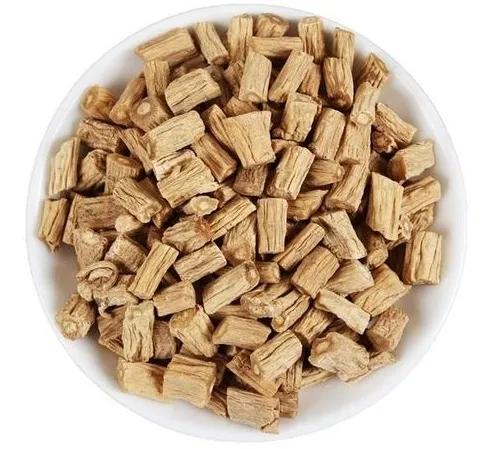
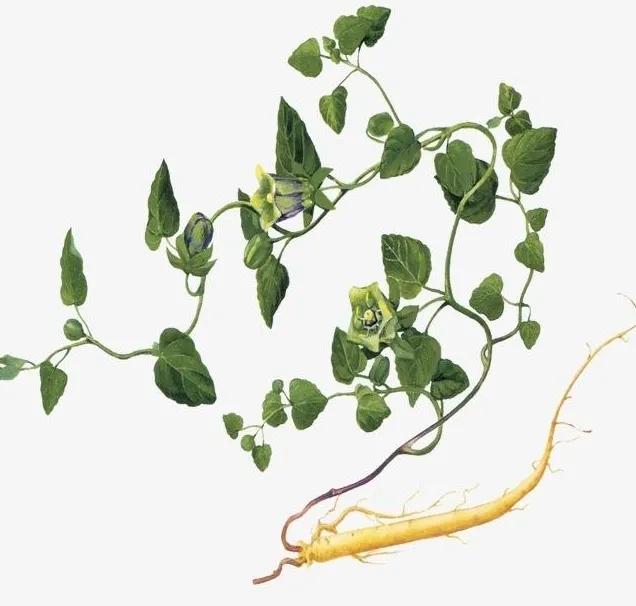
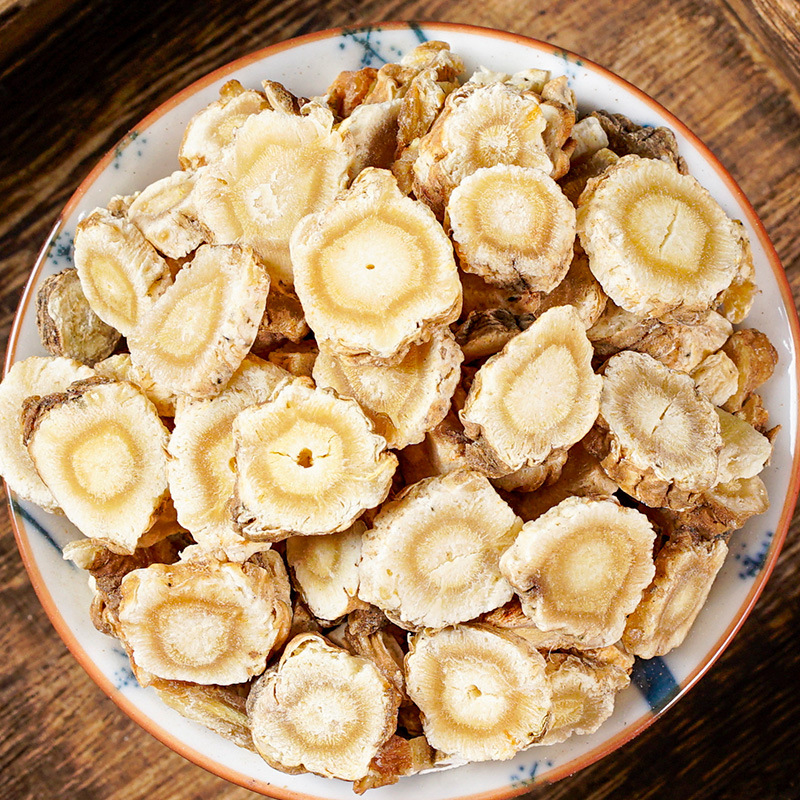
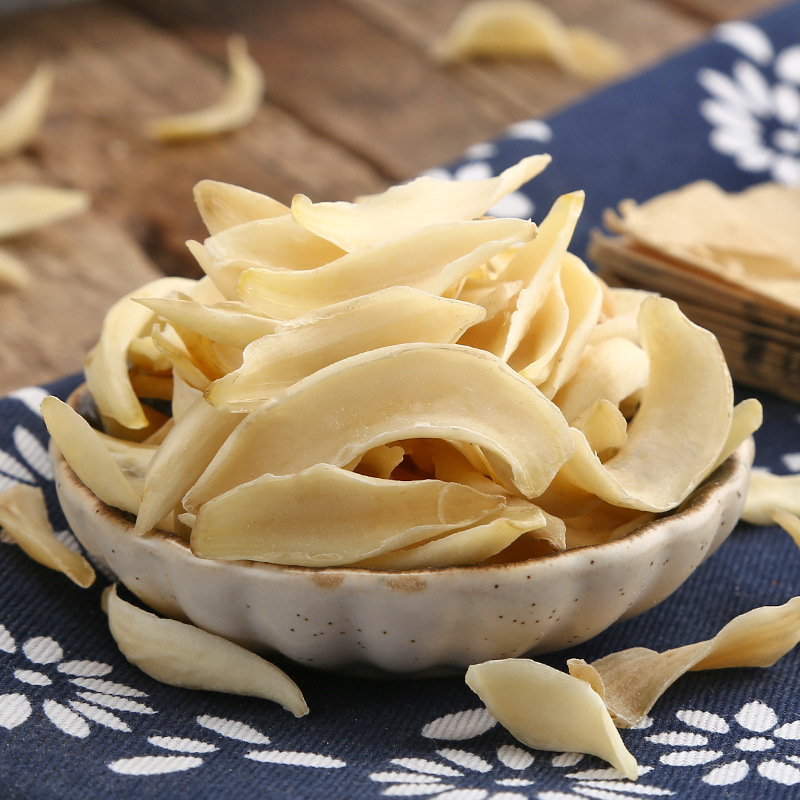
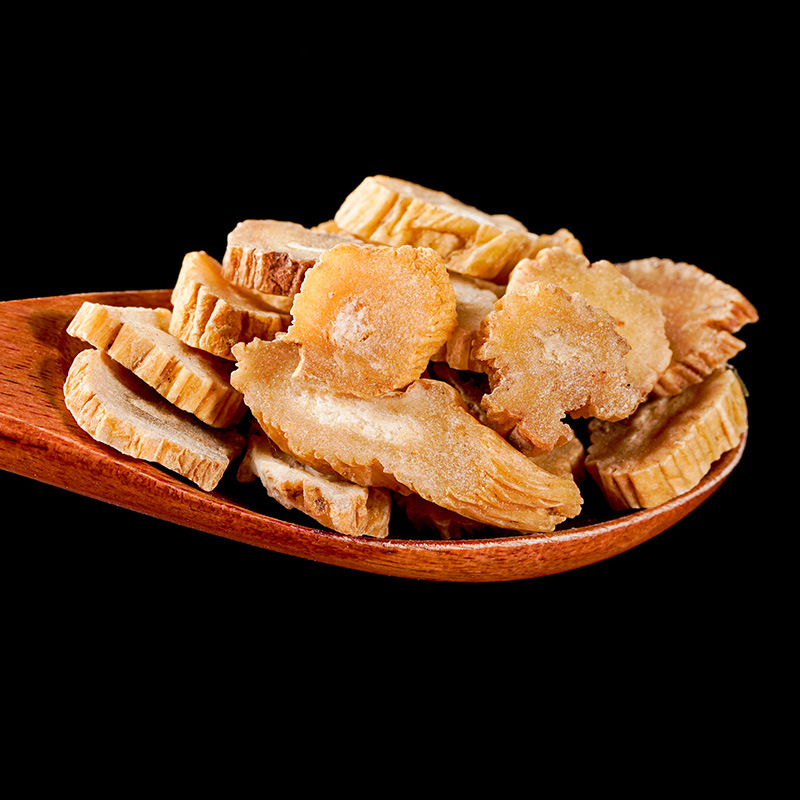
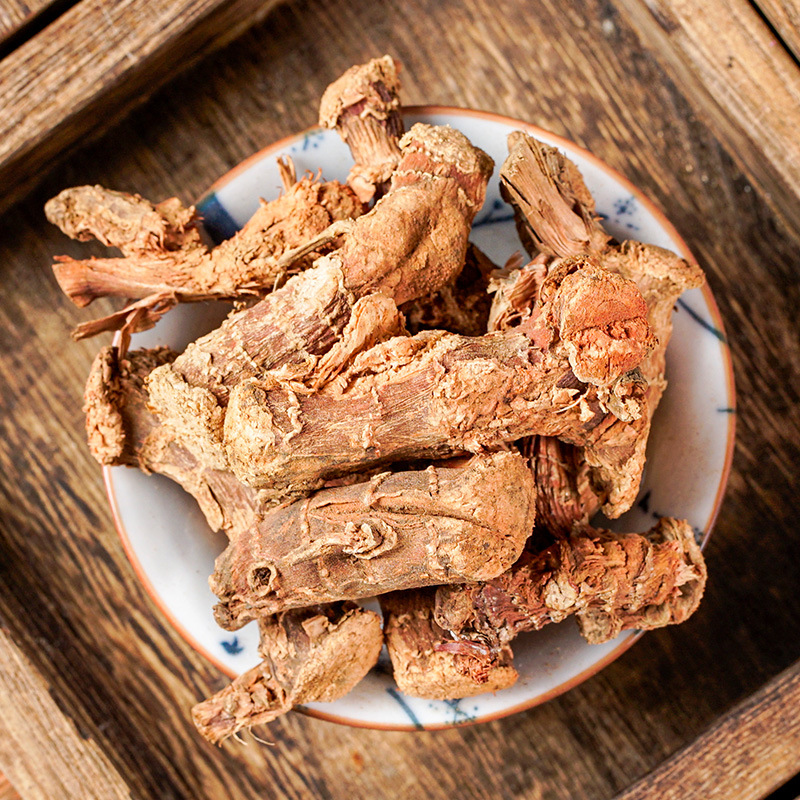
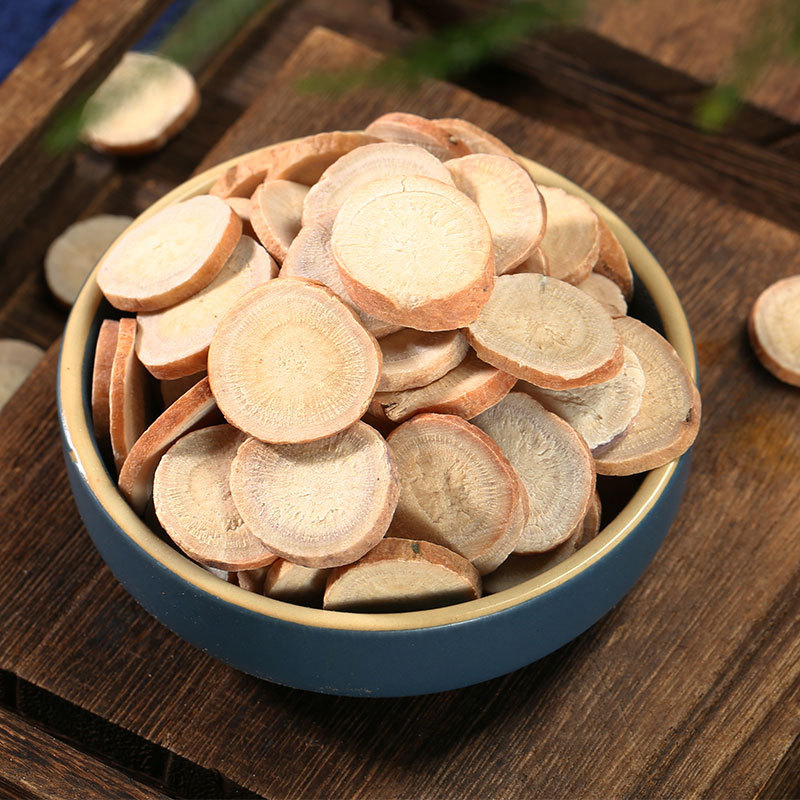
Codonopsis is the root of the plant Codonopsis pilosula and other species of the same genus in the Campanulaceae family. It is named as such because it is produced in the Shangdang region of Luzhou, Shanxi, and its effects are similar to those of ginseng. It should be noted that the Codonopsis used today is not the same as the Shangdang ginseng mentioned in ancient texts. The Shangdang ginseng used in ancient literature refers to ginseng from the Araliaceae family, while the Codonopsis used today belongs to the Campanulaceae family and has been in use only since the Ming Dynasty. The ginseng mentioned in the "Treatise on Cold Damage Disorders" refers to the Araliaceae Shangdang ginseng, which is now extinct. Today, when ginseng is used in classical formulas, it is often replaced by Jilin ginseng or Codonopsis.
I. Efficacy and Application
Codonopsis pilosula tastes sweet and is neutral in nature. It belongs to the spleen and lung meridians.
Efficacy can tonify the middle and boost qi, generate fluids and nourish blood, support the healthy and dispel pathogens. Its characteristics are similar to ginseng in terms of tonifying effects, but it is weaker in strength and more affordable, making it more suitable for general use. It is indeed an essential herb for tonifying qi and generating fluids.
It is commonly used for the treatment of spleen and lung qi deficiency, reduced appetite and fatigue, cough and asthmatic deficiency, qi and blood deficiency, sallow complexion, palpitations and shortness of breath, fluid injury and thirst, internal heat and diabetes, chronic diarrhea and rectal prolapse, and other syndromes. For general deficiency syndromes, it can be used as a substitute for ginseng; however, for severe deficiency and collapse syndromes, ginseng is still preferable.
Summary of Masterpieces by Renowned Authors:
Ben Cao Cong Xin: "Tonifies the middle and augments qi, harmonizes the spleen and stomach, eliminates vexation and thirst. For weak middle qi, it is used for regulation and supplementation, and is very safe."
Compendium of Materia Medica Supplement: "Treats lung deficiency, can benefit lung qi."
"Compendium of Materia Medica": "Its power can tonify the spleen and nourish the stomach, moisten the lungs and promote fluid production, invigorate the middle qi, which is not far from that of ginseng. What is particularly valuable is that it strengthens the spleen and promotes movement without being drying, nourishes stomach yin without causing dampness, moistens the lungs without being cold or cool, enriches the blood without being overly greasy, stimulates clear yang, invigorates middle qi, and lacks the drawbacks of harsh dryness."
Manual of Chinese Medicinal Materials: "Treats internal injuries from deficiency and fatigue, cold in the stomach and intestines, chronic diarrhea and dysentery, shortness of breath and excessive thirst, fever and spontaneous sweating, as well as various conditions in women such as metrorrhagia and complications during pregnancy and childbirth."
II. Compatibility and Application
1. For deficiency of middle qi and weakness of spleen qi. Codonopsis pilosula can tonify the middle and replenish qi, and it is inexpensive, so it is widely used today. For treating deficiency of middle qi, reduced appetite, loose stools, and fatigue in the limbs, it is often combined with Atractylodes macrocephala, Poria cocos, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis, which is known as the Four Gentlemen Decoction; if combined with Astragalus membranaceus, Angelica sinensis, Citrus reticulata, and Bupleurum chinense, it is known as the Center-Supplementing and Qi-Boosting Decoction. Both formulas can use Codonopsis pilosula or Panax ginseng, depending on the severity of the condition.
2. For lung qi deficiency. Codonopsis can tonify spleen qi, benefit lung qi, and cultivate earth to generate metal. It is used to treat symptoms such as shortness of breath, cough, wheezing, weak speech, and low voice caused by lung qi deficiency. It is often combined with Astragalus and Schisandra, as in the formula Bufei Tang.
If treating deficiency of both spleen and lung, shortness of breath, cough, reduced food intake, loose stools, limb fatigue and weakness, etc., it is often combined with Poria, Atractylodes macrocephala, tangerine peel, lotus seeds, etc., which is Ginseng, Poria and Atractylodes Macrocephala Powder.
3. For heat disease damaging body fluids, shortness of breath and thirst. Codonopsis pilosula can replenish qi and generate fluids. To treat dual damage to qi and fluids, with restlessness, thirst and fatigue, it is often combined with Ophiopogon japonicus and Schisandra chinensis, known as Shengmai Yin.
4. For blood deficiency with sallow complexion, dizziness, and palpitations. Codonopsis pilosula has the effect of tonifying qi and nourishing blood. To treat dual deficiency of qi and blood, it is often combined with Rehmannia glutinosa (prepared), Angelica sinensis, Ligusticum chuanxiong, Atractylodes macrocephala, and Glycyrrhiza uralensis to achieve the dual tonification of qi and blood, known as Bazhen Tang (Eight-Treasure Decoction); if Astragalus membranaceus and Cinnamomum cassia are added, it becomes the renowned formula for dual tonification of qi and blood, Shiquan Dabu Tang (Ten-Ingredient Great Tonifying Decoction).
5. For deficiency of the body with external contraction, or interior excess with deficiency of the body. Codonopsis pilosula can replenish qi and release the exterior, support the healthy qi and dispel the pathogenic qi. For deficiency of the body with external contraction, or accompanied by diarrhea and dysentery that is difficult to cure for a long time, it can be used according to the method of Ginseng Antiphlogistic Powder.
III. Usage and Dosage
Codonopsis pilosula is often used in decoctions, as well as in pills and powders. The typical dosage in decoctions ranges from over ten grams to several tens of grams. It can also be used as a substitute for ginseng, and when ginseng is unavailable, the dosage of Codonopsis pilosula can be doubled.
However, Codonopsis pilosula does not possess the ability to greatly tonify primordial qi, and its efficacy is insufficient for emergency use in stabilizing collapse.
"Compendium of Materia Medica": "Dangshen has the ability to tonify the spleen and nourish the stomach, moisten the lungs and promote fluid production, invigorate the middle qi, and is not significantly different from ginseng. Its most valuable aspect is that it strengthens the spleen and promotes movement without being drying, nourishes stomach yin without causing dampness, moistens the lungs without being cold or cool, enriches the blood without being overly greasy, stimulates clear yang, invigorates middle qi, and lacks the drawbacks of harsh dryness. Therefore, in all ancient and modern formulas that use ginseng, it can be replaced by Ludangshen, and in all treatments that require ginseng, Ludangshen can also be used."
Zhang Xichun said, "If there is no ginseng, double the dosage of Codonopsis pilosula."
IV. Application Precautions
Codonopsis is most suitable for deficiency-cold syndrome, but it should not be used alone in cases of excess syndrome or heat syndrome.
Practical Notes on Traditional Chinese Medicine: 20.11.7