Food is the paramount necessity of the people, and the condition of our digestive system greatly impacts our health.
There is a type of stomach pain called burning pain—sometimes even a burp can bring a reflux of sour and bitter fluid into the mouth, causing a tightness in the throat and a burning sensation behind the breastbone. At such moments, the body involuntarily shudders, and tears follow.
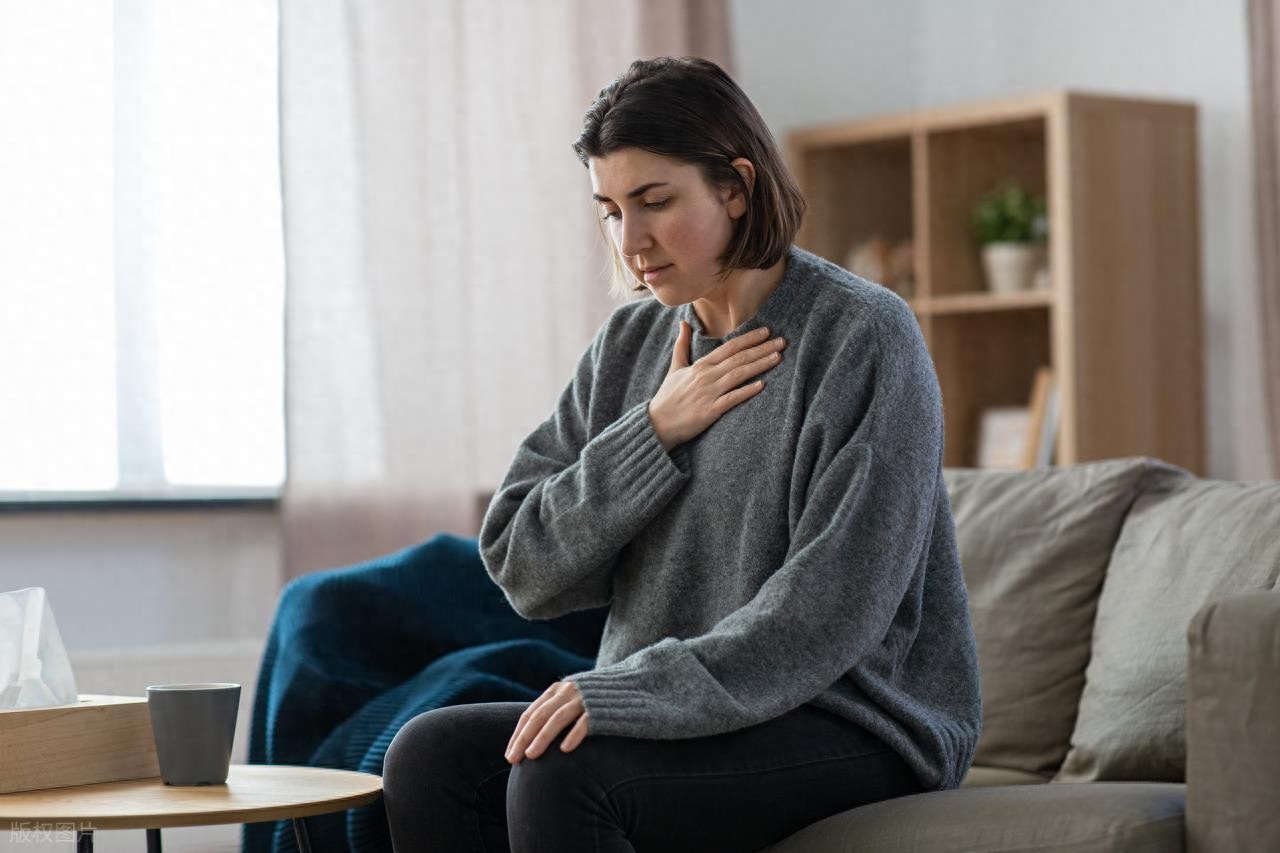

These are the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease, with reflux esophagitis being the most common type.
Typical Symptoms
The typical symptoms of this disease include three main characteristics: heartburn, acid reflux, and retrosternal pain. Heartburn is a burning sensation that extends upward behind the sternum, often occurring after meals or when lying flat. Acid reflux refers to the backflow of stomach contents into the throat, leaving a sour and bitter taste. In severe cases, it can even lead to erosion of tooth enamel due to the stimulation and corrosion caused by the refluxed material.
What is even more troubling is that some patients experience chronic coughing and hoarseness due to stomach acid irritating the throat, often misdiagnosed as a respiratory condition.
Current Situation
The fast pace of modern life—high-pressure work, high-fat fast food, coffee, alcohol, and more—artificially creates an acidic constitution, causing the esophageal mucosa to be soaked in an "acid pool" for extended periods, leading to various stomach ailments.
For the treatment of these diseases, conventional acid-suppressing drugs can provide relief, but recurrence is common after discontinuation, and long-term use may lead to side effects such as osteoporosis. Therefore, how to explore alternative treatment options in traditional Chinese medicine has garnered widespread attention.
Today we will introduce a traditional Chinese medicine that can treat reflux esophagitis: Jiawei Zuojin Wan.
Pathogenesis of Reflux Esophagitis
Imbalance of ascending and descending is the core pathogenesis of reflux disease. When ascending exceeds descending, reflux occurs. In traditional Chinese medicine theory, reflux esophagitis falls under the categories of "swallowing acid," "vomiting acid," and "chest impediment."
The core pathogenesis is summarized as "stomach failing to descend and turbid yin ascending counterflow" — in the normal physiological state, the spleen governs the ascent of the clear, while the stomach governs the descent of the turbid, the two revolving like yin and yang in Tai Chi.
Once the balance is disrupted, stomach qi fails to descend and instead rises, carrying sour and putrid substances upward into the esophagus, thus forming this disease.
How does Jiawei Zuojin Wan extinguish esophageal fire
Faced with complex pathogenesis, an ancient formula from one of the Four Great Masters of the Jin and Yuan Dynasties, Zhu Danxi—Zuojin Pill—stands out.
The formula consists of only two herbs: Coptis chinensis and Evodia rutaecarpa, yet it effectively protects the stomach.
Jiawei Zuojin Wan is based on Zuojin Wan with the addition of many herbs that soothe the liver, relieve depression, regulate qi, and alleviate pain, such as Scutellaria baicalensis, Bupleurum, and Aucklandia.
Therefore, it is more suitable for patients with severe liver stagnation or liver fire, manifested as stomach pain radiating to the hypochondrium, irritability, belching, and acid regurgitation, which are more severe.
Why is it called Zuojin Pill
Liver Wood is restrained by Lung Metal, then the generation and transformation are normal.
Zuojin Pill clears heart fire, allowing lung metal to be fearless and execute the metal command on the left to pacify the liver, hence it is named "Zuojin Pill".
As stated in the "Medical Formulas Explained": "Left Metal refers to the use of Coptis chinensis to purge heart fire, thereby allowing lung metal to be free from fear and able to exert its influence on the left to pacify the liver, hence the name Left Metal."
Jiawei Zuojin Wan
Ingredients:Rhizoma Zingiberis Preparata, Fructus Evodiae Preparata, Radix Scutellariae, Radix Bupleuri, Radix Aucklandiae, Rhizoma Cyperi Preparata, Radix Curcumae, Radix Paeoniae Alba, Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae Viride Preparata, Fructus Aurantii Preparata, Pericarpium Citri Reticulatae, Rhizoma Corydalis Preparata, Radix Angelicae Sinensis, Radix Glycyrrhizae.
Functions and IndicationsCalming the liver to lower adverse qi, relieving depression to stop pain. It is used for chest and epigastric stuffiness and oppression, irritability and susceptibility to rage, belching and acid regurgitation, stomachache and poor appetite caused by liver depression transforming into fire and liver-stomach disharmony.
Analysis of Medicinal Efficacy
Coptis chinensis:Bitter and cold to directly reduce, clearing and purging excess fire in the liver and stomach, eliminating the root cause of inflammation.
Evodia Fruit:Warm and pungent to open stagnation, soothe the liver and direct qi downward, guide heat to descend.
The combination of the two herbs creates a dynamic of "pungent opening and bitter descending": the bitterness of Coptis chinensis can clear heat, while the pungency of Evodia rutaecarpa can disperse stagnation, as if opening a downward pathway for rebellious stomach qi. Even more ingeniously, the warmth of Evodia rutaecarpa moderates the cold nature of Coptis chinensis, preventing excessive bitterness and cold from harming the stomach, embodying the wisdom of "mutual opposition and complementarity" in herbal pairing.
Jiawei Zuojin Pill is based on Zuojin Pill and adds twelve traditional Chinese medicines such as Scutellaria baicalensis. It not only clears liver fire but also soothes the liver to relieve depression, regulates qi, and alleviates pain. It is suitable for complex conditions involving liver qi stagnation and liver fire attacking the stomach.
The core pathogenesis of reflux is qi counterflow. The liver is the largest qi pivot in the human body. The liver governs free flow; if liver qi stagnates and fails to flow smoothly, it may transversely invade the stomach, leading to reflux and other conditions.
Therefore, increasing the dosage of liver-soothing and qi-regulating herbs can achieve the effect of lowering adverse qi.
Bupleurum, Cyperus, Turmeric: Bupleurum soothes the liver and relieves depression, Cyperus works with Bupleurum to soothe liver qi, and Turmeric combined with Bupleurum soothes liver blood.
Green Tangerine Peel, Bitter OrangeWiden the chest and break the qi, open the stagnant qi in the liverCostus root and tangerine peel:Smooth the flow of qi and restore the unobstructed movement of qi.
White Peony Root + Chinese Angelica Root:After Yujin and Chaihu have effectively regulated liver blood, Baishao and Danggui can better nourish and replenish liver blood, restoring normal blood circulation.
Scutellaria baicalensis:Long-term depression transforms into fire, Scutellaria baicalensis clears heat and purges fire, cools blood and stops bleeding.
Corydalis Yanhusuo:Skilled in promoting qi circulation and relieving pain, licorice regulates the stomach and harmonizes the middle, harmonizing all medicines.
Conclusion: The combination of prescriptions that treat both the symptoms and the root cause
Reflux esophagitis is a typical example of psychosomatic comorbidity, and Jiawei Zuojin Pill, as a representative of traditional Chinese medicine treatment plans, offers an alternative to acid-suppressing drugs.
Its advantage lies in: not only suppressing acid, but also regulating qi movement—by restoring the ascending and descending functions of the spleen and stomach, it reduces reflux from the source. Coptis is bitter, Evodia is pungent, one clears and one descends, containing profound principles; liver fire is pacified, stomach qi harmonized, millennia of heartburn finally finds relief.