periodontal disease can also affect the body's metabolic state, studies have found that people with periodontal disease have a higher risk of diabetes. The National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey found that the prevalence of diabetes in patients with periodontitis was 12.5%, while the prevalence of diabetes without periodontitis was nearly 6.3%, and that diabetic patients with comorbid periodontitis had poorer glycemic control, higher glycosylated hemoglobin, and were more likely to have multiple comorbid diabetic complications. This was observed consistently in type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes and gestational diabetes.
There is a clear correlation between the severity of periodontitis and blood glucose control; the higher the blood glucose, the more likely periodontitis is to occur, and the more severe the periodontitis, the higher the glycated hemoglobin in diabetes.
Periodontal disease is associated with the development of diabetic complications.
A study with 11 years of follow-up found that diabetic patients with periodontitis had a higher rate of more than 1 serious macrovascular complication compared with diabetic patients without periodontitis. Ischemic heart disease was 2.3 times more common and diabetic nephropathy was 8.5 times more common in patients with type 2 diabetes with severe periodontal disease than in patients with type 2 diabetes without periodontal disease or with mild periodontal disease.
More recent studies have shown that diabetes and periodontitis are mutually reinforcing, with the two being concomitant or coexisting diseases. Diabetes is a risk factor for developing periodontitis, while periodontitis is also a negative influence on blood glucose control.
Mechanisms that predispose diabetic patients to periodontitis
Vascular and microvascular lesions
Diabetes mellitus is a metabolic disease characterized by hyperglycemia, which can cause damage to large and small blood vessels. Studies have shown that periodontal tissues undergo changes in microvascular morphology, microvascular blood flow and perivascular morphology.
Leukocyte function defects
Increased inflammatory factors in diabetic patients activate osteoclasts and collagenase, leading to destruction of periodontal tissues. Neutrophils are important defense cells that maintain the health of tissues throughout the body, including the periocular tissues, and their quantitative and qualitative profiles are associated with heavy destruction of periocular tissues, which appear dysfunctional in diabetic patients.
Impaired wound healing in lesions
Diabetic patients are prone to impaired lesion healing. Hyperglycemic state can have been located in the circulating end tissue fibroblasts and osteoblasts activity, so that the bone matrix, collagen production is reduced, resulting in periodontal and other parts of the repair of regenerative capacity, at the same time it can also activate the collagenase, causing collagen destruction, loss of alveolar bone, tooth loosening and loss.
How Periodontitis Promotes Diabetes
The inflammatory response plays an important role in the development of type 2 diabetes. When B cells fail to maintain normal blood glucose levels, a hyperglycemic state develops, with localized inflammatory factors and immune cell infiltration in the pancreatic islets. Elevated pro-inflammatory response factors can contribute to the development of insulin resistance through inhibition of insulin signaling, which further promotes diabetes mellitus. If this state persists for a long time, immune inflammation can damage or destroy pancreatic islet B cells, thus causing or aggravating diabetes.
Periodontitis can affect the psychological state of diabetic patients. by investigating the anxiety and depression state of type 2 diabetic patients with chronic periodontitis, it was found that the prevalence of anxiety and depression state of the patients increased significantly with the worsening of the degree of periodontitis. the severity of the depression and anxiety state of the patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus combined with chronic periodontitis was correlated with the age, the duration of diabetes mellitus, and the number of remaining teeth.
The relationship between diabetes and periodontal disease is underappreciated by both doctors and patients
In practice, what do endocrinologists and people with diabetes know about these two diseases?
Through the research, it was found that patients' knowledge of oral health care was correctly perceived at 1.5-40.2%, while 87% of doctors paid less attention to periodontitis. Doctors' limited energy, patients' lesser complaints and lack of knowledge about periodontitis were the most important reasons for the lack of attention.
Therefore, it is important to improve the education of doctors and patients to raise awareness of oral diseases in clinical practice.
Diabetics can prevent periodontitis through daily habits
Regular oral checkups should be performedThe problem should be treated aggressively to nip oral complications in the bud.
Diabetics should have regular dental cleaningsTo remove calculus and tartar every six months to a year, so as not to give bacteria, fungi and other pathogenic bacteria a chance to hide and grow.
brush one's teeth regularlyBrush your teeth at least once in the morning and once in the evening, and learn the correct way to brush your teeth.
Rinse your mouth oftenAfter eating food, diabetics are advised to rinse their mouths with diluted baking soda or water. Weakly alkaline water corrects the acidic environment in the mouth, inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi, and avoids the occurrence of dental caries and infections.

Choosing the right toothpasteFor patients with dental caries, it is advisable to choose a toothpaste that contains fluoride, and for patients with periodontal disease, choose a toothpaste that is labeled on the instruction manual as being able to alleviate periodontal disease.
Diabetes increases the risk of periodontitis, and periodontitis affects glycemic control and prognosis in diabetes. Patients with diabetes combined with periodontitis have significantly earlier age of tooth loss.
WHO proposed the "8020" program, that is, to have 20 healthy teeth at the age of 80. In China, only 35% of 80-year-olds have 20 teeth, and the number of teeth remaining in people with diabetes combined with periodontitis is significantly less than that in people without diabetes combined with periodontitis.
As a result, there is more pressure on diabetics to realize the dream of the 8020 program, and universal dental health promotion is even more important.

Both diabetic patients and endocrinologists should raise awareness and pay attention to periodontal disease and other oral diseases preventive disease early treatment of periodontal disease. When the time comes, diabetic patients get a higher quality of life.
To summarize: diabetic patients have more periodontal disease, periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus affect each other and coexist, it is very important to keep blood glucose stable and regular dental care and timely treatment of periodontal disease. Doctors and patients do not pay enough attention to periodontal disease, and publicity and education on dental disease should be strengthened.
Thanks for the invite. Periodontitis and diabetes have a complex association! On the one hand, people with diabetes are prone to periodontal disease, the sixth most common complication of diabetes is periodontitis and periodontal disease, and on the other hand, periodontal disease may interfere with diabetes, and periodontal disease increases the risk of diabetes.
Take a look at some of the research data: the risk of periodontitis in patients with type 2 diabetes is about 3 times higher than in non-diabetics, and diabetics with severe periodontal disease have very poor glycemic control, with a difference of about 6 times! An epidemiologic survey of 75-80 year olds in Japan also found that the incidence of type 2 diabetes was significantly lower in those who received periodontal treatment compared to those who did not receive periodontal treatment, and that periodontal treatment, when received, had a beneficial effect on reducing the risk of diabetes!
The fundamental reason for the relationship between diabetes and periodontitis lies in plaque, more precisely in the bacteria in plaque! On the one hand, diabetic patients have poor resistance and are prone to bacterial infections, oral infections are no exception, and periodontitis must be aggravated by poor blood glucose control. On the other hand, periodontitis of the periodontium leads to the entry of periodontal bacteria into the bloodstream, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis, coronary heart disease and diabetes mellitus.
Therefore, understanding the above reasoning, we can know that keeping the mouth clean and dealing with oral plaque in a timely manner has a positive significance in reducing the incidence of diabetes and in controlling blood sugar for those who already have diabetes, and in turn, controlling blood sugar has a positive significance in reducing periodontitis! The two complement each other. Welcome to my headline-Jiangsu Provincial Cancer Hospital Li Feng.
Periodontitis and diabetes both affect each other, patients with diabetes, easy to cause complications, including periodontitis, caused by the long-term presence of high blood sugar, in addition to periodontitis patients, gum bleeding is very frequent, with the escalation of inflammation, bacterial toxins enhancement, the alveolar bone serious resorption, in addition to the teeth loosening, but also increase the risk of diabetes, and even deepen the condition.
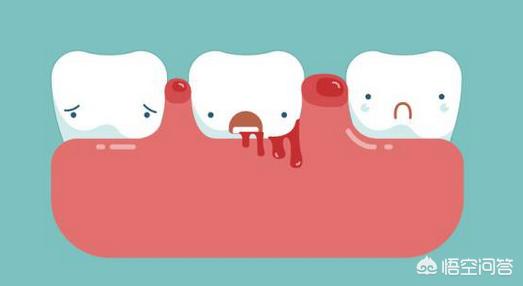
Why is there a link between periodontitis and diabetes?
1, mainly from plaque, there is a large number of bacterial growth, especially dental calculus into blocks, distributed in the gums, direct infection of internal tissues, for diabetic patients, their own immunity is weaker, blocking the bacterial damage, if the blood sugar control is unstable, periodontitis will follow the aggravation of the healing time is longer.
2, and periodontitis patients, bleeding bacteria will enter the body with the blood, reducing insulin function, on the one hand, is not conducive to control, on the other hand, diabetes not only did not get better, and even affects the heart, atherosclerosis and other symptoms, so did not have timely periodontal treatment, the development of severe periodontitis, the diabetes has a direct impact on the timely treatment, then the risk of reducing.
How do you periodontal systemic treatment for periodontitis?
1, the first film examination, scaling shocked off the surface of the teeth plaque, control plaque growth, and then local anesthesia, when probing the depth of the periodontal pockets, more than the subgingival scraping, the roots of the teeth and the dirty things to stimulate the gums, scraping off the rest of the plaque, patients with mild periodontitis can be cured basically.
2, but severe periodontitis requires lengthy treatment, but also periodontal surgery, repair multiple loose teeth, lighter periodontal splints can be fixed, serious to be bonded together with fixed, to avoid occlusal relationship flocculation, postoperative regular checkups, six months a scaling, strengthen oral hygiene, morning and evening brushing, as well as flossing cleaning, to prevent the occurrence of diabetes.
Overall, periodontitis and diabetes both go hand in hand, and by controlling your blood sugar, you can also reduce periodontitis.
Welcome to [Burning Brothers Dental Society], Burning Brothers Dentist to answer your periodontitis questions!
Many people with diabetes have periodontal disease, and many want to know if there is a direct relationship between periodontitis and diabetes, and what kind of connection exists between the two of them.
The occurrence of periodontitis in diabetes has a certain degree of correlation, generally diabetic patients have a certain degree of elevated probability of occurrence of periodontitis, but it does not mean that periodontitis is entirely caused by diabetes, the presence of diabetes only increases the probability of occurrence of periodontitis.
Because the occurrence of diabetes mellitus is mainly due to the body's insulin secretion abnormality, caused by the body's blood glucose can not be effectively controlled for a long time there is an abnormal rise in blood glucose, and blood glucose for a long time for the body's blood vessels are there to a certain extent of damage, periodontal blood vessels are no exception.
In other words, the presence of diabetes mellitus is mainly due to the decline in the health of the periodontal blood vessels, there is an increase in the probability of developing certain periodontal inflammation, not only periodontal disease, but also diabetic patients have more complications, including the susceptibility to diabetic foot, diabetic heart disease, other peripheral vascular disease, and so on.
And because diabetic patients are often accompanied by high blood lipids and high blood pressure, when periodontal disease occurs, the general development of the symptoms of the process is faster, and the body's recovery is slower, so when certain periodontal inflammation symptoms occur, it is necessary to intervene and treat in a timely manner.
For example, usually pay attention to oral hygiene and cleanliness, pay attention to brushing teeth do not consume too hard toothbrush, you can use mouthwash to clean the mouth.
If periodontal inflammation has already occurred, it is necessary to consult a doctor for examination and treatment through the use of medication under the supervision of a doctor.
Hello! Periodontitis and diabetes are related. This is an unexpected statement that many people are surprised to hear. How can periodontitis, an oral problem, be related to diabetes? We have heard that.
Periodontitis is an inflammation that occurs around the dental tissues, mainly caused by plaque and bacteria invading the tissues, and is also a common oral problem. It is important to have good brushing habits and good oral hygiene and cleaning on a daily basis.
And brushing is a measure to maintain dental health, brushing can eliminate food debris in the mouth and part of the plaque on the surface of the teeth, reduce disease-causing factors and bacterial aggregation in the oral environment, and prevent periodontal disease, dental caries, tooth decay and other oral problems.
At the same time, brushing your teeth to keep your mouth healthy has many other benefits for your overall health. Just two years in a row in 2019 and 2020 a study was published on the correlation between.
01 A study published in Diabetologia shows that periodontal disease and missing teeth increase the risk of diabetes. And brushing three or more times a day may reduce the risk of diabetes.

Although this study did not reveal the exact mechanism of the association between oral hygiene and the development of diabetes, that is, it did not show a causal relationship. Instead, the team believes that regular brushing and improvement of oral problems is possible to lower the risk of new-onset diabetes because poor oral hygiene, especially periodontal disease, may lead to the entry of oral bacteria into the bloodstream, causing transient infections and systemic inflammation, and increasing the production and circulation of inflammatory markers, which have been linked to the onset and progression of insulin resistance and diabetes.
02 A recent large study published in the Journal of the European Society for Preventive Cardiology, an affiliate of the European Society of Cardiology, supports the view that "oral health and systemic disease are not completely independent". A 10-year follow-up of 160,000 people showed that brushing regularly, having regular dental cleanings, and reducing atrial fibrillation were associated with a lower risk of heart failure.
And The Lancet, in response to the generalized oral health crisis, also states that "the teeth and mouth are an integral part of the body and support essential body functions."
In any case, periodontal disease oral problems affect a lot of health issues although although the teacher is insignificant.
Hello, periodontitis (periodontal disease) and diabetes are closely related, and there is a vicious circle between the two, which causes and harms each other, aggravating the disease. A large number of studies have now confirmed that periodontal disease is more serious in diabetic patients than in non-diabetic patients, and that diabetes significantly increases the risk of periodontal disease, aggravates the degree of periodontal inflammation, and makes it difficult for wounds to heal. Periodontal disease reduces insulin function, which is not conducive to blood glucose control and increases the risk of diabetic complications. Therefore, everyone should pay attention to periodontal health, strengthen the daily oral hygiene care, morning and evening brush carefully, rinse after meals, the correct use of dental floss, regular oral examination and scaling, can effectively prevent periodontal disease.
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a group of metabolic diseases characterized by chronic hyperglycemia and caused by defective insulin secretion and/or action. Diabetic patients are accompanied by a number of complications, such as diabetic nephropathy, diabetic foot, and retinopathy, which are relatively well known. However, oral lesions in diabetic patients are less well known.
Periodontal disease is currently ranked as the 6th most common complication of diabetes. Numerous studies have shown that diabetes and periodontal disease interact with each other and that periodontal disease has a negative impact on the metabolic control of diabetes. Therefore, people with diabetes need to effectively prevent oral disease from occurring in these areas.
1. Control your blood sugar
Relevant information shows that the level of blood sugar control in diabetic patients is positively correlated with the severity of periodontitis. Sugar lovers must control their blood sugar to reduce the incidence of periodontitis.
2. Active oral hygiene care
Brushing is the most widely used method of keeping the mouth clean. Proper brushing requires a proper combination of toothbrush, tooth cleanser, brushing method, and frequency and duration of brushing:
Toothbrush: It should depend on the age and the specific conditions of the mouth. The oral environment of diabetic patients is relatively poor, the mucous membrane is fragile and wounds are difficult to heal. We should try to minimize the irritation and recommend using a soft-bristled, round-tipped toothbrush.
Dental cleansing agent: dental cleansing agent is an auxiliary product of brushing teeth, can strengthen the friction of brushing teeth clean effect, at present the most widely used is toothpaste; toothpowder, dental water has been less application. At present, the toothpaste on the market in China can be roughly divided into two categories: ordinary toothpaste and efficacious toothpaste. Diabetic patients should be based on their own situation, choose the appropriate efficacy of the type of toothpaste.
Brushing method: Vertical brushing method, brushing teeth now will be the head of the toothbrush oblique to the gums, the bristles attached to the gums, slightly pressure, along the gap between the teeth to the crown side of the brush. When brushing the upper teeth, from the top to the bottom of the brush; when brushing the lower teeth, from the bottom to the top of the brush; teeth of the lips, cheeks and tongue, palate should be brushed separately, in the brush on the upper and lower jaw front teeth, the toothbrush can be erected on the front teeth from the upper downward pull, the lower front teeth from the lower upward pull. When brushing the occlusal surfaces of maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth, the toothbrush can be pressed against the occlusal surfaces and brushed back and forth.
The number of times and time of brushing: it is best to brush once after meals and once before going to bed, if you can't do it after each meal, you should at least do it once in the morning and once in the evening, and you should rinse your mouth after meals. Brush your teeth for 3 minutes each time.
3. Dietary habits
1, reduce the stimulation of the oral mucosa, such as chili peppers, ginger, sour vinegar and other stimulating condiments;
2, reduce the intake of too hard and rough food to reduce friction;
3, pay attention to nutrition, diet structure should be balanced, not only to eat all kinds of meat, but also should eat more fresh fruits and vegetables; Finally, because individuals have differences, sensitivity to things are different, so should be found from the individual recipe easy to cause oral disease food and avoid.
Yes! Both diseases have to be treated and the treatment of patients with both diseases is risky, also both diseases will promote each other. Periodontitis is a bacterial infectious disease, diabetes is a defect in the immune system, one is inflammation a poor anti-inflammatory capacity, we imagine, which is the cause and which is the effect of the final can not be divided!
Diabetes and periodontitis are relatively closely related because the causative factors are mutually reinforcing. In recent years, several studies have found that patients with chronic periodontitis and aggressive periodontitis have elevated serum levels of C-reactive protein, interleukin-6, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and that these inflammatory factors play an important role in decreasing insulin sensitivity, affecting glycemic control, and altering fat metabolism.
.
First, periodontitis is the destruction of tooth-supporting tissues (gingiva, periodontal membrane, alveolar bone, and dentin) due to infection by plaque and a variety of other factors - formation of periodontal pockets with inflammation, loss of attachment and resorption of the alveolar bone, and, in severe cases, loss of teeth. Periodontitis, as a highly prevalent inflammatory disease, is likely to potentially threaten the general health of the host.
The effect of diabetes on periodontitis
- The results of controlled clinical studies have shown that the incidence and severity of periodontal disease is greater in diabetics than in nondiabetics, given similar local irritants. Numerous epidemiologic studies have shown that the extent and severity of periodontitis is higher in diabetics than in nondiabetics: the risk of periodontitis is 2.8 to 3.4 times higher in diabetics than in nondiabetics.
- If patients with type II diabetes mellitus have periodontitis, the inflammation of periodontal tissues is more severe and less controllable than in the general population, and it is the third risk factor for periodontitis after age and calculus.
- Diabetes mellitus mainly affects the onset and course of periodontitis, especially in patients with poor glycemic control, where inflammation of the periodontal tissues is heavier, the gingival margins are red and swollen with granulomatous hyperplasia, bleeding and periodontal abscesses are likely to occur, and the alveolar bone is destroyed rapidly, leading to deep periodontal pockets and loose teeth.
The effect of periodontitis on diabetes
- Moderate to severe periodontitis can significantly increase the risk of developing diabetes and its chronic complications. The commonality between periodontitis and diabetes is that both produce large amounts of inflammatory mediators. Periodontal inflammation is primarily caused by gram-negative bacterial infections, which exacerbate insulin resistance and make glycemic control more difficult. Effective treatment of periodontal inflammation helps restore insulin sensitivity and facilitates diabetes control.
- In recent years, it has been reported both at home and abroad that thorough and effective periodontal treatment can lead to a significant reduction in glycated hemoglobin and a reduction in insulin dosage in diabetic patients.
Other impacts
In addition to its close association with diabetes, periodontitis is an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease, as are hypertension and hyperlipidemia. The causative organisms of periodontitis and their inflammatory metabolites are congruent with the inflammatory bacteria in the plaque of the human blood vessel wall, which can enter the bloodstream and stimulate the endothelial cells of the blood vessels, causing vascular inflammation. Periodontitis may also cause or aggravate other systemic diseases, such as: cause chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, infective endocarditis, gastrointestinal diseases.
Therefore, we should endeavor to keep our mouth clean and hygienic by brushing our teeth daily, rinsing our mouths after meals, using dental floss, dental brushes and other tools effectively for oral hygiene maintenance, and conducting regular oral checkups, maintenance, and scaling every year, as well as actively treating periodontitis and systemic diseases related to periodontitis.
There is actually a relationship between periodontitis and diabetes. If you suffer from periodontitis, which is mainly caused by oral hygiene, coupled with diabetes, it will also affect the recovery of periodontitis. So if you suffer from periodontitis, it is recommended that you pay attention to your diet, do not eat spicy and stimulating food, and you can go to a professional dental clinic for treatment.
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.