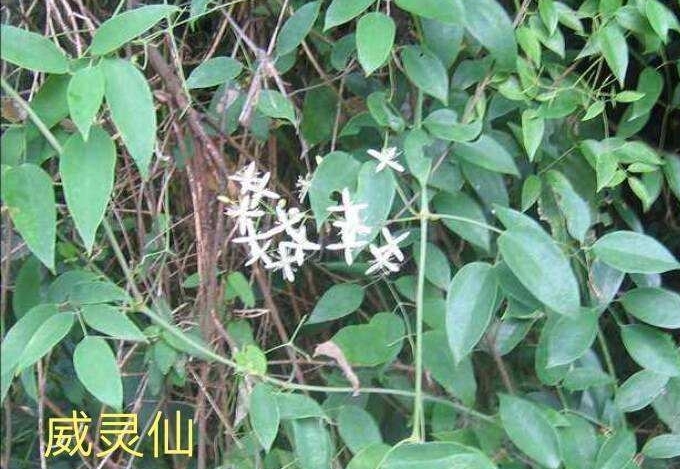
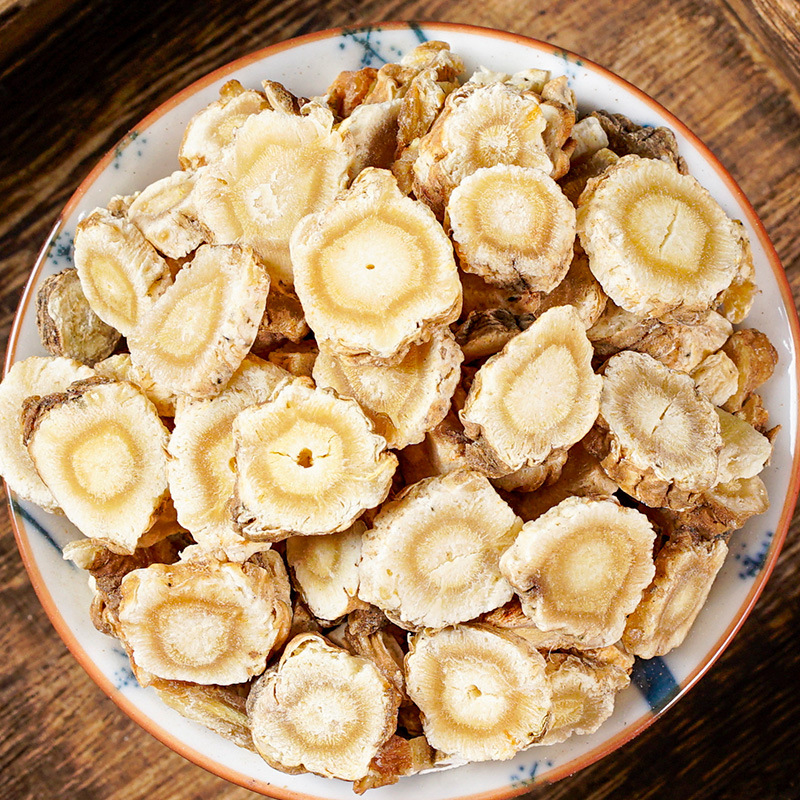
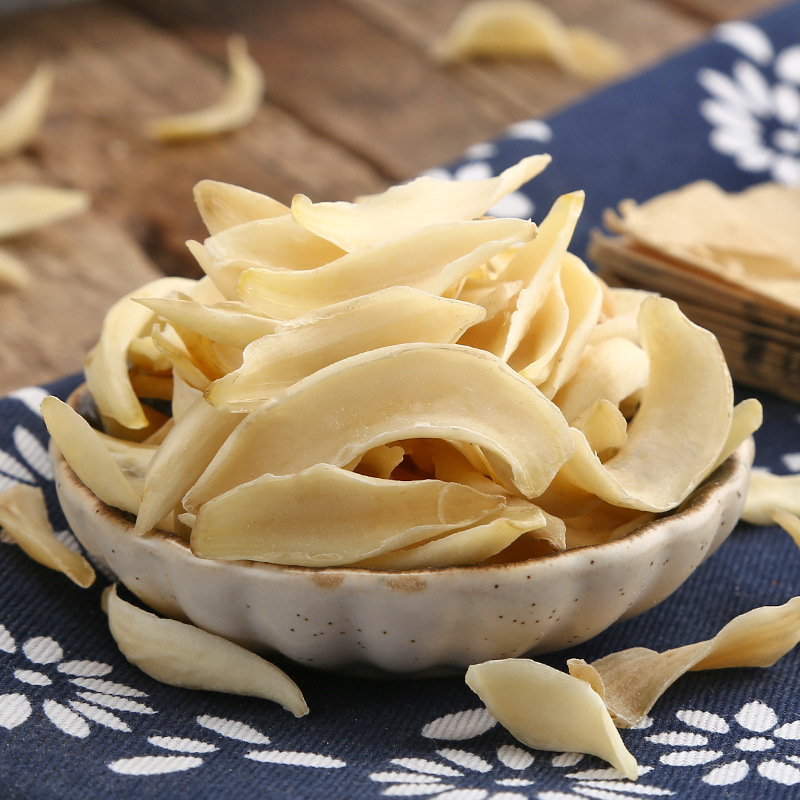
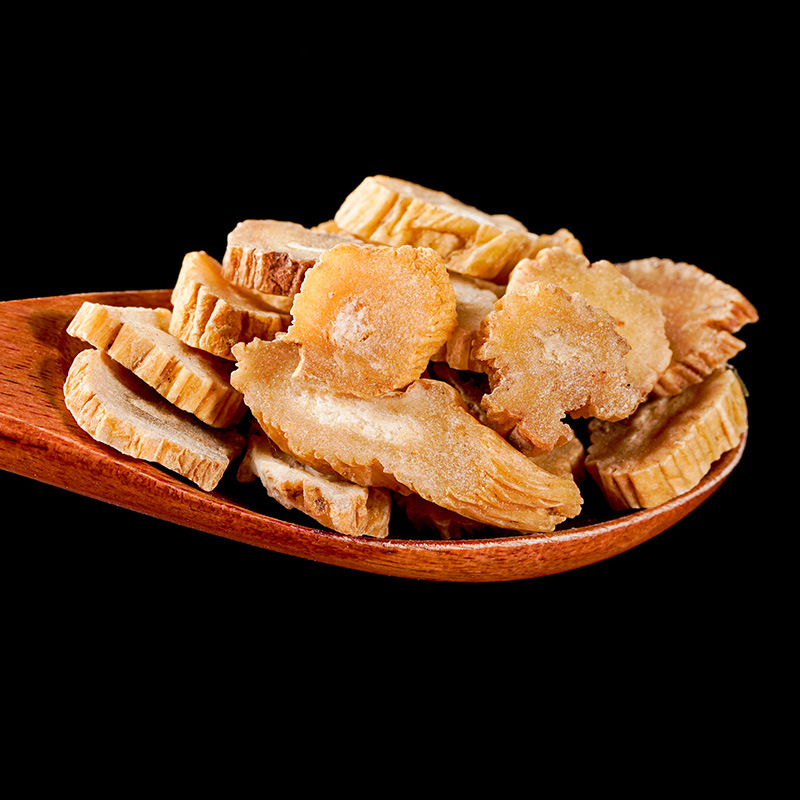
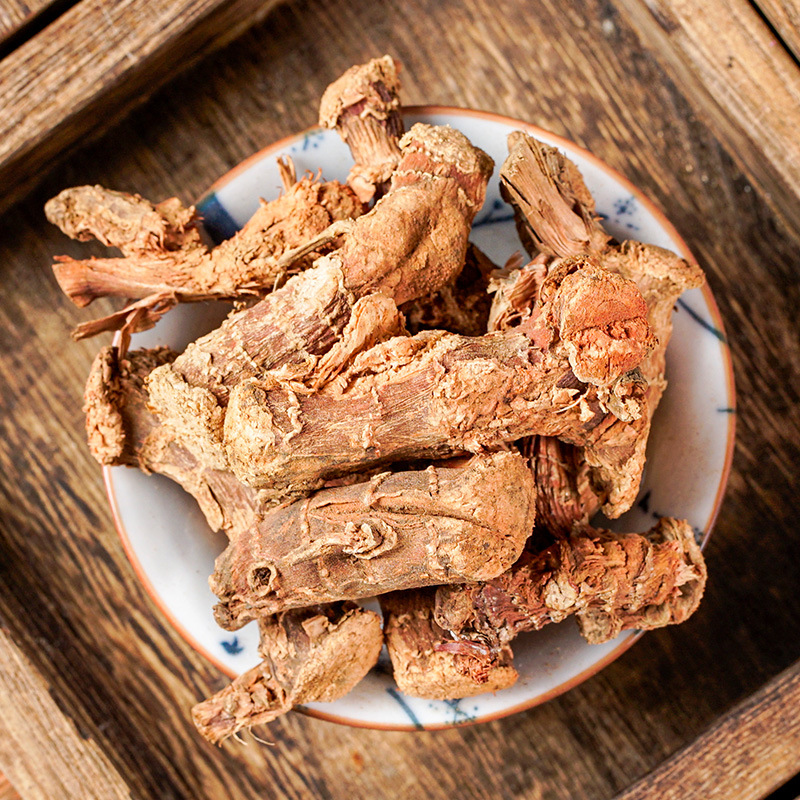
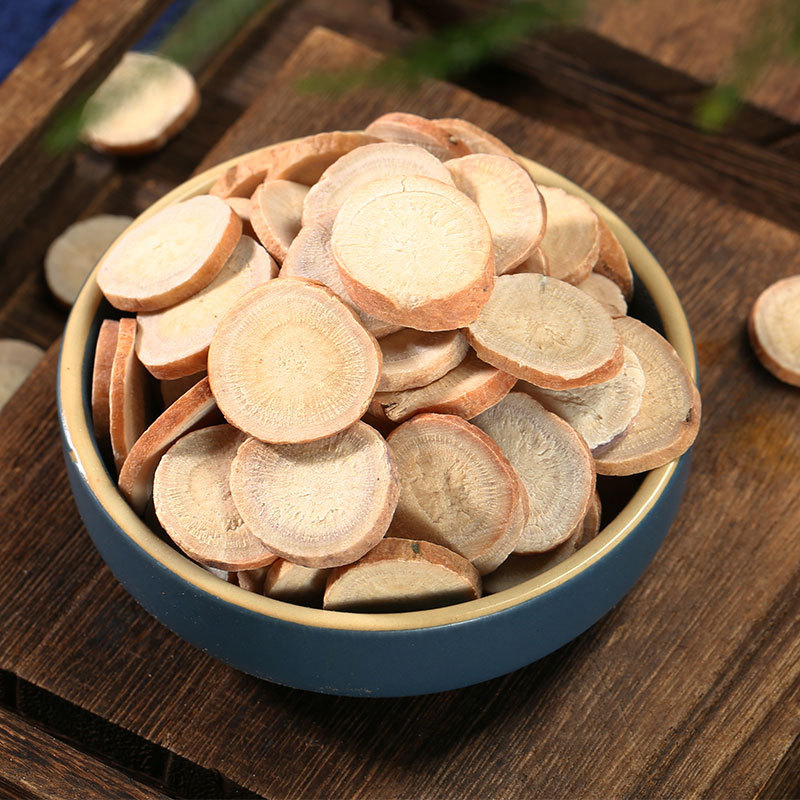
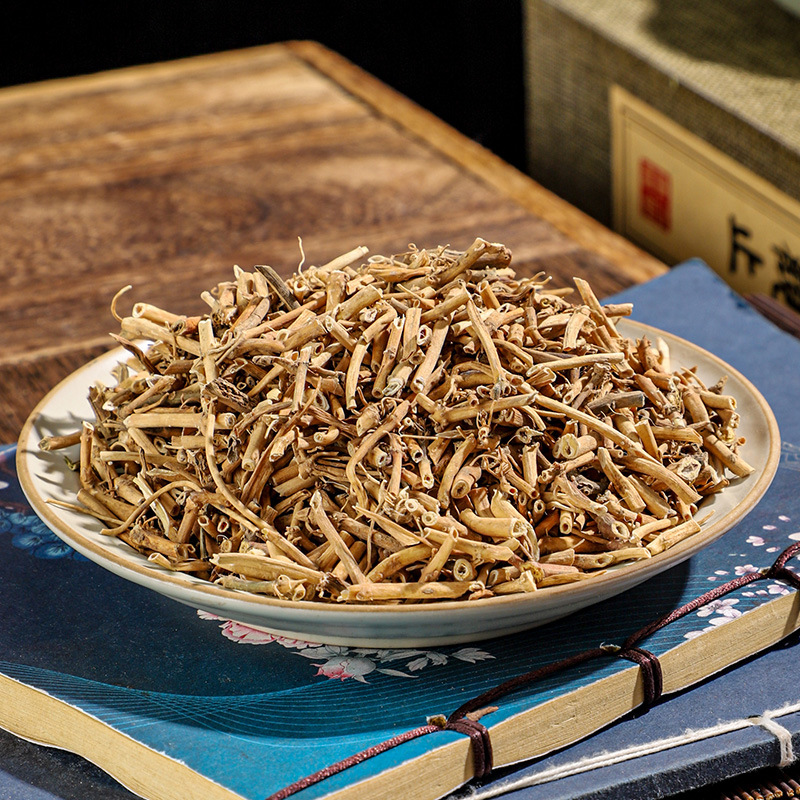
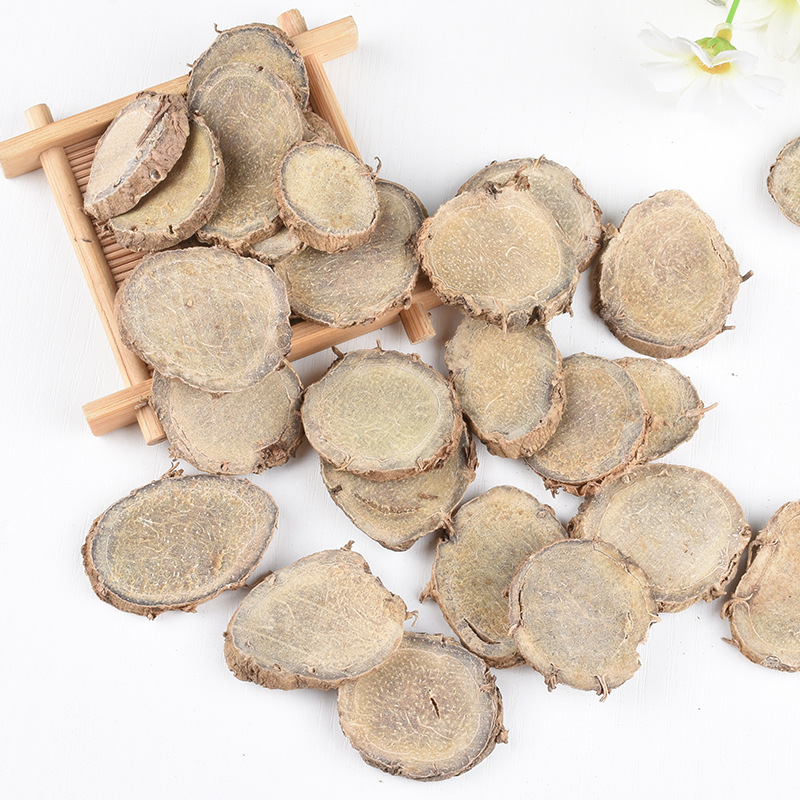
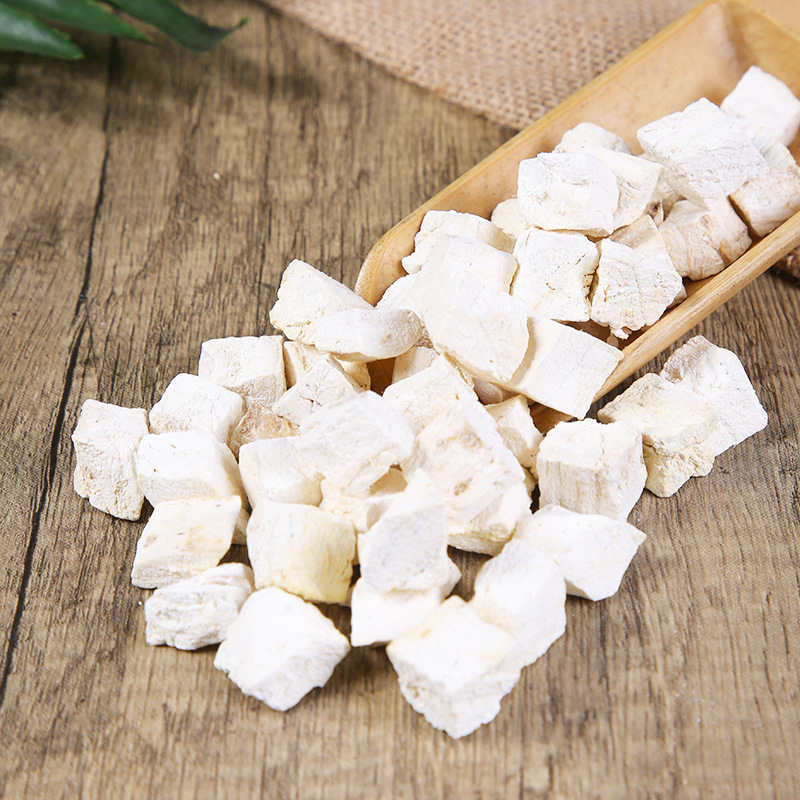
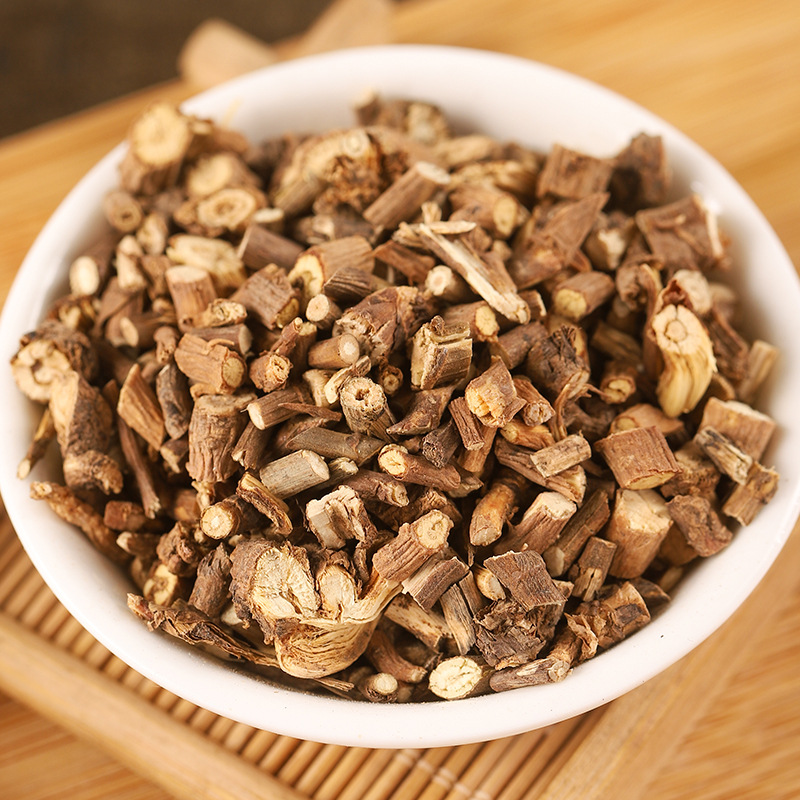
Clematis root is the root and rhizome of Clematis chinensis, Clematis hexapetala, or Clematis manshurica from the Ranunculaceae family. Its name means "mighty and efficacious." It is mainly produced in Jiangsu, Anhui, Zhejiang, and other regions. It is harvested in autumn, cleaned of soil, and dried in the sun. It is often used in its raw form.
I. Efficacy of Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma:
Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma tastes pungent and salty, warm. It belongs to the bladder meridian. Its effects canDispelling Wind and Dampness, Unblocking Collaterals and Relieving PainIt is also effective in treating fish bone stuck in the throat. Its characteristics include being pungent and warm, dispersing and moving without staying, particularly excelling in unblocking collaterals and relieving pain.
Commonly used inRheumatic pain and numbness, limb numbness, muscle and tendon spasm, difficulty in flexion and extensiontreatment of conditions such as
Summary of Famous Works by Renowned Authors
Newly Revised Materia Medica: "For ailments of the waist, kidneys, knees and feet, accumulations, and various cold diseases in the intestines that have not healed for years, taking it is effective."
Ben Cao Zheng Yi: "Weilingxian is known for its ability to disperse and eliminate, making it suitable for conditions such as accumulated dampness, stagnant phlegm, blood stasis, and qi stagnation, all of which are excess patterns."
Jade Carving's Explanation of Medicinals: Clematis root drains dampness and expels wind, moves phlegm and expels rheum, treats stubborn numbness of the hands and feet, lower back pain and weak knees, old blood and longstanding concretions, accumulated water and stagnant phlegm.
"Compendium of Materia Medica": "It has a nature that is adept at moving, capable of dispersing and unblocking the five viscera, and circulating through the twelve meridians. It treats wind stroke and head wind, stubborn wind and obstinate impediment, concretions, conglomerations, accumulations, and gatherings, phlegm and water with long-standing pus, jaundice and edema, constipation of the large and small intestines, wind-damp phlegm qi, and all types of cold pain. Its nature is extremely swift and effective; for those with chronic illnesses that have not healed, taking it yields rapid results."
II. Compatibility and Application of Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma:
1. For rheumatic arthralgia. Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma is adept at moving and dispersing, capable of unblocking collaterals to relieve pain, dispelling wind and eliminating dampness. It can be applied for all cases of rheumatic arthralgia, limb numbness, tendon and vessel spasm, and difficulty in joint flexion and extension. To treat rheumatic arthralgia, it can be used alone by grinding into powder for oral administration, namelyWeilingxian Powder。
If treating rheumatic lumbago, it can be combined with cinnamon bark and Chinese angelica root, namelyShen Ying Wan。
For the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis, which worsens with cold, it is often combined with Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae, Radix Stephaniae Tetrandrae, Fructus Chaenomelis, Rhizoma Homalomenae, Rhizoma Atractylodis, Radix Aconiti Kusnezoffii Praeparata, and Radix Cyathulae, among other herbs, to collectively achieve the effects of unblocking meridians, dispelling wind and dampness, reducing swelling, and alleviating pain.
The Biography of Clematis: "A man had been paralyzed in his hands and feet for decades. He met a monk from Silla who said, 'There is a medicine that can cure you.' He went into the mountains to search for it and found clematis. After taking it, he was cured."
2. For gout and arthralgia. Clematis is also effective in treating gout, often combined with Smilax glabra and Dioscorea hypoglauca. The combination of these three herbs can serve as the foundation for many formulas, with a significant effect on excreting uric acid.
For treating gout and arthralgia, especially with significant redness, swelling, and pain in the lower limb joints, it is often combined with Smilax glabra, Dioscorea hypoglauca, peach kernel, safflower, Lycopus lucidus, Alisma plantago-aquatica, coix seed, plantain seed, Atractylodes lancea, and Cremastra appendiculata, namelyGout Decoction。
3. For fish bone stuck in the throat, bone spur syndrome. Clematis has the effect of relaxing the smooth muscle of the esophagus. A large dose decoction taken slowly can treat fish bone stuck in the throat, or combined with Amomum villosum and granulated sugar, decocted with vinegar, can enhance the therapeutic effect.
Weilingxian can also be used for bone spurs syndrome, when combined with Chushizi, it is namedIron-Resolving PillIt has the power to soften hardness and dissipate nodules. For treating heel spur pain, it is often combined with Broussonetia papyrifera, Achyranthes bidentata, Chaenomeles speciosa, Boswellia carterii, and Commiphora myrrha.
Zhu Liangchun treats bone spurs and hyperosteogeny by focusing on the kidney, employing a comprehensive approach that addresses both the root cause and symptoms through kidney-tonifying and bone-strengthening methods, combined with blood-activating, phlegm-resolving, warm-channel, and turbidity-eliminating therapies. He often pairs Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma with kidney-tonifying herbs such as Rehmanniae Radix Praeparata, Epimedii Folium, Cervi Cornus Colla, Corni Fructus, and Paeoniae Radix Rubra et Alba, as well as blood-activating and collateral-dredging herbs like Eupolyphaga Steleophaga, Drynariae Rhizoma, Pyritum, Dipsaci Radix, Myrrha, Carthami Flos, Pyrolae Herba, and Vespae Nidus. For cervical spine conditions, he adds Puerariae Lobatae Radix and Chuanxiong Rhizoma; for lumbar spine conditions, Eucommiae Cortex and Taxilli Herba; and for knee or heel conditions, Achyranthis Bidentatae Radix. Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma is always an essential component, and his experience is worth learning from.
"Medicinal Properties": "Lingxian is fierce and swift in nature, moving without staying, and it unblocks the twelve meridians. It is primarily used to treat wind, dampness, and phlegm stagnation in the meridians, which can lead to wandering gout, joint pain, swelling, or numbness. By clearing the meridians, it can quickly resolve blood stagnation and phlegm obstruction."
4. For Qi Stagnation. Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma is adept at moving and regulating Qi, and resolving phlegm and fluid. It can be directly used for conditions such as dysphagia and abdominal masses, or combined with other herbs to achieve a "lively and dynamic" effect.
For treating damp-heat jaundice, use Yinchenhao Decoction and similar formulas. Adding Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma to enhance diuresis can achieve rapid relief of jaundice.
In the works of Zhang Xichun, there is a case where a patient suffered from a dry and excess syndrome. The previous physician administered several doses of Chengqi Decoction with no effect. Later, Zhang instructed the patient to take Weilingxian Decoction alone, and shortly thereafter, the patient's bowels moved, and the illness was cured. The previous physician was puzzled and asked for the reason. Zhang explained that the previous medication had stagnated in the stomach and could not be transformed. Taking Weilingxian Decoction focused on regulating and promoting the flow of qi. Once the qi mechanism was unblocked, the efficacy of the previous medication naturally manifested, thus achieving the desired effect. The flexibility in the application of traditional Chinese medicine can be glimpsed from this medical case.
III. Usage and Dosage of Clematis Root:
Clematis root is often used in decoctions, can also be made into pills or powders, and can be applied externally. The usual dosage in decoctions ranges from a few grams to over ten grams; if it is the main ingredient in a prescription, such as for treating bone spurs or fish bone stuck in the throat, it can be used in amounts of several tens of grams or more. For external use, apply an appropriate amount.
IV. Application Notes for Clematis Root:
Clematidis Radix et Rhizoma is pungent and dispersing, and tends to move quickly. Prolonged use may easily damage healthy qi, thereforeThose with qi and blood deficiency, and those without wind, cold, or damp pathogenic factors should use with caution。
"Compendium of Materia Medica": "All diseases caused by blood deficiency generating wind, or qi deficiency generating phlegm, spleen deficiency failing to transport, and qi stagnation generating dampness, phlegm, or fluid retention should be strictly prohibited."
Huang Yuanyu said, "Do not use for those with deficiency."
Wang Ang said, "It disperses and discharges genuine qi, so it should be used cautiously in those who are weak."