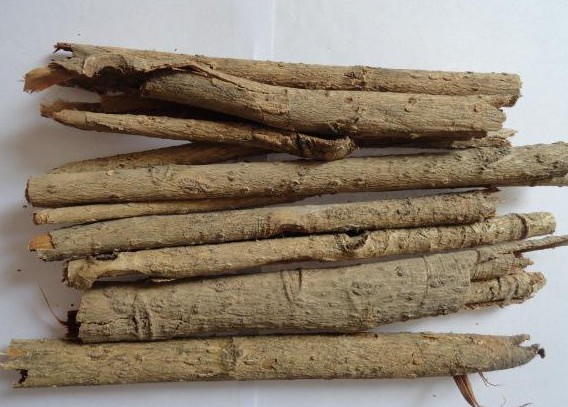
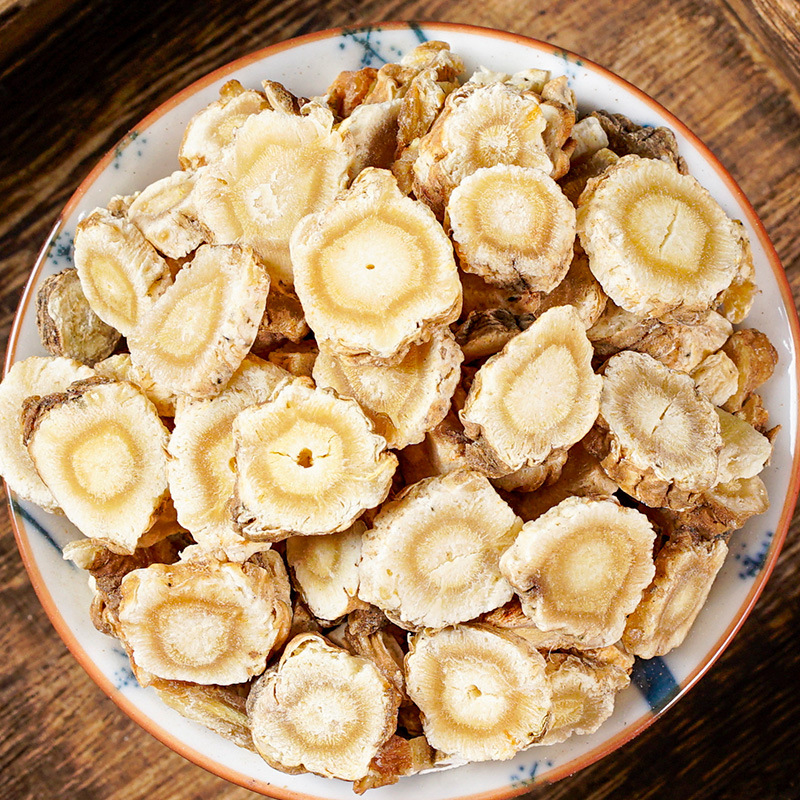
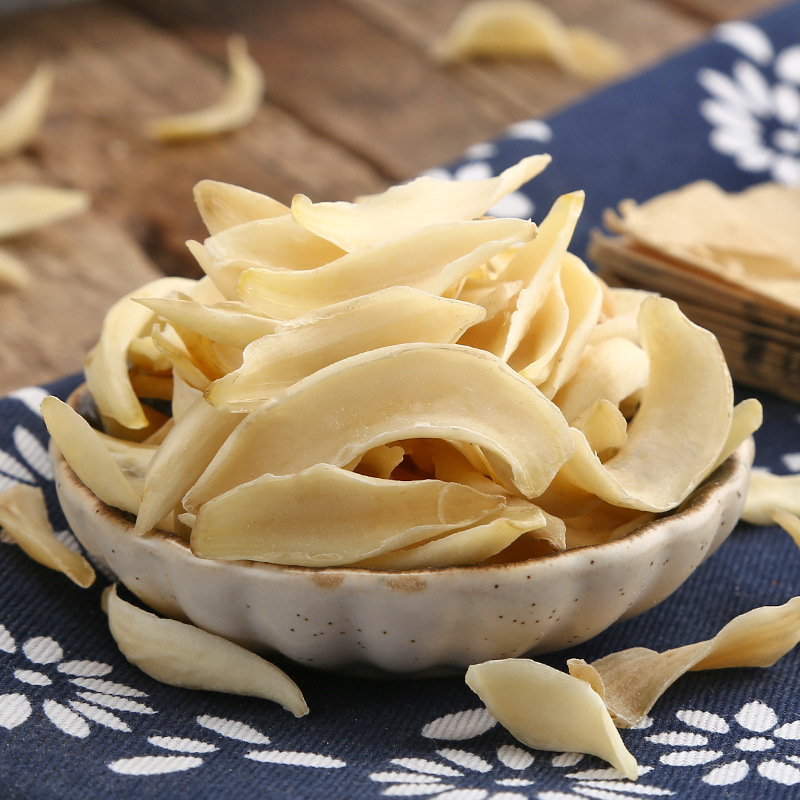
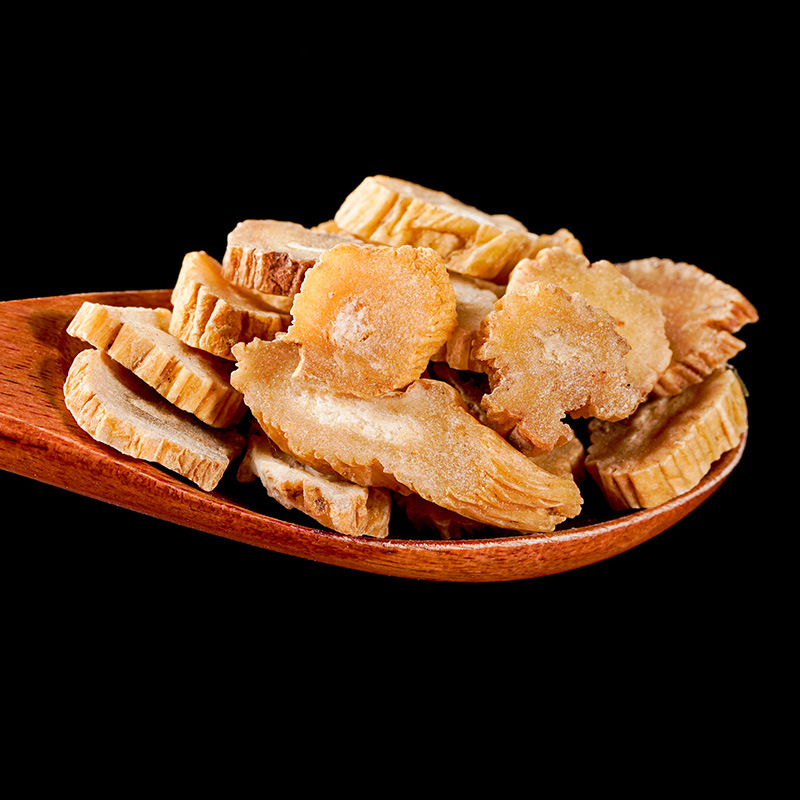
Magnolia officinalis is the root bark and trunk bark of the plant Magnolia officinalis or Magnolia officinalis var. biloba. It is mainly produced in Sichuan, Hubei, Zhejiang, Guizhou, and other regions. The quality of the product from Sichuan is relatively superior, and it is also known as Chuanpu. It is often used raw or processed with ginger juice.
I. Efficacy and Application
Magnolia officinalis tastes bitter and pungent, and its nature is warm. It belongs to the spleen, stomach, lung, and large intestine meridians.
Efficacy It can promote qi circulation, dry dampness, eliminate accumulation, and relieve asthma. Its characteristic is that it is good at eliminating damp stagnation and relieving distension and fullness, making it an essential medicine for relieving distension and fullness. Zhang Xichun described it as an essential medicine for warming the middle and directing qi downward.
It is commonly used for the treatment of damp stagnation injuring the middle, epigastric stuffiness with vomiting and diarrhea, food stagnation with qi stagnation, abdominal distension and constipation, phlegm-fluid retention with panting and cough, and other syndromes.
Abstracts of Famous Works by Renowned Authors:
The Classic of Materia Medica: "It primarily treats wind stroke, cold damage, headache, alternating chills and fever, fright qi, blood impediment, dead flesh, and eliminates three types of parasites."
Zhen Zhu Nang: "Relieve abdominal distension, strengthen the stomach and intestines."
Bie Lu: "It resolves phlegm and directs qi downward, treats cholera and abdominal pain with distention and fullness."
Compendium of Materia Medica: "Magnolia officinalis is a medicinal herb that soothes the middle and resolves stagnation, balancing stomach qi. Whenever qi stagnates in the middle, causing depression and lack of dispersion, food accumulates in the stomach, lingering without movement, or dampness accumulates and fails to disperse, and damp phlegm gathers without clearing, the warmth of Magnolia officinalis can dry dampness, its pungency can clear phlegm, and its bitterness can direct qi downward."
Changsha Materia Medica: "It lowers counterflow to stop coughing, breaks up congestion to calm panting, is excellent for stopping pain, and most effective for eliminating distention and fullness."
Ben Cao Bei Yao: "Bitter descending can drain repletion fullness, acrid warm can disperse dampness fullness. Levels the stomach and harmonizes the middle, disperses phlegm and transforms food, thickens the intestines and stomach, moves stagnant water, breaks old blood, kills visceral worms. Treats counterflow stomach and retching, panting cough diarrhea and dysentery, cold pain and cholera."
"Medical Records of Integrating Chinese and Western Medicine": "Treating upward rebellion of stomach qi, nausea and vomiting, stagnation and binding of stomach qi with distention, fullness, and pain."
II. Compatibility and Application
1. Used for damp obstruction, food stagnation, and qi stagnation leading to disharmony of the spleen and stomach, with abdominal distension and fullness. Magnolia bark is bitter and drying, acrid and dispersing, warm and capable of dispelling cold, excelling in moving qi, drying dampness, and resolving stagnation. It is suitable for abdominal distension and fullness caused by damp obstruction, food stagnation, and qi stagnation, primarily treating excess distension.
For the treatment of dampness obstructing the middle jiao syndrome, presenting with epigastric and abdominal distension and fullness, loss of appetite, bland taste in the mouth, nausea and vomiting, belching of putrid odor and acid regurgitation, heavy sensation in the limbs, lethargy and drowsiness, frequent spontaneous diarrhea, thick white greasy tongue coating, and slow pulse, it is most commonly combined with Atractylodes, Tangerine Peel, and Licorice, forming the Ping Wei San. This formula is now widely used in modern times to treat conditions such as chronic gastritis, gastric and duodenal ulcers, and digestive tract functional disorders, with significant therapeutic effects.
If treating accumulation and constipation, it is often combined with purgative and turbidity-removing herbs such as rhubarb and immature bitter orange, as seen in the Major and Minor Chengqi Decoctions.
If treating abdominal fullness and distension, a condition of deficiency with excess, it is often combined with ginger, pinellia, and licorice, known as Magnolia Bark, Ginger, Pinellia, Licorice, and Ginseng Decoction.
If treating deficiency cold with distention and fullness, it is often combined with ginseng, licorice, and other herbs that benefit qi and warm the middle, incorporating attack within tonification, tonifying without stagnation, truly an excellent method.
It is worth noting that although Magnolia officinalis has a bitter and warm nature, it can be used for Yangming interior heat syndromes, such as in the Major and Minor Chengqi Decoctions and the Mazi Ren Pill. The reason for this lies in its combination with purgative herbs like Rheum palmatum and Natrii Sulfas in the formulas. This demonstrates that the application of traditional Chinese medicine should not rely solely on the properties of individual herbs; rather, one must learn to adapt and combine them flexibly.
Yanyi: "It is most effective in regulating the middle when used in Pingwei Powder, and it remains widely popular to this day. It can both warm the spleen and stomach and dispel cold qi."
Medicine Classification and Image: It can treat abdominal distension, but for those who are weak, even if they have abdominal distension, it should be used with caution. Cold distension is treated by incorporating it into highly warming medicines.
Zhang Yuanshu said, "It can treat abdominal distension. If the primordial qi is weak, even though there is abdominal distension, it should be used with caution, as this is cold distension. When used in combination with highly warming herbs, it disperses stagnation, making it a miraculous medicine."
2. For cough, asthma, and excessive phlegm. Magnolia bark can lower lung qi, eliminate phlegm, and relieve cough and asthma. To treat mild wheezing due to unresolved external pathogens, it is often combined with apricot kernel and added to Cinnamon Twig Decoction, known as Cinnamon Twig Decoction with Magnolia Bark and Apricot Kernel.
If treating cough and asthma due to phlegm and saliva congestion, upper excess and lower deficiency, it is often combined with Perilla Fruit, Pinellia Tuber, and Common Hogfennel Root, which is Perilla Fruit Qi-Directing Decoction.
Wang Haogu said, "The Bie Lu states that Magnolia Bark warms the middle and boosts qi, dispels phlegm and directs qi downward. Does it actually drain qi or boost qi? When used with Immature Bitter Orange and Rhubarb, it drains excess fullness, which is what is meant by dispelling phlegm and directing qi downward. When used with Tangerine Peel and Atractylodes, it eliminates dampness fullness, which is what is meant by warming the middle and boosting qi. When used with resolving and dispersing medicinals, it treats cold damage headache. When used with draining and dispersing medicinals, it thickens the intestines and stomach. Generally, it is bitter in flavor and warm in nature. When bitterness is utilized, it drains; when warmth is utilized, it supplements."
Zhang Xichun said: "When used together with tangerine peel and pinellia, it is good at removing dampness and fullness; when used together with ginger and masterwort, it is good at dispersing cold phlegm accumulation; when used together with mirabilite and rhubarb, it is good at relieving dry stool and constipation; when used together with lindera root, it is good at treating turbid urine due to cold." He also said: "In treating conditions of upward rushing of qi and upward reversal of phlegm and saliva, I always heavily use dragon bone, oyster shell, pinellia, and hematite to lower, suppress, and astringent them, and I must use a small amount of magnolia bark to promote and unblock them. Then the rushing qi and phlegm saliva descend, and the middle qi still rises and falls naturally without obstruction."
III. Usage and Dosage
Magnolia officinalis is often used in decoctions and can also be made into pills or powders. The usual dosage in decoctions ranges from a few grams to several tens of grams. Different dosages yield different effects.
Ancient texts mention using it by "removing the skin," which refers to stripping off the rough outer layer, not the entire bark.
Li Dongyuan said, "Purple ones are best, remove the skin, process with ginger juice, and lightly stir-fry."
Huang Yuanyu said, "Remove the skin, stir-fry with ginger juice."
IV. Application Notes
Magnolia officinalis is bitter and warm, easily damaging healthy qi, so those with weak constitution should use it with caution.
After being processed with ginger juice, it can remove its bitter and dry nature, making it relatively safe.
Wang Ang said, "Incorrect consumption can deplete one's vital energy, and it is contraindicated for pregnant women."
Attached Medicinal Herb: The Efficacy and Application of Magnolia officinalis Flower
The flower bud of Magnolia officinalis is the flower bud of Magnolia officinalis. Its nature and flavor are pungent and warm. Its efficacy is to transform dampness with fragrance, promote qi and widen the chest. It is commonly used in the treatment of symptoms such as abdominal distension, fullness, and pain caused by damp turbidity and qi stagnation. The usual dosage is a few grams.
The medicinal potency of Magnolia officinalis flower is relatively mild, so it can be used as a substitute for Magnolia officinalis in cases of mild dampness and abdominal distension or in individuals with a weak constitution.
Practical Notes on Traditional Chinese Medicine: Second Draft, January 21, 2022