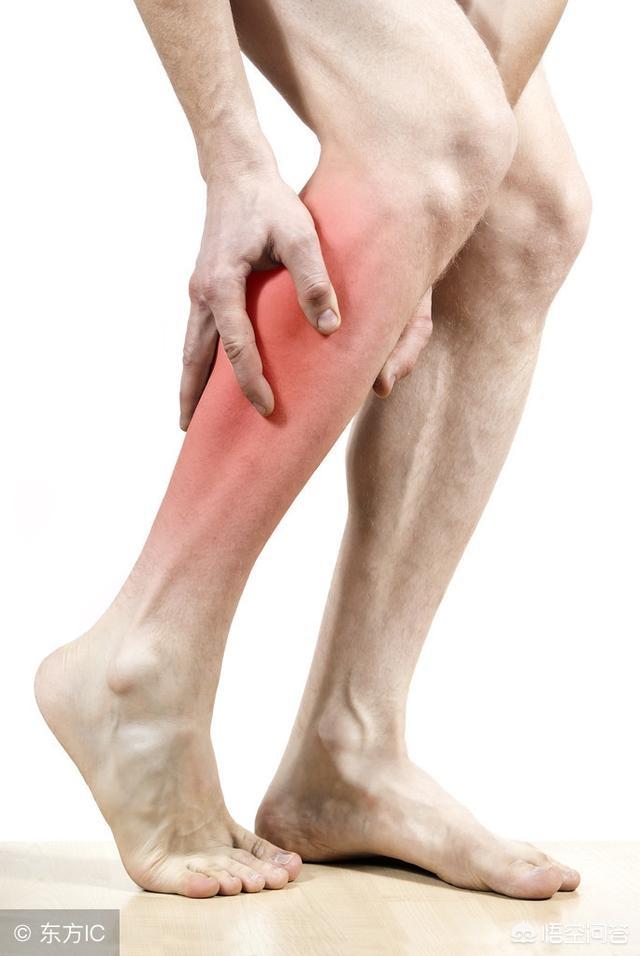
What is the difference between a lumbar strain and a herniated disc?
When we have back pain, the first time how to tell whether it is lumbar muscle strain or lumbar disc herniation problem, I believe this also troubled many of us. Today we are going to discuss the difference between the two, so as to help people get better treatment.

First of all, when it comes to these two monikers that may not be well understood, what is a lumbar strain? And what is a lumbar disc herniation?

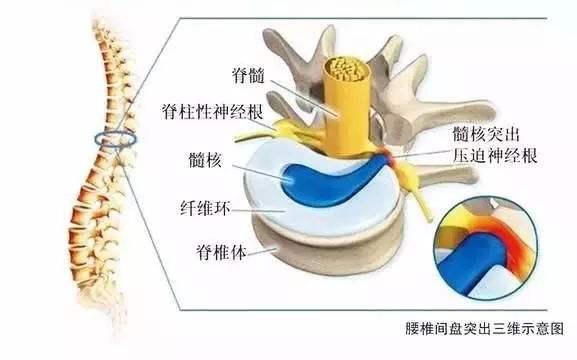
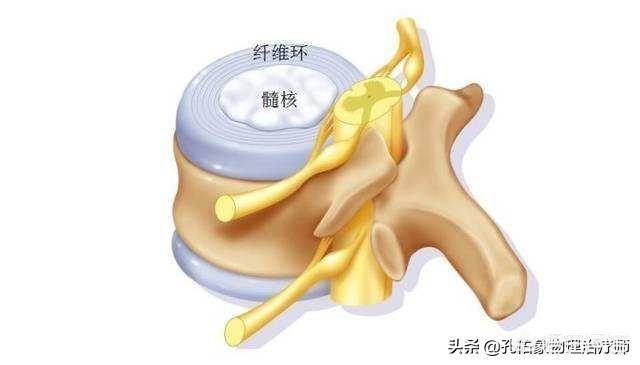
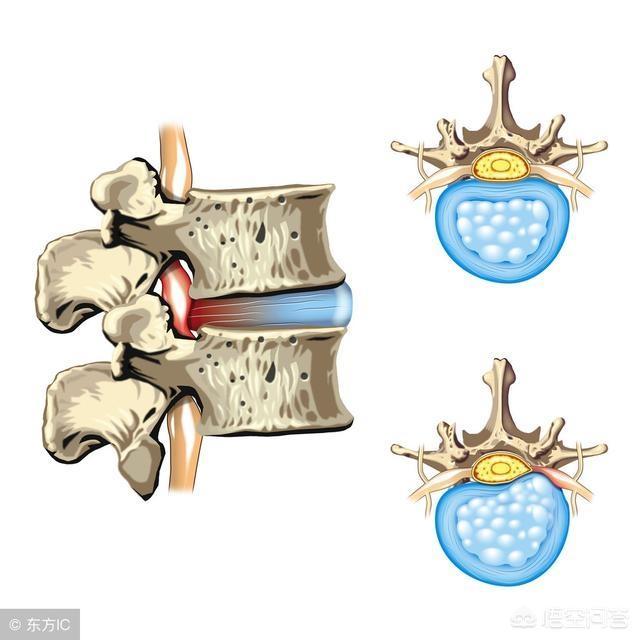
Lumbar disc herniation is a type of low back pain and is also known as specific lower back pain due to its well-defined cause. Intervertebral discs exist between our vertebrae and consist of the nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus and cartilage plates. When the lumbar intervertebral discs have different degrees of degenerative changes, the fibrous annulus of the intervertebral disc ruptures under the action of external factors, and the nucleus pulposus tissue protrudes (or prolapses) from the rupture place in the posterior aspect or in the spinal canal, and the incidence is highest in the case of lumbar 4-5, lumbar 5-sacral 1, which accounts for about 95% of the cases.
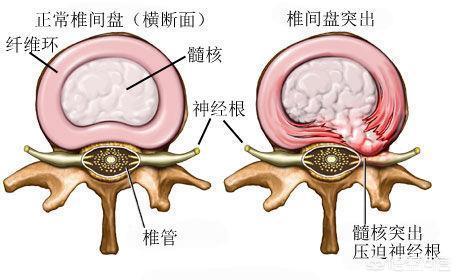
Lumbar strain is a chronic injury to the soft tissues of the lumbar muscles, fascia and ligaments, and is the most common disorder in low back pain, also known as functional low back pain and chronic lower back strain.
So what are the differences between the two?
In terms of etiology and history, lumbar muscle strain has a slow onset and a long history; lumbar disc herniation is mostly related to trauma and tends to have an acute onset, often with a history of chronic low back pain.

2. In terms of symptoms, lumbar muscle strain is mostly confined to the lumbar region, can be unilateral or bilateral onset, most of the pain can be tolerated; lumbar disc herniation, the pain is severe, the activity is severely limited, and can be radiated to the buttocks and legs.
3. In terms of physical signs, lumbar muscle strain has obvious and fixed pressure pain in the lumbar muscles, but no radiating pain; lumbar disc herniation is deep lumbar spine percussion pain, lower extremity muscle weakness and radiating pain.

4. From the imaging, lumbar muscle strain ultrasound can be seen lumbar muscle thickening or atrophy; lumbar disc herniation, lumbar CT or lumbar MRI can confirm the diagnosis.
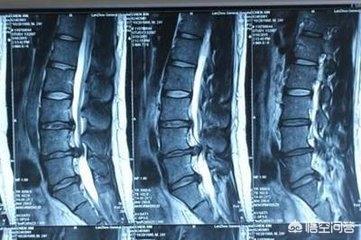
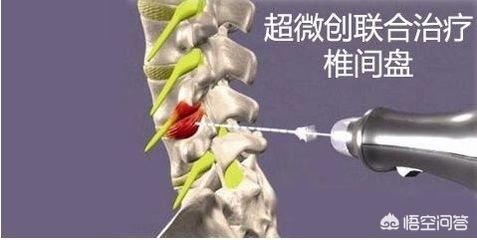
5. From the treatment point of view, lumbar muscle strain is relatively easy to cure, and can be cured by physical therapy, massage, acupuncture and radiofrequency; lumbar disc herniation is more difficult and complex, and is usually treated conservatively, minimally invasively, etc., and surgically if necessary.
For a chronic lumbar muscle strain patients, lumbar disc injury will be relatively high; for a long-term lumbar disc herniation patients, lumbar discomfort and pain will induce lumbar muscle strain. Therefore, once there are symptoms, a period of time can not be recovered, it is best to early detection and early treatment, do not delay to complicate the problem.
Well, that's it for today, I hope it works for you!
Many people may be more or less have felt back pain, in real life, whether young adults or the elderly, whether housewives or working people, no less than a handful of people with back pain.
Under the powerful propaganda of the Internet and the media, many people immediately associate lumbar disc herniation with back pain as soon as it occurs! Even many patients have treated themselves with the powerful Baidu, circle of friends and even rumors in the community.

In fact, there are many causes of back pain, the most common being herniated discs and lumbar strain. How should you differentiate between the two?
Lumbar muscle strain, also known as lumbar dorsal myofasciitis, mainly refers to the lumbosacral muscles, fascia, ligaments and other soft tissues of chronic injuries resulting in localized aseptic inflammation, with no obvious organic lesions. The lumbar disc herniation is the lumbar intervertebral disc medulla outwardly pressing out the nerve causing pain symptoms.
1, the good hair crowd is different
Lumbar disc herniation: it usually occurs between the ages of 20 and 40, and is more common in men, especially those who are too obese or too thin. In addition, labor intensity is greater, often standing personnel are more common.
Lumbar muscle strain: commonly found in heavy manual laborers, triggered by lumbar sprains that are not treated in time or improperly handled. In addition, athletes or people engaged in strenuous exercise for a long time, computer people are also prone to lumbar muscle strain.

2. Different degrees of activity limitation
Lumbar muscle strain: the patient's lumbar mobility is generally unaffected, the pain usually occurs when getting up in the morning or sitting and standing up for a long time, and can be significantly relieved after activities.
Lumbar disc herniation: the presence of low back pain may be accompanied by limited movement of the lower back in one direction or another.
3, pain performance is different
Lumbar muscle strain: it is diffuse pain on one or both sides of the lumbosacral region, often aching pain, occasionally severe pain, the exact location of the pain can not be accurately described more often than not, and there is no obvious pressure point when pressed, usually no radiating pain.
Lumbar disc herniation: radiating pain from the lumbosacral region to the lower limbs along the sciatic nerve course, accompanied by numbness of the limbs and intermittent claudication in severe cases. The pressure point is often located in the middle of the back. The pain is usually vague.
4、Different performance in imaging examination
Lumbar strain: imaging is generally normal.
Lumbar disc herniation: Lumbar spine front and side view films often show lumbar scoliosis, corresponding narrowing of the intervertebral space, unequal width of the two sides, and the formation of bony encumbrances, etc. CT and MRI can accurately see the degree of degeneration of the lumbar vertebrae, and make it clear whether or not there is a lumbar disc herniation.
5. Treatment modalities are not同
Lumbar muscle strain: usually treated conservatively without surgery.
Lumbar disc herniation: In the early stage of the disease, conservative treatment can be used when the general symptoms are not obvious. With the development of the disease, when the symptoms are more serious and conservative treatment is ineffective, surgery can be considered.

Lumbar muscle strain and lumbar intervertebral disc herniation are both common and frequent clinical diseases, and although there are many differences between the two, they have a certain causal relationship. On the one hand, if you let lumbar muscle strain develop without taking any measures, it will reduce the protective effect of muscles and soft tissues on the lumbar spine in the long run, thus triggering intervertebral discs; on the other hand, if the lumbar discs herniate and lead to changes in lumbar postures, it will also cause lumbar muscle strain.
★ If this answer is helpful, please like and support it!
There are many causes of low back pain, lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation belong to the lumbar region itself, there is a certain degree of overlap in the causation of disease, a certain point of view, lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation of the underlying disease, so it is very important to do a good job of differential diagnosis of the two.

What is lumbar strain?
Lumbar muscle strain is one of the chronic strain disorders of the soft tissues of the lumbar region, and there are several other members of this family such as fascial strain and ligament strain. And lumbar muscle strain, which is a chronic injurious inflammation of the lumbar muscles and their attachment points fascia and periosteum, is a common cause of low back pain for most people.
In life, if we are often engaged in stooping or lumbar-weight-bearing labor or sports, often sedentary and lack of exercise, theRepeated accumulation of minor injuries to the lumbar region leads to pathological changes in the lumbar muscle attachment points, periosteum, ligaments, and other tissues, which stimulate or compress the nerve endings to produce symptoms of low back pain, which is called lumbar muscle strain.
The main symptom of lumbar muscle strain is the pain in the lower back, the pain is mostly hidden pain, distension, aggravated in the state of exertion or cold, wet and cold weather, and then relieved after resting or after the weather turns better, the patient, if there is no effective treatment, is prone to recurrence, and with the cumulative symptoms of the strain will be aggravated.Muscle dystrophy, muscle spasm, and muscle contracture as the triad of pathologic responses to lumbar strain injuryIf patients develop the disease because of muscle dysfunction and reduce exercise after the onset of the disease because of pain avoidance, it will easily lead to muscle contracture and atrophy, further aggravating the disease. Therefore, lumbar muscle strain should also be timely intervention at an early stage.
- Patients with lumbar muscle strain, the first thing to do is to reduce the burden for the lumbar spine, change the sedentary, standing, often bending and other bad habits, reduce the burden on the waist of the labor and exercise;
- Secondly, you can relieve the symptoms through physical therapy and Chinese medicine physiotherapy. In addition to going to the hospital for formal treatment, hot compresses at home are also a good choice;
- Finally, patients should pay attention to the lumbar warmth in life, but also adhere to the lumbar back muscle exercise to enhance muscle strength, both to prevent lumbar muscle strain, but also to prevent lumbar spine pathology due to lumbar muscle strain.
What is a lumbar disc herniation?
The main structure of the lumbar spine consists of the cones and the intervertebral discs between the cones, which in turn consists of the outer annulus fibrosus and the inner nucleus pulposus. The nucleus pulposus in the intervertebral disc is rich in water and elastic due to its good deformation, which has the important function of absorbing shock and coordinating the movement of the lumbar spine.Lumbar disc herniation is a disease in which the intervertebral disc undergoes degenerative changes, decreases in elasticity and increases in brittleness, coupled with stimuli such as prolonged and sustained pressure or excessive pressure, the annulus fibrosus ruptures and the nucleus pulposus protrudes from the ruptured annulus fibrosus, compressing the nerve root and causing a series of symptoms such as pain.
In addition to low back pain, lumbar disc herniation is also prone to leg pain due to sciatic nerve involvement.Its pain is characterized by several features:
- Usually low back pain occurs before leg pain, and both may occur at the same time;
- There is a limited pressure point adjacent to the affected spinous process at the site of the herniated disc;
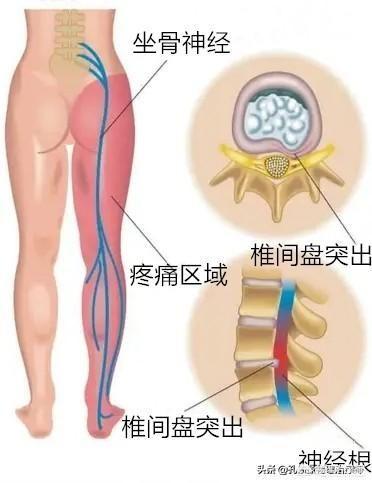
- The pain is radiating from the lumbar region along the sciatic nerve to the lateral calf, dorsum of the foot, or toes, and if the lumbar 4 nerve root is compressed, it can also produce radiating pain to the anterior thigh;
- Painful symptoms are exacerbated during coughing, sneezing and defecation due to increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure;
- The pain is severe with activity and lessens with rest, and the symptoms tend to worsen when the lower back is exposed to cold and moisture;
- In addition to pain, numbness and soreness in the lower back and legs are common symptoms.
In addition to pain, nerve damage from lumbar disc herniation can also lead to symptoms of uncontrolled urination, constipation, sexual dysfunction, and in severe cases, even partial or majority paralysis of the two lower limbs, so early diagnosis and early treatment are very important.Treatments for lumbar disc herniation include:
- The triggering factors of lumbar disc herniation include trauma, chronic strain injury, excessive weight bearing, poor posture, spinal deformity, exposure to cold and moisture, drinking and smoking, etc. The first step in treating lumbar disc herniation is to avoid these dangerous triggers.
- Conservative treatment for lumbar disc herniation, on the other hand, includes physiotherapy or Chinese medicine physiotherapy such as manipulation, traction therapy, Chinese medicine fumigation, medicated hot compresses, and exercise therapy to enhance the muscle strength of the lumbar and abdominal muscles to alleviate the symptoms and control the progression of the disease.
- Patients with lumbar disc herniation often have limited activities during pain episodes. Lack of activity can lead to contracture and atrophy of the lumbar spine and soft tissues around the lumbar spine, which can further worsen the condition, so it is important to promptly alleviate the pain symptoms and restore mobility through medication or hair closure when necessary.
- Surgery is also considered for patients who have a long history of the disease and whose symptoms are not relieved by conservative treatments. Depending on the patient's condition, there are different options for minimally invasive surgery and general surgery.
The difference and connection between lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation
Through the above two parts, we have a certain understanding of lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation, from which we can also see the similarities and differences between the two, for the differences and connections between the two, we briefly summarize:
- The pathology is different.The site of lumbar muscle strain is the lumbar muscles and other soft tissues, which are generally not related to the lumbar spine; the site of lumbar disc herniation is in the intervertebral discs. This can be identified by imaging, although patients with lumbar disc herniation can have lumbar muscle strain.
- Symptoms vary.The pain of lumbar muscle strain is mainly hidden pain and swelling of the muscles in the lower back, and the pain usually does not involve the legs; lumbar disc herniation manifests itself as radiating low back and leg pain, and the pain is more persistent than lumbar muscle strain, and symptoms of nerve root damage such as loss of control of urination, constipation, sexual dysfunction, paralysis, and so on, may also occur.
- Etiologic link.Lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation, there are poor posture, excessive weight bearing, overwork, cold and moisture, spinal deformity, drinking and smoking, trauma and other common triggers, and lumbar muscle strain itself is also a lumbar disc herniation trigger.
- Prevention and control links.The two diseases have common points in prevention and treatment, such as physical therapy for lumbar disc herniation, Chinese medicine physiotherapy, exercise therapy, which is also applicable to patients with lumbar muscle strain, and basically the same life care.

Now there are a lot of people with back pain, go to the hospital side of the clinic, often will be diagnosed by the doctor as lumbar muscle strain or lumbar disc herniation, why a back pain problem, different doctors give out the results are not the same? This is where many patients are confused. What is the difference between the two? Doctors and everyone to talk about it.
First, a conceptual correction for the subject.A herniated lumbar disc does not mean the same thing as a herniated lumbar discThis means that a herniated lumbar disc is only a result of an imaging test and is not the cause of low back pain, whereas a herniated lumbar disc is both a result of an imaging test and the direct cause of your low back pain and other symptoms.
So what the questioner is trying to determine differently is, when you have low back pain, is it a herniated lumbar disc? Or is it a lumbar strain? We will differentiate in detail in the following aspects:
Let's start with your own back pain symptoms.
lumbar muscle strainThe symptoms manifested are: the nature of the pain is soreness and discomfort, sometimes light and sometimes heavy, recurring; when the pain, appropriate rest, appropriate activities or often change the position posture can be alleviated; exertion, the symptoms worsened, and may even appear in the low back muscle stiffness and spasm.
herniated lumbar diskSymptoms manifested are: if only a slight lumbar disc bulge, also often show localized low back pain, but often more often seen is low back pain accompanied by radiating pain in the lower limbs, often along the sciatic nerve travel area radiating pain and numbness (buttocks, back of the thighs, calves, and the dorsum of the foot, etc.).
Distinguishing by etiology
lumbar muscle strainThere are many muscles in the lumbar back, such as the most powerful sacrospinal muscle which is the key muscle to maintain our waist backward and upright, and the transverse process of the vertebrae which has transverse spines, which are the semispinalis, multifidus, and piriformis muscles, and the deeper short muscles such as the intertransverse and interspinous muscles; no matter what position your waist is in, the low back muscles are in a state of contraction and have to resist gravity, which will cause fatigue of the lumbar muscles. Regardless of your posture, the muscles of the low back are in a state of contraction, resisting gravity and causing fatigue of the lumbar muscles.
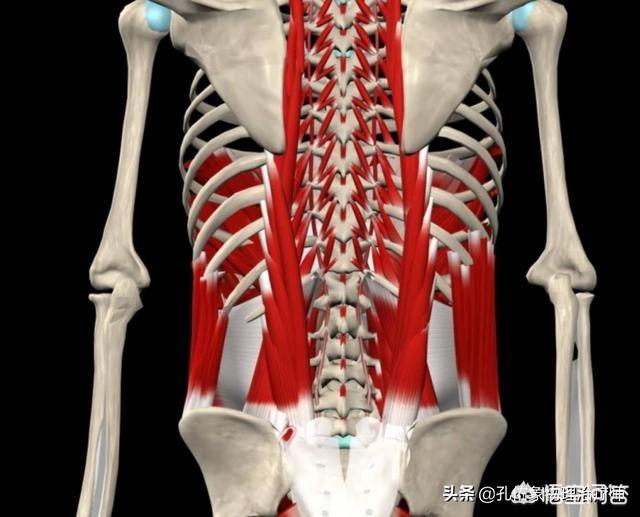
- The most common is chronic poor posture and prolonged stooping and heavy labor;
Lumbar muscle strain is a chronic cumulative injury, mainly due to excessive fatigue of the lumbar muscles, such as long-term stooping work, habitual poor posture, long time in a fixed position, resulting in muscles, fascia and ligaments continue to pull, so that the pressure within the myofascia increased, the blood supply is not good, the muscle fibers in the contraction of the exertion, the consumption of energy can not be timely access to replenish the production of a large number of lactic acid caused by the pain, and the repeated accumulation of changes in thesex, causing inflammatory irritation.
- The lumbar region is not properly treated in a timely manner or incompletely treated after an acute injury or repeated multiple injuries
This, in turn, prevents the injured lumbar myofascia from being fully repaired, localizes aseptic inflammation, impaired circulation, and accumulation of metabolic products such as lactic acid, which irritates the degenerated fibers and produces pain.
herniated lumbar disk:
- Physiologic degeneration of lumbar intervertebral discs
From the age of 20 onwards, a person begins to undergo gradual degenerative changes thatfiber ringDegeneration, thickening and decreased elasticity is a process that everyone goes through. By the age of 30-40 years and beyond, the interstitial disk in thenucleus pulposusIt tends to collagenize and lose elasticity and expansion, and disc degeneration during this period is mainly characterized by the fastest nucleus pulposus change.plate of cartilageIt also thins and becomes incomplete with age.
- Trauma and cumulative strain are important causes of lumbar disc herniation
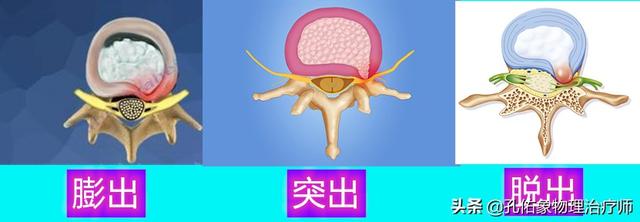
Lumbar discs are thin in the back and thick in the front. When you bend forward, the nucleus pulposus moves backward, and if the pressure is too great, the nucleus pulposus breaks through the degenerated annulus fibrosus and irritates and compresses the nerves.
From the inspection and evaluation
lumbar muscle strain: There are no obvious abnormal findings on general imaging, except in terms of its painful characterization.The pain in the low back is more widespread, recurrent, mild to severe, and stiff in the back muscles。
herniated lumbar disk:
First check: look for neurologic signs
1. Straight leg raise test
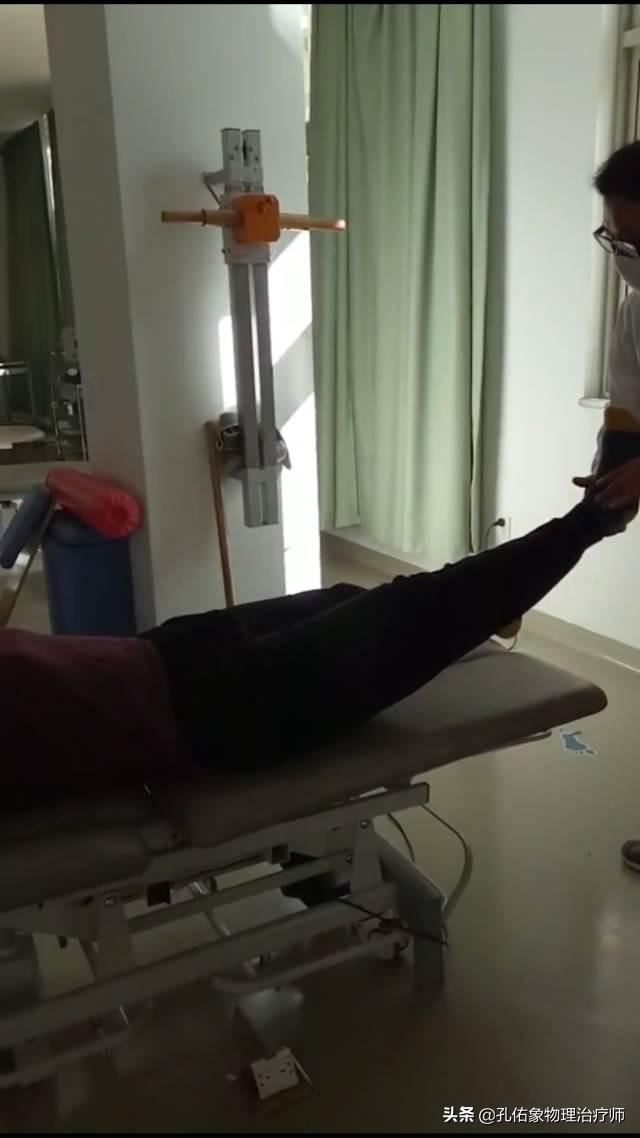
Radiating pain in the lower extremities in passive elevation to 60-70°, i.e., neurologic signs
2. Seragh test
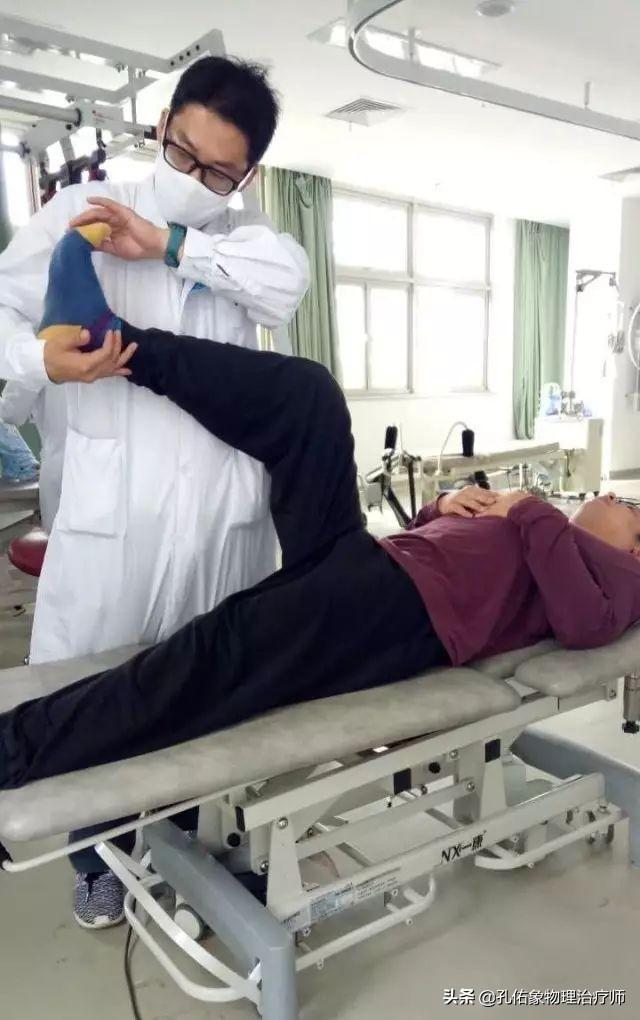
Radiating pain on knee extension suggests neurologic signs.
3. Nerve slip test
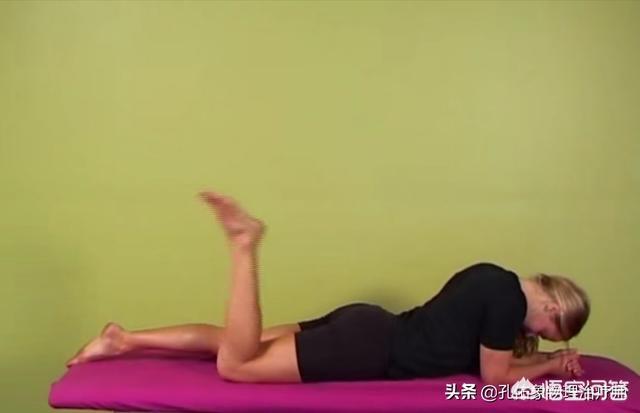

Radiating pain on lowering the head and bending the knees, i.e., a neurologic sign
A positive test on any of these three tests indicates nerve entrapment.The last thing to look for is a decrease in innervated skin sensation and muscle strength. Lastly, look for decreased tendon reflexes in conjunction with a physical examination to look at innervated skin sensation and muscle strength.
4. Imaging:
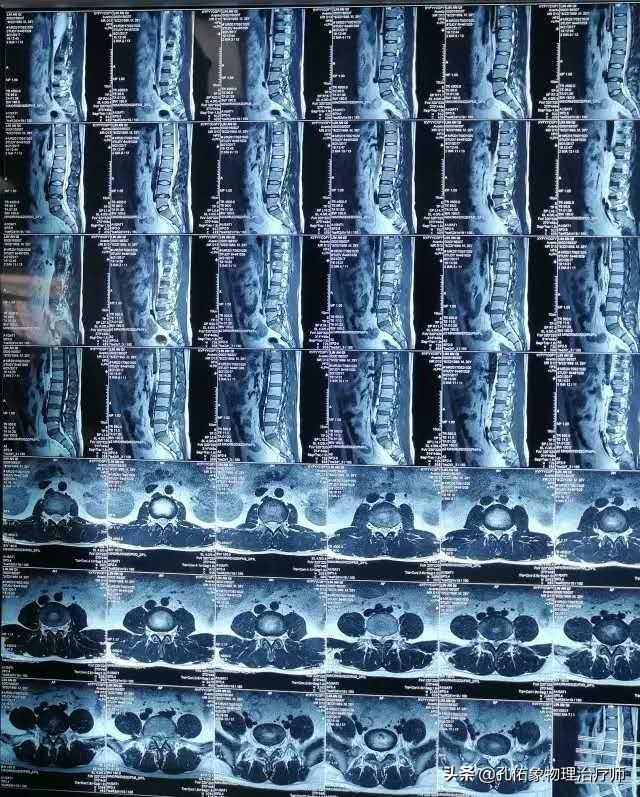

CT or MRI to see if there are any imaging changes of a herniated disc, combined with an evaluation exam.
summarize
For the difference between the two, it is still very easy to judge, as long as careful inspection and analysis, according to the above several steps can be clearly distinguished, I hope my answer is helpful to you.
I am Dr. Kong, who insists on analyzing the knowledge of diseases with his own treatment experience and concepts, it is not easy to code, if you agree with me, please help to click a like or click a concern; sharing is a virtue, the giver of roses, hand to leave a fragrance! Thank you, Dr. Kong.
As lifestyles and work styles change, chronic low back pain, for overtime dogs, has become a worldwide health problem. More than any other problem, it leads to functional disability and raises the unemployment rate.
Some surveys suggest that about 20 to 56 percent of adults will experience low back pain in their lives within a year, and the prevalence continues to increase with age. So once you have low back pain, how can you tell if it's a lumbar strain or a herniated disc?
lumbar muscle strain
Lumbar muscle strain occurs in middle-aged people, the onset of the disease is related to the long-term maintenance of a labor position, such as long-term face to the soil back to the sky farmers uncle. Mainly chronic pain in the lumbar region, and there is no obvious cause, the nature of the pain for the lumbar soreness and pain, can be relieved after resting, in the area of pain, there is a fixed pressure point, if gently knocking the pressure point, the pain symptom instead of alleviation.

If examined by a specialist, a negative straight leg raising test will be found, there are no signs of nerve involvement in the lower extremities, and localized closure of the pressure points will give good results.
herniated lumbar disk
Although it is the same as lumbar strain and back pain, lumbar disc herniation is a different disease now.
Lumbar disc herniation, commonly found in patients aged 20 to 50 years old, the ratio of male to female incidence is about 4-6:1, patients usually have a history of stooped labor or long-term sitting work before the onset of the first onset, usually in the half-bent lifting or suddenly do twisting movements. Its symptoms are mainly:

腰痛
Knife myself is a lumbar disc herniation patients, this lumbar pain experienced, the pain is simply no way to stand and pain, sitting and pain, lying pain, but lying hospitals do not send money na (* ≧ m ≦ *)!
Sciatica (* ̄m ̄)
It is the pain on the back outer side of the buttock thigh, the outer side of the calf sometimes extends to the heel of the foot, and the pain is usually aggravated when you sneeze or cough.
cauda equina syndrome (medicine)
The name sounds scary, mainly refers to the lumbar disc herniation compression of the cauda equina nerve urinary and fecal disorders, etc., if the acute onset of the disease is the need for emergency surgical treatment.
Straight Leg Raise Experiment and Reinforcement Experiment
This would be within the scope of the specialist's examination. Patients with lumbar disc herniation have a positive straight leg raise test and a positive strengthening test. Whereas patients with lumbar strain will not be positive.
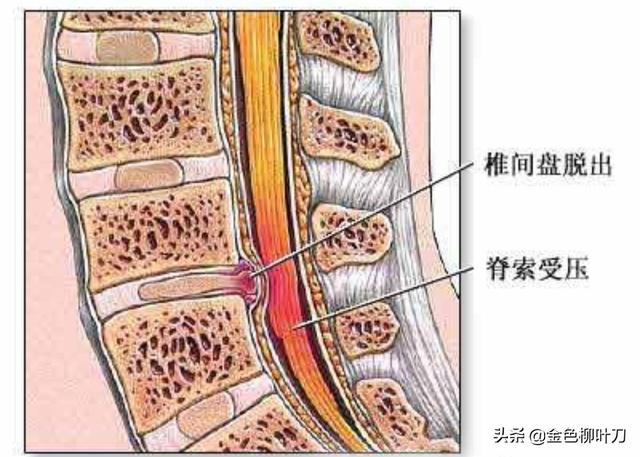
CT and MRI can clearly diagnose lumbar disc herniation and also serve as a differential between the two.
I hope my answer will help you!
Thanks for the invitation! The fact is that this question is certainly want to get the answer is: we personally or to others, especially patients presenting with low back pain, how we do not go to the hospital to be able to roughly determine whether they have lumbar muscle strain or lumbar disc herniation! So, I will avoid the radiographs to share with you how doctors can determine whether it is a lumbar strain or a herniated disc by the patient's subjective feelings!
First of all, there is no doubt that low back pain occurs regardless of whether it is a herniated disc or a lumbar strain!But note: Low back pain may not necessarily be a lumbar strain, and likewise may not always be a herniated disc!Our bodies, from the spine to the skin of the outer back, can suffer from back pain due to sprains, injuries inflammation and so on thus causing discomfort in the lower back!Such things as fasciitis, osteoporosis in the elderly with problems with the vertebrae themselves, compression fractures due to trauma, hyperplasia of the small joints of the spine, and problems with the spinous processes themselves can lead to low back pain!Therefore, in the face of lumbar pain, we should not just think that it is either a herniated disc or lumbar muscle strain, but should analyze it in the light of our own history of illness, age, whether there is any trauma, and specific symptoms!
Secondly, the presence of a herniated disc and a lumbar strain can indeed lead to different symptoms.
- Pain sensations vary.Lumbar muscle strain in fact belongs to the muscle injury inflammation, and relative to the lumbar disc herniation is due to deep vertebral compression fibrosis caused by the pain, the two can obviously feel the pain feeling is different, it may be that patients with lumbar strain you don't have to percuss the area to show pain and discomfort, whereas not particularly severe lumbar disc herniation may need to be felt by doing a deep lumbar percussion will feel a percussive pain!
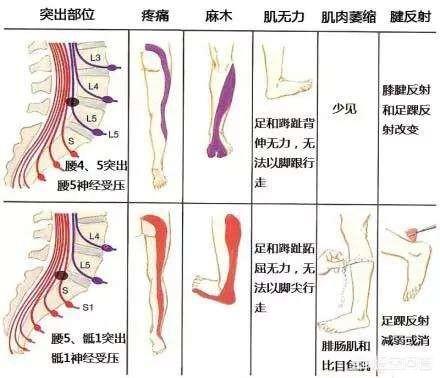
- The location of the pain varies. Lumbar muscle strain is mainly the lumbar lumbar large muscles and other muscles for a long time sedentary and some other reasons lead to strain, the disease development is relatively slow, so itsThe location of the pain is usually single and fixed after all, and this pain is generally tolerableThe lumbar disc herniation may also be caused by a long history of chronic low back pain and an improper lifestyle, but its onset is relatively more acute than lumbar muscle strain and may be related to some acute trauma.It manifests itself in acute episodes, and even some of the pain is so severe that the patient is unable to tolerate it, which must be relieved by the use of other complementary treatments such as some medications. The most important thing is that herniated lumbar disc pain is severe, and there can be severe limitation of movement, theVertebral compression can also radiate to the buttocks and legs, leading to muscle weakness and radiating pain in the lower extremities!
- Treatment results vary. When we have a lumbar strain, we may find that as long as we use some acupuncture, physical therapy and other treatments it is possible toAchieve rapid symptomatic relief and relatively good therapeutic results;And herniated discs may simply some physical therapy andInability to achieve better prolonged symptomatic relief, sometimes more intervention with anti-inflammatory and analgesic medication is requiredIn severe cases, when the pain is so severe that it compresses the nerves and interferes with normal life, surgical treatment may be necessary!
Finally, if we do need to confirm the diagnosis, the tests we go to the hospital to do for both may still be different.Lumbar muscle strain may only require an ultrasoundIt is possible to notice the thickening and atrophy of our lumbar muscles; and theA herniated disc, on the other hand, more often requires a Ct or MRI to detect pathologic changes!
See the folded answer, let you go to the film, but this is not at all a way to determine whether it is a lumbar disc herniation or lumbar muscle strain, shoot CT or MRI, even if the disc is found to be protruding, it does not mean that it must be a lumbar disc herniation, I teach you how to analyze ......
Judging from the symptoms

Most of the patients with lumbar muscle strain, most of the pain is on both sides of the waist, can occur in the entire waist section, will not appear on the leg symptoms, bending over for a long time will feel uncomfortable, cooling, cloudy days when the symptoms will be temporarily aggravated, the heavier patients will wake up with pain in the morning at 4 to 5 o'clock.
Lumbar disc herniation patients, most of them occur on one side, the pain site in the lower lumbar, coughing and sneezing, stool will have pain, there are lower extremity radiating pain, this is to determine the lumbar disc herniation and lumbar muscle strain is very obvious an indication, rest to alleviate, the more the more activities the more serious.
From the inspection
The examination here does not mean to go to take a picture, lumbar muscle strain can be touched on both sides of the waist muscle tension or striated adhesions, pressure will be painful or soreness, of course, it can also occur only on one side of the strain, that is, unilateral have this manifestation.
In lumbar disc herniation, a pain point can be found in the lower lumbar region on the affected side, and pressure will result in low back and leg pain consistent with the symptoms, which is differentiated from the large pressure pain of lumbar muscle strain, in addition to CT or MRI can also reveal the presence of a corresponding disc herniation!
concluding remarks
In short, how to determine what kind of disease caused the pain, to start from the symptoms, combined with palpation examination, imaging, including also ask some medical history or trauma history, multiple aspects of the integrated to determine, not just look at the imaging, or see what symptoms, their own set of disease, diagnosis left to the doctor.
Lumbar disc herniation, or perhaps more accurately, lumbar discogenic back and leg pain, encompasses many types. They have completely different symptoms. Some have obvious pain at night, and the symptoms are relieved or disappear after activities; some have lower limb pain, numbness, weakness, difficulty in movement after weight bearing or bending at the waist, and are relieved after bed rest; some have intermittent claudication, and they have to sit or squat for a while after walking a few steps, and they can continue to walk for a few steps after a little bit of relief; there is also a kind of lower limb sudden and severe pain, and it is difficult to move, and it is uneasy to sit or lie down, and it can't be relieved by bed rest.
These are roughly 4 different types of manifestations after a lumbar disc injury.
1, night pain, can not lie down or sit for a long time, the second half of the night or early in the morning due to lumbar pain can not sleep. But get up and move after the symptoms can basically disappear - such symptoms, many doctors will diagnose as "lumbar muscle strain", "lumbar three transverse processes syndrome". It doesn't really matter what you call it! It is caused by the release of inflammatory substances from the damaged lumbar intervertebral discs, which irritate the nerves in the lumbar region and cause symptoms. It is a relatively mild form of lumbar disc herniation. We often refer to it as "lumbar pain type lumbar herniation".
2. Swelling and soreness of the lower limbs, coldness and numbness after weight-bearing in the lumbar region, with lightness in the morning and heaviness in the evening. The essence of this type of lumbar intervertebral discogenic disease is that after lumbar intervertebral disc injury, it loses the function of bearing the weight of the body, so that its corresponding lumbar vertebral segment is unstable, and it repeatedly stimulates the corresponding lumbar nerve root, producing symptoms. In short, "lumbar instability".
3, intermittent claudication, generally speaking, because of lumbar spine segment injury for a long time, lumbar ligament hypertrophy, bone redundancy formation (that is, commonly referred to as osteophytes), lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion, so that the lumbar spinal canal stenosis or lateral saphenous fossa stenosis. This type of lumbar spine disease, often the pain is not intense, but the patient can not walk long distances, the patient as long as the sitting, lying down, squatting symptoms can be relieved or disappear. This type of disease is usually diagnosed as "lumbar spinal stenosis".
4, the patient's lower extremity pain is severe, tossing and turning, the pain can not be relieved. This type, often because of the huge lumbar disc herniation, compression of the nerve root, producing pain. The principle, because the nerve root is mechanically compressed! So to speak, only this type of lumbar disc herniation is the real "compression of the nerve", the rest of the above types of lower limb pain is not really "nerve compression", but just our doctors in order to tell the convenience of doing a simple description.
5. Other. Small joint disorders of the lumbar spine and synovial inlay cannot be ruled out. But personally, there is not enough evidence to support this diagnosis.
6. Diagnosis of "sciatica" (pyriformis syndrome), gluteal fasciitis, gluteal epiphyseal neuritis, and so on. Years ago I followed these diagnoses very carefully and in accordance with the textbooks. In recent years, however, I have increasingly questioned the scientific validity and veracity of these diagnoses.
So don't bother wondering whether it's a "herniated disc" or a "lumbar strain"! It's just a question of whether it's a "herniated disc" or a "lumbar strain"!
The muscles of the lower back may occasionally be acutely strained. But muscle injuries are never prolonged.
What is lumbar strain?
Lumbar muscle strain, also known as functional low back pain, chronic lower back injury, lumbar gluteal myofasciitis, etc., is actually a chronic injurious inflammation of the lumbar muscles and their attachment points of fascia or periosteum, which is one of the common causes of low back pain.
Main symptoms: lumbar or lumbosacral distension, pain, recurrent, pain can change with climate change or the degree of exertion, such as daytime exertion aggravated, can be alleviated after rest when light or heavy, for the clinical common disease, frequent disease, the onset of more factors. Its accumulation, can make the muscle fiber degeneration, even a small amount of tearing, the formation of scarring, fibrous cord or adhesion, leaving long-term chronic low back pain.
What is a herniated disk?
Lumbar disc herniation is one of the more common diseases, mainly because of the lumbar disc parts (nucleus pulposus, annulus fibrosus and cartilage plate), especially the nucleus pulposus, there are varying degrees of degenerative changes, in the role of external factors, the disc's annulus fibrosus rupture, the nucleus pulposus tissue protrudes from the rupture place (or prolapse) in the posterior or vertebral canal, leading to the adjacent spinal nerve roots suffered from irritation or pressure, thus generating low back pain, numbness and pain in one or both limbs. As a result, a series of clinical symptoms such as lumbar pain, numbness and pain in one or both lower limbs are produced. The incidence of lumbar disc herniation is highest in lumbar 4-5 and lumbar 5-sacral 1, accounting for about 95%.
How can I tell if I have a lumbar strain or a herniated disc?
1. back pain
(1) Herniated lumbar disc
Low back pain is the first symptom that occurs in most patients, with an incidence of about 91%. It is characterized by vague pain. As the outer layer of the fibrous ring and the posterior longitudinal ligament are stimulated by the nucleus pulposus, it produces sensory pain in the lower lumbar region via the sinusoidal nerve, sometimes accompanied by pain in the buttocks.
(2) Lumbar muscle strain
It is characterized by soreness or swelling in the lower back, partly stabbing or burning pain. The degree of pain in the lumbar region is strong and weak at times, starting with intermittent pain, gradually becoming persistent pain, and gradually intensifying. The pain changes with the weather, and is aggravated by cold or rainy days. The pain is felt deeper, aggravated by activity and relieved by bed rest.
2. Prevalent population groups
(1) Herniated lumbar disc
It usually occurs between the ages of 20 - 40, and the incidence of young adults accounts for about 80%. Mostly seen in men, too obese or too thin people are prone to lumbar disc herniation. Labor intensity is greater, often work at the desk and often standing personnel are more common.
(2) Lumbar muscle strain
Acute lumbar sprain in heavy manual laborers can cause the onset of lumbar muscle strain if it is not treated in time or handled properly. Athletes or people engaged in strenuous exercise for a long time, in the strenuous exercise caused by the lumbar muscles of long-term injury. Prolonged seated study, or poor sitting posture in the office, will also form chronic lumbar muscle strain.
Warm Tip:Lumbar disc herniation and lumbar muscle strain are both common diseases in orthopedic clinics. The purpose of identifying these two diseases is that on the basis of a clear diagnosis, we can prescribe the right medicine and improve the efficacy of treatment, otherwise misdiagnosis and misdiagnosis will lead to recurrence of the condition.
For more health information, please follow us by clicking the 'Follow' button at the top of the article!
Kang Aiduo pushes a variety of professional health knowledge for you every day, so that you can learn more health information and get out of the medication error!
Feel free to like, comment or retweet if you like!
Many people are confused about the two conditions, lumbar disc herniation and lumbar strain. So what is the fundamental difference between these two diseases? How should they be distinguished? Here is a look at the science about these two diseases.

Lumbar muscle strain and lumbar disc herniation are two different diseases
Lumbar muscle strain is an injury to the muscles of the low back caused by overwork, fatigue, or trauma, or resulting in damage to the ligaments between the bone and vertebrae. Lumbar muscle strain is relatively common in clinical practice.
Lumbar disc herniation is mainly caused by degeneration of the lumbar discs, which leads to rupture of the fibrous ring outside the discs, resulting in redness, swelling and pain when the nerves in the lumbar spine are compressed. Lumbar disc herniation often occurs in the elderly, but in recent years it has gradually appeared in young people as well, and may be caused by sedentary behavior, poor sitting habits, and so on.

What are the symptoms that should be considered a lumbar strain?
For example, sitting down to do things, find yourself sitting not long, sit for a long time, the waist is sore to the point of no return, then you may be lumbar muscle strain. For example, a little bending over to do things, or wash the clothes for a while, you feel the lumbar soreness and pain, take also may be lumbar muscle strain.
So what do the symptoms of a herniated lumbar disc look like?
Lumbar disc herniation is different from low back pain caused by lumbar muscle strain. The clicking sharp pain in the lower back and legs is accompanied by numbness in the limbs, and the pain lasts for a long time, usually taking several weeks to recover. The pain is not only in the lower back, but also in the buttocks, feet, etc. In severe cases, patients may have difficulty in urinating or defecating.

How can these two diseases be treated and prevented?
Lumbar disc herniation is a conservative treatment of painkillers + hormones for mild patients, and surgery for severe patients. Lumbar muscle strain does not require surgical treatment, you can use hot and cold compresses to relieve pain can be, if necessary, you can also take painkillers.
The prevention of lumbar strain should be to strengthen the muscles of the back and not to have great mental stress. Lumbar disc herniation should be about taking care of your back with moderate exercise and movement.
Lumbar disc herniation and lumbar strain are both relatively common and have somewhat similar symptoms, but they are still very different. Diagnosis and treatment should take care to differentiate between the two conditions.
It's not easy to write, so please give me some credit.
Click on the upper right corner of the "+ attention", daily updated orthopedic science knowledge
If you have any questions or different opinions, please leave them in the comments section!
This question and answer are from the site users, does not represent the position of the site, such as infringement, please contact the administrator to delete.